Abstract
An adenocarcinoma of the appendix invading the urinary bladder, which is difficult to be diagnosed before the operation, is an extremely rare disease. Only a few cases have been reported. Here we reported a case of patient diagnosed with the mucinous adenocarcinoma of the appendix invading the urinary bladder. The case reported in this study was a 54-years old man who was admitted due to a 6-month history of intermittent episodes of irritative voiding symptoms of the bladder, and weight loss. The patient did not have any gastrointestinal symptoms. The physical examination, laboratory examination, cytology of the urine, computed tomography and cystoscopy were inconclusive. The partial cystectomy, subsequent exploratory laparotomy and intraoperative frozen analysis revealed the appendiceal mucinous adenocarcinoma with a fistula to the urinary bladder. The appendectomy and the right hemicolectomy with a ileocolic anastomosis, the lymphadenectomy and the partial cystectomy limited to the anterior wall was performed. Six months after operation, the patient was in a good health with no obvious discomfort, no recurrence or distant metastases. The recommended treatment for the adenocarcinoma of the appendix invading the bladder with a fistula formation is as follows: appendectomy, right hemicolectomy with ileocolic anastomosis, lymphadenectomy, partial cystectomy and intraperitoneal hyperthermic chemoperfusion.
1 Introduction
The primary appendiceal carcinoma is a rare disease. It has an age-adjusted incidence of 0.12 cases per 1,000,000 people per year [1]. It accounts for 0.01%-1% of all gastrointestinal malignancies [2,3], and 4%-6% of appendiceal neoplasms [4]. It is found in only 0.08-0.2% of appendectomy specimens [5].
The international Classification of Diseases for Oncology group divides the adenocarcinoma of the appendix into three categories: colonic, mucinous and signet ring cell adenocarcinoma [1,6]. Among the three types, the signet ring type is extremely rare and the colonic type is the most common type. The mucinous type is usually well differentiated, often produces pseudomyxoma peritonei and is not metastatic until the late stage of the disease. The mean onset age of the mucinous type is between 50 and 60 years old, with a male to female ratio of 3-4:1 [7,8].
It is well known that tumors of the pelvic organs, such as the ovary, the rectum and the sigmoid colon, can invade the urinary bladder due to spatial contiguity. However, the appendiceal mucinous adenocarcinoma infiltrating the bladder is extremely rare and less than 20 cases have been reported [1]. The adenocarcinoma of the appendix invading the bladder with a fistula formation is even rarer. In our review of the literature, there were only 3 cases reported [8, 9, 10]. Here we reported a case of the adenocarcinoma of the appendix invading the urinary bladder and we reviewed the relevant literature.
2 Case report
A 54-years old man with a 6-month history of intermittent episodes of irritative voiding symptoms of the bladder and weight loss was admitted. The patient did not have any gastrointestinal symptoms such as pain, obstruction or melena, and he presented a negative medical history for gastrointestinal diseases. The physical examination was negative. An urine analysis revealed 30 white blood cells and 12 red blood cells per high power field. No malignant cells were observed in the urine. The carcinoembryonic antigen level was normal. The enhanced pelvic computed tomography (CT) scan revealed an irregular and slightly higher density (Figure 1), with the largest cross-section of 5.2 cm×4.8 cm. Its CT value was slightly higher than the intravesical CT value. There was some punctate calcification on the edge and inside the hyperdense area. A cystoscopy showed an edematous broad opening with mucinous components in the right posterior wall of the bladder (Figure 2).
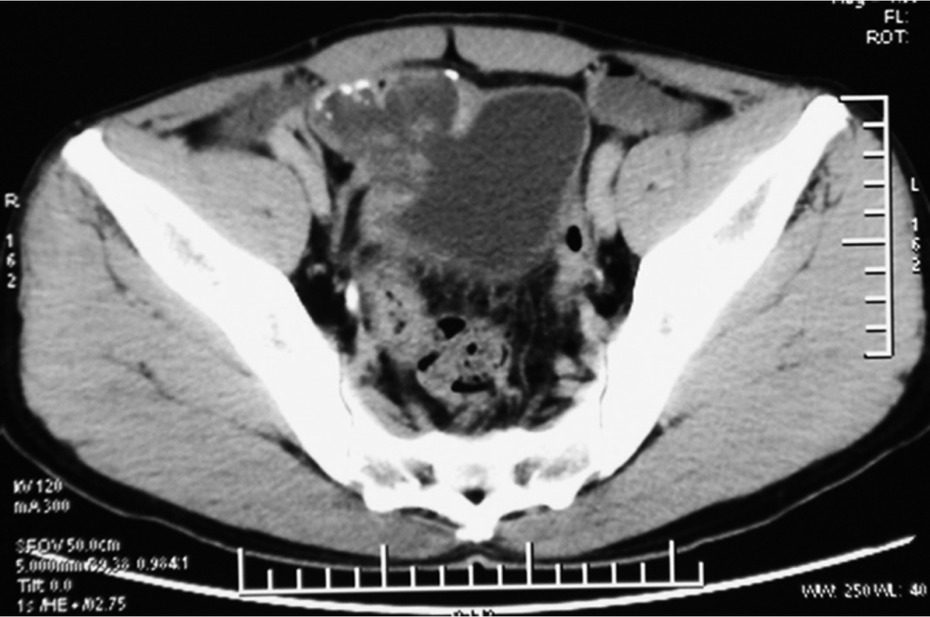
CT scan shows an irregular slightly higher density. The largest cross-section diameter was 5.2 cm×4.8 cm and its CT value was slightly higher than the intravesical CT value. There was some punctate calcification on the edge and inside the hyperdense area.
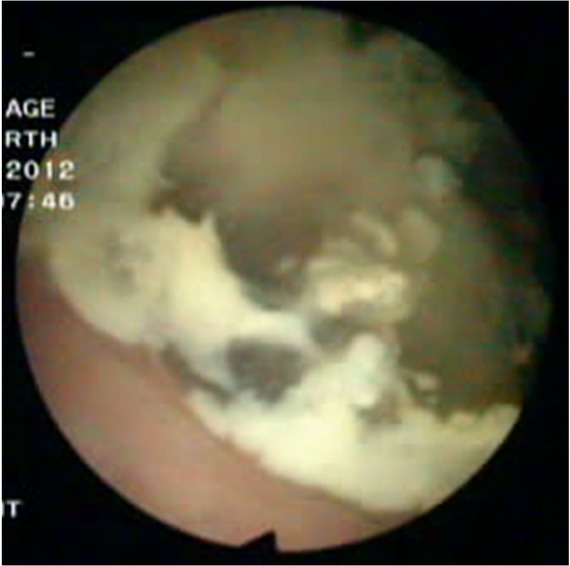
Cystoscopy findings. Cystoscopy was performed and an edematous broad opening with mucinous components in the right posterior wall of the bladder was observed.
The partial cystectomy was therefore performed, and the right posterior wall of the bladder was adherent to the peritonea. It was found, during the subsequent exploratory laparotomy, that the tumor was located between the ileocecum and the bladder. The appendix was not observed. The ileocecum firmly adhered to the bladder posterior wall with a fistula, which was full of mucus. The intraoperative frozen analysis revealed appendiceal mucinous adenocarcinoma. Thus, the mucinous adenocarcinoma of the appendix with a fistula to the urinary bladder was diagnosed. The following procedures: appendectomy, right hemicolectomy with ileocolic anastomosis, lymphadenectomy, and partial cystectomy limited to the anterior wall, were performed.
On a gross examination, accumulation of mucus within in the lumen and thickening of the wall were observed. A pathological examination confirmed a mucinous adenocarcinoma of the appendix with a transmural growth to the right posterior wall of the bladder (Figure 3). The lymph node metastasis was not observed. A pathological staging was pT4N0M0 (the TNM classification), and stage B (Ducks, Astler and Coller classification). The patient was discharged on the 15th postoperative day. He did not received chemotherapy due to economical reason. No obvious discomfort, no recurrence or distant metastases were observed in postoperative outpatient periodic review for 1 year.
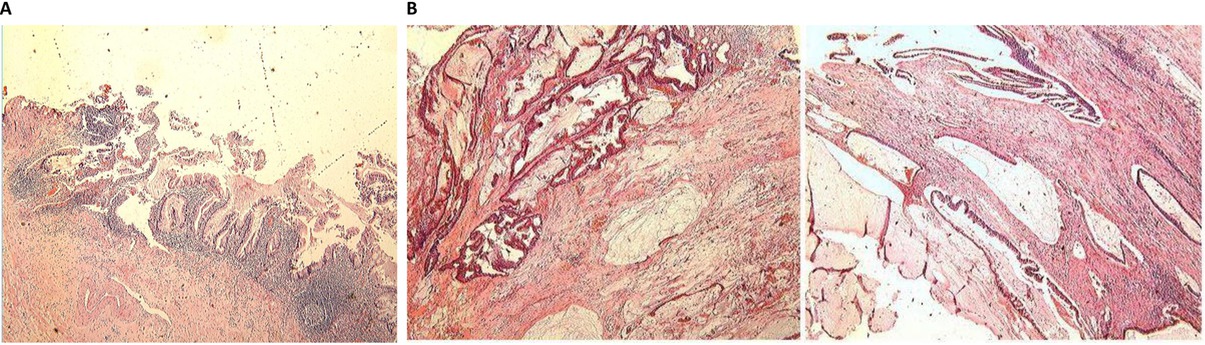
Pathological morphology by HE staining. Postoperative pathological examination confirmed the diagnosis of mucinous adenocarcinoma of the appendix (A). The entire bladder was filled with mucinous adenocarcinoma (B).
Informed consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study.
Ethical approval: The research related to human use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations, institutional policies and in accordance the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and has been approved by the authors’ institutional review board or equivalent committee
3 Discussion
The adenocarcinoma of the appendix invading the urinary bladder is an extremely rare disease. To our best knowledge, only a few cases have been reported in the world [1,3], and this disease is very difficult to be diagnosed before operation.
An appendicovesical fistula accounts for 5% of intestinal vesical fistula [11], and the most often cause is a delayed treatment of an acute appendicitis. The peak onset age of appendicovesical fistula is between the ages of 10 to 60, but the mean one age of appendiceal neoplasm invading the bladder, which occurs more often in males, is older [8].
An appendiceal neoplasm most often presents as an acute appendicitis or as a palpable abdominal mass. The mucinous adenocarcinoma invading the bladder does not have classical symptoms of gastrointestinal tracts and vesicoenteric fistula, such as abdominal pain and pneumaturia. Only irritative symptoms of the bladder or the gross hematuria are manifested. Therefore, it is difficult to make an early and accurate preoperative diagnosis of the appendicovesical fistula.
The key to diagnosis is the awareness and the vigilance for this disease. When the thickened appendix full of mucus was found during surgery, the mucinous adenocarcinoma invading the bladder should be considered, and the intraoperative frozen biopsy should be immediately performed. If the diagnosis is clear, the formal right hemicolectomy is considered as the traditional treatment for the patients with the non-metastatic adenocarcinoma of the appendix. The use of the appendectomy is limited to a small area of the appendix, especially for in situ and localized cases [12]. The 5-year survival rate was 20% with the appendectomy alone, while it was 45-63% with right hemicolectomy [13,14]. The mucinous adenocarcinoma has the tendency to produce conditions such as pseudomyxoma peritonei. In addition to the right hemicolectomy, the intraperitoneal chemotherapy or more accurate intraperitoneal hyperthermic chemoperfusion is recommended for mucinous adenocarcinoma of the appendix invading the bladder [12,15].
4 Conclusion
The adenocarcinoma of the appendix invading the urinary bladder is an extremely rare disease. Surgeons should be familiar with the necessary knowledge to make an appropriate and accurate diagnosis, which will lead to a prompt and correct treatment. The recommended treatment for the adenocarcinoma of the appendix invading the bladder with a fistula formation is as follows: appendectomy, right hemicolectomy with ileocolic anastomosis, lymphadenectomy, partial cystectomy and intraperitoneal hyperthermic chemoperfusion.
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest
References
[1] Tsutsumi S, Murata A, Yamauchi Y, Okano K, Yokoyama H, Kimura A et al. A Case of Appendiceal Mucinous Adenocarcinoma Detected with a Bladder Tumor. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 2017; 44: 1425-1427Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Hakim S, Amin M, Cappell MS. Limited, local, extracolonic spread of mucinous appendiceal adenocarcinoma after perforation with formation of a malignant appendix-to-sigmoid fistula: Case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22: 8624-863010.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8624Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Kimura S, Kira S, Koide H, Suzuki K, Moritake J, Hiramoto Y et al. [Vesico-appendiceal fistula caused by appendiceal cancer: a case report]. Hinyokika Kiyo 2015; 61: 95-98Suche in Google Scholar
[4] Gourgiotis S, Oikonomou C, Kollia P, Falidas E, Villias C. Persistent Coughing as the First Symptom of Primary Mucinous Appendiceal Adenocarcinoma. J Clin Med Res 2015; 7: 649-65210.14740/jocmr2192wSuche in Google Scholar
[5] Pulighe F, Paliogiannis P, Cossu A, Palmieri G, Colombino M, Scognamillo F et al. Molecular analysis of appendiceal mucinous cystadenoma and rectal adenocarcinoma in a patient with urothelial carcinoma: a case report. J Med Case Rep 2013; 7: 17010.1186/1752-1947-7-170Suche in Google Scholar
[6] Calum M, Constance P, Valerie VH. International classification of diseases for oncology: WHO; 1990Suche in Google Scholar
[7] Chen KT, Spaulding RW. Appendiceal carcinoma masquerading as primary bladder carcinoma. J Urol 1991; 145: 821-82210.1016/S0022-5347(17)38462-8Suche in Google Scholar
[8] Nitecki SS, Wolff BG, Schlinkert R, Sarr MG. The natural history of surgically treated primary adenocarcinoma of the appendix. Ann Surg 1994; 219: 51-5710.1097/00000658-199401000-00009Suche in Google Scholar
[9] Dalton DP, Dalkin BL, Sener SF, Pappas PS, Blum MD. Enterovesical fistula secondary to mucinous adenocarcinoma of appendix. J Urol 1987; 138: 617-61810.1016/S0022-5347(17)43277-0Suche in Google Scholar
[10] Vidarsdottir H, Moller PH, Benediktsdottir KR, Geirsson G. Adenocarcinoma of the appendix with a fistula to the urinary bladder. Scand J Urol Nephrol 2010; 44: 354-35610.3109/00365599.2010.491085Suche in Google Scholar
[11] Ikeda I, Miura T, Kondo I. Case of Vesico-Appendiceal Fistula Secondary to Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Appendix. J Urol 1995; 153: 122010.1016/S0022-5347(01)67558-XSuche in Google Scholar
[12] Athanasios P, Alexandros P, Nikolaos K, Konstantinos B, Konstantinos E, Evaggelos F. Primary appendiceal mucinous adenocarcinoma alongside with situs inversus totalis: a unique clinical case. World J Surg Oncol 2010; 8: 1-5Suche in Google Scholar
[13] Hesketh KT. The management of primary adenocarcinoma of the vermiform appendix. Gut 1963; 4: 158-16810.1136/gut.4.2.158Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Hopkins GB, Tullis RH, Kristensen KA. Primary adenocarcinoma of the vermiform appendix: report of seven cases and review of the literature. Dis Colon Rectum 1973; 16: 140-14410.1007/BF02589930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Stewart JH, Shen P, Russell G, Fenstermaker J, Mcwilliams L, Coldrun FM et al. A Phase I Trial of Oxaliplatin for Intraperitoneal Hyperthermic Chemoperfusion for the Treatment of Peritoneal Surface Dissemination from Colorectal and Appendiceal Cancers. Ann Surg Oncol 2008; 15: 213710.1245/s10434-008-9967-1Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2019 Jiwei Yang et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Plant Sciences
- Extended low temperature and cryostorage longevity of Salix seeds with desiccation control
- Genome-wide analysis of the WRKY gene family and its response to abiotic stress in buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum)
- Differential expression of microRNAs during root formation in Taxus chinensis var. mairei cultivars
- Metabolomics Approach for The Analysis of Resistance of Four Tomato Genotypes (Solanum lycopersicum L.) to Root-Knot Nematodes (Meloidogyne incognita)
- Beneficial Effects of Salt on Halophyte Growth: Morphology, Cells, and Genes
- Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from safflower rhizosphere and their effect on seedling growth
- Anatomy and Histochemistry of the Roots and Shoots in the Aquatic Selenium Hyperaccumulator Cardamine hupingshanensis (Brassicaceae)
- Effects of LED light on Acacia melanoxylon bud proliferation in vitro and root growth ex vitro
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Intensity of stripping and sugar content in the bark and the bast of European beech (Fagus sylvatica)
- Influence of monometallic and bimetallic phytonanoparticles on physiological status of mezquite
- Loci identification of a N-acyl homoserine lactone type quorum sensing system and a new LysR-type transcriptional regulator associated with antimicrobial activity and swarming in Burkholderia gladioli UAPS07070
- Bacillus methylotrophicus has potential applications against Monilinia fructicola
- Evaluation of Heavy Metals and Microbiological Contamination of Selected herbals from Palestine
- The effect of size of black cherry stumps on the composition of fungal communities colonising stumps
- Effect of rhamnolipids on microbial biomass content and biochemical parameters in soil contaminated with coal tar creosote
- Effects of foliar trichomes on the accumulation of atmospheric particulates in Tillandsia brachycaulos
- Isolation and characterisation of the agarolytic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas ruthenica
- Comparison of soil bioconditioners and standard fertilization in terms of the impact on yield and vitality of Lolium perenne and soil biological properties
- Biomedical Sciences
- The number of regulatory B cells is increased in mice with collagen-induced arthritis
- Lactate overload inhibits myogenic activity in C2C12 myotubes
- Diagnostic performance of serum CK-MB, TNF-α and hs-CRP in children with viral myocarditis
- Correlation between PPARGC1A gene rs8192678 G>A polymorphism and susceptibility to type-2 diabetes
- Improving the Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma using serum AFP expression in combination with GPC3 and micro-RNA miR-122 expression
- The ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte is a predictor in endometrial cancer
- Expression of HER2/c-erbB-2, EGFR protein in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance
- Clinical significance of neuropeptide Y expression in pelvic tissue in patients with pelvic floor dysfunction
- Overexpression of RASAL1 indicates poor prognosis and promotes invasion of ovarian cancer
- The effect of adrenaline on the mineral and trace element status in rats
- Effects of Ischemic Post-Conditioning on the Expressions of LC3-II and Beclin-1 in the Hippocampus of Rats after Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion
- Long non-coding RNA DUXAP8 regulates the cell proliferation and invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer
- Risk factors of regional lymph node metastasis in patients with cervical cancer
- Bullous prurigo pigmentosa
- Association of HIF-1α and NDRG2 expression with EMT in gastric cancer tissues
- Decrease in the level of nervonic acid and increased gamma linolenic acid in the plasma of women with polycystic ovary syndrome after a three-month low-glycaemic index and caloric reduction diet
- Depletion of VAX2 restrains the malignant progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma by modulating ERK signaling pathway
- Insulin resistance is a risk factor for mild cognitive impairment in elderly adults with T2DM
- Nurr1 promotes lung cancer apoptosis via enhancing mitochondrial stress and p53-Drp1 pathway
- Predictive significance of serum MMP-9 in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Agmatine prevents oxidative-nitrative stress in blood leukocytes under streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus
- Effect of platelet-rich plasma on implant bone defects in rabbits through the FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- The diagnostic efficacy of thrombelastography (TEG) in patients with preeclampsia and its association with blood coagulation
- Value of NSE and S100 Protein of Kawasaki Disease with aseptic meningitis in Infant
- CB2 receptor agonist JWH133 activates AMPK to inhibit growth of C6 glioma cells
- The effects of various mouthwashes on osteoblast precursor cells
- Co-downregulation of GRP78 and GRP94 induces apoptosis and inhibits migration in prostate cancer cells
- SKA3 up-regulation promotes lung adenocarcinoma growth and is a predictor of poor prognosis
- Protective effects and mechanisms of microRNA-182 on oxidative stress in RHiN
- A case of syphilis with high bone arsenic concentration from early modern cemetery (Wroclaw, Poland)
- Study of LBHD1 Expression with Invasion and Migration of Bladder Cancer
- 1-Hydroxy-8-methoxy-anthraquinon reverses cisplatin resistance by inhibiting 6PGD in cancer cells
- Andrographolide as a therapeutic agent against breast and ovarian cancers
- Accumulation of α-2,6-sialyoglycoproteins in the muscle sarcoplasm due to Trichinella sp. invasion
- Astragalus polysaccharides protects thapsigargin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in HT29 cells
- IGF-1 via PI3K/Akt/S6K signaling pathway protects DRG neurons with high glucose-induced toxicity
- Intra-arterial tirofiban in a male nonagenarian with acute ischemic stroke: A case report
- Effects of Huaiqihuang Granules adjuvant therapy in children with primary nephrotic syndrome
- Immune negative regulator TIPE2 inhibits cervical squamous cancer progression through Erk1/2 signaling
- Asymptomatic mediastinal extra-adrenal paraganglioma as a cause of sudden death: a case Report
- Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma of appendix invading urinary bladder with a fistula: a case report
- Minocycline attenuates experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats
- Neural Remodeling of the Left Atrium in rats by Rosuvastatin following Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Protective effects of emodin on lung injuries in rat models of liver fibrosis
- RHOA and mDia1 promotes apoptosis of breast cancer cells via a high dose of doxorubicin treatment
- Bacteria co-colonizing with Clostridioides difficile in two asymptomatic patients
- A allele of ICAM-1 rs5498 and VCAM-1 rs3181092 is correlated with increased risk for periodontal disease
- Treatment of hepatic cystic echinococcosis patients with clear cell renal carcinoma: a case report
- Edaravone exerts brain protective function by reducing the expression of AQP4, APP and Aβ proteins
- Correlation between neutrophil count and prognosis in STEMI patients with chronic renal dysfunction: a retrospective cohort study
- Bioinformatic analysis reveals GSG2 as a potential target for breast cancer therapy
- Nuciferine prevents hepatic steatosis by regulating lipid metabolismin diabetic rat model
- Analysis of SEC24D gene in breast cancer based on UALCAN database
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Co-cultured Bone-marrow Derived and Tendon Stem Cells: Novel Seed Cells for Bone Regeneration
- Animal Sciences
- Comparative analysis of gut microbiota among the male, female and pregnant giant pandas (Ailuropoda Melanoleuca)
- Adaptive immunity and skin wound healing in amphibian adults
- Hox genes polymorphism depicts developmental disruption of common sole eggs
- The prevalence of virulence genes and multidrug resistance in thermophilic Campylobacter spp. isolated from dogs
- Agriculture
- Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum supplementation on production performance and fecal microbial composition in laying hens
- Identification of Leaf Rust Resistance Genes in Selected Wheat Cultivars and Development of Multiplex PCR
- Determining Potential Feed Value and Silage Quality of Guar Bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba) Silages
- Food Science
- Effect of Thermal Processing on Antioxidant Activity and Cytotoxicity of Waste Potato Juice
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Plant Sciences
- Extended low temperature and cryostorage longevity of Salix seeds with desiccation control
- Genome-wide analysis of the WRKY gene family and its response to abiotic stress in buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum)
- Differential expression of microRNAs during root formation in Taxus chinensis var. mairei cultivars
- Metabolomics Approach for The Analysis of Resistance of Four Tomato Genotypes (Solanum lycopersicum L.) to Root-Knot Nematodes (Meloidogyne incognita)
- Beneficial Effects of Salt on Halophyte Growth: Morphology, Cells, and Genes
- Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from safflower rhizosphere and their effect on seedling growth
- Anatomy and Histochemistry of the Roots and Shoots in the Aquatic Selenium Hyperaccumulator Cardamine hupingshanensis (Brassicaceae)
- Effects of LED light on Acacia melanoxylon bud proliferation in vitro and root growth ex vitro
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- Intensity of stripping and sugar content in the bark and the bast of European beech (Fagus sylvatica)
- Influence of monometallic and bimetallic phytonanoparticles on physiological status of mezquite
- Loci identification of a N-acyl homoserine lactone type quorum sensing system and a new LysR-type transcriptional regulator associated with antimicrobial activity and swarming in Burkholderia gladioli UAPS07070
- Bacillus methylotrophicus has potential applications against Monilinia fructicola
- Evaluation of Heavy Metals and Microbiological Contamination of Selected herbals from Palestine
- The effect of size of black cherry stumps on the composition of fungal communities colonising stumps
- Effect of rhamnolipids on microbial biomass content and biochemical parameters in soil contaminated with coal tar creosote
- Effects of foliar trichomes on the accumulation of atmospheric particulates in Tillandsia brachycaulos
- Isolation and characterisation of the agarolytic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas ruthenica
- Comparison of soil bioconditioners and standard fertilization in terms of the impact on yield and vitality of Lolium perenne and soil biological properties
- Biomedical Sciences
- The number of regulatory B cells is increased in mice with collagen-induced arthritis
- Lactate overload inhibits myogenic activity in C2C12 myotubes
- Diagnostic performance of serum CK-MB, TNF-α and hs-CRP in children with viral myocarditis
- Correlation between PPARGC1A gene rs8192678 G>A polymorphism and susceptibility to type-2 diabetes
- Improving the Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma using serum AFP expression in combination with GPC3 and micro-RNA miR-122 expression
- The ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte is a predictor in endometrial cancer
- Expression of HER2/c-erbB-2, EGFR protein in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance
- Clinical significance of neuropeptide Y expression in pelvic tissue in patients with pelvic floor dysfunction
- Overexpression of RASAL1 indicates poor prognosis and promotes invasion of ovarian cancer
- The effect of adrenaline on the mineral and trace element status in rats
- Effects of Ischemic Post-Conditioning on the Expressions of LC3-II and Beclin-1 in the Hippocampus of Rats after Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion
- Long non-coding RNA DUXAP8 regulates the cell proliferation and invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer
- Risk factors of regional lymph node metastasis in patients with cervical cancer
- Bullous prurigo pigmentosa
- Association of HIF-1α and NDRG2 expression with EMT in gastric cancer tissues
- Decrease in the level of nervonic acid and increased gamma linolenic acid in the plasma of women with polycystic ovary syndrome after a three-month low-glycaemic index and caloric reduction diet
- Depletion of VAX2 restrains the malignant progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma by modulating ERK signaling pathway
- Insulin resistance is a risk factor for mild cognitive impairment in elderly adults with T2DM
- Nurr1 promotes lung cancer apoptosis via enhancing mitochondrial stress and p53-Drp1 pathway
- Predictive significance of serum MMP-9 in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Agmatine prevents oxidative-nitrative stress in blood leukocytes under streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus
- Effect of platelet-rich plasma on implant bone defects in rabbits through the FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- The diagnostic efficacy of thrombelastography (TEG) in patients with preeclampsia and its association with blood coagulation
- Value of NSE and S100 Protein of Kawasaki Disease with aseptic meningitis in Infant
- CB2 receptor agonist JWH133 activates AMPK to inhibit growth of C6 glioma cells
- The effects of various mouthwashes on osteoblast precursor cells
- Co-downregulation of GRP78 and GRP94 induces apoptosis and inhibits migration in prostate cancer cells
- SKA3 up-regulation promotes lung adenocarcinoma growth and is a predictor of poor prognosis
- Protective effects and mechanisms of microRNA-182 on oxidative stress in RHiN
- A case of syphilis with high bone arsenic concentration from early modern cemetery (Wroclaw, Poland)
- Study of LBHD1 Expression with Invasion and Migration of Bladder Cancer
- 1-Hydroxy-8-methoxy-anthraquinon reverses cisplatin resistance by inhibiting 6PGD in cancer cells
- Andrographolide as a therapeutic agent against breast and ovarian cancers
- Accumulation of α-2,6-sialyoglycoproteins in the muscle sarcoplasm due to Trichinella sp. invasion
- Astragalus polysaccharides protects thapsigargin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in HT29 cells
- IGF-1 via PI3K/Akt/S6K signaling pathway protects DRG neurons with high glucose-induced toxicity
- Intra-arterial tirofiban in a male nonagenarian with acute ischemic stroke: A case report
- Effects of Huaiqihuang Granules adjuvant therapy in children with primary nephrotic syndrome
- Immune negative regulator TIPE2 inhibits cervical squamous cancer progression through Erk1/2 signaling
- Asymptomatic mediastinal extra-adrenal paraganglioma as a cause of sudden death: a case Report
- Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma of appendix invading urinary bladder with a fistula: a case report
- Minocycline attenuates experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats
- Neural Remodeling of the Left Atrium in rats by Rosuvastatin following Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Protective effects of emodin on lung injuries in rat models of liver fibrosis
- RHOA and mDia1 promotes apoptosis of breast cancer cells via a high dose of doxorubicin treatment
- Bacteria co-colonizing with Clostridioides difficile in two asymptomatic patients
- A allele of ICAM-1 rs5498 and VCAM-1 rs3181092 is correlated with increased risk for periodontal disease
- Treatment of hepatic cystic echinococcosis patients with clear cell renal carcinoma: a case report
- Edaravone exerts brain protective function by reducing the expression of AQP4, APP and Aβ proteins
- Correlation between neutrophil count and prognosis in STEMI patients with chronic renal dysfunction: a retrospective cohort study
- Bioinformatic analysis reveals GSG2 as a potential target for breast cancer therapy
- Nuciferine prevents hepatic steatosis by regulating lipid metabolismin diabetic rat model
- Analysis of SEC24D gene in breast cancer based on UALCAN database
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Co-cultured Bone-marrow Derived and Tendon Stem Cells: Novel Seed Cells for Bone Regeneration
- Animal Sciences
- Comparative analysis of gut microbiota among the male, female and pregnant giant pandas (Ailuropoda Melanoleuca)
- Adaptive immunity and skin wound healing in amphibian adults
- Hox genes polymorphism depicts developmental disruption of common sole eggs
- The prevalence of virulence genes and multidrug resistance in thermophilic Campylobacter spp. isolated from dogs
- Agriculture
- Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum supplementation on production performance and fecal microbial composition in laying hens
- Identification of Leaf Rust Resistance Genes in Selected Wheat Cultivars and Development of Multiplex PCR
- Determining Potential Feed Value and Silage Quality of Guar Bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba) Silages
- Food Science
- Effect of Thermal Processing on Antioxidant Activity and Cytotoxicity of Waste Potato Juice

