Abstract
In this work, we will introduce two novel positivity preserving operator splitting nonstandard finite difference (NSFD) schemes for the numerical solution of SEIR reaction diffusion epidemic model. In epidemic model of infection diseases, positivity is an important property of the continuous system because negative value of a subpopulation is meaningless. The proposed operator splitting NSFD schemes are dynamically consistent with the solution of the continuous model. First scheme is conditionally stable while second operator splitting scheme is unconditionally stable. The stability of the diffusive SEIR model is also verified numerically with the help of Routh-Hurwitz stability condition. Bifurcation value of transmission coefficient is also carried out with and without diffusion. The proposed operator splitting NSFD schemes are compared with the well-known operator splitting finite difference (FD) schemes.
1 Introduction
In childhood epidemic diseases, Measles is considered as highly infectious disease, spread due to respiratory infection by a traveling virus. In 19th century, Arthur Ransom observed the unevenly recurring nature of Measles. Since 1896, age structures, contact rates and school seasons are known as critical agents for the transmission of Measles in a population. Hamer [1] in 1906 presented a model for transmission dynamics of Measles. Later, the principle of “mass action” was introduced which became a fundamental statute in present theory of infectious disease modeling [2, 3, 4, 5].
Infectious disease dynamics is an important application of dynamical systems. Fixed points, steady states or the equilibrium points of a continuous dynamical systems are the values of variables that do not change over time. If a system starts at a nearby state and converges to the equilibrium point, then this equilibrium point is attractive. Many dynamical systems in different fields of science and engineering show the chaotic behavior. If a numerical method produces chaos and it is not the feature of continuous system, then this is called contrived chaos. Many existing numerical techniques show the contrived chaos. If a continuous dynamical system demonstrates a property P, then it is necessary for the numerical method to preserve that property P. This is called dynamical consistency, in the literature, Twizzell et al and various authors [6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13] discussed about the contrived chaos and loss of the dynamical consistency in the finite difference scheme. Similarly, Fernández [14] discussed about the same drawbacks exhibited in different series solution techniques. The aim of this work is to develop and investigate such numerical schemes whose equilibrium points coincide with the equilibrium points of the continuous system and preserve all the essential properties demonstrated by the continuous system.
In this work, we consider SEIR epidemic model with diffusion presented by Al-Shawaikh and Twizell [15]. This model describes the transmission dynamics of measles. In this model, the total population is taken as ‘N’ and it is categorized in four classes i.e. susceptible population, exposed population, infected population and recovered population denoted by S, E, I and R respectively. It is assumed that the total population ‘N’ is constant i.e. birth and death rates in the population are equal. Mathematical model of SEIR epidemic model with diffusion is
Since R is not present in first three equations so we can write the system as
with the initial conditions
and homogeneous Neumann boundary conditions are
As discussed above, the purpose of this work is to construct positivity preserving operator splitting nonstandard finite difference schemes for the system (5)-(7). Since SEIR reaction diffusion system (5)-(7) is a population model therefore negative values of susceptible, exposed and infected population is meaningless. Nonstandard finite difference method is a structural preserving numerical method which is developed by Mickens [16]. NSFD method is an important tool to solve ordinary and partial differential equations [9, 10, 11, 17, 18] as it preserves the properties possessed by continuous system.
2 Equilibrium Points
There are two steady states [15] of the system (5)-(7), disease-free and endemic steady state. Disease-free state is
and the endemic steady state is
where
R0 is the reproductive and if R0 < 1 then the system possesses disease free state and if R0 > 1 then system possesses endemic state.
3 Stability of Equilibrium of the System
The system (5)-(7) is linearized about the equilibrium point (S*, E*, I*) to have small perturbations S(x, t), E(x, t) and I(x, t) as describe in [19]
Suppose that the system (14)-(16) possesses Fourier series solution as mentioned in [19], then
where k represents the wave number for the node n and k = nπ/2, (n = 1, 2, 3, …). Replacing the values of S1(x, t), E1(x, t) and I1(x, t) in the system, it is transformed into
The variational matrix 𝓥 is for the equation (20)-(22) is
where
The characteristics equation for matrix 𝓥 is
The Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion gives
and
4 Bifurcation Value of Transmission Coefficient β
The values of S*, E* and I* are substituted in a11, a22, ⋅ ⋅ ⋅, to obtain
The Routh-Hurwitz criterion for stability gives
The equation f2(β) = 0 provides the bifurcation value of β, which shifts the stability of the equilibrium point (i.e. from stable to unstable). The solution for f2(β) gives 0.000001455. The point of equilibrium is unstable for any value of β less than 0.000001455. Similarly, the bifurcation value of β for system without diffusion is 0.000001462. The equilibrium point of the system without diffusion is not stable for any value of β less than 0.000001462. It is concluded that bifurcation value of β with diffusion is less than bifurcation value of β without diffusion. In order to find the bifurcation value of β we consider case 1 in Table 1 and dS = 0.05, dE = 0.01, dI = 0.001.
Values of parameters.
| cases | β | σ | γ | μ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.3×10–5 | 45.6 | 73 | 0.02 |
| 2 | 0.5×10–4 | 50 | 80 | 0.02 |
| 3 | 0.8×10–3 | 58 | 85 | 0.02 |
| 4 | 0.9×10–3 | 65 | 90 | 0.02 |
| 5 | 0.3×10–2 | 77 | 99 | 0.02 |
Stability of Equilibrium.
| cases | Point of Equilibrium | n | η1 | η2 | η1η2–η3 | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (2.435 × 107, 1.125 × 104, 7022.67) | 1 | 1.1883 × 102 | 7.0491× 10 | 2.4758× 103 | Stable |
| 2 | (1.6010 × 106, 1.9352 × 104, 1.2092× 104) | 1 | 130.8151 | 2.4215× 103 | 1.0579× 104 | Stable |
| 3 | (1.0631 × 105, 1.7199 × 104, 1.1733× 104) | 1 | 152.5968 | 4.6323× 104 | 1.6207× 105 | Stable |
| 4 | (1.0005 × 105, 1.5349 × 104, 1.1083× 104) | 1 | 165.1852 | 5.8407× 104 | 2.0116× 105 | Stable |
| 5 | (3.3015 × 104, 1.2975 × 104, 1.0090× 104) | 1 | 206.4796 | 2.3093× 105 | 8.7524× 105 | Stable |
5 Numerical Methods
In order to handle the complexity and nonlinearity of the reaction-diffusion system (5)-(7), we implement two classical and two proposed nonstandard operator splitting finite difference methods. Operator splitting FD schemes are used by various authors to solve complex problems containing differential equations [19, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30]. Generally, the SEIR reaction-diffusion equations are split into two systems of equations. The nonlinear reaction steps
which are used for the first half step for time and the linear diffusion equation
which are implemented for the second half step of time. Firstly, we present forward Euler FD and Backward Euler schemes to solve the equations.
where
The procedure for the backward Euler FD scheme is
Nowwe construct nonstandard FD schemes. By applying rules defined by Mickens [16], both nonstandard FD schemes at first half time step are
Positivity of the solution requires that if
The procedure is different for both NSFD operator splitting schemes at second half-time step. For explicit NSFD operator splitting scheme, we use
The procedure for the implicit NSFD operator splitting scheme at second half time step is
where
5.1 Accuracy and Stability of the Numerical Methods
In operator splitting methods, the stability and consistency depends on their split solutions [21, 22]. In all the above splitting methods, the reaction step is solved exactly and time derivative has O(τ) accuracy [21, 22]. Similarly, the diffusion step has O(h2) accuracy and the cumulative accuracy of all numerical schemes is first order in time and second order in space [21, 22]. For the stability, the reaction step is unconditionally stable in all cases as it is solved exactly [21, 22]. In forward Euler method operator splitting FD method and explicit NSFD operator splitting method (32)-(34), the stability region of diffusion step is
In the backward Euler method operator splitting FD method and implicit NSFD operator splitting method, the diffusion step is unconditionally stable.
5.2 Positivity of NSFD methods
It can be observed that NSFD methods in reaction step (39)-(41) preserve the positivity property of the solution. For the diffusion step, explicit NSFD method (43)-(45) gives the positive solution if
This implies that
which is the stability condition (49) of NSFD method (39)-(41). This proves that the first NSFD method preserves the positivity property in its stability region. In order to prove the positivity of unconditionally stable implicit NSFD method (46)-(48), we use M-matrix theory [33].
5.2.1 Theorem [31, 32]
For any h > 0 and τ > 0, the system (46)-(48) is positive, i.e. Sm > 0, Em > 0 and Im > 0 for all m = 0, 1, 2...
Proof
The system (46)-(48) can be written as
where A, B and C are the square matrices
and
The off-diagonal entries of A are a1 = −2λ1, a2 = −λ1 and a3 = 1 + 2λ1. The off-diagonal entries of B are b1 = −2λ1, b2 = −λ1and diagonal entries are b3 = 1 + 2λ2. The off-diagonal entries of C are c1 = −2λ3, c2 = −λ3and diagonal entries are c3 = 1 + 2λ3. Thus A, B and C are M-matrices. Hence equation (50), (51) and (52) become
If we consider that Sm > 0, Em > 0 and Im > 0, then from the property of M-matrix and (56)-(58) we get Sm+1 > 0, Em+1 > 0 and Im+1 > 0 . So by the induction, the theorem is proved.
It follows from Theorem 5.2.1 that implicit NSFD operator splitting scheme preserve positivity property unconditionally.
6 Numerical Experiment
In this section, we perform a numerical experiment for all the methods at both equilibrium points. For the numerical test, the following values of parameters are used for disease-free equilibrium [15, 20]
For endemic equilibrium points, the following parametric values are used [15, 20]
In this experiment we take dS = 0.05, dE = 0.01, dI = 0.001. The initial conditions for the system (5)-(7) are
Now the graphs of all the schemes at disease free equilibrium point is presented. First of all we show the graphs of Forward Euler operator splitting FD scheme.
The figures 1-3 indicate the graphs of disease free equilibrium using forward Euler operator splitting FD scheme at h = 0.1 and λ1 = 0.09375, λ2 = 0.01875 and λ3 = 0.001875. Figure 2 and figure 3 show that forward Euler operator splitting FD scheme fails to preserve the positivity property.
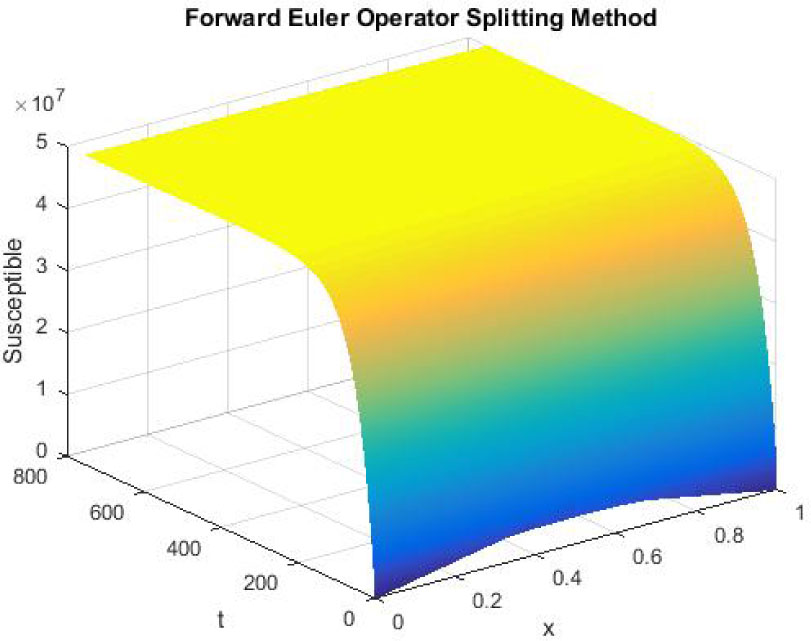
Mesh graph of Susceptible Individuals for DFE
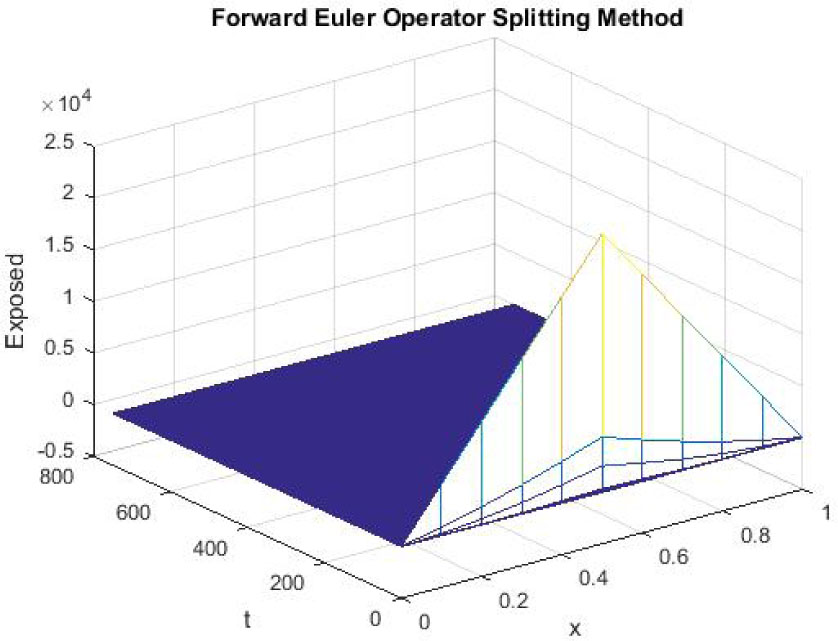
Mesh graph of Exposed Individuals for DFE
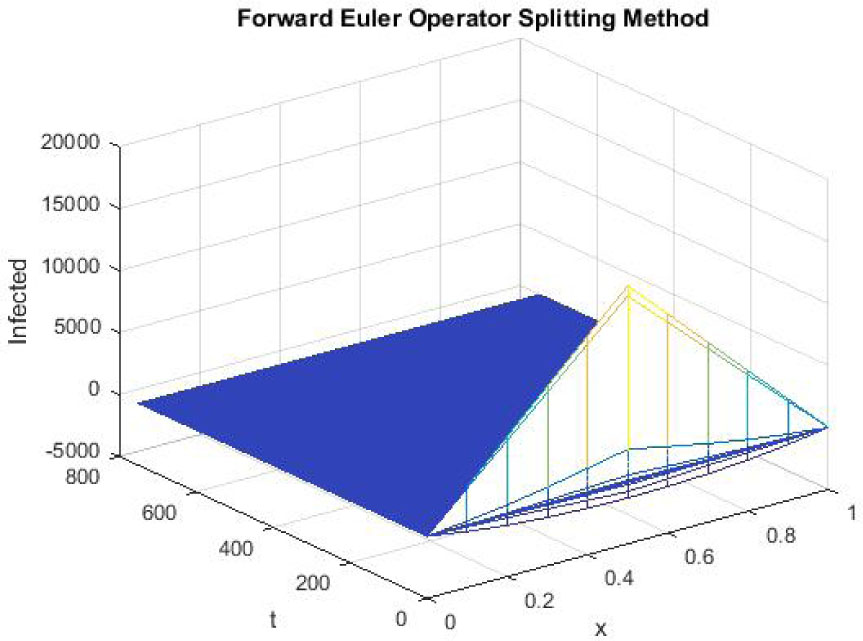
Mesh graph of Infected Individuals for DFE
The figures 4-6 represent the mesh graphs of susceptible, exposed and infected individuals using forward Euler explicit operator splitting FD scheme at h = 0.1 and λ1 = 0.25, λ2 = 0.05 and λ3 = 0.005. It can be seen that all the graphs in figures 4-6 show overflow and divergence. Remember that these are the graphs at endemic equilibrium point. Forward Euler explicit operator splitting FD scheme fails to converge to the endemic equilibrium point. Secondly we present the simulation of backward Euler implicit operator splitting FD scheme.
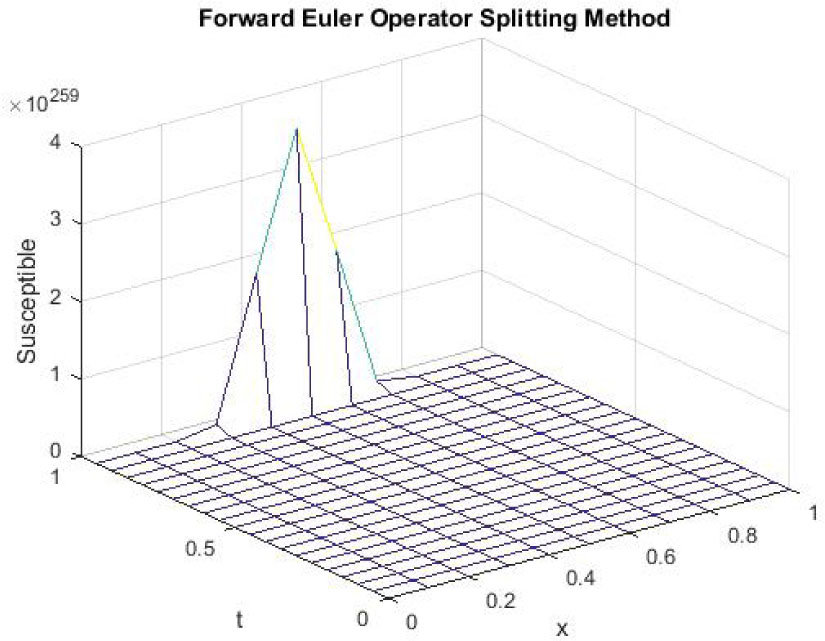
Mesh graph of Susceptible Individuals for EE
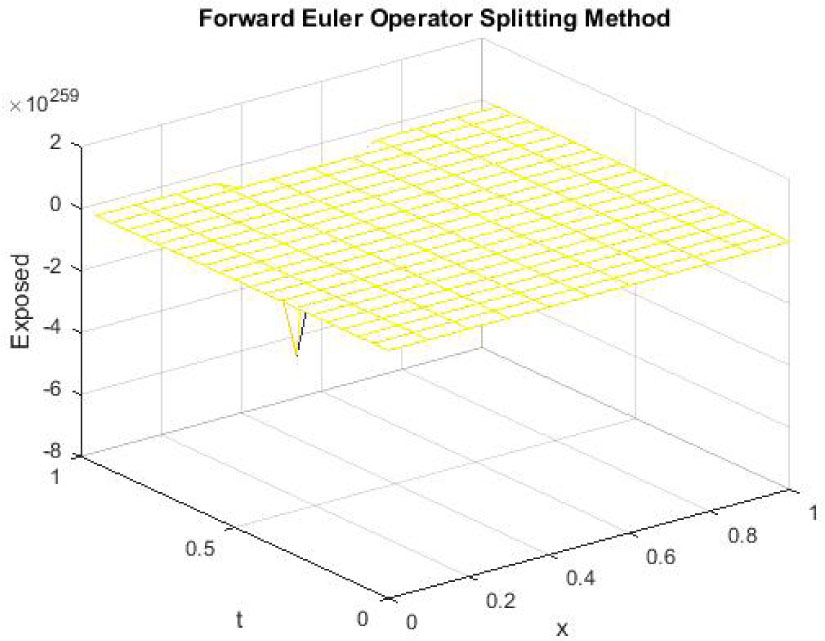
Mesh graph of Exposed Individuals for EE
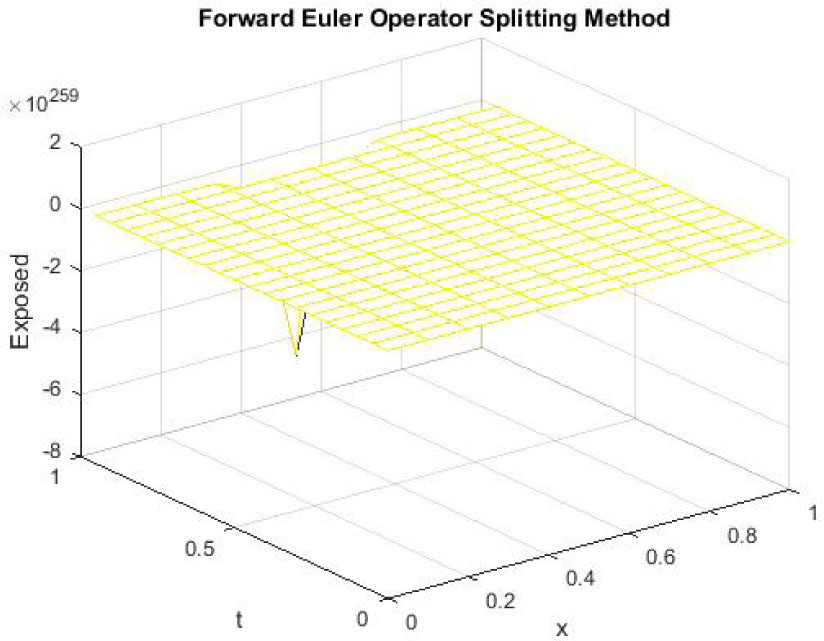
Mesh graph of Infected Individuals for EE
The figures 7-9 reflect the graphs of disease free equilibrium using backward Euler implicit operator splitting FD scheme at h = 0.1 and λ1 = 0.09375, λ2 = 0.01875 and λ3 = 0.001875. Figure 8 and figure 9 show that backward Euler implicit operator splitting FD scheme also fails to preserve the positivity property.
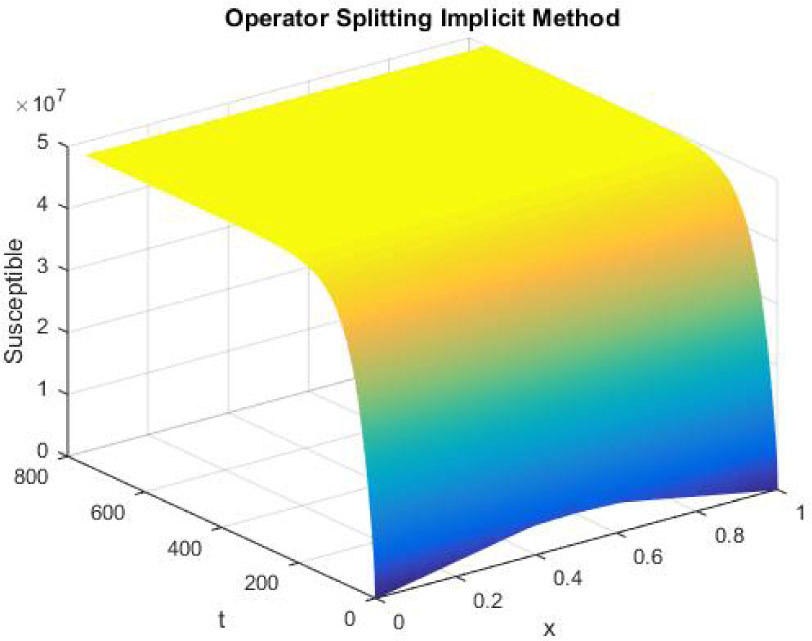
Mesh graph of Susceptible Individuals for DFE
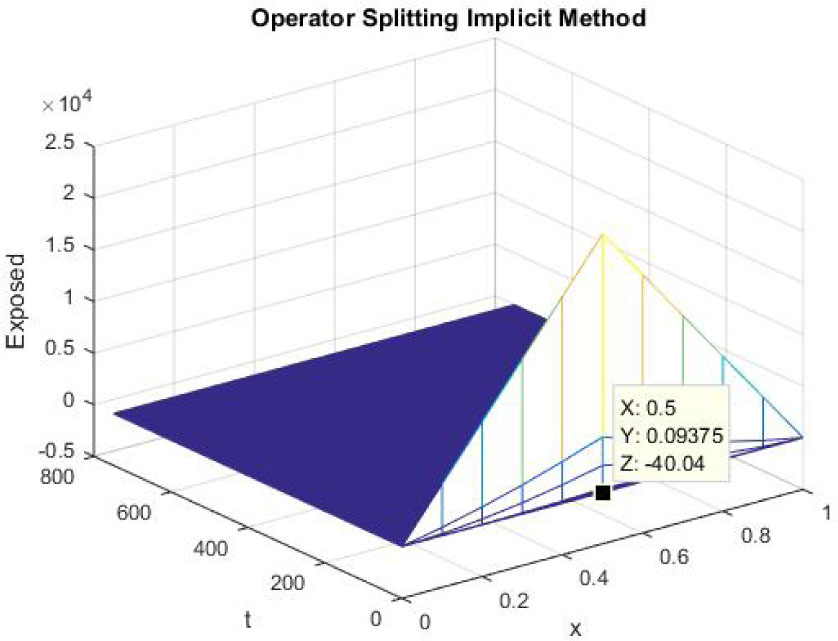
Mesh graph of Exposed Individuals for DFE
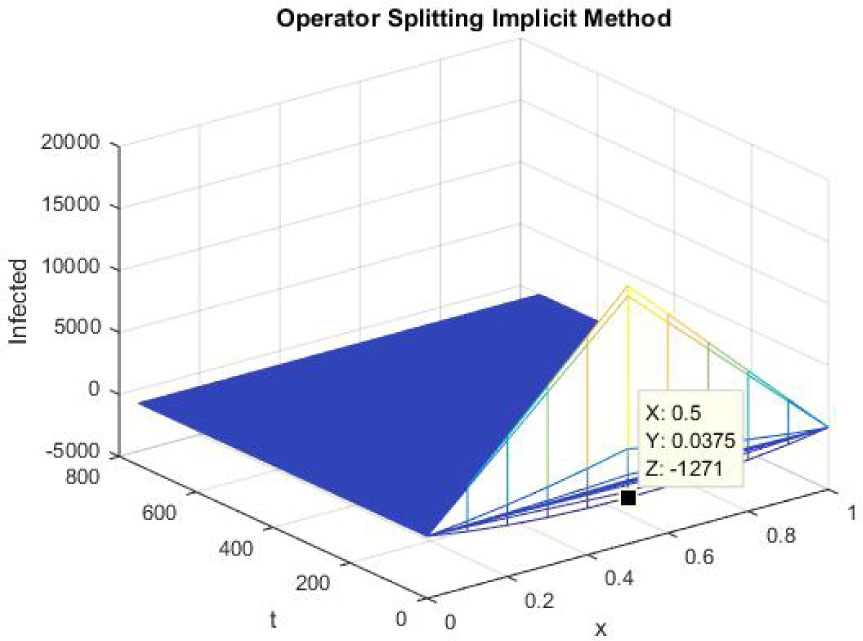
Mesh graph of Infected Individuals for DFE
The figures 10-12 represent the mesh graphs of susceptible, exposed and infected individuals using backward Euler implicit operator splitting FD scheme at h = 0.1 and λ1 = 0.25, λ2 = 0.05 and λ3 = 0.005. It can be seen that all the graphs in figures 10-12 show overflow and divergence. Remember that these are the graphs at endemic equilibrium point. Backward Euler implicit operator splitting FD scheme fails to converge to the endemic equilibrium point. Thirdly, the graphs of susceptible, exposed and infected population at disease free and endemic equilibrium point using nonstandard operator splitting explicit FD method are presented.
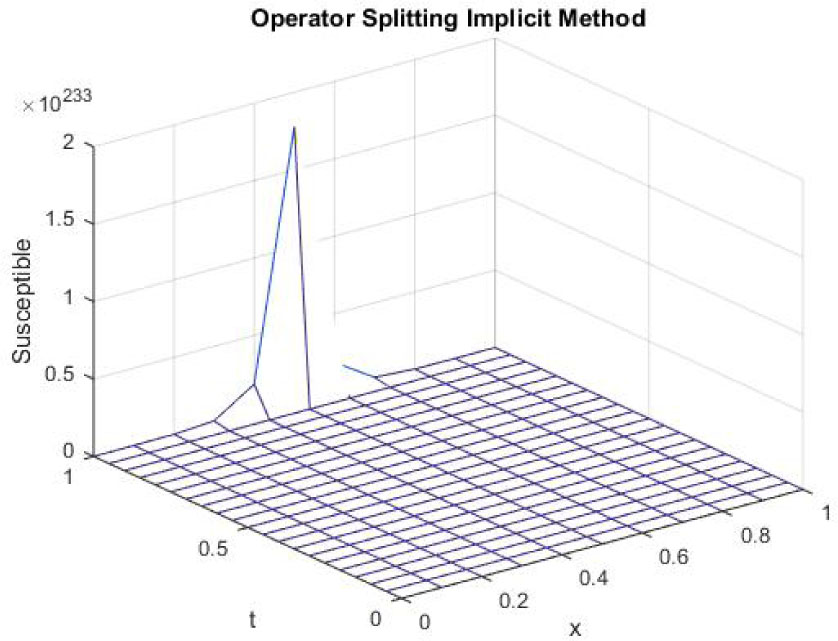
Mesh graph of Susceptible Individuals for EE
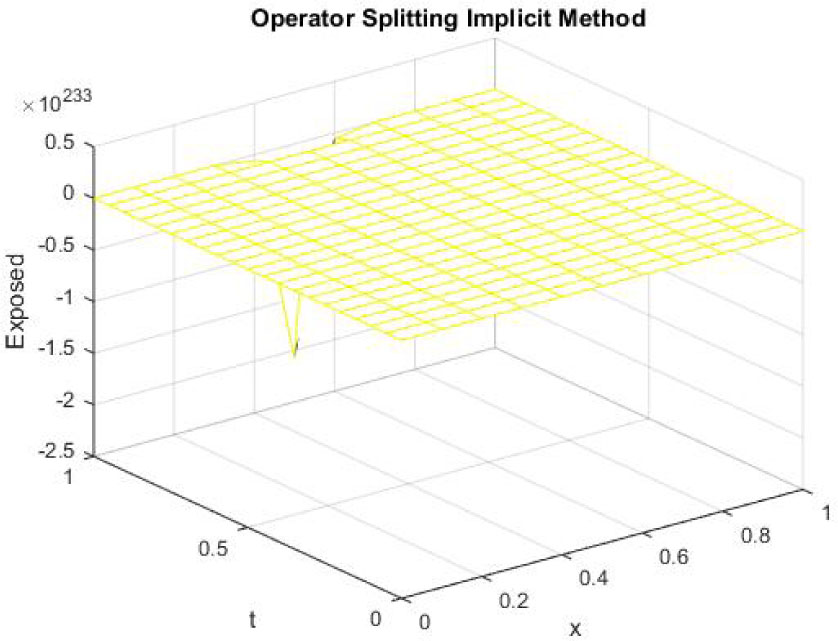
Mesh graph of Exposed Individuals for EE
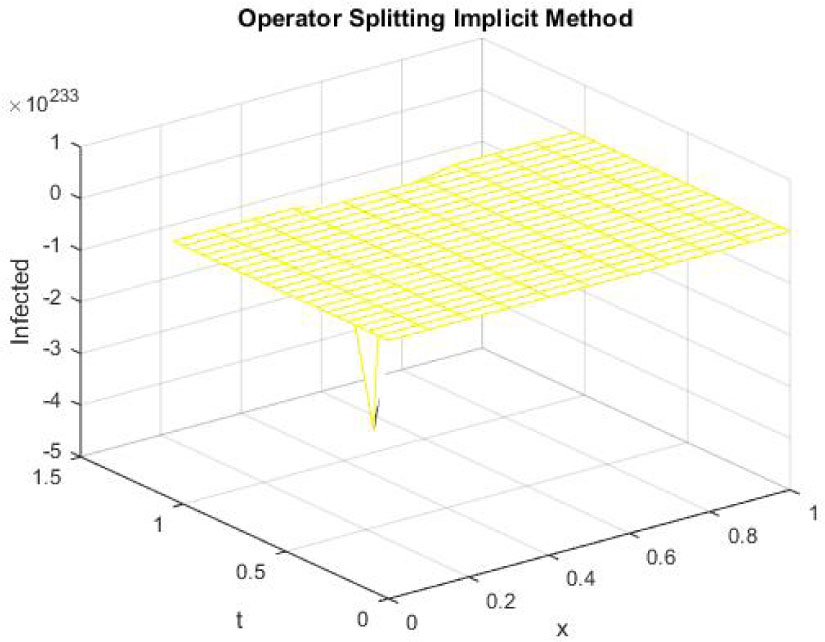
Mesh graph of Infected Individuals for EE
The figures 13-15 reflect the graphs of disease free equilibrium using NSFD explicit operator splitting scheme at h = 0.1 and λ1 = 0.09375, λ2 = 0.01875 and λ3 = 0.001875. Graphs clearly show that NSFD operator splitting explicit scheme preserves the positivity property and converges to the disease free equilibrium point (S0, E0, I0).
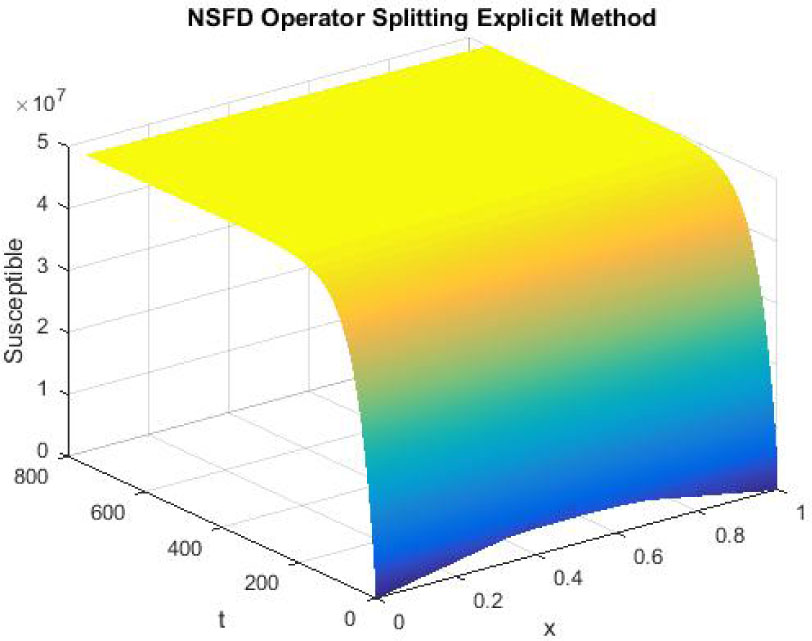
Mesh graph of Susceptible Individuals for DFE
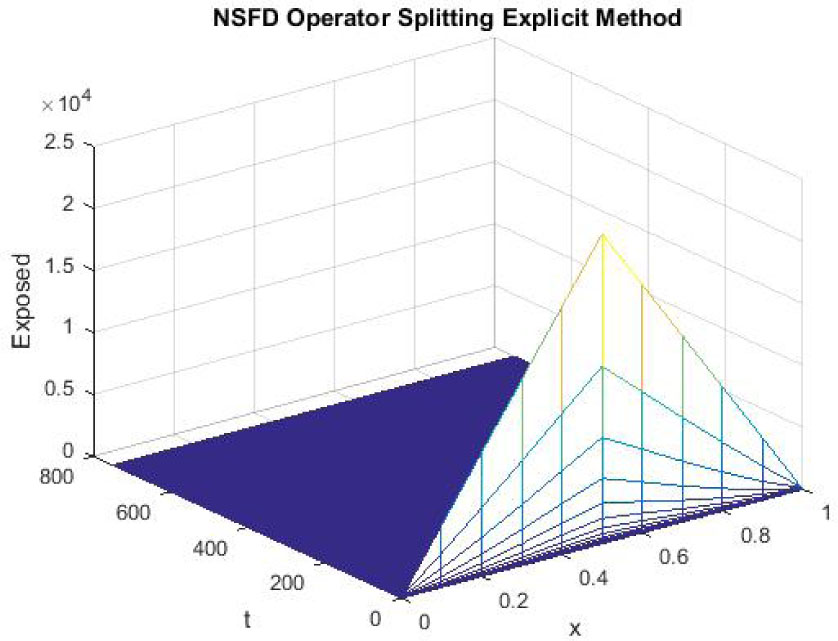
Mesh graph of Exposed Individuals for DFE
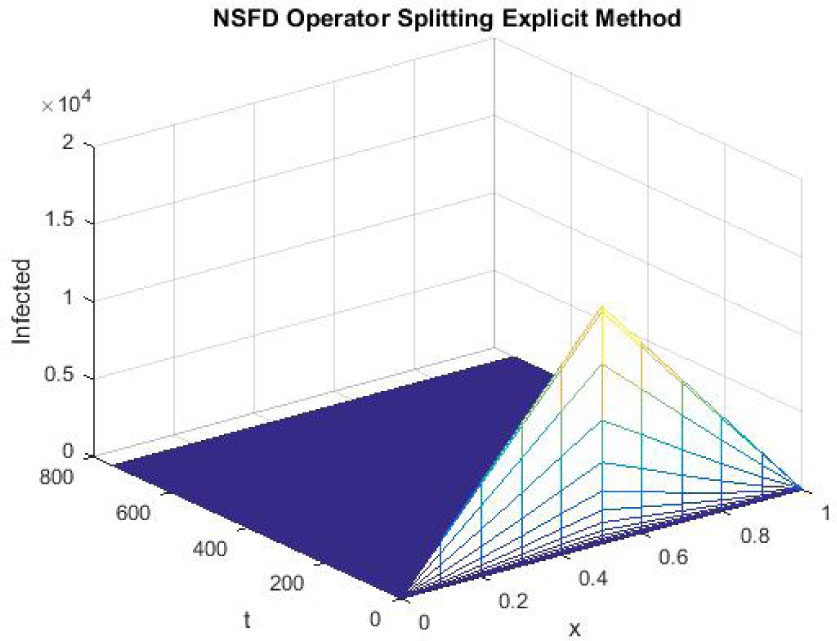
Mesh graph of Infected Individuals for DFE
The figures 16-18 represent the graphs of endemic equilibrium point for susceptible, exposed and infected individuals using NSFD operator splitting explicit scheme at h = 0.1 and λ1 = 0.25, λ2 = 0.05 and λ3 = 0.005. Graphs show that NSFD operator splitting explicit scheme preserves the positivity property and converges to the endemic equilibrium point (S*, E*, I*). At the end, we present the simulations using NSFD operator splitting implicit method.
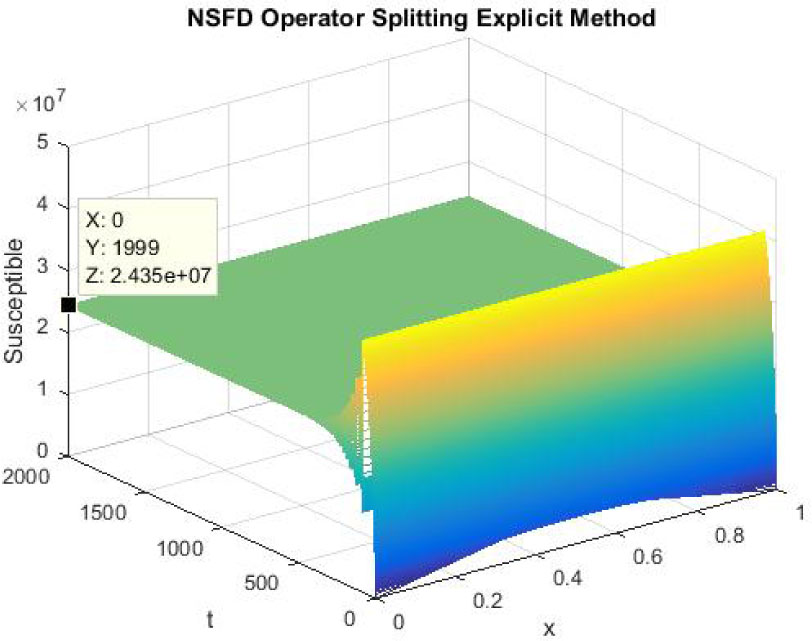
Mesh graph of Susceptible Individuals for EE
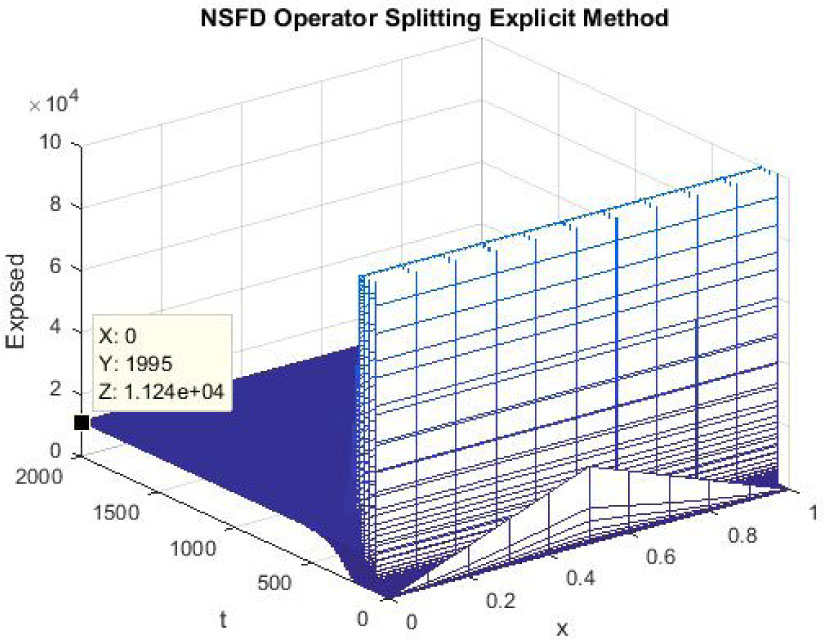
Mesh graph of Exposed Individuals for EE
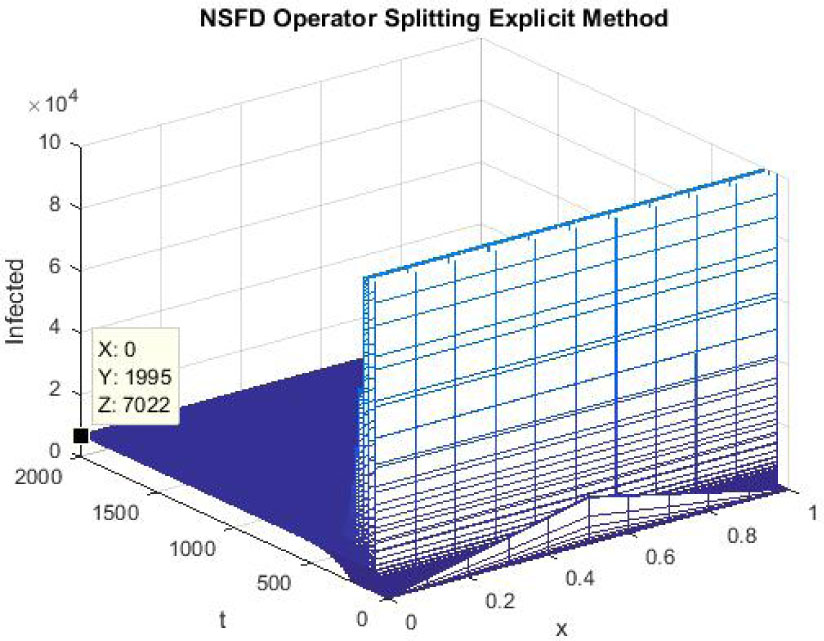
Mesh graph of Infected Individuals for EE
Figures 19-21 reflect the graphs of disease free equilibrium using NSFD operator splitting implicit scheme at h = 0.1 and λ1 = 0.09375, λ2 = 0.01875 and λ3 = 0.001875. Graphs clearly show that NSFD operator splitting implicit scheme preserves the positivity property and converges to the disease free equilibrium point (S0, E0, I0).
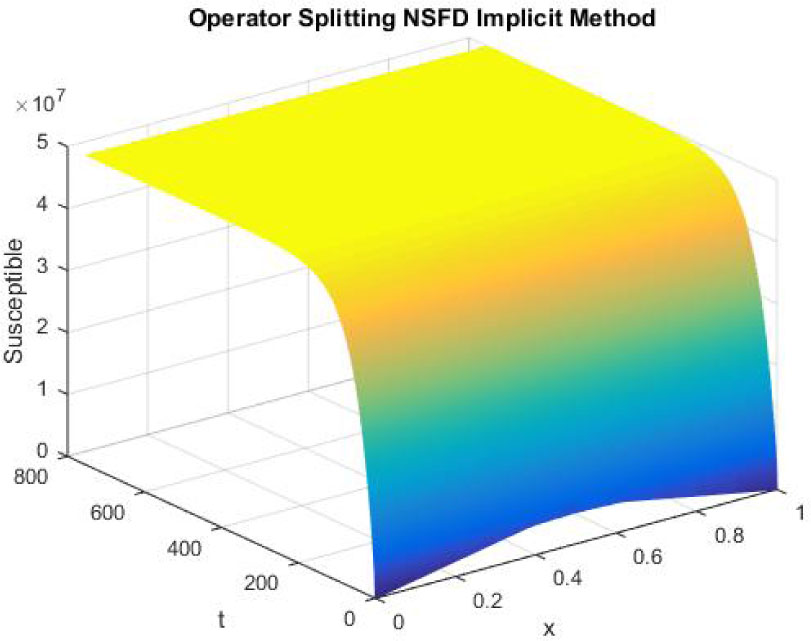
Mesh graph of Susceptible Individuals for DFE
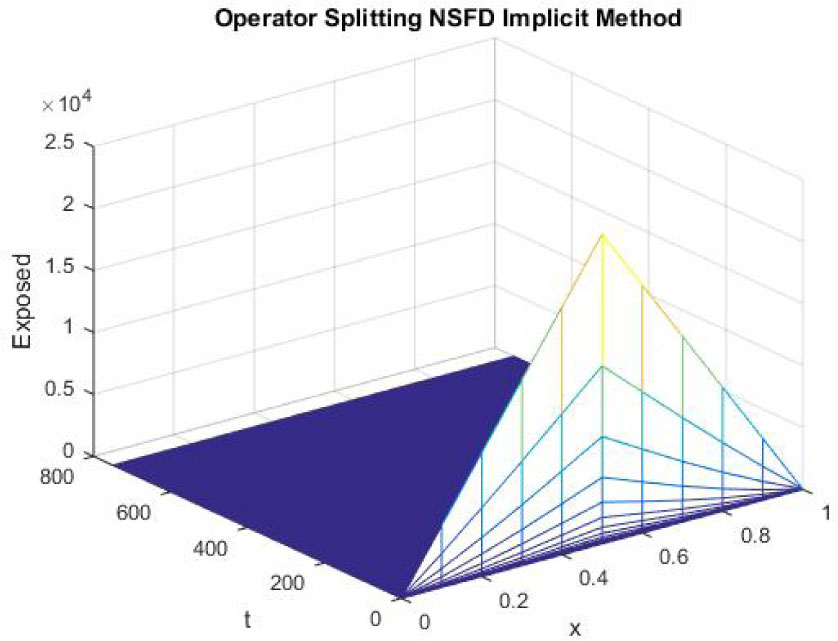
Mesh graph of Exposed Individuals for DFE
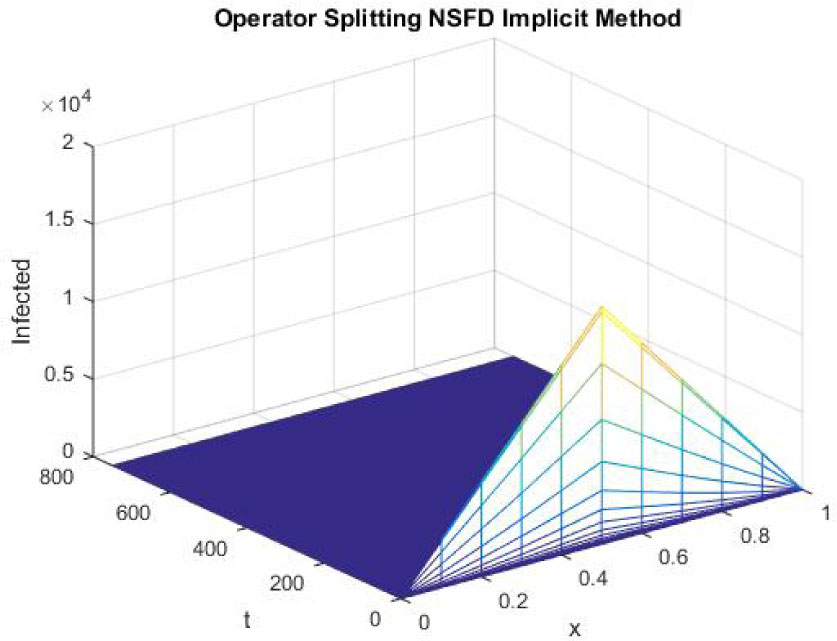
Mesh graph of Infected Individuals for DFE
The figures 22-24 represent the graphs of endemic equilibrium point for susceptible, exposed and infected individuals using NSFD operator splitting implicit scheme at h = 0.1 and λ1 = 0.25, λ2 = 0.05 and λ3 = 0.005. Graphs show that NSFD operator splitting implicit method preserves the positivity property and converges to the endemic equilibrium point (S*, E*, I*).
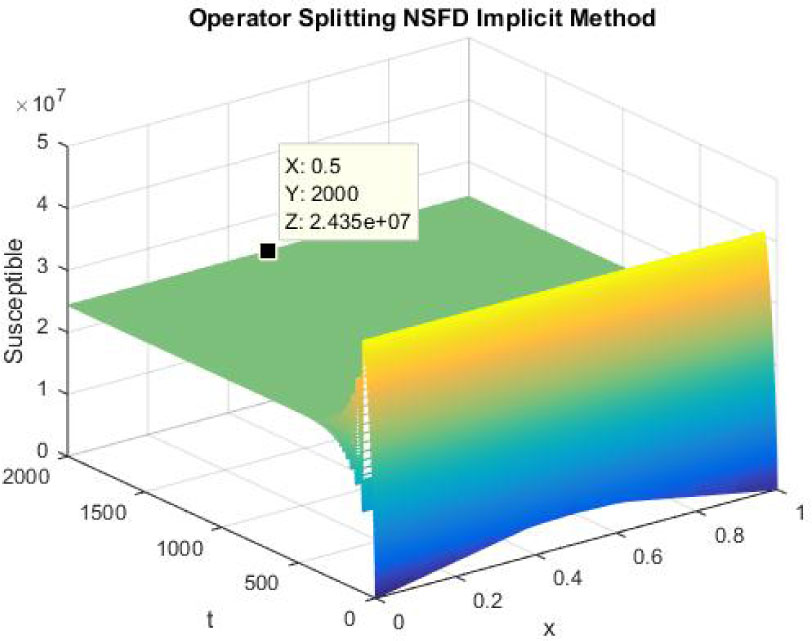
Mesh graph of Susceptible Individuals for EE
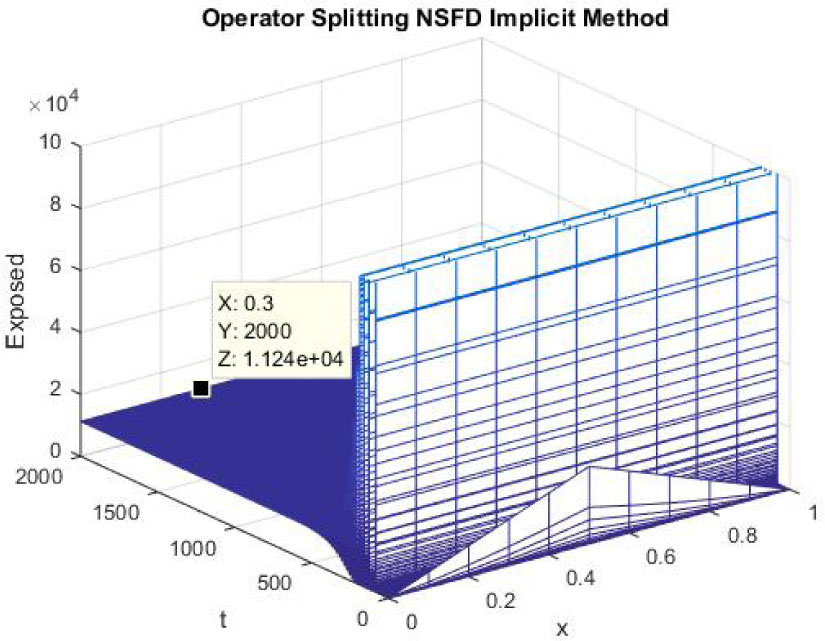
Mesh graph of Exposed Individuals for EE
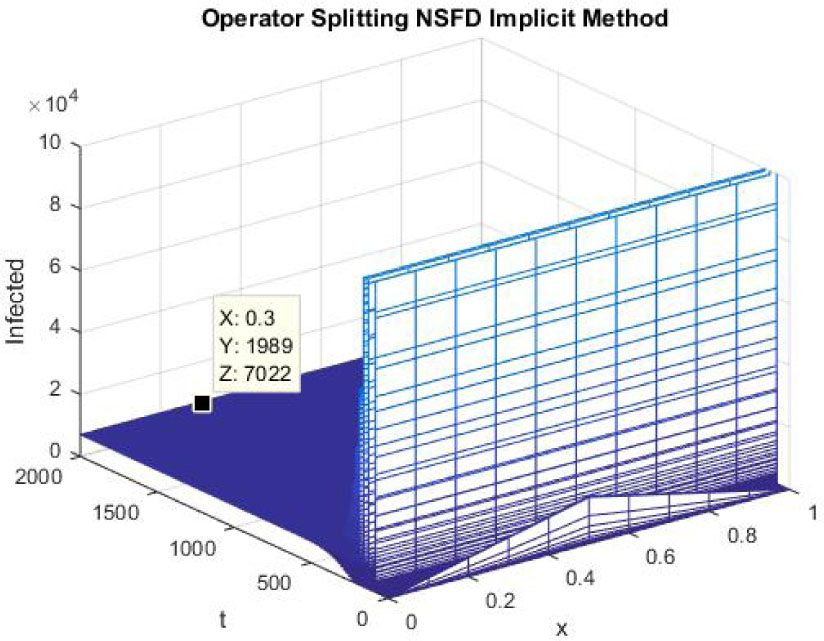
Mesh graph of Infected Individuals for EE
7 Conclusion
In this work, we developed two positivity preserving nonstandard finite difference schemes which did not bring contrived chaos. The proposed NSFD schemes are operator splitting FD schemes. We showed that classical operator splitting FD schemes bring the contrived chaos which lead to the numerical instabilities. We also give the stability analysis of SEIR reaction-diffusion system and find out the bifurcation value of transmission coefficient with the help of Routh-Hurwitz criteria. The proposed NSFD operator splitting schemes should prove to be of value in the solution of nonlinear continuous dynamical systems. Our future plane includes the construction of NSFD operator splitting techniques for hidden attractors in continuous dynamical systems [34, 35, 36, 37].
Acknowledgement
We are thankful to the reviewer for spending his time and giving his valuable suggestions to improve this manuscript.
References
[1] Hamer, W. H., Epidemic disease in England, Lancet, (1906), 1, 733–739.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Kaninda, A.V., Legros, D., Jataou, I.M., Malfait, P., Maisonneuve, M., Paquet, C., Moren, A., Measles vaccine Effectiveness in Standard and Early Immunization Strategies, Niger. Pediatr. Infect., (1998), 17, 1034–1039.10.1097/00006454-199811000-00014Search in Google Scholar
[3] Hethcote, H.W., Optimal ages for vaccination for Measles, Math. Biosci, (1989), 89, 29-52.10.1016/0025-5564(88)90111-3Search in Google Scholar
[4] Bakare, E. A., Adekunle, Y. A., Kadiri, K. O., Modeling and Simulation of the dynamics of the transmission of Measles, International journal of Computer Trends and Technology, (2012), 3(1), 174-177.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Okosun, K. O., Mukamuri, M., Makinde, D. O., Global stability analysis and control of leptospirosis, Open Math., (2016), 14, 567–585.10.1515/math-2016-0053Search in Google Scholar
[6] Ahmed, N., Rafiq, M., Rehman, M. A., Iqbal, M. S., Ali, M. Numerical modelling of three dimensional Brusselator reaction diffusion system, AIP Advances, (2019), 9, 01520510.1063/1.5070093Search in Google Scholar
[7] Fatima, U., Ali, M., Ahmed, N., Rafiq, M., Numerical modeling of susceptible latent breaking-out quarantine computer virus epidemic dynamics, Heliyon, (2018), 4, e00631.10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00631Search in Google Scholar
[8] Twizell, E.H., Wang, Y., Price, W.G., Chaos-free numerical solutions of reaction-diffusion equations, Proc.R. Soc. Lond. A, (1991), 430, 541-576.10.1098/rspa.1990.0106Search in Google Scholar
[9] Rafiq, M., Numerical Modeling of Infectious Diseases Dynamics, (PhD thesis), Lahore: University of Engineering and Technology.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Ahmed, N., Jawaz, M., Rafiq, M., Rehman, M. A., Ali, M., Ahmad, M. O., Numerical Treatment of an Epidemic Model with Spatial Diffusion, J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci., (2018), 8(6), 17-29.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Ahmed, N., Shahid, N., Iqbal, Z., Jawaz, M., Rafiq, M., Tahira. S. S., Ahmad, M. O., Numerical Modeling of SEIQV Epidemic Model with Saturated Incidence Rate, J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci., (2018), 8(4).Search in Google Scholar
[12] Ahmed, N., Rafiq, M., Rehman, M. A., Ali, M., Ahmad, M. O., Numerical Modeling of SEIR Measles Dynamics with Diffusion, Communications in Mathematics and Applications, (2018), 9(3), 315–326,Search in Google Scholar
[13] Chinviriyasit, S., Chinviriyasit, W., Numerical modeling of SIR epidemic model with diffusion, Appl. Math. Comp., (2010), 216, 395–409.10.1016/j.amc.2010.01.028Search in Google Scholar
[14] Fernández, Francisco M., On some approximate methods for nonlinear models, Applied Mathematics and Computation, (2009), 215, 168–174.10.1016/j.amc.2009.04.060Search in Google Scholar
[15] Al-Showaikh, F., Twizell, E., One-dimensional measles dynamics, Appl. Math. Comput., (2004), 152, 169-194.10.1016/S0096-3003(03)00554-XSearch in Google Scholar
[16] Mickens, R. E., Nonstandard Finite Difference Models of Differential Equations, (1994), World Scientific.10.1142/2081Search in Google Scholar
[17] Mickens, R. E., A nonstandard finite difference scheme for a Fisher PDE having nonlinear diffusion, Computer and Mathematics with Application, (2003), 45, 429-436.10.1016/S0898-1221(03)80028-7Search in Google Scholar
[18] Mickens, R. E., A nonstandard finite difference scheme for an advection-reaction equation, J. Diff. Eq. Appl., (2004), 10, 1307-1312.10.1080/10236190410001652838Search in Google Scholar
[19] Chakrabrty, A., Singh, M., Lucy, B., Ridland, P., Predator-prey model with pry- taxis and diffusion, Math. Comput. Modeling, (2007), 46, 482-498.10.1016/j.mcm.2006.10.010Search in Google Scholar
[20] Jansen, H., Twizell, E. H., An unconditionally convergent discretization of the SEIR model, MATH COMPUT SIMULAT., (2002), 58, 147-158.10.1016/S0378-4754(01)00356-1Search in Google Scholar
[21] Harwood, R. C. Operator splitting method and applications for semilinear parabolic partial differential equations (Ph.D. dissertation), (2011), Pullman: Dept. Math., Washington State Univ.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Harwood, R. C., Manoranjan, V. S., Edwards, D. B., Lead-acid battery model under discharge with a fast splitting method, IEEE Trans. Energy Convers., (2011), 26 (4), 1109-1117.10.1109/TEC.2011.2162093Search in Google Scholar
[23] Yanenko, N. N., The Method of Fractional Steps (Springer-Verlag, 1971).10.1007/978-3-642-65108-3Search in Google Scholar
[24] Zharnitsky, V., Averaging for split-step scheme, Nonlinearity, (2003), 16, 1359-1366.10.1088/0951-7715/16/4/310Search in Google Scholar
[25] Ansarizadeh, F., Singh, M., Richards, D., Modelling of tumor cells regression in response to chemotherapeutic treatment, Applied Mathematical Modeling, (2017), 48, 96-112.10.1016/j.apm.2017.03.045Search in Google Scholar
[26] Naheed, A., Singh, M., Lucy, D., Effect of Treatment on Transmission Dynamics of SARS Epidemic, J. Infect. Non. Infect. Dis., (2016).10.24966/INID-8654/100016Search in Google Scholar
[27] Naheed, A., A Study of Spatio-Temporal Spread of Infectious Disease:SARS, (Ph.D. thesis), (2015),, Australia: Swinburne University of Technology.Search in Google Scholar
[28] Naheed, A., Singh, M., Lucy, D., Numerical study of SARS epidemic model with the inclusion of diffusion in the system, Applied Mathematics and computation, (2014), 229, 480-498.10.1016/j.amc.2013.12.062Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Samsuzzoha, Md., A Study on numerical solutions of epidemic models, (2012), (Ph.D. thesis), Australia: Swinburne University of Technology.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Wang, H. Q., Numerical studies on the split-step finite difference method for nonlinear Schrödinger equations, Applied Mathematics and Computation, (2005), 170, 17-3510.1016/j.amc.2004.10.066Search in Google Scholar
[31] Manna, K., Chakrabarty, S. P., Global stability and a non-standard finite difference scheme for a diffusion driven HBV model with capsids, J. Differ. Equ. Appl., (2015), 21, 918-933.10.1080/10236198.2015.1056524Search in Google Scholar
[32] Qin, W., Wang, L., Ding, X., A non-standard finite difference method for a hepatitis B virus infection model with spatial diffusion, J. Differ. Equ. Appl., (2014), 20(12), 1641–1651.10.1080/10236198.2014.968565Search in Google Scholar
[33] Fujimoto, T., Ranade, R., Two characterizations of inverse–positive matrices: The Hawkins–Simon condition and the Le Chatelier–Braun principle, Electron. J. Linear Algebra, (2004), 11, 59–65.10.13001/1081-3810.1122Search in Google Scholar
[34] Wei, Z.C., Moroz, I., Sprott, J.C., Akgul, A., Zhang, W., Hidden hyperchaos and electronic circuit application in a 5D self-exciting homopolar disc dynamo, Chaos, (2017), 27, 033101.10.1063/1.4977417Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[35] Wei, Z.C., Moroz, I., Sprott, J.C., Wang, Z., Zhang, W., Detecting hidden chaotic regions and complex dynamics in the self-exciting homopolar disc dynamo, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos, (2017), 27, 1730008.10.1142/S0218127417300087Search in Google Scholar
[36] Wei, Z., Yu, P., Zhang, W., Minghui Yao, Study of hidden attractors, multiple limit cycles from Hopf bifurcation and boundedness of motion in the generalized hyperchaotic Rabinovich system, Nonlinear Dyn., (2015), 10.1007/s11071-015-2144-8.10.1007/s11071-015-2144-8Search in Google Scholar
[37] Wei, Z., Zhua B., Yanga, J., Perc, M., Slavinec, M., Bifurcation analysis of two disc dynamos with viscous friction and multiple time delays, Applied Mathematics and Computation, (2019), 347, 265–28110.1016/j.amc.2018.10.090Search in Google Scholar
© 2019 Ahmed et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- On the Gevrey ultradifferentiability of weak solutions of an abstract evolution equation with a scalar type spectral operator of orders less than one
- Centralizers of automorphisms permuting free generators
- Extreme points and support points of conformal mappings
- Arithmetical properties of double Möbius-Bernoulli numbers
- The product of quasi-ideal refined generalised quasi-adequate transversals
- Characterizations of the Solution Sets of Generalized Convex Fuzzy Optimization Problem
- Augmented, free and tensor generalized digroups
- Time-dependent attractor of wave equations with nonlinear damping and linear memory
- A new smoothing method for solving nonlinear complementarity problems
- Almost periodic solution of a discrete competitive system with delays and feedback controls
- On a problem of Hasse and Ramachandra
- Hopf bifurcation and stability in a Beddington-DeAngelis predator-prey model with stage structure for predator and time delay incorporating prey refuge
- A note on the formulas for the Drazin inverse of the sum of two matrices
- Completeness theorem for probability models with finitely many valued measure
- Periodic solution for ϕ-Laplacian neutral differential equation
- Asymptotic orbital shadowing property for diffeomorphisms
- Modular equations of a continued fraction of order six
- Solutions with concentration and cavitation to the Riemann problem for the isentropic relativistic Euler system for the extended Chaplygin gas
- Stability Problems and Analytical Integration for the Clebsch’s System
- Topological Indices of Para-line Graphs of V-Phenylenic Nanostructures
- On split Lie color triple systems
- Triangular Surface Patch Based on Bivariate Meyer-König-Zeller Operator
- Generators for maximal subgroups of Conway group Co1
- Positivity preserving operator splitting nonstandard finite difference methods for SEIR reaction diffusion model
- Characterizations of Convex spaces and Anti-matroids via Derived Operators
- On Partitions and Arf Semigroups
- Arithmetic properties for Andrews’ (48,6)- and (48,18)-singular overpartitions
- A concise proof to the spectral and nuclear norm bounds through tensor partitions
- A categorical approach to abstract convex spaces and interval spaces
- Dynamics of two-species delayed competitive stage-structured model described by differential-difference equations
- Parity results for broken 11-diamond partitions
- A new fourth power mean of two-term exponential sums
- The new operations on complete ideals
- Soft covering based rough graphs and corresponding decision making
- Complete convergence for arrays of ratios of order statistics
- Sufficient and necessary conditions of convergence for ρ͠ mixing random variables
- Attractors of dynamical systems in locally compact spaces
- Random attractors for stochastic retarded strongly damped wave equations with additive noise on bounded domains
- Statistical approximation properties of λ-Bernstein operators based on q-integers
- An investigation of fractional Bagley-Torvik equation
- Pentavalent arc-transitive Cayley graphs on Frobenius groups with soluble vertex stabilizer
- On the hybrid power mean of two kind different trigonometric sums
- Embedding of Supplementary Results in Strong EMT Valuations and Strength
- On Diophantine approximation by unlike powers of primes
- A General Version of the Nullstellensatz for Arbitrary Fields
- A new representation of α-openness, α-continuity, α-irresoluteness, and α-compactness in L-fuzzy pretopological spaces
- Random Polygons and Estimations of π
- The optimal pebbling of spindle graphs
- MBJ-neutrosophic ideals of BCK/BCI-algebras
- A note on the structure of a finite group G having a subgroup H maximal in 〈H, Hg〉
- A fuzzy multi-objective linear programming with interval-typed triangular fuzzy numbers
- Variational-like inequalities for n-dimensional fuzzy-vector-valued functions and fuzzy optimization
- Stability property of the prey free equilibrium point
- Rayleigh-Ritz Majorization Error Bounds for the Linear Response Eigenvalue Problem
- Hyper-Wiener indices of polyphenyl chains and polyphenyl spiders
- Razumikhin-type theorem on time-changed stochastic functional differential equations with Markovian switching
- Fixed Points of Meromorphic Functions and Their Higher Order Differences and Shifts
- Properties and Inference for a New Class of Generalized Rayleigh Distributions with an Application
- Nonfragile observer-based guaranteed cost finite-time control of discrete-time positive impulsive switched systems
- Empirical likelihood confidence regions of the parameters in a partially single-index varying-coefficient model
- Algebraic loop structures on algebra comultiplications
- Two weight estimates for a class of (p, q) type sublinear operators and their commutators
- Dynamic of a nonautonomous two-species impulsive competitive system with infinite delays
- 2-closures of primitive permutation groups of holomorph type
- Monotonicity properties and inequalities related to generalized Grötzsch ring functions
- Variation inequalities related to Schrödinger operators on weighted Morrey spaces
- Research on cooperation strategy between government and green supply chain based on differential game
- Extinction of a two species competitive stage-structured system with the effect of toxic substance and harvesting
- *-Ricci soliton on (κ, μ)′-almost Kenmotsu manifolds
- Some improved bounds on two energy-like invariants of some derived graphs
- Pricing under dynamic risk measures
- Finite groups with star-free noncyclic graphs
- A degree approach to relationship among fuzzy convex structures, fuzzy closure systems and fuzzy Alexandrov topologies
- S-shaped connected component of radial positive solutions for a prescribed mean curvature problem in an annular domain
- On Diophantine equations involving Lucas sequences
- A new way to represent functions as series
- Stability and Hopf bifurcation periodic orbits in delay coupled Lotka-Volterra ring system
- Some remarks on a pair of seemingly unrelated regression models
- Lyapunov stable homoclinic classes for smooth vector fields
- Stabilizers in EQ-algebras
- The properties of solutions for several types of Painlevé equations concerning fixed-points, zeros and poles
- Spectrum perturbations of compact operators in a Banach space
- The non-commuting graph of a non-central hypergroup
- Lie symmetry analysis and conservation law for the equation arising from higher order Broer-Kaup equation
- Positive solutions of the discrete Dirichlet problem involving the mean curvature operator
- Dislocated quasi cone b-metric space over Banach algebra and contraction principles with application to functional equations
- On the Gevrey ultradifferentiability of weak solutions of an abstract evolution equation with a scalar type spectral operator on the open semi-axis
- Differential polynomials of L-functions with truncated shared values
- Exclusion sets in the S-type eigenvalue localization sets for tensors
- Continuous linear operators on Orlicz-Bochner spaces
- Non-trivial solutions for Schrödinger-Poisson systems involving critical nonlocal term and potential vanishing at infinity
- Characterizations of Benson proper efficiency of set-valued optimization in real linear spaces
- A quantitative obstruction to collapsing surfaces
- Dynamic behaviors of a Lotka-Volterra type predator-prey system with Allee effect on the predator species and density dependent birth rate on the prey species
- Coexistence for a kind of stochastic three-species competitive models
- Algebraic and qualitative remarks about the family yy′ = (αxm+k–1 + βxm–k–1)y + γx2m–2k–1
- On the two-term exponential sums and character sums of polynomials
- F-biharmonic maps into general Riemannian manifolds
- Embeddings of harmonic mixed norm spaces on smoothly bounded domains in ℝn
- Asymptotic behavior for non-autonomous stochastic plate equation on unbounded domains
- Power graphs and exchange property for resolving sets
- On nearly Hurewicz spaces
- Least eigenvalue of the connected graphs whose complements are cacti
- Determinants of two kinds of matrices whose elements involve sine functions
- A characterization of translational hulls of a strongly right type B semigroup
- Common fixed point results for two families of multivalued A–dominated contractive mappings on closed ball with applications
- Lp estimates for maximal functions along surfaces of revolution on product spaces
- Path-induced closure operators on graphs for defining digital Jordan surfaces
- Irreducible modules with highest weight vectors over modular Witt and special Lie superalgebras
- Existence of periodic solutions with prescribed minimal period of a 2nth-order discrete system
- Injective hulls of many-sorted ordered algebras
- Random uniform exponential attractor for stochastic non-autonomous reaction-diffusion equation with multiplicative noise in ℝ3
- Global properties of virus dynamics with B-cell impairment
- The monotonicity of ratios involving arc tangent function with applications
- A family of Cantorvals
- An asymptotic property of branching-type overloaded polling networks
- Almost periodic solutions of a commensalism system with Michaelis-Menten type harvesting on time scales
- Explicit order 3/2 Runge-Kutta method for numerical solutions of stochastic differential equations by using Itô-Taylor expansion
- L-fuzzy ideals and L-fuzzy subalgebras of Novikov algebras
- L-topological-convex spaces generated by L-convex bases
- An optimal fourth-order family of modified Cauchy methods for finding solutions of nonlinear equations and their dynamical behavior
- New error bounds for linear complementarity problems of Σ-SDD matrices and SB-matrices
- Hankel determinant of order three for familiar subsets of analytic functions related with sine function
- On some automorphic properties of Galois traces of class invariants from generalized Weber functions of level 5
- Results on existence for generalized nD Navier-Stokes equations
- Regular Banach space net and abstract-valued Orlicz space of range-varying type
- Some properties of pre-quasi operator ideal of type generalized Cesáro sequence space defined by weighted means
- On a new convergence in topological spaces
- On a fixed point theorem with application to functional equations
- Coupled system of a fractional order differential equations with weighted initial conditions
- Rough quotient in topological rough sets
- Split Hausdorff internal topologies on posets
- A preconditioned AOR iterative scheme for systems of linear equations with L-matrics
- New handy and accurate approximation for the Gaussian integrals with applications to science and engineering
- Special Issue on Graph Theory (GWGT 2019)
- The general position problem and strong resolving graphs
- Connected domination game played on Cartesian products
- On minimum algebraic connectivity of graphs whose complements are bicyclic
- A novel method to construct NSSD molecular graphs
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- On the Gevrey ultradifferentiability of weak solutions of an abstract evolution equation with a scalar type spectral operator of orders less than one
- Centralizers of automorphisms permuting free generators
- Extreme points and support points of conformal mappings
- Arithmetical properties of double Möbius-Bernoulli numbers
- The product of quasi-ideal refined generalised quasi-adequate transversals
- Characterizations of the Solution Sets of Generalized Convex Fuzzy Optimization Problem
- Augmented, free and tensor generalized digroups
- Time-dependent attractor of wave equations with nonlinear damping and linear memory
- A new smoothing method for solving nonlinear complementarity problems
- Almost periodic solution of a discrete competitive system with delays and feedback controls
- On a problem of Hasse and Ramachandra
- Hopf bifurcation and stability in a Beddington-DeAngelis predator-prey model with stage structure for predator and time delay incorporating prey refuge
- A note on the formulas for the Drazin inverse of the sum of two matrices
- Completeness theorem for probability models with finitely many valued measure
- Periodic solution for ϕ-Laplacian neutral differential equation
- Asymptotic orbital shadowing property for diffeomorphisms
- Modular equations of a continued fraction of order six
- Solutions with concentration and cavitation to the Riemann problem for the isentropic relativistic Euler system for the extended Chaplygin gas
- Stability Problems and Analytical Integration for the Clebsch’s System
- Topological Indices of Para-line Graphs of V-Phenylenic Nanostructures
- On split Lie color triple systems
- Triangular Surface Patch Based on Bivariate Meyer-König-Zeller Operator
- Generators for maximal subgroups of Conway group Co1
- Positivity preserving operator splitting nonstandard finite difference methods for SEIR reaction diffusion model
- Characterizations of Convex spaces and Anti-matroids via Derived Operators
- On Partitions and Arf Semigroups
- Arithmetic properties for Andrews’ (48,6)- and (48,18)-singular overpartitions
- A concise proof to the spectral and nuclear norm bounds through tensor partitions
- A categorical approach to abstract convex spaces and interval spaces
- Dynamics of two-species delayed competitive stage-structured model described by differential-difference equations
- Parity results for broken 11-diamond partitions
- A new fourth power mean of two-term exponential sums
- The new operations on complete ideals
- Soft covering based rough graphs and corresponding decision making
- Complete convergence for arrays of ratios of order statistics
- Sufficient and necessary conditions of convergence for ρ͠ mixing random variables
- Attractors of dynamical systems in locally compact spaces
- Random attractors for stochastic retarded strongly damped wave equations with additive noise on bounded domains
- Statistical approximation properties of λ-Bernstein operators based on q-integers
- An investigation of fractional Bagley-Torvik equation
- Pentavalent arc-transitive Cayley graphs on Frobenius groups with soluble vertex stabilizer
- On the hybrid power mean of two kind different trigonometric sums
- Embedding of Supplementary Results in Strong EMT Valuations and Strength
- On Diophantine approximation by unlike powers of primes
- A General Version of the Nullstellensatz for Arbitrary Fields
- A new representation of α-openness, α-continuity, α-irresoluteness, and α-compactness in L-fuzzy pretopological spaces
- Random Polygons and Estimations of π
- The optimal pebbling of spindle graphs
- MBJ-neutrosophic ideals of BCK/BCI-algebras
- A note on the structure of a finite group G having a subgroup H maximal in 〈H, Hg〉
- A fuzzy multi-objective linear programming with interval-typed triangular fuzzy numbers
- Variational-like inequalities for n-dimensional fuzzy-vector-valued functions and fuzzy optimization
- Stability property of the prey free equilibrium point
- Rayleigh-Ritz Majorization Error Bounds for the Linear Response Eigenvalue Problem
- Hyper-Wiener indices of polyphenyl chains and polyphenyl spiders
- Razumikhin-type theorem on time-changed stochastic functional differential equations with Markovian switching
- Fixed Points of Meromorphic Functions and Their Higher Order Differences and Shifts
- Properties and Inference for a New Class of Generalized Rayleigh Distributions with an Application
- Nonfragile observer-based guaranteed cost finite-time control of discrete-time positive impulsive switched systems
- Empirical likelihood confidence regions of the parameters in a partially single-index varying-coefficient model
- Algebraic loop structures on algebra comultiplications
- Two weight estimates for a class of (p, q) type sublinear operators and their commutators
- Dynamic of a nonautonomous two-species impulsive competitive system with infinite delays
- 2-closures of primitive permutation groups of holomorph type
- Monotonicity properties and inequalities related to generalized Grötzsch ring functions
- Variation inequalities related to Schrödinger operators on weighted Morrey spaces
- Research on cooperation strategy between government and green supply chain based on differential game
- Extinction of a two species competitive stage-structured system with the effect of toxic substance and harvesting
- *-Ricci soliton on (κ, μ)′-almost Kenmotsu manifolds
- Some improved bounds on two energy-like invariants of some derived graphs
- Pricing under dynamic risk measures
- Finite groups with star-free noncyclic graphs
- A degree approach to relationship among fuzzy convex structures, fuzzy closure systems and fuzzy Alexandrov topologies
- S-shaped connected component of radial positive solutions for a prescribed mean curvature problem in an annular domain
- On Diophantine equations involving Lucas sequences
- A new way to represent functions as series
- Stability and Hopf bifurcation periodic orbits in delay coupled Lotka-Volterra ring system
- Some remarks on a pair of seemingly unrelated regression models
- Lyapunov stable homoclinic classes for smooth vector fields
- Stabilizers in EQ-algebras
- The properties of solutions for several types of Painlevé equations concerning fixed-points, zeros and poles
- Spectrum perturbations of compact operators in a Banach space
- The non-commuting graph of a non-central hypergroup
- Lie symmetry analysis and conservation law for the equation arising from higher order Broer-Kaup equation
- Positive solutions of the discrete Dirichlet problem involving the mean curvature operator
- Dislocated quasi cone b-metric space over Banach algebra and contraction principles with application to functional equations
- On the Gevrey ultradifferentiability of weak solutions of an abstract evolution equation with a scalar type spectral operator on the open semi-axis
- Differential polynomials of L-functions with truncated shared values
- Exclusion sets in the S-type eigenvalue localization sets for tensors
- Continuous linear operators on Orlicz-Bochner spaces
- Non-trivial solutions for Schrödinger-Poisson systems involving critical nonlocal term and potential vanishing at infinity
- Characterizations of Benson proper efficiency of set-valued optimization in real linear spaces
- A quantitative obstruction to collapsing surfaces
- Dynamic behaviors of a Lotka-Volterra type predator-prey system with Allee effect on the predator species and density dependent birth rate on the prey species
- Coexistence for a kind of stochastic three-species competitive models
- Algebraic and qualitative remarks about the family yy′ = (αxm+k–1 + βxm–k–1)y + γx2m–2k–1
- On the two-term exponential sums and character sums of polynomials
- F-biharmonic maps into general Riemannian manifolds
- Embeddings of harmonic mixed norm spaces on smoothly bounded domains in ℝn
- Asymptotic behavior for non-autonomous stochastic plate equation on unbounded domains
- Power graphs and exchange property for resolving sets
- On nearly Hurewicz spaces
- Least eigenvalue of the connected graphs whose complements are cacti
- Determinants of two kinds of matrices whose elements involve sine functions
- A characterization of translational hulls of a strongly right type B semigroup
- Common fixed point results for two families of multivalued A–dominated contractive mappings on closed ball with applications
- Lp estimates for maximal functions along surfaces of revolution on product spaces
- Path-induced closure operators on graphs for defining digital Jordan surfaces
- Irreducible modules with highest weight vectors over modular Witt and special Lie superalgebras
- Existence of periodic solutions with prescribed minimal period of a 2nth-order discrete system
- Injective hulls of many-sorted ordered algebras
- Random uniform exponential attractor for stochastic non-autonomous reaction-diffusion equation with multiplicative noise in ℝ3
- Global properties of virus dynamics with B-cell impairment
- The monotonicity of ratios involving arc tangent function with applications
- A family of Cantorvals
- An asymptotic property of branching-type overloaded polling networks
- Almost periodic solutions of a commensalism system with Michaelis-Menten type harvesting on time scales
- Explicit order 3/2 Runge-Kutta method for numerical solutions of stochastic differential equations by using Itô-Taylor expansion
- L-fuzzy ideals and L-fuzzy subalgebras of Novikov algebras
- L-topological-convex spaces generated by L-convex bases
- An optimal fourth-order family of modified Cauchy methods for finding solutions of nonlinear equations and their dynamical behavior
- New error bounds for linear complementarity problems of Σ-SDD matrices and SB-matrices
- Hankel determinant of order three for familiar subsets of analytic functions related with sine function
- On some automorphic properties of Galois traces of class invariants from generalized Weber functions of level 5
- Results on existence for generalized nD Navier-Stokes equations
- Regular Banach space net and abstract-valued Orlicz space of range-varying type
- Some properties of pre-quasi operator ideal of type generalized Cesáro sequence space defined by weighted means
- On a new convergence in topological spaces
- On a fixed point theorem with application to functional equations
- Coupled system of a fractional order differential equations with weighted initial conditions
- Rough quotient in topological rough sets
- Split Hausdorff internal topologies on posets
- A preconditioned AOR iterative scheme for systems of linear equations with L-matrics
- New handy and accurate approximation for the Gaussian integrals with applications to science and engineering
- Special Issue on Graph Theory (GWGT 2019)
- The general position problem and strong resolving graphs
- Connected domination game played on Cartesian products
- On minimum algebraic connectivity of graphs whose complements are bicyclic
- A novel method to construct NSSD molecular graphs

