Abstract
Introduction
To study the impact on adult’s fertility of serum inhibin B levels in adolescent patients with idiopathic varicocele after minimally invasive surgical correction and to compare fluctuation of pituitary-testis hormonal values and testicular volumes. Materials and Methods: A case-control study was carried out on a group adolescent patients (n=60) affected by idiopathic left varicocele (group V) and compared with control adolescents (n=40) in the Paediatric Surgery Section of Siena (from June 1993 till September 2013). Inhibin B levels and testicular volume before (T0) and after at 6 and 12 months from surgery (T1 and T2) were evaluated. Results: A positive correlation between testicular growth at T1 and T2 (P<0.001) was found. Linear regression analysis showed a positive correlation between inhibin B levels and testicular volume (expressed as the sum of the right and left values) (P<0.0001). Conclusions: Inhibin B levels are a valid marker for studying the effects of varicocele on the testicular function and confirm the necessity of early surgical correction for preventing the trophic testicular damage and male infertility.
1 Introduction
Varicocele is the most commonly diagnosed pre-pubertal andrological condition, with an impact on adult’s fertility. It has an incidence of 10-15% between adolescents [1].
A time-dependent decline in testicular function has been clearly documented in children with varicocele [2]. An open debate exists on the gold standard of surgical treatment and follow up (timing and existence of predictive factors of outcome).
Inhibin B is a glycoprotein secreted by Sertoli cells that has a role in the control of spermatogenesis, through a mechanism of negative feedback on follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion. This mechanism is activated during pubertal stage G3 according to Tanner’s classification [3]. Serum inhibin B levels are low and correlated with testicular volume in patients with varicocele during Tanner stages G4/G5 [4]. Surgical treatment in adult’s var-icocele increases serum inhibin B levels in the postoperative period, with positive effects on testicular viability [5].
The aim of the present study was to analyze inhibin B in adolescent patients with idiopathic varicocele after minimally invasive surgical correction, comparing fluctuation of hormonal values and testicular volumes.
2 Materials and methods
A case-control study was carried out on a population of adolescent patients (n=60) with idiopathic left varicocele of grade III after Horner (group V), in the Paediatric Surgery Section of Siena (from June 1993 to September 2013). The pathology was diagnosed after clinical examination and confirmed by colour Doppler sonography of the spermatic vessels. All patients in the study population were in pubertal stages classifiable as between G4 and G5 according to Tanner’s classification. These patients were compared to control adolescents (n=44) – who were not affected by endocrine pathologies – with the same Tanner stages G4-G5 (group C). Informed consent was requested and obtained from both groups, following authorization by the local Ethics Committee. The patients in group V had a mean age at diagnosis of 15.5 years (range: 12.5-17 years); group C had a mean age of 15.1 years (range: 13-16.5 years).
At diagnosis (T0) blood samples were taken from all patients to assess basal serum inhibin B levels and tes-ticular volume was determined by clinical evaluation and ultrasound exam. Palomo varicocelectomy through a minimally invasive approach was performed in all cases within one month of diagnosis.
After surgery, all patients were submitted to a follow up evaluation (6 and 12 months) by measuring serum inhibin B levels and testicular volume (T1 and T2, respectively). All data are expressed as mean and median +-/± 2 standard error of mean (SEM). The differences in serum inhibin B levels between the two groups were compared by an unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction, while testicular volumes were compared by a paired t-test. Qualitative analysis between independent variables was done by linear regression analysis. The differences were considered significant in all cases in which the P value was below 0.05.
Ethical approval: The research related to human use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations, institutional policies and in accordance the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and has been approved by the authors’ institutional review board or equivalent committee.
3 Results
Serum inhibin B levels and testicular volume at T0, T1 and T2 are reported in Table 1. Inhibin B values in patients at T0 were lower than in controls (P<0.0001); inhibin B values between T1 and T2 showed a significant increase (Figure 1). Left testicular volume of patients was lower than in controls at T0 (P<0.0001), but not at T2 (P=0.7841). A positive correlation was found between testicular growth at T1 and T2 (P<0.001) (Figure 2).
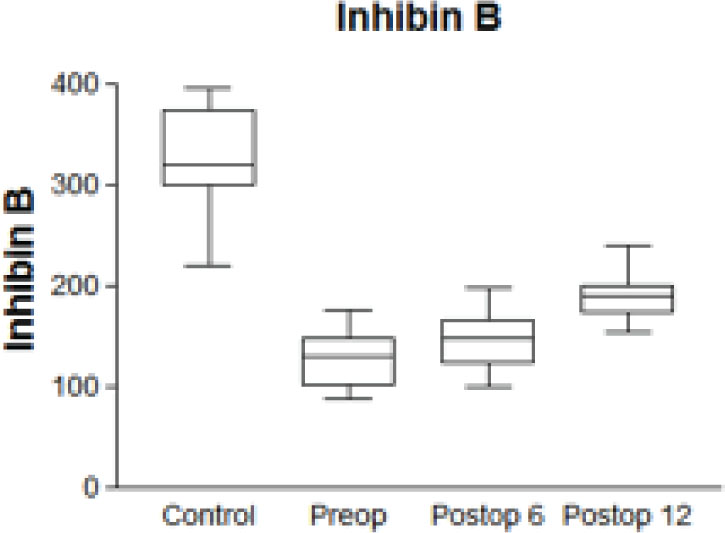
Statistical analysis about serum levels of inhibin B.
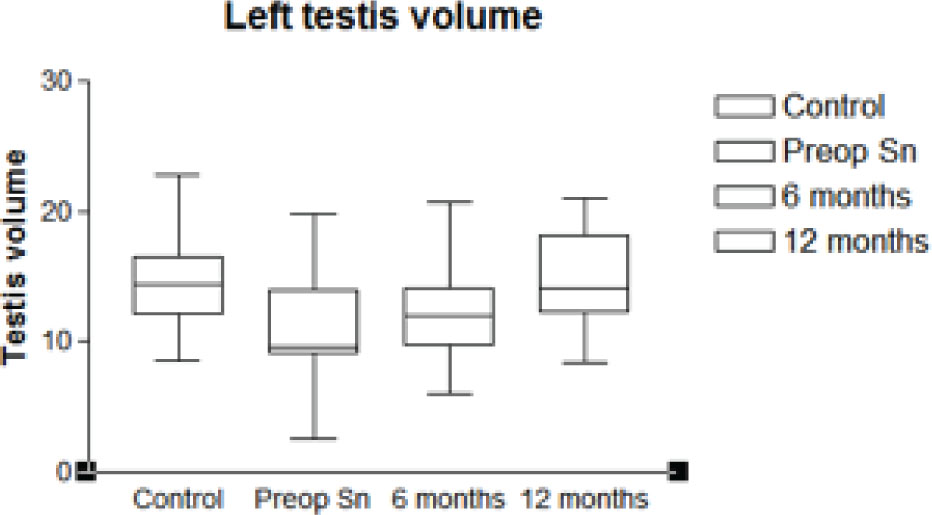
Statistical analysis about left testis volumes expressed in ml.
Values expressed as mean -+ standard error of mean serum levels of inhibin B and testicular volumes at T0, T1 and T2.
| PATIENTS | CONTROLS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | ||
| INHIBIN B (pg/ml) | 125.3 +- 3.603 | 145.1 +- 3.819 | 190.8 +- 3.027 | 324.6 +- 6.512 |
| RIGHT VOLUME (ml) | 12.44 +- 0.521 | 12.84 +- 0.518 | 13.18 +- 0.528 | 14.68 +- 0.726 |
| LEFT VOLUME (ml) | 10.83 +- 0.535 | 12.02 +-0.461 | 14.75 +- 0.463 | 14.55 +- 0.561 |
Linear regression analysis showed a positive correlation between inhibin B values in group V and testicular volume (expressed as the sum of the right and left values) (P<0.0001) (Figures 3).
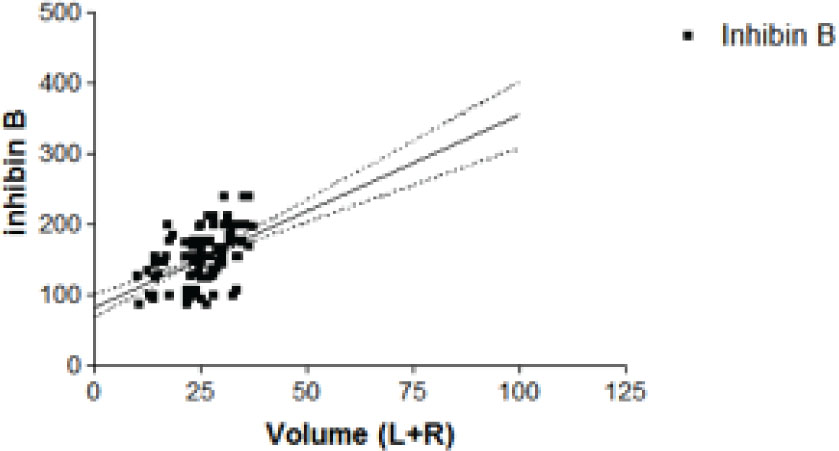
Linear regression analysis between inhibin B values and testicular volumes expressed as L+R.
4 Discussion
The correlation between varicocele and infertility is of particular interest since varicocele has a negative effect on spermatogenesis [6]. The restoration of fertility in an azoospermic patient following correction of the venous pathology of the pampiniform plexus has been clearly shown [7]. However, the mechanisms by which varicocele negatively affects spermatogenesis are still unknown, but effects on hormonal dysfunctions on the hypothalamus-hypophysis/pituitary-gonad axis may be suggested [8].
The effect of varicocelectomy on fertility and improvements in sperm concentration, motility and testicular volume has been reported [8,9], even though recent randomized trials have highlighted contradicting results concerning the effects of varicocelectomy on fertility [9,10].
Serum inhibin B levels are recognized as high sensitivity and specificity markers of spermatogenesis [11]. This glycoprotein is produced/secreted by Sertoli cells and directly by spermatic cells in response to FSH and regulates the production of FSH via negative feedback to the hypothalamus-hypophysis/pituitary axis. Inhibin B serum levels are positively correlated with sperm count, testicular volume and the state of the spermatogenetic epithelium evaluated by biopsies on testicular tissue [11,12]. Starting from the hypothesis that serum levels of inhibin B reflect the functionality of Sertoli cells in the presence of germinal cells, inhibin B levels were evaluated in adolescent varicocele [11]. Studies carried out on adult patients with varicocele showed a positive correlation between serum levels of inhibin B and sperm concentration following surgical correction. Pierik et al. demonstrated an increase in inhibin B concentration following surgical treatment of varicocele, thus suggesting that corrective treatment may promote functional repair of Sertoli cells, with undoubtedly positive effects on fertility [11,13]. The same Authors pointed out that an increase in serum levels of inhibin B was associated with an increase in the number of sperm/sperm concentration and an improvement in motility [12].
While Romeo et al. demonstrated a difference between untreated adolescent patients with varicocele and healthy controls in terms of basal serum concentrations of inhibin B [4], our study investigated both preoperative and postoperative aspects, and highlighted the reduced plasma concentrations of inhibin B in the preoperative period in varicocele patients in comparison to healthy controls (T0). Comparison between the inhibin B levels at 6 and 12 months (T1, T2) showed a statistically significant increase representing a sign of trophic improvement in post-varicocelectomy gonadic tissue and restoration of Sertoli cell function and spermatogenesis. At Tanner stages IV and V, in fact, the production of inhibin B is strongly influenced by the interaction between Sertoli cells and spermatids, which are very sensitive to variations in testicular temperature. The correction of varicocele ensures a reduction in scrotal temperature sufficient to bring about the functional restoration of spermatogenesis [13,14]. However, there is still a significant difference in inhibin B levels between surgically treated individuals and controls, meaning that long-term follow-up studies are necessary in order to identify any further increases in the serum inhibin B at a greater time from surgery.
The analysis of testicular volume highlighted a reduction in the left testicle in subjects with varicocele in comparison to controls at T0, demonstrating the effect of the pathology on testicular trophism in untreated subjects [15,16,17]. The right testicular volumes of subjects with varicocele were no different from controls. Trigo et al. reported an equally significant reduction in left testicular volume in patients with varicocele during Tanner stages III, IV and V. This can be explained by the hypothesis that varicocele may progressively damage seminiferous tubule function in the late phases of pubertal development [18]. The regression analysis conducted on the variations in testicular volume at T0, T1 and T2 and the increase in serum levels of inhibin B demonstrated a positive relationship between the two parameters, confirming that an increase in testicular volume is accompanied by a constant increase in inhibin B values.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, our present study showed that inhibin B levels are lower in adolescent with idiopathic varicocele than in healthy controls and that surgical correction of varicocele brings an increase in inhibin B concentration in the postoperative period, supporting the importance of early treatment of the pathology to ensure the rapid functional restoration of spermatogenesis. Serum Inhibin B levels are a valid markers for studying the effects of varicocele, before and after varicocelectomy, on the testicular function confirming the necessity of an early surgical correction for preventing trophic testicular damage and male infertility.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors state no conflict of interest
References
[1] World Health Organization: The influence of varicocele on parameters of fertility in a large group of men presenting to infertility clinic. Fertil Steril 1992;57;1289-129310.1016/S0015-0282(16)55089-4Search in Google Scholar
[2] Cheval MJ, Purcell MH. Deteriorations of semen parameters over time in men with untreated varicocele: Evidence of progressive testicular damage. Fertil Steril 1992;57:174-17710.1016/S0015-0282(16)54796-7Search in Google Scholar
[3] Di Bisceglie C, Bertagna A, Baldi M, Lanfranco F, Tagliabue M, Gazzera C, Gandini G, Manieri C. Varicocele sclerotherapy improves serum inhibin B levels and seminal parameters. Int J Androl. 2007; 2210.1111/j.1365-2605.2007.00747.xSearch in Google Scholar
[4] Romeo C, Arrigo T, Impellizzeri P, Manganaro A, Antonuccio P, Di Pasquale G, Messina MF, Marseglia L, Formica I, Zuccarello B. Altered serum inhibin b levels in adolescents with varicocele. J Pediatr Surg. 2007;42(2):390-39410.1016/j.jpedsurg.2006.10.013Search in Google Scholar
[5] Mormandi E, Levalle O, Ballerini MG, Hermes R, Calandra RS, Campo S. Serum levels of dimeric and monomeric inhibins and the degree of seminal alteration in infertile men with varicocele. Andrologia. 2003 Apr;35(2):106-11110.1046/j.1439-0272.2003.00546.xSearch in Google Scholar
[6] Fujisawa M, Dobashi M, Yamasaki T, Kanzaki M, Okada H, Arakawa S, Kamidono S. Significance of serum inhibin B concentration for evaluating improvement in spermatogenesis after varicocelectomy. Hum Reprod. 2001;16(9):1945-194910.1093/humrep/16.9.1945Search in Google Scholar
[7] Tulloch WS. Varicocele in subfertility. Results of treatment. 1955. J Urol. 2002;167(2 Pt 2):1184-5; discussion 118610.1016/S0022-5347(02)80378-0Search in Google Scholar
[8] Mordel N, Mor-Yosef S, Margalioth EJ, Simon A, Menashe M, Berger M, Schenker JG. Spermatic vein ligation as treatment for male infertility. Justification by postoperative semen improvement and pregnancy rates. J Reprod Med. 1990;35(2):123-127Search in Google Scholar
[9] Madgar I, Weissenberg R, Lunenfeld B, Karasik A, Goldwasser B. Controlled trial of high spermatic vein ligation for varicocele in infertile men. Fertil Steril. 1995;63(1):120-12410.1016/S0015-0282(16)57306-3Search in Google Scholar
[10] Nieschlag E, Hertle L, Fischedick A, Abshagen K, Behre HM. Update on treatment of varicocele: counselling as effective as occlusion of the vena spermatica. Hum Reprod. 1998;13(8):2147-215010.1093/humrep/13.8.2147Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Bordallo MA, Guimaraes MM, Pessoa CH, Carrico MK, Dimetz T, Gazolla HM, Dobbin J, Castilho IA. Decreased serum inhibin B/ FSH ratio as a marker of Sertoli cell function in male survivors after chemotherapy in childhood and adolescence. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2004;17(6):879-88710.1515/JPEM.2004.17.6.879Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Bohring C, Krause W. Serum levels of inhibin B in men with different causes of spermatogenic failure. Andrologia. 1999;31(3):137-14110.1111/j.1439-0272.1999.tb01400.xSearch in Google Scholar
[13] Pierik FH, Abdesselam SA, Vreeburg JT, Dohle GR, De Jong FH, Weber RF. Increased serum inhibin B levels after varicocele treatment. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2001;54(6):775-78010.1046/j.1365-2265.2001.01302.xSearch in Google Scholar
[14] Foresta C, Bettella A, Petraglia F, Pistorello M, Luisi S, Rossato M. Inhibin B levels in azoospermic subjects with cytologically characterized testicular pathology. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1999;50(6):695-70110.1046/j.1365-2265.1999.00659.xSearch in Google Scholar
[15] Laven JS, Haans LC, Mali WP, te Velde ER, Wensing CJ, Eimers JM. Effects of varicocele treatment in adolescents: a randomized study. Fertil Steril. 1992;58(4):756-76210.1016/S0015-0282(16)55324-2Search in Google Scholar
[16] Messina M, Zagordo L, Di Maggio G, Molinaro F, Abate V, Nardi N. Testicular hypotrophy in varicocele: pre and postoperative echographic follow-up in the pediatric age. Minerva Urol Nefrol 2006;58:151-155Search in Google Scholar
[17] Mancini S, Bulotta AL, et al. Surgical retroperitoneoscopic and transperitoneoscopic access in varicocelectomy: Duplex scan results in pediatric population. J Pediatr Urol 2014 Apr 13. Pii: S1477-5131(14)00110-710.1016/j.jpurol.2014.02.017Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Jensen TK, Andersson AM, Hjollund NH, Scheike T, Kolstad H, Giwercman A, Henriksen TB, Ernst E, Bonde JP, Olsen J, McNeilly A, Groome NP, Skakkebaek NE. Inhibin B as a serum marker of spermatogenesis: correlation to differences in sperm concentration and follicle-stimulating hormone levels. A study of 349 Danish men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(12):4059-406310.1210/jcem.82.12.4456Search in Google Scholar
© 2016 Francesco Molinaro et al.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Article
- The possible molecular regulation mechanism of CIK cells inhibiting the proliferation of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma NCL-H157 Cells
- Case Report
- Urethral stone of unexpected size: case report and short literature review
- Case Report
- Complete remission through icotinib treatment in Non-small cell lung cancer epidermal growth factor receptor mutation patient with brain metastasis: A case report
- Research Article
- FPL tendon thickness, tremor and hand functions in Parkinson’s disease
- Research Article
- Diagnostic value of circulating tumor cells in cerebrospinal fluid
- Research Article
- A meta-analysis of neuroprotective effect for traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in the treatment of glaucoma
- Research Article
- MiR-218 increases sensitivity to cisplatin in esophageal cancer cells via targeting survivin expression
- Research Article
- Association of HOTAIR expression with PI3K/Akt pathway activation in adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction
- Research Article
- The role of interleukin genes in the course of depression
- Case Report
- A rare case of primary pulmonary diffuse large B cell lymphoma with CD5 positive expression
- Research Article
- DWI and SPARCC scoring assess curative effect of early ankylosing spondylitis
- Research Article
- The diagnostic value of serum CEA, NSE and MMP-9 for on-small cell lung cancer
- Case Report
- Dysphonia – the single symptom of rifampicin resistant laryngeal tuberculosis
- Review Article
- Development of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M. Mutation in non small-cell lung carcinoma
- Research Article
- Negative regulation of CDC42 expression and cell cycle progression by miR-29a in breast cancer
- Research Article
- Expression analysis of the TGF-β/SMAD target genes in adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction
- Research Article
- Blood cells in thyroid cancer patients: a possible influence of apoptosis
- Research Article
- Detected EGFR mutation in cerebrospinal fluid of lung adenocarcinoma patients with meningeal metastasis
- Mini-review
- Pathogenesis-oriented approaches for the management of corticosteroid-resistant or relapsedprimary immune thrombocytopenia
- Research Article
- GSTP1 A>G polymorphism and chemosensitivity of osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis
- Research Article
- A meta-analysis of adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke susceptibility
- Research Article
- The diagnosis and pathological value of combined detection of HE4 and CA125 for patients with ovarian cancer
- Research Article
- SOX7 inhibits tumor progression of glioblastoma and is regulated by miRNA-24
- Research Article
- Sevoflurane affects evoked electromyography monitoring in cerebral palsy
- Case Report
- A case report of hereditary spherocytosis with concomitant chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Case Report
- A case of giant saphenous vein graft aneurysm followed serially after coronary artery bypass surgery
- Research Article
- LncRNA TUG1 is upregulated and promotes cell proliferation in osteosarcoma
- Review Article
- Meningioma recurrence
- Case Report
- Endobronchial amyloidosis mimicking bronchial asthma: a case report and review of the literature
- Case Report
- A confusing case report of pulmonary langerhans cell histiocytosis and literature review
- Research Article
- Effect of hesperetin on chaperone activity in selenite-induced cataract
- Research Article
- Clinical value of self-assessment risk of osteoporosis in Chinese
- Research Article
- Correlation analysis of VHL and Jade-1 gene expression in human renal cell carcinoma
- Research Article
- Is acute appendicitis still misdiagnosed?
- Retraction
- Retraction of: application of food-specific IgG antibody detection in allergy dermatosis
- Review Article
- Platelet Rich Plasma: a short overview of certain bioactive components
- Research Article
- Correlation between CTLA-4 gene rs221775A>G single nucleotide polymorphism and multiple sclerosis susceptibility. A meta-analysis
- Review Article
- Standards of anesthesiology practice during neuroradiological interventions
- Research Article
- Expression and clinical significance of LXRα and SREBP-1c in placentas of preeclampsia
- Letter to the Editor
- ARDS diagnosed by SpO2/FiO2 ratio compared with PaO2/FiO2 ratio: the role as a diagnostic tool for early enrolment into clinical trials
- Research Article
- Impact of sensory integration training on balance among stroke patients: sensory integration training on balance among stroke patients
- Review Article
- MicroRNAs as regulatory elements in psoriasis
- Review Article
- Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and postpandemic influenza in Lithuania
- Review Article
- Garengeot’s hernia: two case reports with CT diagnosis and literature review
- Research Article
- Concept of experimental preparation for treating dentin hypersensitivity
- Research Article
- Hydrogen water reduces NSE, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Research Article
- Xanthogranuloma of the sellar region diagnosed by frozen section
- Case Report
- Laparoscopic antegrade cholecystectomy: a standard procedure?
- Case Report
- Maxillary fibrous dysplasia associated with McCune-Albright syndrome. A case study
- Regular Article
- Sialoendoscopy, sialography, and ultrasound: a comparison of diagnostic methods
- Research Article
- Antibody Response to Live Attenuated Vaccines in Adults in Japan
- Conference article
- Excellence and safety in surgery require excellent and safe tutoring
- Conference article
- Suggestions on how to make suboptimal kidney transplantation an ethically viable option
- Regular Article
- Ectopic pregnancy treatment by combination therapy
- Conference article
- Use of a simplified consent form to facilitate patient understanding of informed consent for laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Regular Article
- Cusum analysis for learning curve of videothoracoscopic lobectomy
- Regular Article
- A meta-analysis of association between glutathione S-transferase M1 gene polymorphism and Parkinson’s disease susceptibility
- Conference article
- Plastination: ethical and medico-legal considerations
- Regular Article
- Investigation and control of a suspected nosocomial outbreak of pan-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an intensive care unit
- Regular Article
- Multifactorial analysis of fatigue scale among nurses in Poland
- Regular Article
- Smoking cessation for free: outcomes of a study of three Romanian clinics
- Regular Article
- Clinical efficacy and safety of tripterygium glycosides in treatment of stage IV diabetic nephropathy: A meta-analysis
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Prevention and treatment of peritoneal adhesions in patients affected by vascular diseases following surgery: a review of the literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Surgical treatment of recidivist lymphedema
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- CT and MR imaging of the thoracic aorta
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Role of FDG-PET scan in staging of pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Sternal reconstruction by extracellular matrix: a rare case of phaces syndrome
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Prenatal diagnosis, 3-D virtual rendering and lung sparing surgery by ligasure device in a baby with “CCAM and intralobar pulmonary sequestration”
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Serum levels of inhibin B in adolescents after varicocelelectomy: A long term follow up
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Our experience in the treatment of Malignant Fibrous Hystiocytoma of the larynx: clinical diagnosis, therapeutic approach and review of literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Delayed recurrent nerve paralysis following post-traumatic aortic pseudoaneurysm
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Integrated therapeutic approach to giant solitary fibrous tumor of the pleura: report of a case and review of the literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Celiac axis compression syndrome: laparoscopic approach in a strange case of chronic abdominal pain in 71 years old man
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- A rare case of persistent hypoglossal artery associated with contralateral proximal subclavian stenosis
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Contralateral risk reducing mastectomy in Non-BRCA-Mutated patients
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Professional dental and oral surgery liability in Italy: a comparative analysis of the insurance products offered to health workers
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Informed consent in robotic surgery: quality of information and patient perception
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Malfunctions of robotic system in surgery: role and responsibility of surgeon in legal point of view
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Medicolegal implications of surgical errors and complications in neck surgery: A review based on the Italian current legislation
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Iatrogenic splenic injury: review of the literature and medico-legal issues
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Donation of the body for scientific purposes in Italy: ethical and medico-legal considerations
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Cosmetic surgery: medicolegal considerations
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Voluntary termination of pregnancy (medical or surgical abortion): forensic medicine issues
- Review Article
- Role of Laparoscopic Splenectomy in Elderly Immune Thrombocytopenia
- Review Article
- Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of neuroendocrine tumors of the digestive system
- Review Article
- Efficacy and safety of splenectomy in adult autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Research Article
- Relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease and Ph nose and salivary: proposal of a simple method outpatient in patients adults
- Case Report
- Idiopathic pleural panniculitis with recurrent pleural effusion not associated with Weber-Christian disease
- Research Article
- Morbid Obesity: treatment with Bioenterics Intragastric Balloon (BIB), psychological and nursing care: our experience
- Research Article
- Learning curve for endorectal ultrasound in young and elderly: lights and shades
- Case Report
- Uncommon primary hydatid cyst occupying the adrenal gland space, treated with laparoscopic surgical approach in an old patient
- Research Article
- Distraction techniques for face and smile aesthetic preventing ageing decay
- Research Article
- Preoperative high-intensity training in frail old patients undergoing pulmonary resection for NSCLC
- Review Article
- Descending necrotizing mediastinitis in the elderly patients
- Research Article
- Prophylactic GSV surgery in elderly candidates for hip or knee arthroplasty
- Research Article
- Diagnostic yield and safety of C-TBNA in elderly patients with lung cancer
- Research Article
- The learning curve of laparoscopic holecystectomy in general surgery resident training: old age of the patient may be a risk factor?
- Research Article
- Self-gripping mesh versus fibrin glue fixation in laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: a randomized prospective clinical trial in young and elderly patients
- Research Article
- Anal sphincter dysfunction in multiple sclerosis: an observation manometric study
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Article
- The possible molecular regulation mechanism of CIK cells inhibiting the proliferation of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma NCL-H157 Cells
- Case Report
- Urethral stone of unexpected size: case report and short literature review
- Case Report
- Complete remission through icotinib treatment in Non-small cell lung cancer epidermal growth factor receptor mutation patient with brain metastasis: A case report
- Research Article
- FPL tendon thickness, tremor and hand functions in Parkinson’s disease
- Research Article
- Diagnostic value of circulating tumor cells in cerebrospinal fluid
- Research Article
- A meta-analysis of neuroprotective effect for traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in the treatment of glaucoma
- Research Article
- MiR-218 increases sensitivity to cisplatin in esophageal cancer cells via targeting survivin expression
- Research Article
- Association of HOTAIR expression with PI3K/Akt pathway activation in adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction
- Research Article
- The role of interleukin genes in the course of depression
- Case Report
- A rare case of primary pulmonary diffuse large B cell lymphoma with CD5 positive expression
- Research Article
- DWI and SPARCC scoring assess curative effect of early ankylosing spondylitis
- Research Article
- The diagnostic value of serum CEA, NSE and MMP-9 for on-small cell lung cancer
- Case Report
- Dysphonia – the single symptom of rifampicin resistant laryngeal tuberculosis
- Review Article
- Development of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M. Mutation in non small-cell lung carcinoma
- Research Article
- Negative regulation of CDC42 expression and cell cycle progression by miR-29a in breast cancer
- Research Article
- Expression analysis of the TGF-β/SMAD target genes in adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction
- Research Article
- Blood cells in thyroid cancer patients: a possible influence of apoptosis
- Research Article
- Detected EGFR mutation in cerebrospinal fluid of lung adenocarcinoma patients with meningeal metastasis
- Mini-review
- Pathogenesis-oriented approaches for the management of corticosteroid-resistant or relapsedprimary immune thrombocytopenia
- Research Article
- GSTP1 A>G polymorphism and chemosensitivity of osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis
- Research Article
- A meta-analysis of adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke susceptibility
- Research Article
- The diagnosis and pathological value of combined detection of HE4 and CA125 for patients with ovarian cancer
- Research Article
- SOX7 inhibits tumor progression of glioblastoma and is regulated by miRNA-24
- Research Article
- Sevoflurane affects evoked electromyography monitoring in cerebral palsy
- Case Report
- A case report of hereditary spherocytosis with concomitant chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Case Report
- A case of giant saphenous vein graft aneurysm followed serially after coronary artery bypass surgery
- Research Article
- LncRNA TUG1 is upregulated and promotes cell proliferation in osteosarcoma
- Review Article
- Meningioma recurrence
- Case Report
- Endobronchial amyloidosis mimicking bronchial asthma: a case report and review of the literature
- Case Report
- A confusing case report of pulmonary langerhans cell histiocytosis and literature review
- Research Article
- Effect of hesperetin on chaperone activity in selenite-induced cataract
- Research Article
- Clinical value of self-assessment risk of osteoporosis in Chinese
- Research Article
- Correlation analysis of VHL and Jade-1 gene expression in human renal cell carcinoma
- Research Article
- Is acute appendicitis still misdiagnosed?
- Retraction
- Retraction of: application of food-specific IgG antibody detection in allergy dermatosis
- Review Article
- Platelet Rich Plasma: a short overview of certain bioactive components
- Research Article
- Correlation between CTLA-4 gene rs221775A>G single nucleotide polymorphism and multiple sclerosis susceptibility. A meta-analysis
- Review Article
- Standards of anesthesiology practice during neuroradiological interventions
- Research Article
- Expression and clinical significance of LXRα and SREBP-1c in placentas of preeclampsia
- Letter to the Editor
- ARDS diagnosed by SpO2/FiO2 ratio compared with PaO2/FiO2 ratio: the role as a diagnostic tool for early enrolment into clinical trials
- Research Article
- Impact of sensory integration training on balance among stroke patients: sensory integration training on balance among stroke patients
- Review Article
- MicroRNAs as regulatory elements in psoriasis
- Review Article
- Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and postpandemic influenza in Lithuania
- Review Article
- Garengeot’s hernia: two case reports with CT diagnosis and literature review
- Research Article
- Concept of experimental preparation for treating dentin hypersensitivity
- Research Article
- Hydrogen water reduces NSE, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Research Article
- Xanthogranuloma of the sellar region diagnosed by frozen section
- Case Report
- Laparoscopic antegrade cholecystectomy: a standard procedure?
- Case Report
- Maxillary fibrous dysplasia associated with McCune-Albright syndrome. A case study
- Regular Article
- Sialoendoscopy, sialography, and ultrasound: a comparison of diagnostic methods
- Research Article
- Antibody Response to Live Attenuated Vaccines in Adults in Japan
- Conference article
- Excellence and safety in surgery require excellent and safe tutoring
- Conference article
- Suggestions on how to make suboptimal kidney transplantation an ethically viable option
- Regular Article
- Ectopic pregnancy treatment by combination therapy
- Conference article
- Use of a simplified consent form to facilitate patient understanding of informed consent for laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Regular Article
- Cusum analysis for learning curve of videothoracoscopic lobectomy
- Regular Article
- A meta-analysis of association between glutathione S-transferase M1 gene polymorphism and Parkinson’s disease susceptibility
- Conference article
- Plastination: ethical and medico-legal considerations
- Regular Article
- Investigation and control of a suspected nosocomial outbreak of pan-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an intensive care unit
- Regular Article
- Multifactorial analysis of fatigue scale among nurses in Poland
- Regular Article
- Smoking cessation for free: outcomes of a study of three Romanian clinics
- Regular Article
- Clinical efficacy and safety of tripterygium glycosides in treatment of stage IV diabetic nephropathy: A meta-analysis
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Prevention and treatment of peritoneal adhesions in patients affected by vascular diseases following surgery: a review of the literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Surgical treatment of recidivist lymphedema
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- CT and MR imaging of the thoracic aorta
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Role of FDG-PET scan in staging of pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Sternal reconstruction by extracellular matrix: a rare case of phaces syndrome
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Prenatal diagnosis, 3-D virtual rendering and lung sparing surgery by ligasure device in a baby with “CCAM and intralobar pulmonary sequestration”
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Serum levels of inhibin B in adolescents after varicocelelectomy: A long term follow up
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Our experience in the treatment of Malignant Fibrous Hystiocytoma of the larynx: clinical diagnosis, therapeutic approach and review of literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Delayed recurrent nerve paralysis following post-traumatic aortic pseudoaneurysm
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Integrated therapeutic approach to giant solitary fibrous tumor of the pleura: report of a case and review of the literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Celiac axis compression syndrome: laparoscopic approach in a strange case of chronic abdominal pain in 71 years old man
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- A rare case of persistent hypoglossal artery associated with contralateral proximal subclavian stenosis
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Contralateral risk reducing mastectomy in Non-BRCA-Mutated patients
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Professional dental and oral surgery liability in Italy: a comparative analysis of the insurance products offered to health workers
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Informed consent in robotic surgery: quality of information and patient perception
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Malfunctions of robotic system in surgery: role and responsibility of surgeon in legal point of view
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Medicolegal implications of surgical errors and complications in neck surgery: A review based on the Italian current legislation
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Iatrogenic splenic injury: review of the literature and medico-legal issues
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Donation of the body for scientific purposes in Italy: ethical and medico-legal considerations
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Cosmetic surgery: medicolegal considerations
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Voluntary termination of pregnancy (medical or surgical abortion): forensic medicine issues
- Review Article
- Role of Laparoscopic Splenectomy in Elderly Immune Thrombocytopenia
- Review Article
- Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of neuroendocrine tumors of the digestive system
- Review Article
- Efficacy and safety of splenectomy in adult autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Research Article
- Relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease and Ph nose and salivary: proposal of a simple method outpatient in patients adults
- Case Report
- Idiopathic pleural panniculitis with recurrent pleural effusion not associated with Weber-Christian disease
- Research Article
- Morbid Obesity: treatment with Bioenterics Intragastric Balloon (BIB), psychological and nursing care: our experience
- Research Article
- Learning curve for endorectal ultrasound in young and elderly: lights and shades
- Case Report
- Uncommon primary hydatid cyst occupying the adrenal gland space, treated with laparoscopic surgical approach in an old patient
- Research Article
- Distraction techniques for face and smile aesthetic preventing ageing decay
- Research Article
- Preoperative high-intensity training in frail old patients undergoing pulmonary resection for NSCLC
- Review Article
- Descending necrotizing mediastinitis in the elderly patients
- Research Article
- Prophylactic GSV surgery in elderly candidates for hip or knee arthroplasty
- Research Article
- Diagnostic yield and safety of C-TBNA in elderly patients with lung cancer
- Research Article
- The learning curve of laparoscopic holecystectomy in general surgery resident training: old age of the patient may be a risk factor?
- Research Article
- Self-gripping mesh versus fibrin glue fixation in laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: a randomized prospective clinical trial in young and elderly patients
- Research Article
- Anal sphincter dysfunction in multiple sclerosis: an observation manometric study


