Abstract
C9H10ClNO3, monoclinic, P21 (no. 4), a = 10.677(2) Å, b = 4.0074(8) Å, c = 11.866(2) Å, β = 112.108(6)°, V = 470.37(17) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0515 wR ref (F 2) = 0.1258, T = 183 K.
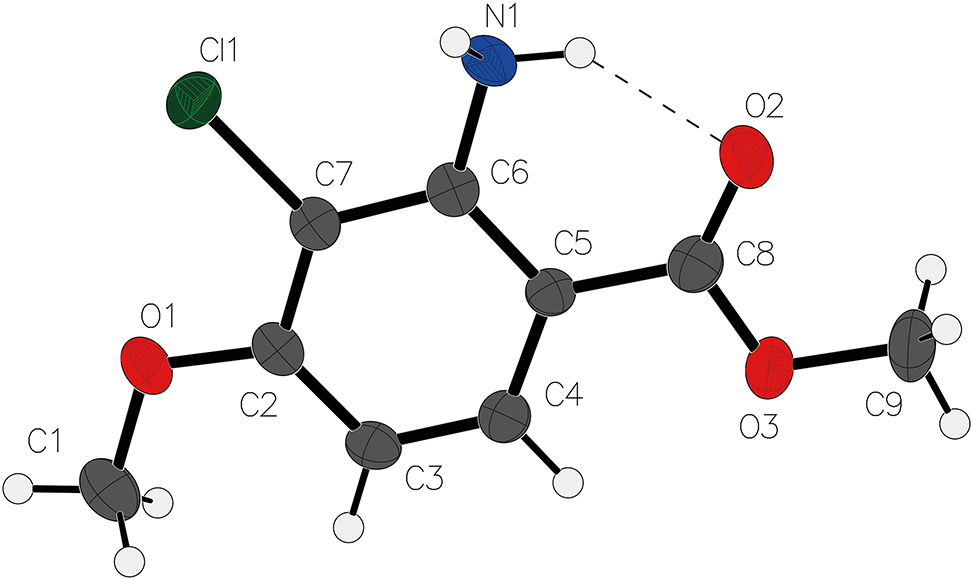
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data and the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.08 × 0.05 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.39 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω scans |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.5°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured , N(hkl)unique, R int: | 5155, 1661, 0.083 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 1,352 |
| N(param)refined: | 130 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX, 2 , 3 Olex2 4 |
1 Source of materials
Methyl 2-amino-4-methoxybenzoate (5.0 g, 27.6 mmol) and N-chlorosuccinimide (4.4 g, 33.1 mmol) were added to N,N-dimethylformamide (100 mL) separately, and the reaction system was stirred at 5 °C for 16 h. After the reaction was completed, monitored by TLC, the mixture was diluted with water (100 mL) and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 60 mL). The organic phase was washed with brine (3 × 60 mL), dried with anhydrous sulfate, and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain the crude product. The crude product was further purified by flash silica chromatography to afford a single crystal of high quality. For crystal growth, the crude product was dissolved in a minimal amount of hot ethanol and slowly cooled to room temperature. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 7.77 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.76 (brs, 2H), 6.47 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.80 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 167.66, 159.27, 148.45, 131.29, 105.83, 104.81, 100.42, 56.72, 52.07.
2 Experimental details
The crystal structure was solved by Direct Methods using SHELXT 2 and refined with SHELXL 3 within the Olex2 software suite. 4 Non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically to model thermal displacement parameters, while hydrogen atoms were placed at idealized positions with geometrical constraints.
3 Comment
Chlorine- and amino-substituted benzoic acids and their derivatives have significant applications in pharmaceutical research and coordination complex materials development. 5 , 6 , 7 , 8
The title compound exhibits a substituted benzene ring bearing four distinct functional groups: an amino (–NH2) group at C6, a chlorine atom at C7, a methoxy (–OCH3) group at C2, and a methyl ester (–COOCH3) group at C5. Bond length analysis reveals characteristic structural features: the C5–C8 bond of the ester moiety measures 1.465(8) Å, consistent with typical C–O single bonds in esters. The shortened C6–N1 bond (1.366(7) Å) suggests partial double-bond character arising from resonance interactions between the amino group and aromatic system. 9 , 10 The C7–Cl1 bond length (1.727(7) Å) aligns with standard C–Cl covalent bonds (1.72–1.76 Å).
Notably, all non-hydrogen atoms lie within a near-perfect plane (maximum deviation < 0.03 Å), indicating extensive conjugation across the aromatic system and ester group. This planar conformation is further supported by the near-linear geometry of the ester group (C5–C8–O3–O2 = 179.2°).
The crystal packing mechanism is dominated by weak intermolecular forces, with face-to-face π–π stacking interactions between adjacent benzene rings and van der Waals contacts.
Funding source: The projects of Social Development in Shaanxi Province Science and Technology Department
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2023-YBSF-036
Funding source: The 2024 Key Scientific Research Program Projects of the Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education (Key Laboratory Projects)
Award Identifier / Grant number: 24JS004
Funding source: The 2023 research and development project of the Xianyang Science and Technology Bureau
Award Identifier / Grant number: L2023-ZDYF-SF-030
Funding source: Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Drug Synthesis of Xianyang city
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2021QXNL-PT-0008
Funding source: School-level Scientific and Technological Innovation Team for Design, Synthesis and Structural Modification of Drug Molecules
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2024KCTD04
-
Research funding: This work was financially supported by the projects of Social Development in Shaanxi Province Science and Technology Department (2023-YBSF-036), the projects of Natural Science Foundation of Shannxi Province (2025JC–YBMS-1076), the 2024 Key Scientific Research Program Projects of the Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education (Key Laboratory Projects, 24JS004), the 2023 research and development project of the Xianyang Science and Technology Bureau (L2023-ZDYF-SF-030), Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Drug Synthesis of Xianyang city (2021QXNL-PT-0008), School-level Scientific and Technological Innovation Team for Design, Synthesis and Structural Modification of Drug Molecules (2024KCTD04).
References
1. Bruker. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
5. Rzaçzyńska, Z.; M. R.; S.-I. M.; Głowiak, T. The Crystal Structures of Ammonium and Sodium 2-Amino-3,5-Dichlorobenzoates. J. Coord. Chem. 2000, 49, 189–199; https://doi.org/10.1080/00958970008022571.Search in Google Scholar
6. Ha, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Song, Y.; Kim, S.; Park, M. H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Yoon, M.; Kim, M. Effect of the Metal Within Regioisomeric paddle-wheel-type Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 14414–14420; https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201903210.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Kim, M.; Boissonnault, J. A.; Dau, P. V.; Cohen, S. M. Metal–Organic Framework Regioisomers Based on Bifunctional Ligands. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 12193–12196; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201106429.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Lim, S. H.; Su, Y.; Cohen, S. M. Supramolecular Tetrahedra of Phosphines and Coinage Metals. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5106–5109; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201200730.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Arora, S. K.; Pant, L. M. The Structure of 3,5-Dichloroanthranilic Acid. Acta Crystallogr. Secti. B 1969, 25, 1045–1049; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0567740869003517.Search in Google Scholar
10. Tang, W.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Z. Crystal Structure of Ethyl 2-((4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)benzoate. Z. Kristallogr. - N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 33–34; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0423.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structure of [K3:N1:N2:N4-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazole] binuclear Ni(II) complex[Ni2(C7H5N4)2(C7H4ClO2)2]
- The crystal structure of di(thiocyanato-κ1N)-bis(methanol)-di(1,3-bis((pyridin-4-ylthio)methyl)benzene)-iron(II), C40H40FeN6O2S6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 3 O,O′:O″)-(μ 4-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 4 O,O′,O″,O‴)-dicadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C47H30Cd2F8N3O12
- The crystal structure of a 3d-4f complex based on 2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-6-methoxyphenol C31H27N4O13S2CoEr
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-yl)benzene-k 2 N:N′)(μ 4-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-k 4 O,O,O,O)dizinc(II)] dihydrate, C40H28Zn2N8O9
- The crystal structure of 4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, C11H13Cl2NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of-(10S,13S,16R,Z) −17-ethylidene-16-hydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3 H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one, C21H32O2
- The crystal structure of catena-((μ 2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ 2 N:N′)-bis(4-fluorobenzoato-κ1O)-copper(II)), C24H16F2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(ethylenediamine-κ2 N,N′)-μ-tetraoxomolybdato(VI) zinc(II)], C2H8MoN2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid, C4H3ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of bepotastine besilate, C27H31ClN2O6S
- The crystal structure of (η 6-p-cymene)benzyldiphenylphosphine-diiodido-ruthenium(II) dichloromethane solvate
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4- (imidazol-1′-yl-methyl)benzene κ 2 N:N′)-(μ 2-3-nitrobenzene -1,2-dicarboxylato-k4,O,O′:O′′,O′′′]zinc(II)-κ 2, C21H15N5O6Zn
- The crystal structure of (2R,4S)-5-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-2-methyl pentanoic acid, C23H29NO4
- The crystal strucure of [2,2′-{1,2-phenylenebis [(azanylylidene)methanylylidene]}bis(4-fluorophenolato)-κ4 N,N′,O,O′] nickel(II) N, N-dimethylformamide solvate, C23H19F2N3NiO3
- The structure of (E)-6-(cyclopropylmethyl)-11-(2,2-difluoropropylidene)-2-methyl-6, 11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C21H21F2NO2S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-(2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzyl)-1H-imidazole κ2N:N′)- (μ 2-cyclohexane-1,2-dicarboxylato κ2O,O′)cobalt(II) monohydrate]
- The crystal structure of 3,5,7-trinitro-1,3,5,7-oxatriazocane
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ3 O,O′:O′′)(μ2-1-[(2-propyl-1H-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-k2 N:N′)silver(I)], C17H17AgN6O3
- The crystal structure of (5-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)-2-sulfanylidene-1,3,4-oxadiazol-3(2H)-yl)(3-methylphenyl)methanone, C18H14N2O4S
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O]-cobalt(II), C11H11Co0.5N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-N-(4-morpholinophenyl)propanamide, C24H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of sodium methylsulfonate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(isothiocyanate κ 1 N)-(μ 2-3,3ʹ-methylenebis(1-methyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazole-2-thione)-κ 2 S:S′)-cobalt(II)], C11H12CoN6S4
- The crystal structure of {hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ 1N)nickel(II)} (μ 2-oxo)-hexaoxido-di-molybdenum(VI)─1-methyl-1H-imidazole (1/2), C32H48NiMo2N16O7
- 6-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3′,6′-tris(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C62H38N5O4P
- The crystal structure of R-2′-amino-N-methyl-N-(1-phenylethyl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxamide, C22H22N2O
- The crystal structure of bis{tetrakis(n-butyl)(μ-hydroxy)(2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoate) (μ 3 -oxo)ditin(IV)}
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ 2(3,4-dimethylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O:O′)-(3,6-bis(4′-pyridyl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine-κ 1 N)zinc(II)], C22H16N6O5S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-5-cyano–N-(5-(cyanomethyl)quinolin-8-yl)pentanamide, C19H15BrN4O
- The crystal structure of bis(tetramethylammonium) (di-μ2-aqua)hexaaqua-dibarium(II)) decavanadate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(bis(μ 2-chlorido)- (μ 2-4′-(pyridin-4-yl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine–N′, N″, N‴:N″″) -chlorido-dicopper(I,II)) monohydrate, C20H16N4OCl3Cu2
- Crystal structure of spiropachysine, C31H46N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 2 N: O)-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 3-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 2-nitrite-κ 3 O: O′: O″)dicadmium(II) monohydrate], C19H12Br3Cd2N3O9
- The crystal structure of 2-acetylpyridine-ortho-fluoro-phenylhydrazone, C14H12FN3O
- The crystal structure of poly(triaqua-(m 2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 2 O:O′)-bis(m 2-2-2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 4 O,O′:O″:O‴)dierbium(III)) hydrate, C36H26Er2N6O16
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(phenazine-5,10-diyl)bis(heptan-1-one), C26H34N2O2
- The crystal structure of (4-([2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridin]-4′-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C21H16BN3O2
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazine-5,7(6H)-dione, C6H3N3O3
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide ethanol solvate, C23H30N2O4
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis[1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-K2 O,O′]lutetium(III) C20F12H16LuO8C5H6N
- Crystal structure of dichlorido–tetrakis{3-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylpentan-3-ol-k 1N}cobalt(II), C64H88O4N12Cl6Co
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(4-allyl-2-methoxyphenyl nicotinato-k 1 N)bis(thiocyanato-k 1 N)cobalt(II)
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H21Cl2NO3
- The crystal structure of (E)–N-(4-chlorobenzylidene)(4-chlorophenyl)methanamine, C14H11Cl2N
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-ethylbenzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H22O4
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C4H2N3O4⋅C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of-(1S,4aR,5S)-5,6,7-trihydroxy-8-isopropyl-1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5,10,11,11a-octahydro-4a,1-(epoxymethano)dibenzo[a,d][7]annulen-13-one C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 7,9-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4-propylbenzo[f]isoquinolin-5-yl 4-bromobenzoate, C26H24BrNO4
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylbutanaminium)tridecathiotrimolybdate(2−), (BuMe3N)2[Mo3S13]
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-methylpiperazine-1-carbothioamide, C16H27N3S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2,2′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylenesulfanediyl)]dibenzoato-κ 4 O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ 2-1,1′-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-benzimidazole)-κ 2 N:N′)cadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C51H41N5O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,2′-pyran]-3-one, C19H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-cyanobenzyl)-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C20H15N3
- Crystal structure of (1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C22H22BrO2P
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrachloridomanganese(II)
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxyphenyl)-4,6-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine, C33H39N3O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(5-carboxypyridine-2-carboxylate-κ 2N,O)(2,5-pyridine-dicarboxylate-κ 4O,O′:N:O″)bismuth(III)], C14H9BiN2O9
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-fluoro-4-(2-(phenylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C14H11FO2S
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-amino-3-chloro-4-methoxybenzoate, C9H10ClNO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structure of [K3:N1:N2:N4-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazole] binuclear Ni(II) complex[Ni2(C7H5N4)2(C7H4ClO2)2]
- The crystal structure of di(thiocyanato-κ1N)-bis(methanol)-di(1,3-bis((pyridin-4-ylthio)methyl)benzene)-iron(II), C40H40FeN6O2S6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 3 O,O′:O″)-(μ 4-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 4 O,O′,O″,O‴)-dicadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C47H30Cd2F8N3O12
- The crystal structure of a 3d-4f complex based on 2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-6-methoxyphenol C31H27N4O13S2CoEr
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-yl)benzene-k 2 N:N′)(μ 4-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-k 4 O,O,O,O)dizinc(II)] dihydrate, C40H28Zn2N8O9
- The crystal structure of 4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, C11H13Cl2NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of-(10S,13S,16R,Z) −17-ethylidene-16-hydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3 H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one, C21H32O2
- The crystal structure of catena-((μ 2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ 2 N:N′)-bis(4-fluorobenzoato-κ1O)-copper(II)), C24H16F2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(ethylenediamine-κ2 N,N′)-μ-tetraoxomolybdato(VI) zinc(II)], C2H8MoN2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid, C4H3ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of bepotastine besilate, C27H31ClN2O6S
- The crystal structure of (η 6-p-cymene)benzyldiphenylphosphine-diiodido-ruthenium(II) dichloromethane solvate
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4- (imidazol-1′-yl-methyl)benzene κ 2 N:N′)-(μ 2-3-nitrobenzene -1,2-dicarboxylato-k4,O,O′:O′′,O′′′]zinc(II)-κ 2, C21H15N5O6Zn
- The crystal structure of (2R,4S)-5-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-2-methyl pentanoic acid, C23H29NO4
- The crystal strucure of [2,2′-{1,2-phenylenebis [(azanylylidene)methanylylidene]}bis(4-fluorophenolato)-κ4 N,N′,O,O′] nickel(II) N, N-dimethylformamide solvate, C23H19F2N3NiO3
- The structure of (E)-6-(cyclopropylmethyl)-11-(2,2-difluoropropylidene)-2-methyl-6, 11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C21H21F2NO2S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-(2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzyl)-1H-imidazole κ2N:N′)- (μ 2-cyclohexane-1,2-dicarboxylato κ2O,O′)cobalt(II) monohydrate]
- The crystal structure of 3,5,7-trinitro-1,3,5,7-oxatriazocane
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ3 O,O′:O′′)(μ2-1-[(2-propyl-1H-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-k2 N:N′)silver(I)], C17H17AgN6O3
- The crystal structure of (5-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)-2-sulfanylidene-1,3,4-oxadiazol-3(2H)-yl)(3-methylphenyl)methanone, C18H14N2O4S
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O]-cobalt(II), C11H11Co0.5N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-N-(4-morpholinophenyl)propanamide, C24H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of sodium methylsulfonate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(isothiocyanate κ 1 N)-(μ 2-3,3ʹ-methylenebis(1-methyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazole-2-thione)-κ 2 S:S′)-cobalt(II)], C11H12CoN6S4
- The crystal structure of {hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ 1N)nickel(II)} (μ 2-oxo)-hexaoxido-di-molybdenum(VI)─1-methyl-1H-imidazole (1/2), C32H48NiMo2N16O7
- 6-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3′,6′-tris(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C62H38N5O4P
- The crystal structure of R-2′-amino-N-methyl-N-(1-phenylethyl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxamide, C22H22N2O
- The crystal structure of bis{tetrakis(n-butyl)(μ-hydroxy)(2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoate) (μ 3 -oxo)ditin(IV)}
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ 2(3,4-dimethylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O:O′)-(3,6-bis(4′-pyridyl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine-κ 1 N)zinc(II)], C22H16N6O5S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-5-cyano–N-(5-(cyanomethyl)quinolin-8-yl)pentanamide, C19H15BrN4O
- The crystal structure of bis(tetramethylammonium) (di-μ2-aqua)hexaaqua-dibarium(II)) decavanadate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(bis(μ 2-chlorido)- (μ 2-4′-(pyridin-4-yl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine–N′, N″, N‴:N″″) -chlorido-dicopper(I,II)) monohydrate, C20H16N4OCl3Cu2
- Crystal structure of spiropachysine, C31H46N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 2 N: O)-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 3-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 2-nitrite-κ 3 O: O′: O″)dicadmium(II) monohydrate], C19H12Br3Cd2N3O9
- The crystal structure of 2-acetylpyridine-ortho-fluoro-phenylhydrazone, C14H12FN3O
- The crystal structure of poly(triaqua-(m 2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 2 O:O′)-bis(m 2-2-2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 4 O,O′:O″:O‴)dierbium(III)) hydrate, C36H26Er2N6O16
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(phenazine-5,10-diyl)bis(heptan-1-one), C26H34N2O2
- The crystal structure of (4-([2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridin]-4′-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C21H16BN3O2
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazine-5,7(6H)-dione, C6H3N3O3
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide ethanol solvate, C23H30N2O4
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis[1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-K2 O,O′]lutetium(III) C20F12H16LuO8C5H6N
- Crystal structure of dichlorido–tetrakis{3-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylpentan-3-ol-k 1N}cobalt(II), C64H88O4N12Cl6Co
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(4-allyl-2-methoxyphenyl nicotinato-k 1 N)bis(thiocyanato-k 1 N)cobalt(II)
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H21Cl2NO3
- The crystal structure of (E)–N-(4-chlorobenzylidene)(4-chlorophenyl)methanamine, C14H11Cl2N
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-ethylbenzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H22O4
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C4H2N3O4⋅C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of-(1S,4aR,5S)-5,6,7-trihydroxy-8-isopropyl-1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5,10,11,11a-octahydro-4a,1-(epoxymethano)dibenzo[a,d][7]annulen-13-one C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 7,9-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4-propylbenzo[f]isoquinolin-5-yl 4-bromobenzoate, C26H24BrNO4
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylbutanaminium)tridecathiotrimolybdate(2−), (BuMe3N)2[Mo3S13]
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-methylpiperazine-1-carbothioamide, C16H27N3S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2,2′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylenesulfanediyl)]dibenzoato-κ 4 O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ 2-1,1′-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-benzimidazole)-κ 2 N:N′)cadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C51H41N5O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,2′-pyran]-3-one, C19H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-cyanobenzyl)-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C20H15N3
- Crystal structure of (1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C22H22BrO2P
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrachloridomanganese(II)
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxyphenyl)-4,6-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine, C33H39N3O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(5-carboxypyridine-2-carboxylate-κ 2N,O)(2,5-pyridine-dicarboxylate-κ 4O,O′:N:O″)bismuth(III)], C14H9BiN2O9
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-fluoro-4-(2-(phenylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C14H11FO2S
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-amino-3-chloro-4-methoxybenzoate, C9H10ClNO3

