Crystal structure of diethyl 3,9-diphenyl-6,12-bis(3-methoxyphenyl)-3,9-diazahexacyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]dodecane-1,11-dicarboxylate, C42H42N2O6
Abstract
C42H42N2O6, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 6.9848(14) Å, b = 20.816(4) Å, c = 11.543(2) Å, β = 99.745(5)°, V = 1654.1(6) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0377, wRref(F2) = 0.1019, T = 113(2) K.
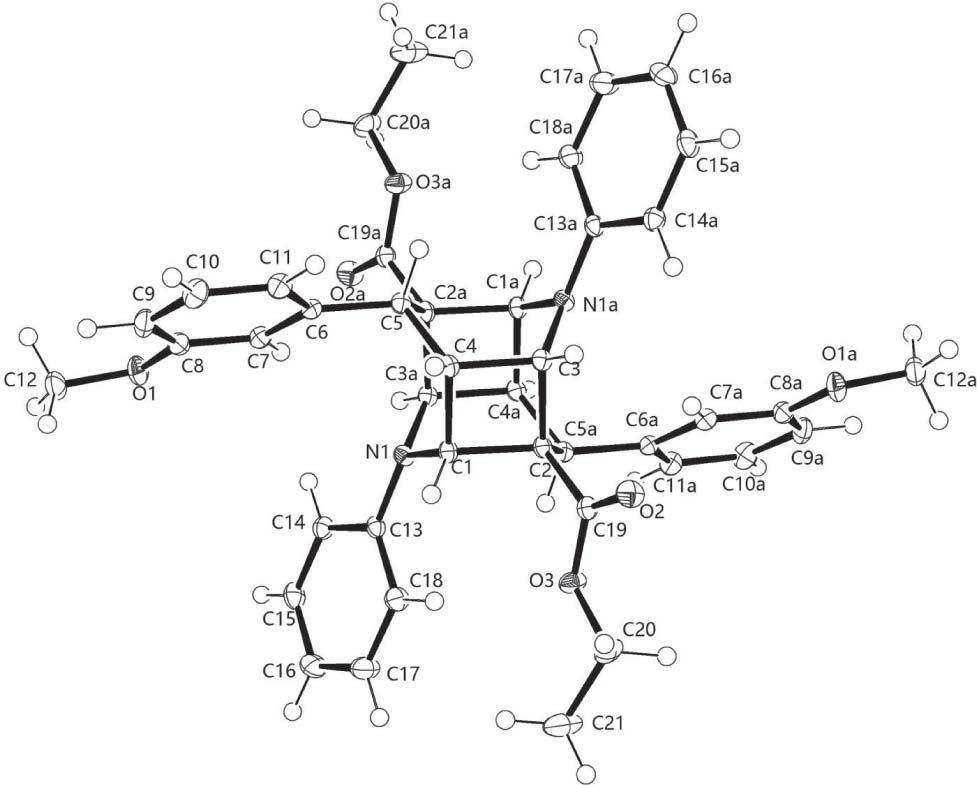
The centrosymmetric cage dimeric title structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless prism |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.9 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Rigaku XtaLAB P200, φ and ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 55°, >99.6% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 16568, 3779, 0.0352 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3129 |
| N(param)refined: | 228 |
| Programs: | Rigaku [1], SHELX [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | −0.27129(13) | 0.55565(5) | 0.95362(8) | 0.0195(2) |
| O2 | 0.44732(12) | 0.39885(4) | 0.42556(8) | 0.0192(2) |
| O3 | 0.22737(12) | 0.33065(4) | 0.47684(8) | 0.0185(2) |
| N1 | −0.08299(13) | 0.44852(5) | 0.62036(8) | 0.0123(2) |
| C1 | 0.11432(16) | 0.44996(6) | 0.59723(10) | 0.0121(2) |
| H1 | 0.2030 | 0.4217 | 0.6522 | 0.015* |
| C2 | 0.13796(16) | 0.43926(6) | 0.46339(10) | 0.0118(2) |
| C3 | 0.21163(16) | 0.50990(6) | 0.45941(10) | 0.0120(2) |
| H3 | 0.3490 | 0.5121 | 0.4456 | 0.014* |
| C4 | 0.19616(16) | 0.51902(6) | 0.59185(10) | 0.0124(2) |
| H4 | 0.3271 | 0.5234 | 0.6419 | 0.015* |
| C5 | 0.05948(16) | 0.57366(6) | 0.61423(10) | 0.0121(2) |
| H5 | 0.1119 | 0.6143 | 0.5856 | 0.015* |
| C6 | 0.05427(17) | 0.58228(6) | 0.74456(10) | 0.0131(2) |
| C7 | −0.10626(17) | 0.56572(6) | 0.79516(10) | 0.0142(2) |
| H7 | −0.2196 | 0.5494 | 0.7470 | 0.017* |
| C8 | −0.10255(17) | 0.57283(6) | 0.91574(11) | 0.0155(2) |
| C9 | 0.06284(18) | 0.59590(6) | 0.98779(11) | 0.0186(3) |
| H9 | 0.0668 | 0.6002 | 1.0701 | 0.022* |
| C10 | 0.22239(18) | 0.61260(7) | 0.93666(11) | 0.0198(3) |
| H10 | 0.3358 | 0.6287 | 0.9850 | 0.024* |
| C11 | 0.22006(18) | 0.60635(6) | 0.81700(11) | 0.0169(3) |
| H11 | 0.3306 | 0.6184 | 0.7841 | 0.020* |
| C12 | −0.2689(2) | 0.55604(7) | 1.07762(11) | 0.0217(3) |
| H12A | −0.1643 | 0.5281 | 1.1162 | 0.033* |
| H12B | −0.3938 | 0.5404 | 1.0942 | 0.033* |
| H12C | −0.2469 | 0.5999 | 1.1076 | 0.033* |
| C13 | −0.15685(17) | 0.39275(6) | 0.66632(10) | 0.0131(2) |
| C14 | −0.33332(17) | 0.39502(6) | 0.70993(10) | 0.0152(2) |
| H14 | −0.4056 | 0.4339 | 0.7052 | 0.018* |
| C15 | −0.40215(18) | 0.34088(6) | 0.75966(11) | 0.0184(3) |
| H15 | −0.5227 | 0.3430 | 0.7872 | 0.022* |
| C16 | −0.2986(2) | 0.28370(7) | 0.77002(12) | 0.0221(3) |
| H16 | −0.3461 | 0.2471 | 0.8054 | 0.027* |
| C17 | −0.1241(2) | 0.28105(7) | 0.72769(12) | 0.0233(3) |
| H17 | −0.0513 | 0.2423 | 0.7342 | 0.028* |
| C18 | −0.05509(18) | 0.33461(6) | 0.67579(11) | 0.0183(3) |
| H18 | 0.0635 | 0.3317 | 0.6462 | 0.022* |
| C19 | 0.28929(16) | 0.38898(6) | 0.45105(10) | 0.0133(2) |
| C20 | 0.36169(19) | 0.27741(6) | 0.47523(12) | 0.0217(3) |
| H20A | 0.4945 | 0.2903 | 0.5121 | 0.026* |
| H20B | 0.3645 | 0.2637 | 0.3934 | 0.026* |
| C21 | 0.2896(2) | 0.22368(7) | 0.54347(15) | 0.0309(3) |
| H21A | 0.2915 | 0.2374 | 0.6248 | 0.046* |
| H21B | 0.3738 | 0.1861 | 0.5425 | 0.046* |
| H21C | 0.1565 | 0.2125 | 0.5075 | 0.046* |
Source of material
The title compound was synthesized by ethyl 1-phenyl-1,4-dihydro-4-(3-methoxyphenyl)pyridine-3-carboxylate under irradiation of UV-light in methanol/THF solution. After approximately 48 h irradiation was stopped and the product was purified by TL chromatography using ethyl acetate-petroleum ether (1:30 v/v). After concentration in vacuum, colorless solids were collected, dried, and recrystallized from methanol. Colorless crystals were obtained 3 days later.
Experimental details
All H atoms were placed in idealized positions (C—H = 0.95-1.00 Å) and refined as riding atoms. The Uiso values were set to be 1.5Ueq of the carrier atom for nitrogen H atoms and 1.2Ueq for the remaining H atoms. The hydrogen atoms attached to carbon were placed on calculated positions with the help of the SHELX program (AFIX 23, 43 or 137 option) [2].
Discussion
The title compound is a derivative of 3,9-diazatetraasteranes and plays important roles in synthetic, therapeutic, and bioorganic chemistry, for example, it shows anti-HIV PR activity [3]. As competitive inhibitors [4], 3,9-diazatetraasteranes are among the most promising classes of novel inhibitors of HIV-1 PR. In general, they have unique caged structures as well as lipophilic properties [5]. Furthermore, cage dimeric HIV-1 PR inhibitors have been introduced as novel lead structures [6]. Only a small number of 3,9-diazatetraasteranes have been reported so far [7]. In order to search for new 3,9-diazatetraasteranes, the title compound was synthesized and its crystal structure was determined.
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in the figure. It displays exact centrosymmetry. The substitution at the central cage is such that at the C2—C5a—C4a joint of the piperidine rings there is one bulky substituent at C2 and C5a, while at the C3—N1a—C1a joint there is only one non-H substituent. Apart from this group, the N1a atom bears no other substituent, not even a hydrogen atom. This generates much more crowding at C4 and C2 of the cyclobutane ring than at C3 and C1. Because of the Csp2 nature of the substituent at C5a, the orientation of the phenyl ring around the C5a—C6a bond is characterized by the following torsion angles: C4a—C5a—C6a—C7: 108.93°, C2—C5a—C6a—C7: −13.91°. The C2—C5a—C4a prow is inclined at very similar angles to the bottoms of both piperidinyl moieities (134.7° and 135.7°). The corresponding C—C5a distances are 1.535(2) Å, and the C2—C5a—C4a angle is 107.14(9)°. At the same time, the piperidinyl C—C—C5a valence angles are all very similar (113.0(2)−113.7(1)°, average 113.3° and correspond very well to the substituent angles in planar cyclobutane rings (113.1(6)°) calculated by Allen [8]. All bond lengths and angles are within normal ranges [9].
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Key Projects in the Hebei Youth Natural Science Foundation (No. H2014209241).
References
Rigaku: RAPID-AUTO. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan (1998).Suche in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar
Hilgeroth, A.; Tykarska, E.; Jaskolski, M.: Crystal structure of a novel synthetic inhibitor of HIV-1 protease. J. Mol. Struct. 605 (2002) 63–70.10.1016/S0022-2860(01)00751-7Suche in Google Scholar
Wollmann, J.; Baumert, C.; Erlenkamp, G.; Sippl, W.; Hilgeroth, A.: Novel insight into inhibitor binding of highly symmetric HIV-1 protease. ChemBioChem 9 (2008) 874–878.10.1002/cbic.200700646Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
Hilgeroth, A.; Fleischer, R.; Wiese, M.; Heinemann, F. W.: Comparison of azacyclic urea A-98881 as HIV-1 protease inhibitor with cage dimeric N-benzyl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine as representative of a novel class of HIV-1 protease inhibitors: A molecular modeling study. J. Comput. Aid. Mol. Des. 13 (1999) 233–242.10.1023/A:1008038608460Suche in Google Scholar
Wlodawer, A.; Vondrasek, J.: Crystal structure of a novel synthetic inhibitor of HIV-1 protease. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. struct. 27 (1998) 249–284.10.1146/annurev.biophys.27.1.249Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
Hilgeroth, A.; Billich, A.: Cage dimeric 4-aryl-1,4-dihydropyridines as promising lead structures for the development of a novel class of HIV-1 protease inhibitors. Cheminform. 332 (1999) 3–5.10.1002/(SICI)1521-4184(19991)332:1<3::AID-ARDP3>3.0.CO;2-1Suche in Google Scholar
Allen, F. H.: The geometry of small rings. VI. Geometry and bonding in cyclobutane and cyclobutene. Acta Crystallogr. 40 (1984) 64–72.10.1107/S0108768184001750Suche in Google Scholar
Allen, F. H.; Kennard, O.; Watson, D. G.; Brammer, L.; Orpen, A. G.; Taylor, R.: Tables of bond lengths determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction. Part 1. Bond lengths in organic compounds. Perkin Trans. 2. 2 (1987) S1–S19.10.1039/p298700000s1Suche in Google Scholar
©2018 Hao Zhu et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure and optical properties of diaqua-tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(p-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κN)praseodymium(III), C24H36N9O15Pr
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-bis(μ2-methanol-κ2O:O)-bis{3-((4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olato-κ3O,N,O′}dimanganese(II), C38H38Mn2N2O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-(2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κ3O,O′:O′)calcium(II)], C56H48N4Ca2Cl8O12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(isophthalato-κO)-(μ2-1,6-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)hexane-κ2N:N′)]nickel(II), C20H28N4NiO7
- Crystal structure of cyclo[hexaqua-bis[1-[(2-ethyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl) methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′]-bis(sulfato-κ1O)dicadmium(II)] monohydrate, C24H42Cd2N10O16S2
- Crystal Structure of bis(2-fluorbenzoato-κO)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) dihydrate, C38H28F2MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium 5-hydroxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C20H41NO9
- Crystal structural of 2-amino-4-(3-bromophenyl)-3-cyano-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4H-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyran, C18H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structural of 2-amino-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C17H16N2O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ2-1,3-bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-5-(tert-butyl)isophthalate-κ3O,O′:O′′)nickel(II)], C29H30N4NiO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-dicyanamido-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O′)copper(II)], C9H8CuN4O
- Crystal structure of bis(5,5′-((butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-(ethoxycarbonyl)-2,4-dimethylpyrrol-1-ido-k4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)copper(II), C24H32CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of the formamide solvate of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol, C19H27NO3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxylato-κ2N:O)nickel(II)] dihydrate, C16H18N4NiO8
- Crystal structure of dibromido[(1,2-bis(diisopropylphosphino)-1,2-dicarba-closo-dodecaborane-κ2P,P′]nickel(II), C14H38B10NiBr2P2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aquachlorido(3,3′-([4,4′-bipyridine]-1,1′-diium-1,1′-diylbis(methylene))dibenzoato-κ2O:O′)copper(II)] chloride dihydrate, C26H26Cl2CuN2O7
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-nitrobenzylidene)-2-phenylacetohydrazide, C15H13N3O3
- Crystal structure of dichlorido bis[1-[(2-methyl-1H-benzoimidazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ1N]cadmium(II), C30H26CdCl2N10
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(3-(2-pyridyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N,N′)copper(II) sulfate tetrahydrate, C24H28CuN10O9S
- Crystal structure of dibromido-carbonyl-(η6-p-cymene)osmium(II), C11H14Br2OOs
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-chlorido)-bis(imidazole-κN)copper(II)] C6H8Cl2CuN4
- Crystal structure of [(1,2-bis(dicyclohexylphosphino)-1,2-dicarba-closo-dodecaborane-κ2P,P′]dibromidonickel(II)), C26H54B10NiBr2P2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido[1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)ferrocene-κ2P,P′]zinc(II), C34H28FeCl2P2Zn
- Crystal structure of tris(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)-trithiocyanato-κN-dicobalt(III), C24H24Co2N6O3S3
- The crystal structure of diaqua-2,2′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))diphenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) perchlorate, C20H24MnClN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-chlorido)-bis(μ2-chlorido)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-bis (diphenylmethyl)-4-t-butylphenolato)tetralithium(I)dicobalt(II) toluene solvate, C75.5H70Cl2CoLi2O2
- The crystal structure of hexaaqua-bis(μ2-3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-tetrakis(3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κO)dierbium(III) octahydrate, C60H76N18O32Er2
- Crystal structure of dimethylammonium bis(naphthalene-2,3-diolato)borate, C22H20BNO4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-nitro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H17N3O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-2-(((5-methylpyridin-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylbutanaminium) poly[heptaselenidotristannate(IV)], C14H36N2Se7Sn3
- The crystal structure of N-((3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)(phenyl)methyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide, C28H35N3S
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine, C17H13Cl1N2
- The Crystal structure of 2-iodo-1-(p-tolyl)propan-1-one, C10H11IO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-bromobenzyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C19H17FN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-2,5-dihydroxyterephthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)], C8H8O8Cd
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis[6-(1H-imidazol-1-yl-κN)nicotinato]zinc(II), C18H20N6O8Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(N-phenyl-2-(quinolin-8-yloxy)acetamide-κ2N,O) – acetone (2/1), C35.5H31N4O4.5Cl2Cu
- Crystal Structure of ethyl (E)-3,4-dimethyl-5-((2-(4-methylbenzoyl)hydrazono)methyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate — water — ethanol (1/1/1), C20H29N3O5
- Crystal structure of 5-((4-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-2-methoxyphenoxy)methyl)-2-chlorothiazole - trichloromethane - methanol (1/1/1), C20H19Cl4N3O3S
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative: 41S,7aS,12S,13aR,13bR)-12-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)dodecahydro-1H,5H,10H-dipyrido[2,1-f:3′,2′,1′-ij][1,6]naphthyridin-10-one, C20H34N4O
- Crystal structure of cesium beryllophosphate, Be3Cs2P4O14
- Crystal Structure of 3-((3-hydroxybenzyl)ammonio)-3-phenylpropanoate, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium chloride — 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid — water (2/1/5), C48H54N2Cl2O17
- The crystal structure of (1R, 2R)-N1,N2-diferrocenyl-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxamide, C28H30Fe2N2O2
- Crystal structure of N-(2-methylphenyl)ethoxycarbothioamide, C10H13NOS
- Crystal Structure of ethyl (E)-2,4-dimethyl-5-((2-tosylhydrazono)methyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate monohydrate, C17H23N3O5
- Crystal structure of Diiodo-(N′-((quinolin-8-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide κ3N,N′,O)cadium(II) – dimethylformamide (1/1), C19H19N5O2CdI2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-(N′-((quinolin-8-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide κ3-N,N′,O)copper(II), C16H12N6O7Cu
- Crystal structure of benzoato-κO-bis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane-κP)silver(I) monohydrate C19H31AgN6O3P2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(anthracen-9-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C16H13N3S
- The crystal structure of 8-chloro-7-ethyl-1,3-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6(3H,7H)-dione, C9H11ClN4O2
- Crystal structure of {5,5′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-(ethoxycarbonyl)-2,4-dimethylpyrrol-1-ido)-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}zinc(II), C23H30N4O4Cu
- Crystal structure of bis(4-dimethylamino-pyridin-1-ium)tetrafluorosuccinate, C18H22F4N4O4
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,9-dibenzyl-6,12-dicyclohexyl-3,9-diazahexacyclo [6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]-dodecane-1,11-dicarboxylate, C40H50N2O4
- Crystal structure of diethyl 3,9-diphenyl-6,12-bis(3-methoxyphenyl)-3,9-diazahexacyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]dodecane-1,11-dicarboxylate, C42H42N2O6
- Crystal structure of bis(acetato-κO)-bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-one oxime-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C18H22N4NiO6
- Crystal structure of (N-(3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-4-fluorobenzohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)-diphenyltin(IV), C28H23FN2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of {N-(3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-4-fluorobenzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,O′}dimethyltin(IV), C18H19FN2O3Sn
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure and optical properties of diaqua-tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(p-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κN)praseodymium(III), C24H36N9O15Pr
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-bis(μ2-methanol-κ2O:O)-bis{3-((4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olato-κ3O,N,O′}dimanganese(II), C38H38Mn2N2O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-(2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κ3O,O′:O′)calcium(II)], C56H48N4Ca2Cl8O12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(isophthalato-κO)-(μ2-1,6-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)hexane-κ2N:N′)]nickel(II), C20H28N4NiO7
- Crystal structure of cyclo[hexaqua-bis[1-[(2-ethyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl) methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′]-bis(sulfato-κ1O)dicadmium(II)] monohydrate, C24H42Cd2N10O16S2
- Crystal Structure of bis(2-fluorbenzoato-κO)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) dihydrate, C38H28F2MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium 5-hydroxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C20H41NO9
- Crystal structural of 2-amino-4-(3-bromophenyl)-3-cyano-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4H-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyran, C18H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structural of 2-amino-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C17H16N2O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ2-1,3-bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-5-(tert-butyl)isophthalate-κ3O,O′:O′′)nickel(II)], C29H30N4NiO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-dicyanamido-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O′)copper(II)], C9H8CuN4O
- Crystal structure of bis(5,5′-((butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-(ethoxycarbonyl)-2,4-dimethylpyrrol-1-ido-k4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)copper(II), C24H32CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of the formamide solvate of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol, C19H27NO3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxylato-κ2N:O)nickel(II)] dihydrate, C16H18N4NiO8
- Crystal structure of dibromido[(1,2-bis(diisopropylphosphino)-1,2-dicarba-closo-dodecaborane-κ2P,P′]nickel(II), C14H38B10NiBr2P2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aquachlorido(3,3′-([4,4′-bipyridine]-1,1′-diium-1,1′-diylbis(methylene))dibenzoato-κ2O:O′)copper(II)] chloride dihydrate, C26H26Cl2CuN2O7
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-nitrobenzylidene)-2-phenylacetohydrazide, C15H13N3O3
- Crystal structure of dichlorido bis[1-[(2-methyl-1H-benzoimidazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ1N]cadmium(II), C30H26CdCl2N10
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(3-(2-pyridyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N,N′)copper(II) sulfate tetrahydrate, C24H28CuN10O9S
- Crystal structure of dibromido-carbonyl-(η6-p-cymene)osmium(II), C11H14Br2OOs
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-chlorido)-bis(imidazole-κN)copper(II)] C6H8Cl2CuN4
- Crystal structure of [(1,2-bis(dicyclohexylphosphino)-1,2-dicarba-closo-dodecaborane-κ2P,P′]dibromidonickel(II)), C26H54B10NiBr2P2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido[1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)ferrocene-κ2P,P′]zinc(II), C34H28FeCl2P2Zn
- Crystal structure of tris(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-olato-κ3N,O:O)-trithiocyanato-κN-dicobalt(III), C24H24Co2N6O3S3
- The crystal structure of diaqua-2,2′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))diphenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) perchlorate, C20H24MnClN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-chlorido)-bis(μ2-chlorido)-tetrakis(μ2-2,6-bis (diphenylmethyl)-4-t-butylphenolato)tetralithium(I)dicobalt(II) toluene solvate, C75.5H70Cl2CoLi2O2
- The crystal structure of hexaaqua-bis(μ2-3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κ2O:O′)-tetrakis(3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propanoato-κO)dierbium(III) octahydrate, C60H76N18O32Er2
- Crystal structure of dimethylammonium bis(naphthalene-2,3-diolato)borate, C22H20BNO4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-nitro-phenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H17N3O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-2-(((5-methylpyridin-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylbutanaminium) poly[heptaselenidotristannate(IV)], C14H36N2Se7Sn3
- The crystal structure of N-((3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)(phenyl)methyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide, C28H35N3S
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine, C17H13Cl1N2
- The Crystal structure of 2-iodo-1-(p-tolyl)propan-1-one, C10H11IO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-bromobenzyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C19H17FN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-2,5-dihydroxyterephthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)], C8H8O8Cd
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis[6-(1H-imidazol-1-yl-κN)nicotinato]zinc(II), C18H20N6O8Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(N-phenyl-2-(quinolin-8-yloxy)acetamide-κ2N,O) – acetone (2/1), C35.5H31N4O4.5Cl2Cu
- Crystal Structure of ethyl (E)-3,4-dimethyl-5-((2-(4-methylbenzoyl)hydrazono)methyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate — water — ethanol (1/1/1), C20H29N3O5
- Crystal structure of 5-((4-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-2-methoxyphenoxy)methyl)-2-chlorothiazole - trichloromethane - methanol (1/1/1), C20H19Cl4N3O3S
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative: 41S,7aS,12S,13aR,13bR)-12-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)dodecahydro-1H,5H,10H-dipyrido[2,1-f:3′,2′,1′-ij][1,6]naphthyridin-10-one, C20H34N4O
- Crystal structure of cesium beryllophosphate, Be3Cs2P4O14
- Crystal Structure of 3-((3-hydroxybenzyl)ammonio)-3-phenylpropanoate, C16H17NO3
- Crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium chloride — 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid — water (2/1/5), C48H54N2Cl2O17
- The crystal structure of (1R, 2R)-N1,N2-diferrocenyl-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxamide, C28H30Fe2N2O2
- Crystal structure of N-(2-methylphenyl)ethoxycarbothioamide, C10H13NOS
- Crystal Structure of ethyl (E)-2,4-dimethyl-5-((2-tosylhydrazono)methyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate monohydrate, C17H23N3O5
- Crystal structure of Diiodo-(N′-((quinolin-8-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide κ3N,N′,O)cadium(II) – dimethylformamide (1/1), C19H19N5O2CdI2
- Crystal structure of dinitrato-(N′-((quinolin-8-yl)methylene)isonicotinohydrazide κ3-N,N′,O)copper(II), C16H12N6O7Cu
- Crystal structure of benzoato-κO-bis(1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane-κP)silver(I) monohydrate C19H31AgN6O3P2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(anthracen-9-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C16H13N3S
- The crystal structure of 8-chloro-7-ethyl-1,3-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6(3H,7H)-dione, C9H11ClN4O2
- Crystal structure of {5,5′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-(ethoxycarbonyl)-2,4-dimethylpyrrol-1-ido)-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}zinc(II), C23H30N4O4Cu
- Crystal structure of bis(4-dimethylamino-pyridin-1-ium)tetrafluorosuccinate, C18H22F4N4O4
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 3,9-dibenzyl-6,12-dicyclohexyl-3,9-diazahexacyclo [6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]-dodecane-1,11-dicarboxylate, C40H50N2O4
- Crystal structure of diethyl 3,9-diphenyl-6,12-bis(3-methoxyphenyl)-3,9-diazahexacyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]dodecane-1,11-dicarboxylate, C42H42N2O6
- Crystal structure of bis(acetato-κO)-bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-one oxime-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C18H22N4NiO6
- Crystal structure of (N-(3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-4-fluorobenzohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)-diphenyltin(IV), C28H23FN2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of {N-(3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-4-fluorobenzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,O′}dimethyltin(IV), C18H19FN2O3Sn

