Abstract
Several studies have investigated the correlation between adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke risk. However, the results were not conclusive with each other. Therefore, to overcome this obstacle, we performed this meta-analysis to further explicate the adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke susceptibility. Case-control or cohort studies focused on adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke risk were electronic searched in the databases of Medline, Pubmed, Cochrane library, Excerpta Medica database(EMBASE) and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI). All the potentially relevant studies were included in this meta-analysis. The association between adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke was expressed by odds ratio with its confidence interval. Publication bias has been assessed by begg’s funnel plot. All the analyses have been performed by Revman 5.1 statistical software. Finally, a total of six studies with 1,345 cases and 1,421 controls were included in this meta-analysis. Our results demonstrated that there was a significant association between adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke risk (p<0.05). People with G single nucleotide of adiponectin gene have the increased risk of developing ischemic stroke compared to T single nucleotide.
1 Introduction
World Health Organization (WHO) defined stroke as a “neurological deficit of cerebrovascular cause that persists beyond 24 hours or is interrupted by death within 24 hours” [1]. The ischemic stroke is referred when the blood supply to part of the brain is decreased or diminished, leading to dysfunction of the brain tissue in that area. The epidemiology study showed that the stroke was the second leading cause of death worldwide accounting for 6.2 million deaths [2] although the mechanism of stroke was not fully understood. Previous, studies [3-5] have reported the association between single-nucleotide polymorphism and stroke susceptibility, but most of them had conflict in their results.
Several studies [6-7] have investigated the association between the adiponectin gene polymorphisms and the risk of ischemic stroke susceptibility. Therefore, we collected all the published case-control or cohort studies in relation to the adiponectin polymorphisms and ischemic stroke and performed this meta-analysis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Publication search
Databases such as Medline, Pubmed, Cochrane library, Excerpta Medica database (EMBASE) and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI)were used for systemic searches. All the potential relevant studies were included in this meta-analysis. The following medical subject headings terms and free words were used: “adiponectin” OR “ADIPOQ” and “polymorphism” or “variant” and “ischemic stroke” OR “stroke”. The last search was performed on November 10, 2015. The search was limited to human beings with language restrictions of English and Chinese.
2.2 Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows:
The study types were restricted to case-control study or cohort study;
The frequency of genotype can be extracted from the studies;
Articles were published in English or Chinese;
The diagnosis of ischemic stroke was in accordance with WHO criteria.
3 Data extraction
Two reviewers independently investigated the information from each included study. The below information and data were carefully extracted and checked by reviewers. (1) The first and corresponding author; (2) Country the study was performed; (3) The year of publication; (4) Genotype distribution; (5) Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium; (6) Genotyping methods; (7) Control population. The above information with data extracted by two reviewers were then checked by a third reviewer as described in the Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews.
3.1 Statistical analysis
All the data have been analyzed by Revman 5.1 statistical software. Statistical heterogeneity among studies was evaluated by chi-square (χ2) test [8]. The association between adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke risk was demonstrated by odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval. The Begg’s funnel plotwas used to evaluate the potential publication bias[9].
4 Results
4.1 Eligible studies
By searching the above mentioned databases, 6 studies with 1345 cases and 1421 controls were included in this meta-analysis. Five studies were published in Chinese and 1 in English. The genotyping method was PCR-RFLP. Four articles used the hospital-based controls and other two used the community-based controls. The general characteristic of the included six articles are demonstrated in Table 1.
The main information of the studies included in this meta-analysis
| Study | Control resource | Genotyping | Case | Control | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCR-RFLP | TT | TG | GG | TT | TG | GG | ||
| Xiang 2014[10] | Hospital | PCR-RFLP | 221 | 123 | 28 | 248 | 139 | 29 |
| He 2013[11] | Hospital | PCR-RFLP | 64 | 40 | 16 | 63 | 43 | 14 |
| Liu 2011[12] | Hospital | PCR-RFLP | 157 | 123 | 22 | 187 | 136 | 15 |
| Xin 2009[6] | Hospital | PCR-RFLP | 3 | 9 | 39 | 14 | 27 | 23 |
| Li 2009[13] | Community | PCR-RFLP | 192 | 117 | 36 | 221 | 95 | 18 |
| Yang 2008[7] | Community | PCR-RFLP | 88 | 59 | 8 | 95 | 51 | 3 |
4.2 Quality evaluation
The quality of the included studies were assessed by Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) [14]. The NOS score ranged from 5-8 with the mean score of 6.8±1.2 which indicates the quality of the included studies was moderate (Table 2).
4.3 Quantitative synthesis
4.3.1 GG vs TT
No statistical heterogeneity was found among GG vs TT genetic model. The data was pooled by fixed effect model. Significant association was found between GG genotype and ischemic stroke susceptibility (OR=1.73, 95% CI:1.29-2.33, p=0.0003) (Figure 1). The result indicated the ischemic stroke risk was significant increased for people with GG genotype compared to TT genotype.
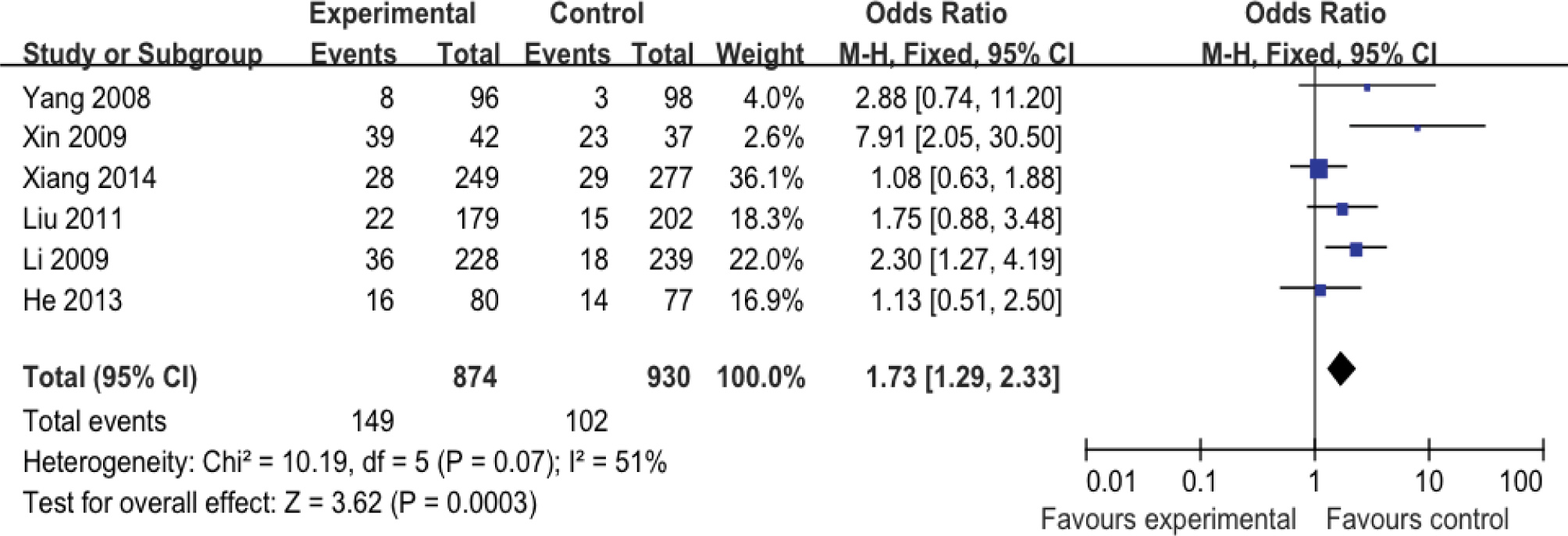
Forest plot of correlation between adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke in GG vs TT genetic model
4.3.2 (GT+GG) vs TT
The data was calculated by fixed effect mode for no statistical heterogeneity across the included studies. The pooled results indicated that population with GT or GG genetic model have increased risk of ischemic stroke compared to TT genotype (OR=1.73, 95%CI: 1.05-1.42, p=0.001), Figure 2.
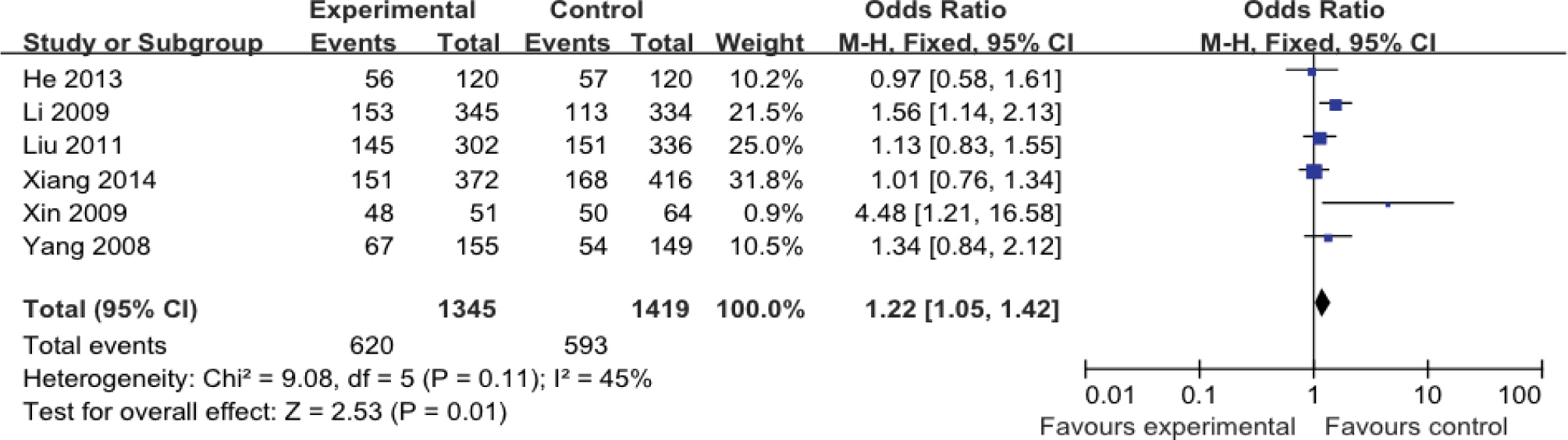
Forest plot of correlation between adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke in GT+GG vs TT genetic model
4.3.3 GG vs (GT+TT)
The statistical heterogeneity was significant in GG vs (GT+TT) genetic model. The data was pooled by random effect model with OR=1.78, 95%CI:1.35-2.35, p<0.0001. The pooled results indicated that GG genotype increased the risk of developing ischemic stroke compared to GT or TT genotype.
4.3.4 Publication bias
The begg’s funnel plot was performed in this meta-analysis in order to evaluate the publication bias. For the three genetic models, the funnel plots were generally symmetric which indicated no significant publication bias was existed in this meta-analysis, Figure 4.
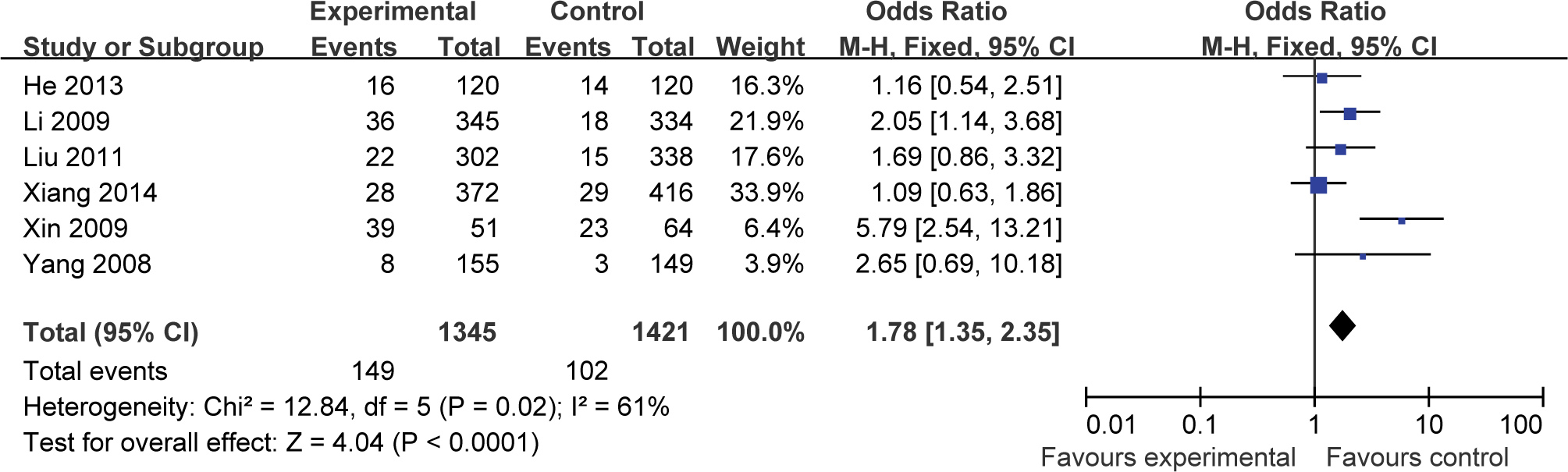
Forest plot of correlation between adiponectin gene rs22411766T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke in GG vs GT+TT genetic model
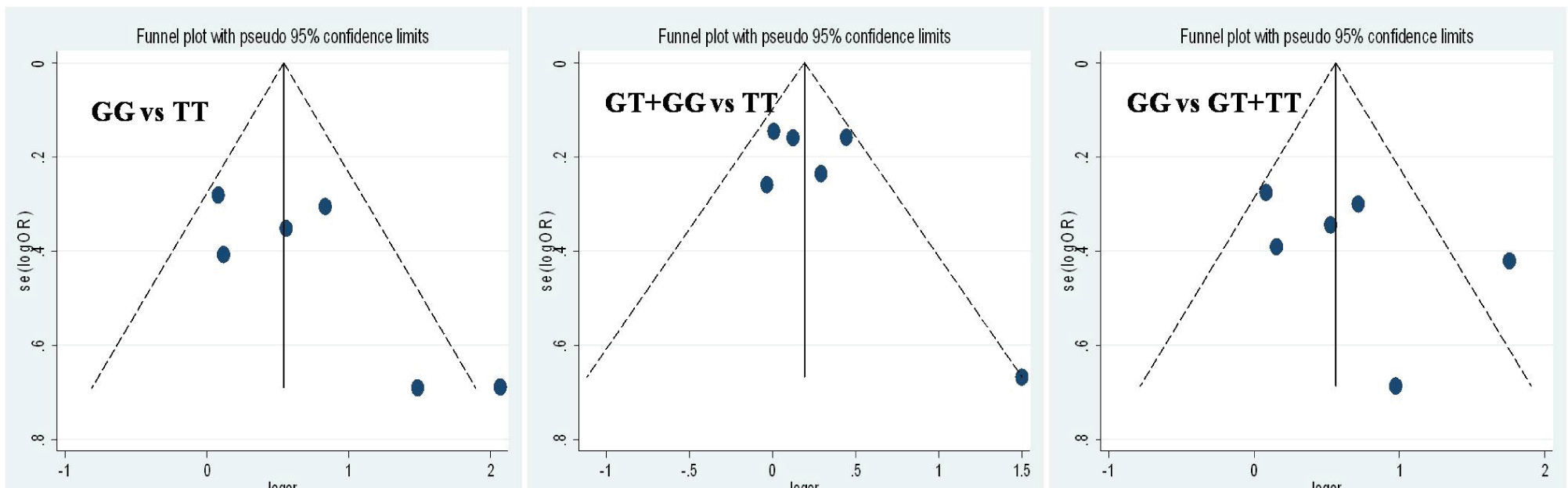
The begg’s funnel plot for evaluation publication bias
5 Discussion
Adiponectin is encoded by the ADIPOQ gene in human being [15]. It is involved in regulating glucose levels as well as fatty acid breakdown. It plays an important role in regulating energy homeostasis, glucose and lipid metabolism, and anti-inflammatory responses in the vascular system.
Adiponectin is associated with obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and coronary artery diseases. Polymorphism of adiponectin gene and correlation with ischemic stroke was also reported in some populations. Hegener et al.,[16] performed a nested case-control study in order to evaluate the adiponectin gene variations with risk of incident myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke in American population. They found that association of haplotype G-T-G (OR, 0.28; 95% CI, 0.09-0.87; P=0.03) with decreased risk of ischemic stroke. Hegener’s prospective investigation provides further evidence for a protective role of adiponectin gene variation in the risk of ischemic stroke. And several studies had also investigated the adiponectin gene polymorphism and ischemic susceptibility. Nevertheless, the conclusions were not-inconclusive. Li et al., [13] investigated the adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke risk in Chinese Han population of Heilongjiang province in north of China. They found that rs2241766 allele T and G mutations of adiponectin gene increased the risk of ischemic stroke. On the contrary, Yang et al., [7] found that there was no significant association between diponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic susceptibility in people dwelled in south of China.
Although several published articles have investigated the association between diponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic risk, the results was not definitive with the reasons of small sample size for each published studies [7,13,17,18]. Thus, we performed this meta-analysis in order to quantify the association by pooling the data from previously published articles, which can increase the statistical power.
In our present meta-analysis, we included in 6 published case-control studies which discussed the association between diponectin gene polymorphism and ischemic risk. The combined data showed that the significant association between adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke risk in GG vs TT, (GT+GG) vs TT or GG vs (GT+TT) genetic model. We find that people with G single nucleotide of adiponectin gene have the increased risk of developing ischemic stroke compared to T single nucleotide.
Two limitations have been found in this study. Firstly, the cases and controls number were relative small for each included study, which can decreased the statistical power; Secondly, 5 of included studies were written in Chinese with relatively low quality. So, multicentre studies with more cases and controls were need for further evaluation the association between adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke susceptibility.
Conflict of interest statement: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Norrving B, Kissela B: The global burden of stroke and need for a continuum of care. Neurology 2013; 80: S5-1210.1212/WNL.0b013e3182762397Search in Google Scholar
[2] Nagata K, Suzuki K:Update on stroke epidemiology. Brain and nerve 2013; 65: 857-870Search in Google Scholar
[3] Wang D, Zhang FH, Zhao YT, Xiao XG, Liu S, Shi HB, Lin AL, Wang YJ, Han Q, Sun QM: Association of polymorphism in ICAM-1 (K469E) and cytology parameters in patients’ initial blood test with acute ischemic stroke. Genet Mol Res 2015; 14: 15520-1552910.4238/2015.December.1.2Search in Google Scholar
[4] Li XX, Guan HJ, Liu JP, Guo YP, Yang Y, Niu YY, Yao LY, Yang YD, Yue HY, Meng LL, Cui XY, Yang XW, Gao JX:. Association of selenoprotein S gene polymorphism with ischemic stroke in a Chinese case-control study. Blood coagulation &fibrinolysis 2015; 26: 131-13510.1097/MBC.0000000000000202Search in Google Scholar
[5] Han D, Ma J, Zhang X, Cai J, Li J, Tuerxun T, Hao C, Du L, Lei J:. Correlation of PCSK9 gene polymorphism with cerebral ischemic stroke in Xinjiang Han and Uygur populations. Medical science monitor 2014;20: 1758-176710.12659/MSM.892091Search in Google Scholar
[6] Yaping X, Suhe Z, Qingju L, Tian Chenguang, Zhang Dongming, Fu Yanqin, Li: Relationship between adiponectin SNP45 and cerebral infarction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of practical Neruous Diseases 2009;22: 29-30Search in Google Scholar
[7] Xiujuan Y, Hongwei X, Ning Y: Distribution of adiponectin gene polymorphism in Hunan Han population and its relationship with atherosclerotic cerebral infarction and related risk factors. Chinese Journal of Arteriosclerosis 2008;16: 905-909Search in Google Scholar
[8] DerSimonian R, Laird N: Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 1986;7:177-18810.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2Search in Google Scholar
[9] Egger M, Davey SG, Schneider M, Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997;315:629-63410.1136/bmj.315.7109.629Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Xiang Bo, Ding Xiaojie, Zhang Lei, Wang Chao, Wang Xiaoqing, Pan Xudong: Correlation of adiponectin gene polymorphisms (-11377C/G, -3964A/G, -45T/G) and cerebral infarction in Chinese Han population. Journal of Apoplexy and Nervous Diseases 2014;31: 125-129Search in Google Scholar
[11] Ping H, Yipeng D, Xiaoling C. The association between APM-1 gene 45T/G, 276G/T polymorphism and ischemic stroke risk in Chinese population: Chinese Journal of Gerontology 2013;.33: 3592-3594Search in Google Scholar
[12] Liu F, He Z, Deng S, Zhang H, Li N, Xu J: Association of adiponectin gene polymorphisms with the risk of ischemic stroke in a Chinese Han population. Mol Biol Rep 2011;38: 1983-198810.1007/s11033-010-0320-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Xiaoxia L, Hongjun G, Yupeng G, Chen Xiaoliang, Yang Yindong, Zhou Jun, Cheng Jiquan, Nie Shaofa:. Relationship between adiponectin gene polymorphism and ischemic stroke. Chinese Journal of Public Health. 2009;25: 1341-1343Search in Google Scholar
[14] Margulis AV, Pladevall M, Riera-Guardia N, Varas-Lorenzo C, Hazell L, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, Perez-Gutthann S: Quality assessment of observational studies in a drug-safety systematic review, comparison of two tools: the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale and the RTI item bank. Clin Epidemiol 2014; 6: 359-36810.2147/CLEP.S66677Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Esper RM, Dame M, McClintock S, Holt PR, Dannenberg AJ, Wicha MS, Brenner DE: Leptin and Adiponectin Modulate the Self-renewal of Normal Human Breast Epithelial Stem Cells. Cancer prevention research (Philadelphia, Pa.) 2015; 8: 1174-118310.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-14-0334Search in Google Scholar
[16] Hegener HH, Lee IM, Cook NR, Ridker PM, Zee RY: Association of adiponectin gene variations with risk of incident myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke: a nested case-control study. Clin Chem 2006; 52: 2021-202710.1373/clinchem.2006.074476Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Kuwashiro T, Ago T, Kamouchi M, Matsuo R, Hata J, Kuroda J, Fukuda K, Sugimori H, Fukuhara M, Awano H, Isomura T, Suzuki K, Yasaka M, Okada Y, Kiyohara Y, Kitazono T: Significance of plasma adiponectin for diagnosis, neurological severity and functional outcome in ischemic stroke-Research for Biomarkers in Ischemic Stroke (REBIOS). Metabolism 2014; 63: 1093-110310.1016/j.metabol.2014.04.012Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Bidulescu A, Liu J, Chen Z, Hickson DA, Musani SK, Samdarshi TE, Fox ER, Taylor HA, Gibbons GH: Associations of adiponectin and leptin with incident coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke in african americans: the jackson heart study. Frontiers in public health 2013; 1: 1610.3389/fpubh.2013.00016Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2016 Chen Xiuju et al.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Article
- The possible molecular regulation mechanism of CIK cells inhibiting the proliferation of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma NCL-H157 Cells
- Case Report
- Urethral stone of unexpected size: case report and short literature review
- Case Report
- Complete remission through icotinib treatment in Non-small cell lung cancer epidermal growth factor receptor mutation patient with brain metastasis: A case report
- Research Article
- FPL tendon thickness, tremor and hand functions in Parkinson’s disease
- Research Article
- Diagnostic value of circulating tumor cells in cerebrospinal fluid
- Research Article
- A meta-analysis of neuroprotective effect for traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in the treatment of glaucoma
- Research Article
- MiR-218 increases sensitivity to cisplatin in esophageal cancer cells via targeting survivin expression
- Research Article
- Association of HOTAIR expression with PI3K/Akt pathway activation in adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction
- Research Article
- The role of interleukin genes in the course of depression
- Case Report
- A rare case of primary pulmonary diffuse large B cell lymphoma with CD5 positive expression
- Research Article
- DWI and SPARCC scoring assess curative effect of early ankylosing spondylitis
- Research Article
- The diagnostic value of serum CEA, NSE and MMP-9 for on-small cell lung cancer
- Case Report
- Dysphonia – the single symptom of rifampicin resistant laryngeal tuberculosis
- Review Article
- Development of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M. Mutation in non small-cell lung carcinoma
- Research Article
- Negative regulation of CDC42 expression and cell cycle progression by miR-29a in breast cancer
- Research Article
- Expression analysis of the TGF-β/SMAD target genes in adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction
- Research Article
- Blood cells in thyroid cancer patients: a possible influence of apoptosis
- Research Article
- Detected EGFR mutation in cerebrospinal fluid of lung adenocarcinoma patients with meningeal metastasis
- Mini-review
- Pathogenesis-oriented approaches for the management of corticosteroid-resistant or relapsedprimary immune thrombocytopenia
- Research Article
- GSTP1 A>G polymorphism and chemosensitivity of osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis
- Research Article
- A meta-analysis of adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke susceptibility
- Research Article
- The diagnosis and pathological value of combined detection of HE4 and CA125 for patients with ovarian cancer
- Research Article
- SOX7 inhibits tumor progression of glioblastoma and is regulated by miRNA-24
- Research Article
- Sevoflurane affects evoked electromyography monitoring in cerebral palsy
- Case Report
- A case report of hereditary spherocytosis with concomitant chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Case Report
- A case of giant saphenous vein graft aneurysm followed serially after coronary artery bypass surgery
- Research Article
- LncRNA TUG1 is upregulated and promotes cell proliferation in osteosarcoma
- Review Article
- Meningioma recurrence
- Case Report
- Endobronchial amyloidosis mimicking bronchial asthma: a case report and review of the literature
- Case Report
- A confusing case report of pulmonary langerhans cell histiocytosis and literature review
- Research Article
- Effect of hesperetin on chaperone activity in selenite-induced cataract
- Research Article
- Clinical value of self-assessment risk of osteoporosis in Chinese
- Research Article
- Correlation analysis of VHL and Jade-1 gene expression in human renal cell carcinoma
- Research Article
- Is acute appendicitis still misdiagnosed?
- Retraction
- Retraction of: application of food-specific IgG antibody detection in allergy dermatosis
- Review Article
- Platelet Rich Plasma: a short overview of certain bioactive components
- Research Article
- Correlation between CTLA-4 gene rs221775A>G single nucleotide polymorphism and multiple sclerosis susceptibility. A meta-analysis
- Review Article
- Standards of anesthesiology practice during neuroradiological interventions
- Research Article
- Expression and clinical significance of LXRα and SREBP-1c in placentas of preeclampsia
- Letter to the Editor
- ARDS diagnosed by SpO2/FiO2 ratio compared with PaO2/FiO2 ratio: the role as a diagnostic tool for early enrolment into clinical trials
- Research Article
- Impact of sensory integration training on balance among stroke patients: sensory integration training on balance among stroke patients
- Review Article
- MicroRNAs as regulatory elements in psoriasis
- Review Article
- Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and postpandemic influenza in Lithuania
- Review Article
- Garengeot’s hernia: two case reports with CT diagnosis and literature review
- Research Article
- Concept of experimental preparation for treating dentin hypersensitivity
- Research Article
- Hydrogen water reduces NSE, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Research Article
- Xanthogranuloma of the sellar region diagnosed by frozen section
- Case Report
- Laparoscopic antegrade cholecystectomy: a standard procedure?
- Case Report
- Maxillary fibrous dysplasia associated with McCune-Albright syndrome. A case study
- Regular Article
- Sialoendoscopy, sialography, and ultrasound: a comparison of diagnostic methods
- Research Article
- Antibody Response to Live Attenuated Vaccines in Adults in Japan
- Conference article
- Excellence and safety in surgery require excellent and safe tutoring
- Conference article
- Suggestions on how to make suboptimal kidney transplantation an ethically viable option
- Regular Article
- Ectopic pregnancy treatment by combination therapy
- Conference article
- Use of a simplified consent form to facilitate patient understanding of informed consent for laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Regular Article
- Cusum analysis for learning curve of videothoracoscopic lobectomy
- Regular Article
- A meta-analysis of association between glutathione S-transferase M1 gene polymorphism and Parkinson’s disease susceptibility
- Conference article
- Plastination: ethical and medico-legal considerations
- Regular Article
- Investigation and control of a suspected nosocomial outbreak of pan-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an intensive care unit
- Regular Article
- Multifactorial analysis of fatigue scale among nurses in Poland
- Regular Article
- Smoking cessation for free: outcomes of a study of three Romanian clinics
- Regular Article
- Clinical efficacy and safety of tripterygium glycosides in treatment of stage IV diabetic nephropathy: A meta-analysis
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Prevention and treatment of peritoneal adhesions in patients affected by vascular diseases following surgery: a review of the literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Surgical treatment of recidivist lymphedema
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- CT and MR imaging of the thoracic aorta
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Role of FDG-PET scan in staging of pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Sternal reconstruction by extracellular matrix: a rare case of phaces syndrome
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Prenatal diagnosis, 3-D virtual rendering and lung sparing surgery by ligasure device in a baby with “CCAM and intralobar pulmonary sequestration”
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Serum levels of inhibin B in adolescents after varicocelelectomy: A long term follow up
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Our experience in the treatment of Malignant Fibrous Hystiocytoma of the larynx: clinical diagnosis, therapeutic approach and review of literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Delayed recurrent nerve paralysis following post-traumatic aortic pseudoaneurysm
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Integrated therapeutic approach to giant solitary fibrous tumor of the pleura: report of a case and review of the literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Celiac axis compression syndrome: laparoscopic approach in a strange case of chronic abdominal pain in 71 years old man
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- A rare case of persistent hypoglossal artery associated with contralateral proximal subclavian stenosis
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Contralateral risk reducing mastectomy in Non-BRCA-Mutated patients
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Professional dental and oral surgery liability in Italy: a comparative analysis of the insurance products offered to health workers
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Informed consent in robotic surgery: quality of information and patient perception
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Malfunctions of robotic system in surgery: role and responsibility of surgeon in legal point of view
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Medicolegal implications of surgical errors and complications in neck surgery: A review based on the Italian current legislation
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Iatrogenic splenic injury: review of the literature and medico-legal issues
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Donation of the body for scientific purposes in Italy: ethical and medico-legal considerations
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Cosmetic surgery: medicolegal considerations
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Voluntary termination of pregnancy (medical or surgical abortion): forensic medicine issues
- Review Article
- Role of Laparoscopic Splenectomy in Elderly Immune Thrombocytopenia
- Review Article
- Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of neuroendocrine tumors of the digestive system
- Review Article
- Efficacy and safety of splenectomy in adult autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Research Article
- Relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease and Ph nose and salivary: proposal of a simple method outpatient in patients adults
- Case Report
- Idiopathic pleural panniculitis with recurrent pleural effusion not associated with Weber-Christian disease
- Research Article
- Morbid Obesity: treatment with Bioenterics Intragastric Balloon (BIB), psychological and nursing care: our experience
- Research Article
- Learning curve for endorectal ultrasound in young and elderly: lights and shades
- Case Report
- Uncommon primary hydatid cyst occupying the adrenal gland space, treated with laparoscopic surgical approach in an old patient
- Research Article
- Distraction techniques for face and smile aesthetic preventing ageing decay
- Research Article
- Preoperative high-intensity training in frail old patients undergoing pulmonary resection for NSCLC
- Review Article
- Descending necrotizing mediastinitis in the elderly patients
- Research Article
- Prophylactic GSV surgery in elderly candidates for hip or knee arthroplasty
- Research Article
- Diagnostic yield and safety of C-TBNA in elderly patients with lung cancer
- Research Article
- The learning curve of laparoscopic holecystectomy in general surgery resident training: old age of the patient may be a risk factor?
- Research Article
- Self-gripping mesh versus fibrin glue fixation in laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: a randomized prospective clinical trial in young and elderly patients
- Research Article
- Anal sphincter dysfunction in multiple sclerosis: an observation manometric study
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Article
- The possible molecular regulation mechanism of CIK cells inhibiting the proliferation of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma NCL-H157 Cells
- Case Report
- Urethral stone of unexpected size: case report and short literature review
- Case Report
- Complete remission through icotinib treatment in Non-small cell lung cancer epidermal growth factor receptor mutation patient with brain metastasis: A case report
- Research Article
- FPL tendon thickness, tremor and hand functions in Parkinson’s disease
- Research Article
- Diagnostic value of circulating tumor cells in cerebrospinal fluid
- Research Article
- A meta-analysis of neuroprotective effect for traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in the treatment of glaucoma
- Research Article
- MiR-218 increases sensitivity to cisplatin in esophageal cancer cells via targeting survivin expression
- Research Article
- Association of HOTAIR expression with PI3K/Akt pathway activation in adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction
- Research Article
- The role of interleukin genes in the course of depression
- Case Report
- A rare case of primary pulmonary diffuse large B cell lymphoma with CD5 positive expression
- Research Article
- DWI and SPARCC scoring assess curative effect of early ankylosing spondylitis
- Research Article
- The diagnostic value of serum CEA, NSE and MMP-9 for on-small cell lung cancer
- Case Report
- Dysphonia – the single symptom of rifampicin resistant laryngeal tuberculosis
- Review Article
- Development of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M. Mutation in non small-cell lung carcinoma
- Research Article
- Negative regulation of CDC42 expression and cell cycle progression by miR-29a in breast cancer
- Research Article
- Expression analysis of the TGF-β/SMAD target genes in adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction
- Research Article
- Blood cells in thyroid cancer patients: a possible influence of apoptosis
- Research Article
- Detected EGFR mutation in cerebrospinal fluid of lung adenocarcinoma patients with meningeal metastasis
- Mini-review
- Pathogenesis-oriented approaches for the management of corticosteroid-resistant or relapsedprimary immune thrombocytopenia
- Research Article
- GSTP1 A>G polymorphism and chemosensitivity of osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis
- Research Article
- A meta-analysis of adiponectin gene rs22411766 T>G polymorphism and ischemic stroke susceptibility
- Research Article
- The diagnosis and pathological value of combined detection of HE4 and CA125 for patients with ovarian cancer
- Research Article
- SOX7 inhibits tumor progression of glioblastoma and is regulated by miRNA-24
- Research Article
- Sevoflurane affects evoked electromyography monitoring in cerebral palsy
- Case Report
- A case report of hereditary spherocytosis with concomitant chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Case Report
- A case of giant saphenous vein graft aneurysm followed serially after coronary artery bypass surgery
- Research Article
- LncRNA TUG1 is upregulated and promotes cell proliferation in osteosarcoma
- Review Article
- Meningioma recurrence
- Case Report
- Endobronchial amyloidosis mimicking bronchial asthma: a case report and review of the literature
- Case Report
- A confusing case report of pulmonary langerhans cell histiocytosis and literature review
- Research Article
- Effect of hesperetin on chaperone activity in selenite-induced cataract
- Research Article
- Clinical value of self-assessment risk of osteoporosis in Chinese
- Research Article
- Correlation analysis of VHL and Jade-1 gene expression in human renal cell carcinoma
- Research Article
- Is acute appendicitis still misdiagnosed?
- Retraction
- Retraction of: application of food-specific IgG antibody detection in allergy dermatosis
- Review Article
- Platelet Rich Plasma: a short overview of certain bioactive components
- Research Article
- Correlation between CTLA-4 gene rs221775A>G single nucleotide polymorphism and multiple sclerosis susceptibility. A meta-analysis
- Review Article
- Standards of anesthesiology practice during neuroradiological interventions
- Research Article
- Expression and clinical significance of LXRα and SREBP-1c in placentas of preeclampsia
- Letter to the Editor
- ARDS diagnosed by SpO2/FiO2 ratio compared with PaO2/FiO2 ratio: the role as a diagnostic tool for early enrolment into clinical trials
- Research Article
- Impact of sensory integration training on balance among stroke patients: sensory integration training on balance among stroke patients
- Review Article
- MicroRNAs as regulatory elements in psoriasis
- Review Article
- Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and postpandemic influenza in Lithuania
- Review Article
- Garengeot’s hernia: two case reports with CT diagnosis and literature review
- Research Article
- Concept of experimental preparation for treating dentin hypersensitivity
- Research Article
- Hydrogen water reduces NSE, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Research Article
- Xanthogranuloma of the sellar region diagnosed by frozen section
- Case Report
- Laparoscopic antegrade cholecystectomy: a standard procedure?
- Case Report
- Maxillary fibrous dysplasia associated with McCune-Albright syndrome. A case study
- Regular Article
- Sialoendoscopy, sialography, and ultrasound: a comparison of diagnostic methods
- Research Article
- Antibody Response to Live Attenuated Vaccines in Adults in Japan
- Conference article
- Excellence and safety in surgery require excellent and safe tutoring
- Conference article
- Suggestions on how to make suboptimal kidney transplantation an ethically viable option
- Regular Article
- Ectopic pregnancy treatment by combination therapy
- Conference article
- Use of a simplified consent form to facilitate patient understanding of informed consent for laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Regular Article
- Cusum analysis for learning curve of videothoracoscopic lobectomy
- Regular Article
- A meta-analysis of association between glutathione S-transferase M1 gene polymorphism and Parkinson’s disease susceptibility
- Conference article
- Plastination: ethical and medico-legal considerations
- Regular Article
- Investigation and control of a suspected nosocomial outbreak of pan-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an intensive care unit
- Regular Article
- Multifactorial analysis of fatigue scale among nurses in Poland
- Regular Article
- Smoking cessation for free: outcomes of a study of three Romanian clinics
- Regular Article
- Clinical efficacy and safety of tripterygium glycosides in treatment of stage IV diabetic nephropathy: A meta-analysis
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Prevention and treatment of peritoneal adhesions in patients affected by vascular diseases following surgery: a review of the literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Surgical treatment of recidivist lymphedema
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- CT and MR imaging of the thoracic aorta
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Role of FDG-PET scan in staging of pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Sternal reconstruction by extracellular matrix: a rare case of phaces syndrome
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Prenatal diagnosis, 3-D virtual rendering and lung sparing surgery by ligasure device in a baby with “CCAM and intralobar pulmonary sequestration”
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Serum levels of inhibin B in adolescents after varicocelelectomy: A long term follow up
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Our experience in the treatment of Malignant Fibrous Hystiocytoma of the larynx: clinical diagnosis, therapeutic approach and review of literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Delayed recurrent nerve paralysis following post-traumatic aortic pseudoaneurysm
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Integrated therapeutic approach to giant solitary fibrous tumor of the pleura: report of a case and review of the literature
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- Celiac axis compression syndrome: laparoscopic approach in a strange case of chronic abdominal pain in 71 years old man
- Special Issue on Italian Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies
- A rare case of persistent hypoglossal artery associated with contralateral proximal subclavian stenosis
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Contralateral risk reducing mastectomy in Non-BRCA-Mutated patients
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Professional dental and oral surgery liability in Italy: a comparative analysis of the insurance products offered to health workers
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Informed consent in robotic surgery: quality of information and patient perception
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Malfunctions of robotic system in surgery: role and responsibility of surgeon in legal point of view
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Medicolegal implications of surgical errors and complications in neck surgery: A review based on the Italian current legislation
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Iatrogenic splenic injury: review of the literature and medico-legal issues
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Donation of the body for scientific purposes in Italy: ethical and medico-legal considerations
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Cosmetic surgery: medicolegal considerations
- Focus on Medico-Legal and Ethical Topics in Surgery in Italy
- Voluntary termination of pregnancy (medical or surgical abortion): forensic medicine issues
- Review Article
- Role of Laparoscopic Splenectomy in Elderly Immune Thrombocytopenia
- Review Article
- Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of neuroendocrine tumors of the digestive system
- Review Article
- Efficacy and safety of splenectomy in adult autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Research Article
- Relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease and Ph nose and salivary: proposal of a simple method outpatient in patients adults
- Case Report
- Idiopathic pleural panniculitis with recurrent pleural effusion not associated with Weber-Christian disease
- Research Article
- Morbid Obesity: treatment with Bioenterics Intragastric Balloon (BIB), psychological and nursing care: our experience
- Research Article
- Learning curve for endorectal ultrasound in young and elderly: lights and shades
- Case Report
- Uncommon primary hydatid cyst occupying the adrenal gland space, treated with laparoscopic surgical approach in an old patient
- Research Article
- Distraction techniques for face and smile aesthetic preventing ageing decay
- Research Article
- Preoperative high-intensity training in frail old patients undergoing pulmonary resection for NSCLC
- Review Article
- Descending necrotizing mediastinitis in the elderly patients
- Research Article
- Prophylactic GSV surgery in elderly candidates for hip or knee arthroplasty
- Research Article
- Diagnostic yield and safety of C-TBNA in elderly patients with lung cancer
- Research Article
- The learning curve of laparoscopic holecystectomy in general surgery resident training: old age of the patient may be a risk factor?
- Research Article
- Self-gripping mesh versus fibrin glue fixation in laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: a randomized prospective clinical trial in young and elderly patients
- Research Article
- Anal sphincter dysfunction in multiple sclerosis: an observation manometric study


