Abstract
C9H7ClN2OS, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 8.3507(3) Å, b = 12.3768(4) Å, c = 10.2340(4) Å, β = 96.857(4)°, V = 1050.17(7) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt (F) = 0.0673, wRref (F 2) = 0.2013, T = 296(2) K.
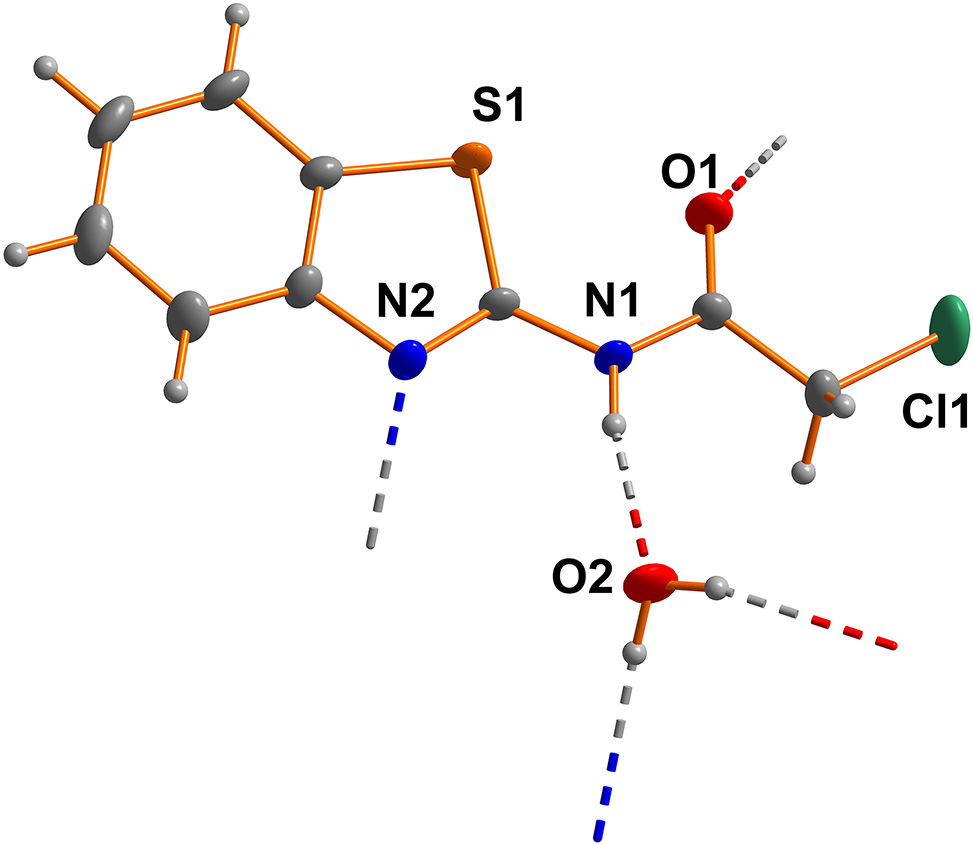
The crystal structure is shown in the figure above. Tables 1–2 contain details of the measurement method and a list of atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.12 × 0.11 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: μ: |
Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) 4.94 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: θ max, completeness: |
New Gemini, ω
72.1°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 3775, 2021, 0.063 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 1734 |
| N(param)refined: | 144 |
| Programs: | SHELX 1 , 3 , Olex2 2 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.31615 (14) | 0.93636 (7) | 0.54550 (10) | 0.0520 (4) |
| S1 | 0.55038 (9) | 0.53525 (6) | 0.73413 (7) | 0.0265 (3) |
| O1 | 0.4705 (3) | 0.74346 (19) | 0.6681 (2) | 0.0338 (6) |
| N1 | 0.3053 (3) | 0.6184 (2) | 0.5616 (2) | 0.0222 (6) |
| N2 | 0.3123 (3) | 0.4335 (2) | 0.5997 (2) | 0.0227 (6) |
| C00A | 0.2488 (4) | 0.8039 (2) | 0.5109 (3) | 0.0281 (7) |
| H00A | 0.138843 | 0.796718 | 0.531461 | 0.034* |
| H00B | 0.248728 | 0.789664 | 0.417658 | 0.034* |
| C1 | 0.3752 (4) | 0.5285 (2) | 0.6236 (3) | 0.0200 (6) |
| C2 | 0.4064 (4) | 0.3556 (2) | 0.6712 (3) | 0.0221 (6) |
| C3 | 0.3761 (4) | 0.2443 (3) | 0.6676 (3) | 0.0289 (7) |
| H3 | 0.287502 | 0.216333 | 0.614633 | 0.035* |
| C4 | 0.4802 (4) | 0.1769 (3) | 0.7442 (3) | 0.0326 (8) |
| H4 | 0.459930 | 0.103026 | 0.743973 | 0.039* |
| C5 | 0.6156 (4) | 0.2176 (3) | 0.8221 (3) | 0.0332 (8) |
| H5 | 0.684539 | 0.170482 | 0.872398 | 0.040* |
| C6 | 0.6483 (4) | 0.3276 (3) | 0.8252 (3) | 0.0305 (7) |
| H6 | 0.738299 | 0.354831 | 0.877074 | 0.037* |
| C007 | 0.3539 (4) | 0.7216 (2) | 0.5888 (3) | 0.0217 (6) |
| C7 | 0.5426 (3) | 0.3963 (3) | 0.7485 (3) | 0.0226 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0328 (3) | 0.5976 (2) | 0.3794 (3) | 0.0422 (7) |
| H2A | −0.063869 | 0.592092 | 0.396973 | 0.063* |
| H2B | 0.034887 | 0.636194 | 0.310951 | 0.063* |
| H1 | 0.223 (5) | 0.604 (3) | 0.514 (4) | 0.021 (9)* |
1 Source of material
1.0 g(6.66 mmol) 2-aminobenzothiazole, 1.06 ml (13.32 mmol) chloroacetyl chloride and 20 ml tetrahydrofuran were added to a 250 ml round flask and stirred to dissolve, stirred at room temperature for 2 h. After the reaction was completed, poured the reaction liquid into a 500 ml beaker, added an appropriate amount of distilled water, precipitate the solid, and then filter the solid after precipitation. By recrystallization of anhydrous ethanol gave the white solid (1.31 g, 86.8 %). 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) d 7.82 (s, 1H), 7.48 (s, 1H), 7.84 (s, 1H), 7.36 (s, 1H), 4.32 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) d 164.43, 156.60, 152.07, 126.53, 126.27, 124.52, 121.52, 121.43, 42.11. MS (ESI): m/z = 227.0030 [M+H]+. FTIR (KBr, cm−1) 3506.54 (nNH secondary amine), 3381.16 (nNH acylamino), 2920.18 (nCH methylene), 2864.25 (nasCH methylene), 1693.48 (nC=O carbonyl), 1597.04 (nC=N thiazole), 1562.32 (nasC-C benzene), 1176.56 (nCH benzene), 773.44 (nCCl).
2 Experimental details
The carbon-bound hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms.
3 Comment
Benzothaizole (BTA) is a fused benzoheterocyle which is present in many naturally occurring products and is responsible for the medicinal, pharmacological and pharmaceutical applications of such natural products. 4 Benzothiazole is a heterocyclic organic compound with a wide range of biological activities. 5 – 9
The basic structure of the title compound is a benzothiazole. The key lengths and angles obtained from the title structure are within the normal range and are consistent with those previously reported in similar structures. 10 , 11 The compound is prepared by the reaction of 2-aminobenzothiazole with chloroacetyl chloride. The crystal structure proves that the compound has been successfully acylated, and the bond length of the C=O bond is 1.221(6) Å. The benzothiazole ring and the phenyl ring have a dihedral angle of 0.18°. The nitrogen atom of the amide bond and the oxygen atom of the water form the intermolecular hydrogen bonds (see the figure).
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Excellent youth project of Heilongjiang Natural Science Foundation (YQ2021H027), and the project of Cultivating Young Innovative Talents in Heilongjiang Province (UNPYSCT-2020056), and National Fund Cultivation Program of Jiamusi University (JMSUGPZR2022-007).
-
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Keri, R. S.; Patil, M. R.; Patil, S. A.; Budagumpi, S. A Comprehensive Review in Current Developments of Benzothiazole-Based Molecules in Medicinal Chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 207–251; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.10.059.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Haroun, M.; Tratrat, C.; Petrou, A.; Geronikaki, A.; Ivanov, M.; Ćirić’, A.; Soković’, M.; Nagaraja, S.; Venugopala, K. N.; Balachandran Nair, A.; Elsewedy, H. S.; Kochkar, H. Exploration of the Antimicrobial Effects of Benzothiazolylthiazolidin-4-One and In Silico Mechanistic Investigation. Molecules 2021, 26, 4061; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134061.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Kumar, G.; Singh, N. P. Synthesis, Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Evaluation of Thiazole/oxazole Substituted Benzothiazole Derivatives. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 107, 104608; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104608.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Osmaniye, D.; Levent, S.; Karaduman, A. B. K.; Ilgin, S.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancikli, Z. A. Synthesis of New Benzothiazole Acylhydrazones as Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2018, 23, 1054; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051054.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Khyati, B.; Sarkar, S. Benzothiazole Moiety and its Derivatives as Antiviral Agents. Med. Sci. Forum 2021, 7, 2–7.Search in Google Scholar
9. Nath, R.; Shahar, Y. M.; Pathania, S.; Grover, G.; Debnath, B.; Akhtar, M. J. Synthesis and Anticonvulsant Evaluation of Indoline Derivatives of Functionalized Aryloxadiazole Amine and Benzothiazole Acetamide. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1228, 129742; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129742.Search in Google Scholar
10. Zhao, W. Crystal Structure of 3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-Yl)-5-Bromo-2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde, C14H8BrNO2S. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 281–283; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0527.Search in Google Scholar
11. van Niekerk, X.; Gerber, T. I. A.; Hosten, E. C. Monodentate N/S-Donor Benzothiazole and Benzimidazole Coordination to the [Re(CO)3]+ Core. Polyhedron 2021, 203, 115171; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2021.115171.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of hexaquazinc(II) poly[hexakis(μ2-4-methylbenzenesulfinato-κ2O:O′) dizinc(II)]
- The crystal structure of poly[((2-(4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1,3-dioxoisoindoline-5-carbonyl)oxy)(1-(dimethylamino)ethoxy)zinc[II]], C16H14ZnN4O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(triaqua-4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O ″)cobalt(II)] trihydrate, C14H22N2O17I2Co2
- Crystal structure of bis(methanol-κO)-bis(nitrato-kO)-bis(1-((2-(2-chloro-4-(4-chlorophenoxy)phenyl)-4-methyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-yl)methyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κN)cadmium(II), C40H42O14N8Cl4Cd
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-dichlorido-(μ2-1-[(2,4-dimethyl-1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C11H12CdN6Cl2
- The crystal structure of (3aS, 4R, 7S, 7aR)-hexahydro-4, 7-methano-1H-isoindole-1, 3-(2H)-dione, C9H11NO2
- The crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-4-chloro-N-(4-chloro-butanoyl) butanamide, C21H20Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-dimethoxy-4,4′-oxy-di-benzaldehyde, C16H14O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-2-amino-3,5-dibromobenzoate-κ 2 O:O′)-octakis(n-butyl-κ 1 C)-bis(μ 3-oxo)tetratin(II), C60H92Br8N4O10Sn4
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b] indole-3-carboxylate, C23H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea(1/1)
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-((2-phenylpyrimidine-4,6-diyl)bis(hydrazin-2-yl-1-ylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-methoxyphenol)monohydrate, C26H26N6O5
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylbutanaminium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (BuMe3N)2[WS4]
- The crystal structure of 2,3,9-triphenyl-9-(2-phenylbenzofuran-3-yl)-9H-9λ 5-benzo[4,5][1,2]oxaphospholo[2,3-b][1,2,5]oxadiphosphole 2-oxide, C40H28O4P2
- Crystal structure of 1–methyl-3-propyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid, C8H11N3O4
- Crystal structure of N-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-2-chloroacetamide, C9H7ClN2OS
- The crystal structure of N-benzyl-2-chloro-N-(p-tolyl) acetamide, C16H16ClNO
- Crystal structure of 3,4-dimethoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H24O5
- Crystal structure of 2,5-bis(2,5-dimethoxybenzyl)-3,6-dimethyl-2,5-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4-dione, C26H28N2O6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-5-bromoisophthalato-κ4 O,O′ :O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazole-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2 N:N′)cobalt(II)], C20H15BrCoN6O4
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(piperidin-1-ium-4-yl)-1Hbenzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) dihydrogen decavanadate, C24H36N6O28V10
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine3-carboxylato-O,O′)-cobalt(ii)dihydrate, C26H36N4O14Co
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-bromoisophthalato-κ4 O,O ′:O ″,O ‴)-(μ2-1,4-bis(2-methylimidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-N:N′)cadmium(II)], C24H21BrCdN4O4
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 8-(3-methoxy-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)-4-methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-1,3a,4,8b-tetrahydro-3H-furo[3,4-b]indole-3,3-dicarboxylate. C28H29NO9
- Crystal structure of (3R)-1-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate chloride, C21H23ClN2O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 3-(4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)-2-methyl-4-(methylsulfonyl)benzoic acid, C12H13NO5S
- The crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis-3-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[1,2-α]pyridin-1-yl)benzoate, C36H42N4O10Mg
- Crystal structure of 4-formyl-2-methoxyphenyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C17H14O6
- Crystal structure of poly[octakis(μ-oxido)-tris(μ-1,1′-[[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diylbis(methylene)]bis(1H-imidazole))-tetrakis(oxido)-tetra-vanadium-dimanganese(II)dihydrate], C30H29MnN6O7V2
- Crystal structure of 4,8a-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,5,6-tris(4-fluorobenzyl)-1,4,4a,4b,5,6,8a,8b-octahydrocyclobuta[1,2-b:3,4-c′]dipyridine-3,8-dicarbonitrile, C45H33Cl2F3N4
- Crystal structure of benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H20O5
- Crystal structure of N-benzoyl-N-phenylhydroxylaminato-dicarbonylrhodium(I), [Rh(BNA)CO2]
- The crystal structure of N-(2-((2-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)ethynyl)phenyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide, C26H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of methyl ((4-aminobenzyl)sulfonyl)-d-prolinate, C13H18N2O4S
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-(N-isopropyl-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)propan-2-amine-κ 2 N, N′)palladium(II), C12H20N2PdCl2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-5-hydroxyisophthalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ 2-1,4-bis(2-methylimidazolyl)-1-butene-N:N′)nickel(II)], C20H20NiN4O5
- The crystal structure of {hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ 1 N)cobalt(II)}(μ 2-oxido)-hexaoxido-dimolybdenum(VI)— 1-methyl-1H-imidazole (1/2), C32H48CoMo2N16O7
- Synthesis, crystal structure and nonlinear optical property of 1-((propan-2-ylideneamino)oxy)propan-2-yl-4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C13H19O4NS
- The crystal structure of N,N-(ethane-1,1-diyl)dibenzamide, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxypropan-1-one, C21H18BrO3P
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(bis(3,5-dimethyl-4H-pyrazole)-κ1 N)-((nitrato)-κ1 O)-rhenium(I)— 3,5-dimethyl-4H-pyrazole(1/1), C18H23N7O6Re
- The crystal structure of 4′-chloro-griseofulvin: (2S,6′R)-4′,7-dichloro-4,6-dimethoxy-6′-methyl-3H-spiro[benzofuran-2,1′-cyclohexan]-3′-ene-2′,3-dione, C16H14Cl2O5
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea(1/1)
- Crystal structure of 1-cyclohexyl-4-p-tolyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester, C22H27NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-1,4-bis-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-copper(I)) dichloridocopper(I), {[CuC12H10N4]+[CuCl2]−} n
- The crystal structure of propane-1-aminium-2-carbamate, C4H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 5,6,3′,4′,5′-pentamethoxy-flavone dihydrate, C20H24O9
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(2-bromophenyl)-4-(4-(3,5-dimethoxystyryl)phenoxy)pyrimidin-2-amine, C26H22BrN3O3
- Crystal structure of methyl (3R)-1-(2-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate hydrochloride hydrate, C19H19BrClFN2O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-(p-tolyl)urea, C14H13ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 1-cyclohexyl-3-(p-tolyl)urea, C14H20N2O
- Crystal structure of ((benzyl(hydroxy)-amino)(4-chlorophenyl)methyl)-diphenylphosphine oxide, C26H23ClNO2P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 3-(1-methyl-1H-indole-2-carbonyl)-2-phenylquinoline-4-carboxylate, C28H22N2O3
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1H-imidazol-3-ium-1-yl)benzene dinitrate, C12H12N4 2+·2(NO3 −)
- Crystal structure of tris(hexafluoroacetylacetonato-κ2O,O′) bis(triphenylphosphine oxide-κ1O)samarium(III), C51H33F18O8P2Sm
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-2,3-bis(diphenylphosphoryl)propan-1-one, C35H33NO3P2
- Crystal structure of diaqua[bis(μ 2-pyridine 2,6-dicarboxylato) bismuth(III) potassium(I)], C14H10BiKN2O10
- Crystal structure of (R)-N, N ′-dimethyl-[1, 1′-binaphthalene]-2, 2′-diamine, C22H20N2
- Crystal structure of 1-phenyl-4-(2-furoyl)-3-furyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C18H12N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(14,34-dimethyl[11,21:23,31-terphenyl]-22-yl)diselane, C40H34Se2
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of hexaquazinc(II) poly[hexakis(μ2-4-methylbenzenesulfinato-κ2O:O′) dizinc(II)]
- The crystal structure of poly[((2-(4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1,3-dioxoisoindoline-5-carbonyl)oxy)(1-(dimethylamino)ethoxy)zinc[II]], C16H14ZnN4O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(triaqua-4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O ″)cobalt(II)] trihydrate, C14H22N2O17I2Co2
- Crystal structure of bis(methanol-κO)-bis(nitrato-kO)-bis(1-((2-(2-chloro-4-(4-chlorophenoxy)phenyl)-4-methyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-yl)methyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κN)cadmium(II), C40H42O14N8Cl4Cd
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-dichlorido-(μ2-1-[(2,4-dimethyl-1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C11H12CdN6Cl2
- The crystal structure of (3aS, 4R, 7S, 7aR)-hexahydro-4, 7-methano-1H-isoindole-1, 3-(2H)-dione, C9H11NO2
- The crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-4-chloro-N-(4-chloro-butanoyl) butanamide, C21H20Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-dimethoxy-4,4′-oxy-di-benzaldehyde, C16H14O5
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-2-amino-3,5-dibromobenzoate-κ 2 O:O′)-octakis(n-butyl-κ 1 C)-bis(μ 3-oxo)tetratin(II), C60H92Br8N4O10Sn4
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b] indole-3-carboxylate, C23H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea(1/1)
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-((2-phenylpyrimidine-4,6-diyl)bis(hydrazin-2-yl-1-ylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-methoxyphenol)monohydrate, C26H26N6O5
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylbutanaminium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (BuMe3N)2[WS4]
- The crystal structure of 2,3,9-triphenyl-9-(2-phenylbenzofuran-3-yl)-9H-9λ 5-benzo[4,5][1,2]oxaphospholo[2,3-b][1,2,5]oxadiphosphole 2-oxide, C40H28O4P2
- Crystal structure of 1–methyl-3-propyl-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid, C8H11N3O4
- Crystal structure of N-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-2-chloroacetamide, C9H7ClN2OS
- The crystal structure of N-benzyl-2-chloro-N-(p-tolyl) acetamide, C16H16ClNO
- Crystal structure of 3,4-dimethoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H24O5
- Crystal structure of 2,5-bis(2,5-dimethoxybenzyl)-3,6-dimethyl-2,5-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4-dione, C26H28N2O6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-5-bromoisophthalato-κ4 O,O′ :O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,2-bis(1,2,4-triazole-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2 N:N′)cobalt(II)], C20H15BrCoN6O4
- The crystal structure of bis(2-(piperidin-1-ium-4-yl)-1Hbenzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) dihydrogen decavanadate, C24H36N6O28V10
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine3-carboxylato-O,O′)-cobalt(ii)dihydrate, C26H36N4O14Co
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-bromoisophthalato-κ4 O,O ′:O ″,O ‴)-(μ2-1,4-bis(2-methylimidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-N:N′)cadmium(II)], C24H21BrCdN4O4
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 8-(3-methoxy-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)-4-methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-1,3a,4,8b-tetrahydro-3H-furo[3,4-b]indole-3,3-dicarboxylate. C28H29NO9
- Crystal structure of (3R)-1-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate chloride, C21H23ClN2O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 3-(4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)-2-methyl-4-(methylsulfonyl)benzoic acid, C12H13NO5S
- The crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis-3-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[1,2-α]pyridin-1-yl)benzoate, C36H42N4O10Mg
- Crystal structure of 4-formyl-2-methoxyphenyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C17H14O6
- Crystal structure of poly[octakis(μ-oxido)-tris(μ-1,1′-[[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diylbis(methylene)]bis(1H-imidazole))-tetrakis(oxido)-tetra-vanadium-dimanganese(II)dihydrate], C30H29MnN6O7V2
- Crystal structure of 4,8a-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,5,6-tris(4-fluorobenzyl)-1,4,4a,4b,5,6,8a,8b-octahydrocyclobuta[1,2-b:3,4-c′]dipyridine-3,8-dicarbonitrile, C45H33Cl2F3N4
- Crystal structure of benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H20O5
- Crystal structure of N-benzoyl-N-phenylhydroxylaminato-dicarbonylrhodium(I), [Rh(BNA)CO2]
- The crystal structure of N-(2-((2-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)ethynyl)phenyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide, C26H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of methyl ((4-aminobenzyl)sulfonyl)-d-prolinate, C13H18N2O4S
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-(N-isopropyl-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)propan-2-amine-κ 2 N, N′)palladium(II), C12H20N2PdCl2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-5-hydroxyisophthalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ 2-1,4-bis(2-methylimidazolyl)-1-butene-N:N′)nickel(II)], C20H20NiN4O5
- The crystal structure of {hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ 1 N)cobalt(II)}(μ 2-oxido)-hexaoxido-dimolybdenum(VI)— 1-methyl-1H-imidazole (1/2), C32H48CoMo2N16O7
- Synthesis, crystal structure and nonlinear optical property of 1-((propan-2-ylideneamino)oxy)propan-2-yl-4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C13H19O4NS
- The crystal structure of N,N-(ethane-1,1-diyl)dibenzamide, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxypropan-1-one, C21H18BrO3P
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(bis(3,5-dimethyl-4H-pyrazole)-κ1 N)-((nitrato)-κ1 O)-rhenium(I)— 3,5-dimethyl-4H-pyrazole(1/1), C18H23N7O6Re
- The crystal structure of 4′-chloro-griseofulvin: (2S,6′R)-4′,7-dichloro-4,6-dimethoxy-6′-methyl-3H-spiro[benzofuran-2,1′-cyclohexan]-3′-ene-2′,3-dione, C16H14Cl2O5
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea(1/1)
- Crystal structure of 1-cyclohexyl-4-p-tolyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester, C22H27NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-1,4-bis-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-copper(I)) dichloridocopper(I), {[CuC12H10N4]+[CuCl2]−} n
- The crystal structure of propane-1-aminium-2-carbamate, C4H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 5,6,3′,4′,5′-pentamethoxy-flavone dihydrate, C20H24O9
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(2-bromophenyl)-4-(4-(3,5-dimethoxystyryl)phenoxy)pyrimidin-2-amine, C26H22BrN3O3
- Crystal structure of methyl (3R)-1-(2-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate hydrochloride hydrate, C19H19BrClFN2O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-(p-tolyl)urea, C14H13ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 1-cyclohexyl-3-(p-tolyl)urea, C14H20N2O
- Crystal structure of ((benzyl(hydroxy)-amino)(4-chlorophenyl)methyl)-diphenylphosphine oxide, C26H23ClNO2P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 3-(1-methyl-1H-indole-2-carbonyl)-2-phenylquinoline-4-carboxylate, C28H22N2O3
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1H-imidazol-3-ium-1-yl)benzene dinitrate, C12H12N4 2+·2(NO3 −)
- Crystal structure of tris(hexafluoroacetylacetonato-κ2O,O′) bis(triphenylphosphine oxide-κ1O)samarium(III), C51H33F18O8P2Sm
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-2,3-bis(diphenylphosphoryl)propan-1-one, C35H33NO3P2
- Crystal structure of diaqua[bis(μ 2-pyridine 2,6-dicarboxylato) bismuth(III) potassium(I)], C14H10BiKN2O10
- Crystal structure of (R)-N, N ′-dimethyl-[1, 1′-binaphthalene]-2, 2′-diamine, C22H20N2
- Crystal structure of 1-phenyl-4-(2-furoyl)-3-furyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C18H12N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(14,34-dimethyl[11,21:23,31-terphenyl]-22-yl)diselane, C40H34Se2

