Abstract
C59H64Cl2I4P2Ru2, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 7.5074(2) Å, b = 10.8867(3) Å, c = 18.7012(6)) Å, α = 96.696(1)°, β = 99.956(1)°, γ = 104.730(1)°, V = 1435.14(7) Å3, Z = 1, Rgt (F) = 0.0190, wRref (F 2) = 0.0443, T = 100 K.
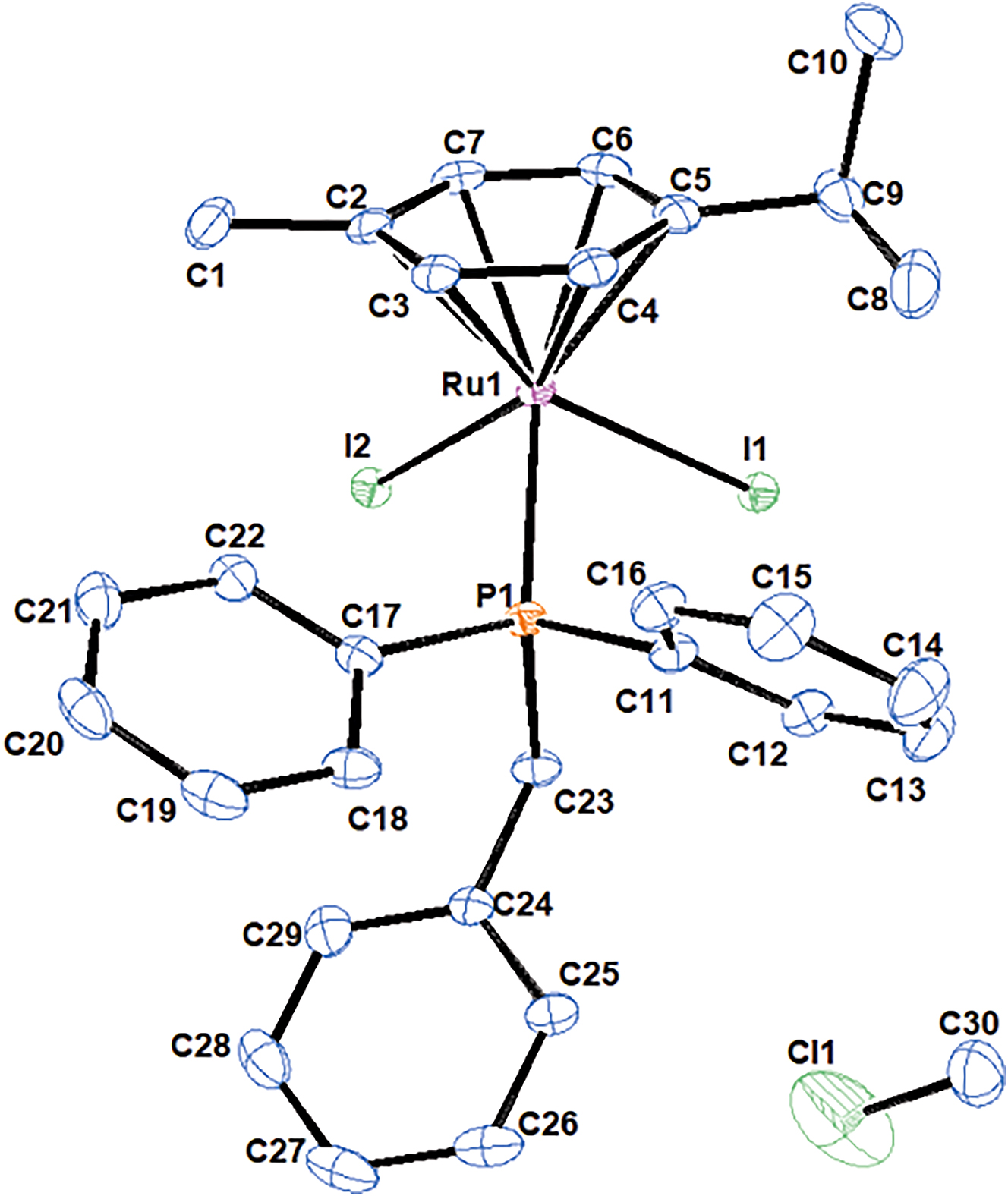
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data. The list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Red block |
| Size: | 0.35 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 2.86 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8, φ and ω scans |
| θ max, completeness: | 27.5°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 86775, 6555, 0.038 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 6,281 |
| N(param)refined: | 319 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX, 2 Olex2 3 , 4 |
1 Source of materials
All reagents are commercially available and were used without further purification. All manipulations were carried out using standard Schlenk techniques under an inert atmosphere of argon. A solution of benzyldiphenylphosphine (PPh2Bn), (0.068 g, 0.246 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (5 mL) was slowly added to a solution of [(η 6-p–cymene)RuI2]2(0.115 g, 0.117 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (5 mL). The resulting dark brown solution was stirred at room temperature for 16 h. After filtration, the solvent was removed in vacuo. The residue was suspended in hexane (15 mL). After filtration, the resulting brown solid was washed with hexane and dried under vacuum. Yield (0.164 g, 91 %). Crystals were obtained from a CH2Cl2 solution of the titled compound layered with Et2O at room temperature.
2 Experimental details
Intensity data was determined on a Bruker D8 Quest Microfocus with a Photon III detector diffractometer. Data reduction was carried out using the SAINT–Plus version 6.02.6 software program, and Sadabs was used to process empirical absorption correction. 1 The aromatic H atoms were placed in geometrically idealised positions and constrained to maintain fixed distances relative to their parent carbon atoms, with a specified C–H bond length of 0.93 Å for aromatic C–H bonds with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C) or Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(C). 2 The structure was solved in the Olex2–1.5 suite of programs and refined with SHELXL-2019/3 refinement package. 3 , 4 Diagrams and publication material were generated using ORTEP-3. 5
3 Discussion
The chemistry of half sandwich (η 6–arene)ruthenium(II) complexes has been widely studied due to the potential of these complexes as diagnostic and therapeutic agents which have significantly impacted anticancer drug development. 6 The ruthenium complexes have unique biochemical properties, such as potential ability to form a labile complex, to have different oxidation states under physiological conditions and to mimic iron ions, all these properties could influence the thermodynamic and kinetic properties of a metallodrug. 7 , 8 , 9 , 10
Phosphine ligands are well known for their electron donor properties and are extensively used in coordination chemistry as spectator ligands to stabilize both low and high transition metals valence states. 11 The triphenylphosphine ligand has been shown to play a crucial role in facilitating the binding of the ruthenium (Ru) complex to DNA, which can lead to the distortion of its secondary and tertiary structures. This interaction is significant in the study of metal-based drugs and their potential applications in medicine, particularly in cancer treatment. 12 However, Ru(II) arene complexes bearing derivative triphenylphosphine ligands have been less widely studied.
The title compound is of interest as it contains a lipophilic benzyldiphenylphosphine ligand as well as two labile iodido ligands in a mutually cis-configuration which could be key structural features for anticancer activity. 13 As steric effects are known to be crucial in the reactivity of transition metal complexes bearing tertiary phosphine ligands, our findings reported here will extend the knowledge of the solid-state molecular structure of this class of complex. 14
The ruthenium coordination sphere in the title structure is constructed with a hexahaptic cymene group, benzyldiphenylphosphine (PPh2Bn) and two iodido ligands forming a pseudo-octahedral structure. The crystal structure includes one half of a CH2Cl2 solvent molecule that resides around an inversion center. The cymene ring is planar, with the π-bonds within the ring having unequal bond lengths ranging from 1.392 Å to 1.436 Å. The η 6-p-cymene ligand is asymmetrically bonded to ruthenium, with Ru – CArene bond lengths in the range 2.209–2.256 Å. The distance between the centroid of the η 6-p-cymene ring and the Ru is 1.725 Å. The bond distances of Ru to the two iodido ligands are 2.7214 (2) Å and 2.7360 (2) Å for I1 and I2, respectively. The I–Ru–I angle measures 90.226(7)° while the P–Ru–I2 angle measures 89.010(14)° and the P–Ru–I1 angle measures 85.422(14)° which supports the pseudo-octahedral geomtery assigned to the molecule. The Ru–P bond length is 2.3566(6) Å. The effective cone angle of the PPh2Bn ligand was measured at 142° using the Tolman cone angle model, this value correlates with the value reported by Muller and Davis for this ligand in the [RuCl2(η 6-benzene){ PPh2(CH2C6H5)-κP }] complex. 15 , 16
References
1. Bruker APEX-5, SAINT-Plus (Version 8.8.4.0, Including XPREP) and SADABS (Version 2016); Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin. USA, 2019.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Bourhis, L. J.; Dolomanov, O. V.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A.; Puschmann, H. The Anatomy of a Comprehensive Constrained, Restrained Refinement Program for the Modern Computing Environment – Olex2 Dissected. Acta Crystallogr. A: Found. Adv. 2015, A71, 59–75; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314022207.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Farrugia, L. J. ORTEP-3 for Windows (Version 2020.1). J. Appl. Cryst. 2012, 45, 849–854; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Yan, Y. K.; Melchart, M.; Habtemaria, A.; Sadler, P. J. Organometallic Chemistry, Biology and Medicine: Ruthenium Arene Anticancer Complexes. ChemComm 2005, 38, 4764–4776.10.1039/b508531bSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Bruijnincx, P. C.; Sadler, P. J. Controlling Platinum, Ruthenium, and Osmium Reactivity for Anticancer Drug Design. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 61, 1–62; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0898-8838(09)00201-3.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Yousuf, I.; Bashir, M.; Arjmand, F.; Tabassum, S. Advancement of Metal Compounds as Therapeutic and Diagnostic Metallodrugs: Current Frontiers and Future Perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214104; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214104.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Sonkar, C.; Sarkar, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Ruthenium(II)–arene Complexes as Anti-metastatic Agents, and Related Techniques. RSC Med. Chem. 2022, 13, 22–38; https://doi.org/10.1039/d1md00220a.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
10. Jabłońska-Wawrzycka, A.; Rogala, P.; Michałkiewicz, S.; Hodorowicz, M.; Barszcz, B. Ruthenium Complexes in Different Oxidation States: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Spectra and Redox Properties. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 6092–6101; https://doi.org/10.1039/c3dt32214a.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Power, P. P. Stable Two-Coordinate, Open-Shell (d1–d9) Transition Metal Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3482–3507; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr2004647.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Sáez, R.; Lorenzo, J.; Prieto, M. J.; Font–Bardia, M.; Calvet, T.; Omeñaca, N.; Moreno, V. Influence of PPh3 Moiety in the Anticancer Activity of New Organometallic Ruthenium Complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 136, 1–12; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.03.002.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Monareng, J. M.; Clayton, H. S. Crystal Structure of dibromo-dicarbonyl-bis(tricyclohexylphosphine)-Osmium(II) Dichloromethane Solvate. Z. Kristallogr. – New Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 689–692; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0153.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Hierso, J. C.; Amardeil, R.; Bentabet, E.; Broussier, R.; Gautheron, B.; Meunier, P.; Kalck, P. Structural Diversity in Coordination Chemistry of Tridentate and Tetradentate Polyphosphines of Group 6 to 10 Transition Metal Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003, 236, 143–206; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0010-8545(02)00221-7.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Tolman, C. A. Steric Effects of Phosphorus Ligands in Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1977, 77, 313–348; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr60307a002.Suche in Google Scholar
16. Muller, A.; Davis, W. (η6-benzene)(benzyldiphenylphosphane) dichloro-Ruthenium(II) Dichloromethane. Acta Crystallogr. 2012, A64, 112–122.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structure of [K3:N1:N2:N4-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazole] binuclear Ni(II) complex[Ni2(C7H5N4)2(C7H4ClO2)2]
- The crystal structure of di(thiocyanato-κ1N)-bis(methanol)-di(1,3-bis((pyridin-4-ylthio)methyl)benzene)-iron(II), C40H40FeN6O2S6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 3 O,O′:O″)-(μ 4-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 4 O,O′,O″,O‴)-dicadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C47H30Cd2F8N3O12
- The crystal structure of a 3d-4f complex based on 2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-6-methoxyphenol C31H27N4O13S2CoEr
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-yl)benzene-k 2 N:N′)(μ 4-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-k 4 O,O,O,O)dizinc(II)] dihydrate, C40H28Zn2N8O9
- The crystal structure of 4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, C11H13Cl2NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of-(10S,13S,16R,Z) −17-ethylidene-16-hydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3 H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one, C21H32O2
- The crystal structure of catena-((μ 2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ 2 N:N′)-bis(4-fluorobenzoato-κ1O)-copper(II)), C24H16F2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(ethylenediamine-κ2 N,N′)-μ-tetraoxomolybdato(VI) zinc(II)], C2H8MoN2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid, C4H3ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of bepotastine besilate, C27H31ClN2O6S
- The crystal structure of (η 6-p-cymene)benzyldiphenylphosphine-diiodido-ruthenium(II) dichloromethane solvate
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4- (imidazol-1′-yl-methyl)benzene κ 2 N:N′)-(μ 2-3-nitrobenzene -1,2-dicarboxylato-k4,O,O′:O′′,O′′′]zinc(II)-κ 2, C21H15N5O6Zn
- The crystal structure of (2R,4S)-5-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-2-methyl pentanoic acid, C23H29NO4
- The crystal strucure of [2,2′-{1,2-phenylenebis [(azanylylidene)methanylylidene]}bis(4-fluorophenolato)-κ4 N,N′,O,O′] nickel(II) N, N-dimethylformamide solvate, C23H19F2N3NiO3
- The structure of (E)-6-(cyclopropylmethyl)-11-(2,2-difluoropropylidene)-2-methyl-6, 11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C21H21F2NO2S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-(2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzyl)-1H-imidazole κ2N:N′)- (μ 2-cyclohexane-1,2-dicarboxylato κ2O,O′)cobalt(II) monohydrate]
- The crystal structure of 3,5,7-trinitro-1,3,5,7-oxatriazocane
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ3 O,O′:O′′)(μ2-1-[(2-propyl-1H-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-k2 N:N′)silver(I)], C17H17AgN6O3
- The crystal structure of (5-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)-2-sulfanylidene-1,3,4-oxadiazol-3(2H)-yl)(3-methylphenyl)methanone, C18H14N2O4S
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O]-cobalt(II), C11H11Co0.5N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-N-(4-morpholinophenyl)propanamide, C24H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of sodium methylsulfonate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(isothiocyanate κ 1 N)-(μ 2-3,3ʹ-methylenebis(1-methyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazole-2-thione)-κ 2 S:S′)-cobalt(II)], C11H12CoN6S4
- The crystal structure of {hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ 1N)nickel(II)} (μ 2-oxo)-hexaoxido-di-molybdenum(VI)─1-methyl-1H-imidazole (1/2), C32H48NiMo2N16O7
- 6-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3′,6′-tris(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C62H38N5O4P
- The crystal structure of R-2′-amino-N-methyl-N-(1-phenylethyl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxamide, C22H22N2O
- The crystal structure of bis{tetrakis(n-butyl)(μ-hydroxy)(2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoate) (μ 3 -oxo)ditin(IV)}
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ 2(3,4-dimethylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O:O′)-(3,6-bis(4′-pyridyl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine-κ 1 N)zinc(II)], C22H16N6O5S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-5-cyano–N-(5-(cyanomethyl)quinolin-8-yl)pentanamide, C19H15BrN4O
- The crystal structure of bis(tetramethylammonium) (di-μ2-aqua)hexaaqua-dibarium(II)) decavanadate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(bis(μ 2-chlorido)- (μ 2-4′-(pyridin-4-yl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine–N′, N″, N‴:N″″) -chlorido-dicopper(I,II)) monohydrate, C20H16N4OCl3Cu2
- Crystal structure of spiropachysine, C31H46N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 2 N: O)-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 3-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 2-nitrite-κ 3 O: O′: O″)dicadmium(II) monohydrate], C19H12Br3Cd2N3O9
- The crystal structure of 2-acetylpyridine-ortho-fluoro-phenylhydrazone, C14H12FN3O
- The crystal structure of poly(triaqua-(m 2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 2 O:O′)-bis(m 2-2-2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 4 O,O′:O″:O‴)dierbium(III)) hydrate, C36H26Er2N6O16
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(phenazine-5,10-diyl)bis(heptan-1-one), C26H34N2O2
- The crystal structure of (4-([2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridin]-4′-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C21H16BN3O2
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazine-5,7(6H)-dione, C6H3N3O3
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide ethanol solvate, C23H30N2O4
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis[1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-K2 O,O′]lutetium(III) C20F12H16LuO8C5H6N
- Crystal structure of dichlorido–tetrakis{3-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylpentan-3-ol-k 1N}cobalt(II), C64H88O4N12Cl6Co
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(4-allyl-2-methoxyphenyl nicotinato-k 1 N)bis(thiocyanato-k 1 N)cobalt(II)
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H21Cl2NO3
- The crystal structure of (E)–N-(4-chlorobenzylidene)(4-chlorophenyl)methanamine, C14H11Cl2N
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-ethylbenzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H22O4
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C4H2N3O4⋅C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of-(1S,4aR,5S)-5,6,7-trihydroxy-8-isopropyl-1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5,10,11,11a-octahydro-4a,1-(epoxymethano)dibenzo[a,d][7]annulen-13-one C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 7,9-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4-propylbenzo[f]isoquinolin-5-yl 4-bromobenzoate, C26H24BrNO4
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylbutanaminium)tridecathiotrimolybdate(2−), (BuMe3N)2[Mo3S13]
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-methylpiperazine-1-carbothioamide, C16H27N3S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2,2′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylenesulfanediyl)]dibenzoato-κ 4 O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ 2-1,1′-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-benzimidazole)-κ 2 N:N′)cadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C51H41N5O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,2′-pyran]-3-one, C19H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-cyanobenzyl)-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C20H15N3
- Crystal structure of (1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C22H22BrO2P
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrachloridomanganese(II)
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxyphenyl)-4,6-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine, C33H39N3O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(5-carboxypyridine-2-carboxylate-κ 2N,O)(2,5-pyridine-dicarboxylate-κ 4O,O′:N:O″)bismuth(III)], C14H9BiN2O9
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-fluoro-4-(2-(phenylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C14H11FO2S
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-amino-3-chloro-4-methoxybenzoate, C9H10ClNO3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structure of [K3:N1:N2:N4-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazole] binuclear Ni(II) complex[Ni2(C7H5N4)2(C7H4ClO2)2]
- The crystal structure of di(thiocyanato-κ1N)-bis(methanol)-di(1,3-bis((pyridin-4-ylthio)methyl)benzene)-iron(II), C40H40FeN6O2S6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 3 O,O′:O″)-(μ 4-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 4 O,O′,O″,O‴)-dicadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C47H30Cd2F8N3O12
- The crystal structure of a 3d-4f complex based on 2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-6-methoxyphenol C31H27N4O13S2CoEr
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-yl)benzene-k 2 N:N′)(μ 4-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-k 4 O,O,O,O)dizinc(II)] dihydrate, C40H28Zn2N8O9
- The crystal structure of 4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, C11H13Cl2NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of-(10S,13S,16R,Z) −17-ethylidene-16-hydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3 H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one, C21H32O2
- The crystal structure of catena-((μ 2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ 2 N:N′)-bis(4-fluorobenzoato-κ1O)-copper(II)), C24H16F2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(ethylenediamine-κ2 N,N′)-μ-tetraoxomolybdato(VI) zinc(II)], C2H8MoN2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid, C4H3ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of bepotastine besilate, C27H31ClN2O6S
- The crystal structure of (η 6-p-cymene)benzyldiphenylphosphine-diiodido-ruthenium(II) dichloromethane solvate
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4- (imidazol-1′-yl-methyl)benzene κ 2 N:N′)-(μ 2-3-nitrobenzene -1,2-dicarboxylato-k4,O,O′:O′′,O′′′]zinc(II)-κ 2, C21H15N5O6Zn
- The crystal structure of (2R,4S)-5-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-2-methyl pentanoic acid, C23H29NO4
- The crystal strucure of [2,2′-{1,2-phenylenebis [(azanylylidene)methanylylidene]}bis(4-fluorophenolato)-κ4 N,N′,O,O′] nickel(II) N, N-dimethylformamide solvate, C23H19F2N3NiO3
- The structure of (E)-6-(cyclopropylmethyl)-11-(2,2-difluoropropylidene)-2-methyl-6, 11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C21H21F2NO2S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-(2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzyl)-1H-imidazole κ2N:N′)- (μ 2-cyclohexane-1,2-dicarboxylato κ2O,O′)cobalt(II) monohydrate]
- The crystal structure of 3,5,7-trinitro-1,3,5,7-oxatriazocane
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ3 O,O′:O′′)(μ2-1-[(2-propyl-1H-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-k2 N:N′)silver(I)], C17H17AgN6O3
- The crystal structure of (5-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)-2-sulfanylidene-1,3,4-oxadiazol-3(2H)-yl)(3-methylphenyl)methanone, C18H14N2O4S
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O]-cobalt(II), C11H11Co0.5N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-N-(4-morpholinophenyl)propanamide, C24H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of sodium methylsulfonate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(isothiocyanate κ 1 N)-(μ 2-3,3ʹ-methylenebis(1-methyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazole-2-thione)-κ 2 S:S′)-cobalt(II)], C11H12CoN6S4
- The crystal structure of {hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ 1N)nickel(II)} (μ 2-oxo)-hexaoxido-di-molybdenum(VI)─1-methyl-1H-imidazole (1/2), C32H48NiMo2N16O7
- 6-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3′,6′-tris(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C62H38N5O4P
- The crystal structure of R-2′-amino-N-methyl-N-(1-phenylethyl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxamide, C22H22N2O
- The crystal structure of bis{tetrakis(n-butyl)(μ-hydroxy)(2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoate) (μ 3 -oxo)ditin(IV)}
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ 2(3,4-dimethylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O:O′)-(3,6-bis(4′-pyridyl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine-κ 1 N)zinc(II)], C22H16N6O5S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-5-cyano–N-(5-(cyanomethyl)quinolin-8-yl)pentanamide, C19H15BrN4O
- The crystal structure of bis(tetramethylammonium) (di-μ2-aqua)hexaaqua-dibarium(II)) decavanadate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(bis(μ 2-chlorido)- (μ 2-4′-(pyridin-4-yl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine–N′, N″, N‴:N″″) -chlorido-dicopper(I,II)) monohydrate, C20H16N4OCl3Cu2
- Crystal structure of spiropachysine, C31H46N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 2 N: O)-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 3-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 2-nitrite-κ 3 O: O′: O″)dicadmium(II) monohydrate], C19H12Br3Cd2N3O9
- The crystal structure of 2-acetylpyridine-ortho-fluoro-phenylhydrazone, C14H12FN3O
- The crystal structure of poly(triaqua-(m 2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 2 O:O′)-bis(m 2-2-2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 4 O,O′:O″:O‴)dierbium(III)) hydrate, C36H26Er2N6O16
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(phenazine-5,10-diyl)bis(heptan-1-one), C26H34N2O2
- The crystal structure of (4-([2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridin]-4′-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C21H16BN3O2
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazine-5,7(6H)-dione, C6H3N3O3
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide ethanol solvate, C23H30N2O4
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis[1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-K2 O,O′]lutetium(III) C20F12H16LuO8C5H6N
- Crystal structure of dichlorido–tetrakis{3-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylpentan-3-ol-k 1N}cobalt(II), C64H88O4N12Cl6Co
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(4-allyl-2-methoxyphenyl nicotinato-k 1 N)bis(thiocyanato-k 1 N)cobalt(II)
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H21Cl2NO3
- The crystal structure of (E)–N-(4-chlorobenzylidene)(4-chlorophenyl)methanamine, C14H11Cl2N
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-ethylbenzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H22O4
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C4H2N3O4⋅C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of-(1S,4aR,5S)-5,6,7-trihydroxy-8-isopropyl-1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5,10,11,11a-octahydro-4a,1-(epoxymethano)dibenzo[a,d][7]annulen-13-one C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 7,9-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4-propylbenzo[f]isoquinolin-5-yl 4-bromobenzoate, C26H24BrNO4
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylbutanaminium)tridecathiotrimolybdate(2−), (BuMe3N)2[Mo3S13]
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-methylpiperazine-1-carbothioamide, C16H27N3S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2,2′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylenesulfanediyl)]dibenzoato-κ 4 O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ 2-1,1′-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-benzimidazole)-κ 2 N:N′)cadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C51H41N5O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,2′-pyran]-3-one, C19H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-cyanobenzyl)-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C20H15N3
- Crystal structure of (1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C22H22BrO2P
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrachloridomanganese(II)
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxyphenyl)-4,6-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine, C33H39N3O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(5-carboxypyridine-2-carboxylate-κ 2N,O)(2,5-pyridine-dicarboxylate-κ 4O,O′:N:O″)bismuth(III)], C14H9BiN2O9
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-fluoro-4-(2-(phenylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C14H11FO2S
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-amino-3-chloro-4-methoxybenzoate, C9H10ClNO3

