Synthesis and crystal structure of (±)-Ethyl 5′-(difluoromethyl)-2-oxo-4′,5′-dihydrospiro[indoline-3,3′-pyrazole]-4′-carboxylate, C14H13F2N3O3
-
Wu-Wu Li
, Min-Yan Zheng
Abstract
C14H13F2N3O3, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 9.4486(7) Å, b = 12.4694(8) Å, c = 13.8690(8) Å, α = 65.734(6)°, β = 74.523(5)°, γ = 83.726(6)°, V = 1435.63(18) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0495, wRref(F2) = 0.1249, T = 293(2) K.
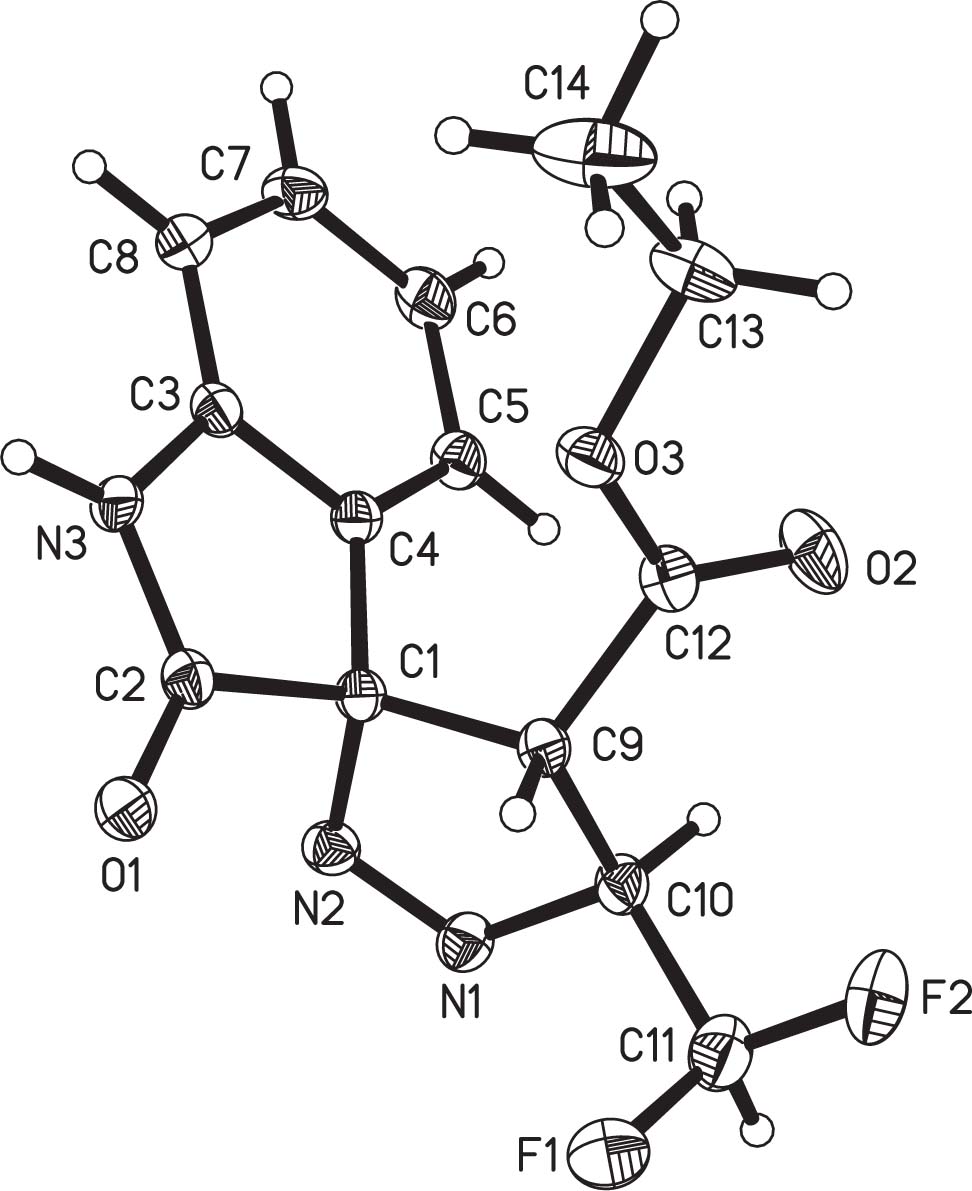
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.22 × 0.16 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.12 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 26.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 12806, 5941, 0.032 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 4624 |
| N(param)refined: | 400 |
| Programs: | SHELX [1], Bruker [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | −0.0749(2) | 0.23340(15) | 0.76413(14) | 0.0160(4) |
| C2 | −0.0381(2) | 0.12764(16) | 0.86157(14) | 0.0168(4) |
| C3 | −0.0693(2) | 0.28591(16) | 0.90792(14) | 0.0167(4) |
| C4 | −0.0994(2) | 0.33038(16) | 0.80553(14) | 0.0161(4) |
| C5 | −0.1429(2) | 0.44558(16) | 0.75910(15) | 0.0200(4) |
| H5 | −0.164611 | 0.475114 | 0.691235 | 0.024* |
| C6 | −0.1538(2) | 0.51690(17) | 0.81634(15) | 0.0232(4) |
| H6 | −0.182530 | 0.595018 | 0.786437 | 0.028* |
| C7 | −0.1218(2) | 0.47161(17) | 0.91758(16) | 0.0234(4) |
| H7 | −0.129210 | 0.520375 | 0.954533 | 0.028* |
| C8 | −0.0788(2) | 0.35484(16) | 0.96565(15) | 0.0202(4) |
| H8 | −0.057426 | 0.324871 | 1.033647 | 0.024* |
| C9 | 0.0407(2) | 0.25558(16) | 0.65561(14) | 0.0161(4) |
| H9 | 0.095063 | 0.182755 | 0.660253 | 0.019* |
| C10 | −0.0564(2) | 0.28369(17) | 0.57617(14) | 0.0194(4) |
| H10 | −0.065046 | 0.369289 | 0.539961 | 0.023* |
| C11 | −0.0060(2) | 0.23396(19) | 0.49080(16) | 0.0272(5) |
| H11 | −0.076300 | 0.252359 | 0.445485 | 0.033* |
| C12 | 0.1470(2) | 0.35188(16) | 0.62703(15) | 0.0188(4) |
| C13 | 0.3302(2) | 0.40651(18) | 0.68647(18) | 0.0295(5) |
| H13A | 0.276493 | 0.470396 | 0.702670 | 0.035* |
| H13B | 0.390371 | 0.438623 | 0.612279 | 0.035* |
| C14 | 0.4238(3) | 0.3456(2) | 0.7644(2) | 0.0431(6) |
| H14A | 0.477484 | 0.283434 | 0.746739 | 0.065* |
| H14B | 0.362882 | 0.313247 | 0.837282 | 0.065* |
| H14C | 0.491521 | 0.400861 | 0.759354 | 0.065* |
| O1 | −0.01762(15) | 0.02754(11) | 0.86557(10) | 0.0219(3) |
| O2 | 0.15592(16) | 0.44614(12) | 0.55093(11) | 0.0300(4) |
| O3 | 0.22838(14) | 0.31851(11) | 0.69918(10) | 0.0215(3) |
| N1 | −0.20270(17) | 0.23436(14) | 0.64525(12) | 0.0202(4) |
| N2 | −0.21353(17) | 0.20732(13) | 0.74359(12) | 0.0190(4) |
| N3 | −0.03136(17) | 0.16603(13) | 0.93806(12) | 0.0174(3) |
| H3 | −0.006910 | 0.122705 | 0.997856 | 0.021* |
| F1 | 0.01448(15) | 0.11520(11) | 0.53827(10) | 0.0388(3) |
| F2 | 0.12883(13) | 0.27960(11) | 0.42869(9) | 0.0346(3) |
| C1A | 0.5974(2) | 0.26070(16) | 0.21774(14) | 0.0176(4) |
| C2A | 0.5569(2) | 0.37141(16) | 0.12584(14) | 0.0186(4) |
| C3A | 0.5867(2) | 0.22169(16) | 0.06779(14) | 0.0183(4) |
| C4A | 0.6213(2) | 0.17050(16) | 0.16873(14) | 0.0181(4) |
| C5A | 0.6638(2) | 0.05416(17) | 0.20900(15) | 0.0227(4) |
| H5A | 0.688088 | 0.019998 | 0.276017 | 0.027* |
| C6A | 0.6696(2) | −0.01105(18) | 0.14691(17) | 0.0266(5) |
| H6A | 0.697350 | −0.089734 | 0.172746 | 0.032* |
| C7A | 0.6343(2) | 0.04077(18) | 0.04745(17) | 0.0266(5) |
| H7A | 0.638876 | −0.003984 | 0.007101 | 0.032* |
| C8A | 0.5918(2) | 0.15860(17) | 0.00542(16) | 0.0232(4) |
| H8A | 0.567997 | 0.192965 | −0.061761 | 0.028* |
| C9A | 0.4808(2) | 0.23099(16) | 0.32695(14) | 0.0177(4) |
| H9A | 0.428262 | 0.302693 | 0.328618 | 0.021* |
| C10A | 0.5771(2) | 0.19000(17) | 0.40784(14) | 0.0198(4) |
| H10A | 0.585727 | 0.104123 | 0.435413 | 0.024* |
| C11A | 0.5269(2) | 0.22515(18) | 0.50298(16) | 0.0265(5) |
| H11A | 0.595783 | 0.196859 | 0.550001 | 0.032* |
| C12A | 0.3732(2) | 0.14108(16) | 0.34273(14) | 0.0184(4) |
| C13A | 0.1915(2) | 0.10870(17) | 0.26876(18) | 0.0292(5) |
| H13C | 0.125991 | 0.073284 | 0.340668 | 0.035* |
| H13D | 0.243422 | 0.046494 | 0.248719 | 0.035* |
| C14A | 0.1069(3) | 0.1820(2) | 0.1874(2) | 0.0424(6) |
| H14D | 0.173254 | 0.217453 | 0.116994 | 0.064* |
| H14E | 0.055103 | 0.242454 | 0.208846 | 0.064* |
| H14F | 0.037880 | 0.133349 | 0.184082 | 0.064* |
| O1A | 0.53441(15) | 0.46797(11) | 0.12974(10) | 0.0237(3) |
| O2A | 0.36167(16) | 0.04148(12) | 0.41016(11) | 0.0289(3) |
| O3A | 0.29505(14) | 0.18741(11) | 0.26836(10) | 0.0196(3) |
| N1A | 0.72388(18) | 0.24281(14) | 0.34234(12) | 0.0227(4) |
| N2A | 0.73507(17) | 0.28148(13) | 0.24255(12) | 0.0204(4) |
| N3A | 0.54801(17) | 0.34044(13) | 0.04538(12) | 0.0189(4) |
| H3A | 0.521907 | 0.387446 | −0.012700 | 0.023* |
| F1A | 0.51216(15) | 0.34467(11) | 0.46668(9) | 0.0377(3) |
| F2A | 0.39011(13) | 0.18027(11) | 0.55989(9) | 0.0320(3) |
Source of material
The mixture of CF2HCH2NH2 (1.0 mmol), tBuONO (1.2 mmol), AcOH (0.15 mmol) and DCM (dichloromethane; 20 mL) was stirred at 70 °C for about 10 min. The mixture was placed at room temperature, then was added (E)-ethyl 2-(2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)acetate (0.3 mmol). The reaction was monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC), which showed the disappearance of (E)-ethyl 2-(2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)acetate that was indicative of the reaction being complete. After DCM was removed under reduced pressure, the residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel column using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (6:1, v/v) to give the corresponding pure title compound. Crystals were obtained at room temperature from the mother liquor.
Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were identified in difference Fourier syntheses and placed in geometrically idealized positions. The Uiso values of the hydrogen atoms of methyl groups were set to 1.Ueq(C) and the Uiso values of all other hydrogen atoms were set to 1.Ueq(C).
Comment
1H-Indole-2,3-dione (isatin) and its derivatives exhibit an extraordinary biological activity. It is well known that isatin was found in human organism and its influence on different systems in organism has long been discussed in the literature [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10]. The biological activity of isatin includes the impact on human brain and protection from different types of infectious diseases [7], [8], [9]. N-Methylisatin-3-thiosemicarbazone (methisazon) is one of the first antivirals used in clinical practice. In recent years, isatin derivatives with acylhydrazone substituents at the C(3) position of the indole cycle have been intensively studied as antituberculosis drugs [10]. N-Alkyl-substituted isatins can act as selective antagonists of cannabinoid receptor 2 in treating neuropathic pain [11]. On the other hand pyrazole derivatives have known to exhibit diverse biological applications such as antidiabetic [12], anaesthetic [13], antimicrobial and antioxidant [14]. According to physiological activity structure combination strategy, indolin-2-one skeleton and 4,5-dihydro-3H-pyrazole ring were joined together and the title compound was synthesized.
The molecular structure of the title structure consists of one indolin-2-one ring, a 4,5-dihydro-3H-pyrazole ring, a difluoromethyl and a ethyl formate group (cf. the figure). The title structure contains two crystallographically independent molecules Mole1 (C1—C14/N1–N3/O1—O3) and Mole2 (C1A—C14A/N1A—N3A/O1A—O3A), Mole1 and Mole2 are a pair of optical isomers. Furthermore the space group symmetry verifies the inverted molecules additionally. The indolin-2-one ring is essentially planar, with a mean deviation from plane of 0.0152(2) Å for Mole1 and 0.0168(2) Å for Mole2. The 4,5-dihydro-3H-pyrazole ring adopts an envelope conformation with C9 atom deviating by 0.3474(3) Å from the plane formed by C1, C10, N1 and N2 for Mole1, C9A atom deviats by 0.3816(2) Å from the plane formed by C1A, C10A, N1A and N2A for Mole2 [15]. The bond lengths and angles of indolin-2-one and 4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole ring are similar to those found in literature [16], [17], [18]. The indolin-2-one ring and 4,5-dihydro-3H-pyrazole ring form spiro structural feature through their third atom (C1). Because C1 is a sp3 hybridized carbon, the indolin-2-one ring is non-coplanar with 4,5-dihydro-3H-pyrazole ring, the dihedral angles between the two rings are 89.793(4)° for Mole1 and 89.471(2)° for Mole2. In the crystal structure of title compound, adjacent molecules are connected by classical hydrogen bonds N3(A)—H3(A)⋯O1(A) and C10(A)—H10(A)⋯O2(A) to form one-dimensional chain along the direction [011].
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (No. 18 J K0837 and 16 J K1822), Natural Science Basic Research Plan Funded by Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2018JM2045 and 2016JM5024), Science and Technology Projects of Xianyang City (No. 2017k02–19), Scientific Research Project Funded by Xianyang Normal University (No. XSYK18006), Youth Backbone Teachers Project Funded by Xianyang Normal University (No. XSYGG201606), University Students Research and Innovation Training Program of Ministry of Education (201810722010), University Students Research and Innovation Training Program of Shaanxi Province (No. 201828010 and 2490), University Students Research and Innovation Training Program of Xianyang Normal University (No. 2018003, 2017060 and 201710722003), and Scientific Research Project Funded by Ministry of Land Resources (No. SXDJ2017–3). The corresponding author confirms explicitly that all listed authors significantly contributed to this work.
References
1. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar
2. Bruker. APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2012).Search in Google Scholar
3. Osipova, V. P.; Kolyada, M. N.; Berberova, N. T.; Milaeva, E. R.; Ponomareva, E. N.; Belaya, M. M.: Cryoprotective effect of phosphorous-containing phenolic anti-oxidant for the cryopreservation of beluga sperm. Cryobiology 69 (2014) 467–472.10.1016/j.cryobiol.2014.10.007Search in Google Scholar
4. Breese, K. D.; Lamethe, J. F.; Dearmitt, C.: Improving synthetic hindered phenol antioxidants: learning from vitamin E. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 70 (2000) 89–96.10.1016/S0141-3910(00)00094-XSearch in Google Scholar
5. Kasza, G.; Mosnackova, K.; Nador, A.; Osvath, Z.; Stumphauser, T.; Szarka, G.; Czanikova, K.; Rychly, J.; Chmela, S.; Ivan, B.; Mosnacek, J.: Synthesis of hyperbranched poly(ethyleneimine) based macromolecular antioxidants and investigation of their efficiency in stabilization of polyolefins. Eur. Polym. J. 68 (2015) 609–671.10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2015.03.037Search in Google Scholar
6. Nugumanova, G. N.; Bukharov, S. V.; Tagasheva, R. G.; Mukmeneva, N. A.; Deberdeev, R. Y.: Antioxidant activity of isatin acylhydrazones with sterically hindered phenol fragments. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 85 (2015) 53–56.10.1134/S1070363215010090Search in Google Scholar
7. Kaynak, F. B.; Ozbey, S.; Karali, N.: Three novel compounds of 5-trifluoromethoxy-1H-indole-2,3-dione 3-thiosemicarbazone: synthesis, crystal structures and molecular interactions. J. Mol. Struct. 1049 (2013) 157–164.10.1016/j.molstruc.2013.06.039Search in Google Scholar
8. Mohd, A. F. A. M.; Tahir, I. M. M.; Crouse, K. A.; How, F. N. F.; Watkin, D. J.: Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of schiff base derived from S-methyldithiocarbazate and methylisatin. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 42 (2012) 173–179.10.1007/s10870-011-0220-6Search in Google Scholar
9. Kumari, G.; Singh, R. K.: Synthesis and in vitro antibacterial activity of schiff bases of N-substituted isatins as effective scaffolds. Med. Chem. Res. 22 (2013) 927–933.10.1007/s00044-012-0087-xSearch in Google Scholar
10. Karali, N.; Gursoy, A.; Kandemirli, F.; Shvets, N.; Kaynak, F. B.; Ozbey, S.; Kovalishyn, V.; Dimoglo, A.: Synthesis and structure antituberculosis activity relationship of 1H-indole-2,3-dione derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 (2007) 5888–5904.10.1016/j.bmc.2007.05.063Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Diaz, P.; Xu, J. J.; Astruc-Diaz, F.; Pan, H. M.; Brown, D. L.; Naguib, M.: Design and synthesis of a novel series of N-alkyl isatin acylhydrazone derivatives that act as selective cannabinoid receptor 2 agonists for the treatment of neuropathic pain. J. Med. Chem. 51 (2008) 4932–4947.10.1021/jm8002203Search in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Amir, M.; Kumar, H.; Khan, S. A.: Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of pyrazoline derivatives as new antiinflammatory and analgesic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18 (2008) 918–922.10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.12.043Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Shivarama Holla, B.; Mahalinga, M.; Boja, P.; Mithun, A.: Synthesis of pyrazolines promoted by Amberlyst-15 catalyst. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 15 (1980) 567–570.Search in Google Scholar
14. Renuka, N.; Ajay Kumar, K.: Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel formyl-pyrazoles bearing coumarin moiety as potent antimicrobial and antioxidant agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23 (2013) 6406–6409.10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.09.053Search in Google Scholar PubMed
15. Cremer, D.; Pople, J. A.: General definition of ring puckering coordinates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97 (1975) 1354–1358.10.1021/ja00839a011Search in Google Scholar
16. Han, W. Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J. S.; Xiang, G. Y.; Zhang, D. L.; Bai, M.; Cui, B. D.; Wan, N. W.; Chen, Y. Z.: Diastereoselective[3 + 2]cycloaddition of 3-ylideneoxindoles with in situ generated CF2HCHN2: syntheses of CF2H-containing spirooxindoles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 15 (2017) 5571–5578.10.1039/C7OB01266GSearch in Google Scholar
17. Li, X. H.; Qin, Z. X.; Cao, S. L.: Crystal structure of methyl (Z)-2-(5-fluoro-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbodithioate. C10H8FN3OS2. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 233 (2018) 131–132.10.1515/ncrs-2017-0218Search in Google Scholar
18. Assem, B.; Naveen, S.; Nagamallu, R.; Ajay, K. K.; Muneer, A.; Ismail, W.; Neratur, K. L.: Crystal structure of 3-(thiophen-2-yl)-5-(p-tolyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carboxamide. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 231 (2016) 267–269.10.1515/ncrs-2015-0116Search in Google Scholar
© 2019 Wu-Wu Li et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(1-((2-aminophenyl)imino)ethyl)-5-fluorophenol, C14H13FN2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(1-((2-aminophenyl)imino)ethyl)-4,6-dichlorophenol, C14H12Cl2N2O
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-(2-nitrophenyl)triaz-1-ene C8H8N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((6-bromopyridin-2-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-bis(ethylamino)-2′,7′-dimethylspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one—methanol (1:1), C32H30N5O2Br ⋅ CH4O
- Crystal structure of 2,4-pentanedione bis(2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone), C17H16N8O8
- Crystal structure of sodium morpholine-4-carbodithioate, (C5H12NNaO3S2)
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorido phosphate), C16H28F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole, C21H16ClFN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3-carboxy-5-methoxybenzoato-κO)-(1,2-bis(imidazol-1-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H28CoN4O12, [Co(C9H6O5)2(H2O)2(C8H10N4)]
- The crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C15H22O4
- Crystal structure of (2,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium trifluoroacetate — trifluoroacetic acid (1/1), C31H27F6O6P
- Crystal structure of 4-tert-butyl-1-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(4-tert-butylpyridinium) tetrachloridocobaltate(II) – dichloromethane (1:1), C20H30Cl6CoN2
- Crystal structure of (4,4′-(ethane-1,2-diylbis((nitrilo)(2-furylmethylylidene)))bis(3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-olato-κ4N,N′,O,O′))-nickel(II)), C32H26N6NiO4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{((E)-((4-((E)-1-(benzyloxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-2-phenolato-κ2N,O}copper(II), C44H38CuN4O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,5-dichloropyridine-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C22H16Cl4CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-2,6-dinitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3,5-dinitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H4Cl2N6O9
- The crystal structure of 3-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydroquinolin — dimethylsulfoxide (1/1), C21H19ClFN3O2S
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(1-butyl-1H-imidazole-κN)zinc(II), C14H24Cl2ZnN4
- (Z)-N-tert-butyl-1-(2-(3,5-dichlorobenzamido)phenyl) methanimine oxide, C18H18Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(3-carboxy-5-bromoisophthalato-κO)-bis(1-(3-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)propyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-κN)nickel(II) bis(3-carboxy-5-bromoisophthalate), C66H54Br4N8NiO18
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-5-methoxyisophthalato-κ2O,O′:O′′)-(1,2-bis(imidazol-1′-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II), C34H36Co2N8O12
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′)manganese(II)] terephthalate tetrahydrate, MnC32H38N10O10
- Crystal structure of the fluorescent fipronil derivative 5,5′-(methylenebis(azanediyl))bis(1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile), C25H6N8O2Cl4F12S2
- Crystal structure of the phosphorescent complex diethyldithiophosphonato-κ2S,S′-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-κ2C,N)iridium(III), C26H26N2O2PS2Ir
- The crystal structure of 4,10-diethoxy-6H,12H-6,12-epoxydibenzo[b,f][1,5]dioxocine, C18H18O5
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(N-benzyl-2-(quinolin-8-yloxy)acetamide-κ2N,O)copper(II) — ethyl acetate (1/1), C38H36N4O6Cl2Cu
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{4-methyl-2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(benzyloxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O}copper(II), C92H84Cu2N8O8
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-trinitro-4,6-diazidobenzene, C6HN9O6
- Crystal structure 1-cinnamyl-2-((Z)-styryl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole — methanol (1/1), C24H20N2 ⋅ CH4O
- The crystal structure of poly[m2-aqua-tetraaqua-bis(m9-4-formylbenzene-1,3-disulfonato)tetrasodium(I) hydrate, C14H18O19S4Na4
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl)(hydroxy)methyl)piperidin-1-ium trifluoroacetate, [C17H17F6N2O][C2F3O2]
- The crystal structure of bis(ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O,O′)bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]copper(II) — acetonitrile(1/2), C40H44CuO4Fe2N6
- Crystal structure of poly[di-μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(μ6-4,4′,4′′-(benzene-1,3,5-triyltris(oxy))tribenzoato-κ6O1:O2:O3:O3:O5:O6)tricadmium(II)] dihydrate, C54H42Cd3O24
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropyl-phenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(3-phenyl-pyridine-κN)palladium(IV), C38H45N3Cl2Pd
- The crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine, C12H8ClN3O
- The crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(phenyl(phenylsulfonyl)methyl)phenol, C27H32O3S
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-bis{(((((1-methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-2-phenolato-κ3N,O:O}copper(II)}, C68H68Cu2N8O8
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ2-2-(4-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ2O:O′)-pentakis(pyridine-κ1N)dinickel(II)], C53H47N5Ni2O13
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5-(3-methoxy-benzylamino)-4-trifluoromethanesulfinyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile, C20H12N4Cl2F6O2S
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis(μ2-di-ethyldithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S;κ3S:S: S′)-hexacarbonyl-di-rhenium(I), C16H20N2O6Re2S4
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-2-phenylacetohydrazide, C19H16O2N2
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-4,8,11b-trimethyltetradecayhdro-8,11-epoxy-6a,9-methanocyclohepta[a]naphthalene-4-carboxylic acid – methanol (1/1), C20H30O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis(3-acetyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II) monohydrate, C22H18O10Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-4-bromoisophthalate-κ2O:O′)-tris(μ2-1-(3-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′)dicobalt(II)] monohydrate, C26H23CoN9O5Br
- A cyclic I102− anion in the layered crystal structure of theophyllinium pentaiodide, C7H9I5N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((4-(pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)phenyl)diazenyl)benzoato-κ3O,O′:N)cadmium(III)], Cd(C19H14O3N3)2(H2O)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-dimethyldithiophosphato-κS)-zinc(II)], {C14H20N2O4P2S4Zn}n
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-2-hydroxy-6-methoxybenzamide hydrate, C16H22N4O7
- Crystal structure of hemikis(cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) (pyridine-2-carboxylate), [C6H16N2]0.5[C6H4NO2]
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-1,3,5-triazine, C10H6ClN3OS
- The crystal structure of 3-butyl-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium catena-poly[tris(μ2-bromido-κ2Br:Br)lead(II)], C8H15Br3N2Pb
- Crystal structure of 3-(5-amino-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)-1-(piperidin-1-yl)propan-1-one, C10H17N5O
- Crystal structure of aqua-2,2′,2′′-(((nitrilo-κN-tris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(azanylylidene-κ3N′,N′′,N′′′))tris(methanylylidene))tris(4-chlorophenolato-κ3O,O′,O′′)neodymium(III), C27H26Cl3N4NdO4
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(μ2-2,2′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)bis(benzen-1-ido)-κ2C:C′)dimercury(II), C12H8Cl2Hg2N2
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-cyanobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one, C27H18FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(pyridine-κN)(2,4,6-tri-2-pyridyl-1,3,5-triazine-κ3N2,N1,N6)nickel(II), C23H17Cl2N7Ni
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of tetrakis(4-chlorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H24Cl4Sn
- The crystal structure of 2,6-bis(pyridin-1-ium-3-ylmethyl)hexahydro-4,8-ethenopyrrolo-[3,4-f] isoindole-1,3,5,7-tetrone tetrachloridocuprate(II) monohydrate, C24H24Cl4CuN4O5
- Crystal structure of cyclo-[octaaqua-tetrakis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)tetramagnesium(II)], C20H24N40O8Mg4
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative, 13-(4-Cl-pyrrole)-matrine, C18H26ClN4O
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)bis(2-chlorobenzyl-κC1)dichloridotin(IV), C28H26Cl4OSSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)(μ2-4-cyanobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-methanol-κ2O:O)copper(II)], C9H8CuN4O3
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-dibenzyl-3,3′-dicyano-1,1′,4,4′-tetrahydro-4,4′-bipyridine, C26H22N4
- Crystal structure of (2-bromobenzyl)((1-bromonaphthalen-2-yl)methyl)sulfane, C18H14Br2S
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-ammoniocyclohexyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)imidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-ium 2-[(2-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dihydrate, [C18H22N4][C14H8O4S2] ⋅ 2H2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-((3R,5S,10S, 13S,14S,17S)-17-((S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl)-2-methylbut-2-enamide – water – methanol (1/1/1), C29H54N2O3
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(3-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C21H15F2N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ4-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato-κ5O1,O2:O3:O4:O5)-(μ2-5-(3-pyridyl)tetrazolato-κ2N1:N3)dizinc(II)], C15H13N5O9Zn2
- Crystal structure of N-(3-methylphenyl)(propan-2-yloxy)carbothioamide, C11H15NOS
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1,3-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)(nitrato-κ1O)cadmium(II)] — water (2/1), C28H32CdN10O7
- Crystal structure of 4-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C8H7N3S
- Crystal structure of benzyltrichloridobis(1H-pyrazole-κ2N)tin(IV), C13H15Cl3N4Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido-4-fluorobenzyl-bis(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)tin(IV), C27H22ClFN2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(O,O′-diisopropyldithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)zinc(II), C36H66N4O8P4S8Zn2
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium 4,4-oxydibenzoate – boric acid – water (1/2/6) C46H98B2N2O17
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[[tribenzyltin(IV)]-(μ2-pyridine-4-carboxylato-κ2N:O)], C27H25NO2Sn
- The synthysis and crystal structure of cyclohexyl 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C18H15N3Cl2F6O3S
- The crystal structure of 5,7-bis(2-hydroxyethoxy)-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one, C19H18O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (±)-Ethyl 5′-(difluoromethyl)-2-oxo-4′,5′-dihydrospiro[indoline-3,3′-pyrazole]-4′-carboxylate, C14H13F2N3O3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(1-((2-aminophenyl)imino)ethyl)-5-fluorophenol, C14H13FN2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(1-((2-aminophenyl)imino)ethyl)-4,6-dichlorophenol, C14H12Cl2N2O
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-(2-nitrophenyl)triaz-1-ene C8H8N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((6-bromopyridin-2-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-bis(ethylamino)-2′,7′-dimethylspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one—methanol (1:1), C32H30N5O2Br ⋅ CH4O
- Crystal structure of 2,4-pentanedione bis(2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone), C17H16N8O8
- Crystal structure of sodium morpholine-4-carbodithioate, (C5H12NNaO3S2)
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorido phosphate), C16H28F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole, C21H16ClFN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3-carboxy-5-methoxybenzoato-κO)-(1,2-bis(imidazol-1-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H28CoN4O12, [Co(C9H6O5)2(H2O)2(C8H10N4)]
- The crystal structure of 3-cyclohexyl-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C15H22O4
- Crystal structure of (2,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium trifluoroacetate — trifluoroacetic acid (1/1), C31H27F6O6P
- Crystal structure of 4-tert-butyl-1-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(4-tert-butylpyridinium) tetrachloridocobaltate(II) – dichloromethane (1:1), C20H30Cl6CoN2
- Crystal structure of (4,4′-(ethane-1,2-diylbis((nitrilo)(2-furylmethylylidene)))bis(3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-olato-κ4N,N′,O,O′))-nickel(II)), C32H26N6NiO4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{((E)-((4-((E)-1-(benzyloxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-2-phenolato-κ2N,O}copper(II), C44H38CuN4O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,5-dichloropyridine-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C22H16Cl4CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-2,6-dinitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3,5-dinitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H4Cl2N6O9
- The crystal structure of 3-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydroquinolin — dimethylsulfoxide (1/1), C21H19ClFN3O2S
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(1-butyl-1H-imidazole-κN)zinc(II), C14H24Cl2ZnN4
- (Z)-N-tert-butyl-1-(2-(3,5-dichlorobenzamido)phenyl) methanimine oxide, C18H18Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(3-carboxy-5-bromoisophthalato-κO)-bis(1-(3-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)propyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-κN)nickel(II) bis(3-carboxy-5-bromoisophthalate), C66H54Br4N8NiO18
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ2-5-methoxyisophthalato-κ2O,O′:O′′)-(1,2-bis(imidazol-1′-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II), C34H36Co2N8O12
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′)manganese(II)] terephthalate tetrahydrate, MnC32H38N10O10
- Crystal structure of the fluorescent fipronil derivative 5,5′-(methylenebis(azanediyl))bis(1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile), C25H6N8O2Cl4F12S2
- Crystal structure of the phosphorescent complex diethyldithiophosphonato-κ2S,S′-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-κ2C,N)iridium(III), C26H26N2O2PS2Ir
- The crystal structure of 4,10-diethoxy-6H,12H-6,12-epoxydibenzo[b,f][1,5]dioxocine, C18H18O5
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(N-benzyl-2-(quinolin-8-yloxy)acetamide-κ2N,O)copper(II) — ethyl acetate (1/1), C38H36N4O6Cl2Cu
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{4-methyl-2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(benzyloxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O}copper(II), C92H84Cu2N8O8
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-trinitro-4,6-diazidobenzene, C6HN9O6
- Crystal structure 1-cinnamyl-2-((Z)-styryl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole — methanol (1/1), C24H20N2 ⋅ CH4O
- The crystal structure of poly[m2-aqua-tetraaqua-bis(m9-4-formylbenzene-1,3-disulfonato)tetrasodium(I) hydrate, C14H18O19S4Na4
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl)(hydroxy)methyl)piperidin-1-ium trifluoroacetate, [C17H17F6N2O][C2F3O2]
- The crystal structure of bis(ferrocenecarboxylato-κ2O,O′)bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]copper(II) — acetonitrile(1/2), C40H44CuO4Fe2N6
- Crystal structure of poly[di-μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(μ6-4,4′,4′′-(benzene-1,3,5-triyltris(oxy))tribenzoato-κ6O1:O2:O3:O3:O5:O6)tricadmium(II)] dihydrate, C54H42Cd3O24
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropyl-phenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(3-phenyl-pyridine-κN)palladium(IV), C38H45N3Cl2Pd
- The crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine, C12H8ClN3O
- The crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(phenyl(phenylsulfonyl)methyl)phenol, C27H32O3S
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-bis{(((((1-methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-2-phenolato-κ3N,O:O}copper(II)}, C68H68Cu2N8O8
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ2-2-(4-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ2O:O′)-pentakis(pyridine-κ1N)dinickel(II)], C53H47N5Ni2O13
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-5-(3-methoxy-benzylamino)-4-trifluoromethanesulfinyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile, C20H12N4Cl2F6O2S
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis(μ2-di-ethyldithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S;κ3S:S: S′)-hexacarbonyl-di-rhenium(I), C16H20N2O6Re2S4
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-2-phenylacetohydrazide, C19H16O2N2
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-4,8,11b-trimethyltetradecayhdro-8,11-epoxy-6a,9-methanocyclohepta[a]naphthalene-4-carboxylic acid – methanol (1/1), C20H30O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis(3-acetyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II) monohydrate, C22H18O10Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-4-bromoisophthalate-κ2O:O′)-tris(μ2-1-(3-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′)dicobalt(II)] monohydrate, C26H23CoN9O5Br
- A cyclic I102− anion in the layered crystal structure of theophyllinium pentaiodide, C7H9I5N4O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((4-(pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)phenyl)diazenyl)benzoato-κ3O,O′:N)cadmium(III)], Cd(C19H14O3N3)2(H2O)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-dimethyldithiophosphato-κS)-zinc(II)], {C14H20N2O4P2S4Zn}n
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-2-hydroxy-6-methoxybenzamide hydrate, C16H22N4O7
- Crystal structure of hemikis(cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium) (pyridine-2-carboxylate), [C6H16N2]0.5[C6H4NO2]
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-1,3,5-triazine, C10H6ClN3OS
- The crystal structure of 3-butyl-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium catena-poly[tris(μ2-bromido-κ2Br:Br)lead(II)], C8H15Br3N2Pb
- Crystal structure of 3-(5-amino-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)-1-(piperidin-1-yl)propan-1-one, C10H17N5O
- Crystal structure of aqua-2,2′,2′′-(((nitrilo-κN-tris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(azanylylidene-κ3N′,N′′,N′′′))tris(methanylylidene))tris(4-chlorophenolato-κ3O,O′,O′′)neodymium(III), C27H26Cl3N4NdO4
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(μ2-2,2′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)bis(benzen-1-ido)-κ2C:C′)dimercury(II), C12H8Cl2Hg2N2
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-cyanobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one, C27H18FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(pyridine-κN)(2,4,6-tri-2-pyridyl-1,3,5-triazine-κ3N2,N1,N6)nickel(II), C23H17Cl2N7Ni
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of tetrakis(4-chlorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H24Cl4Sn
- The crystal structure of 2,6-bis(pyridin-1-ium-3-ylmethyl)hexahydro-4,8-ethenopyrrolo-[3,4-f] isoindole-1,3,5,7-tetrone tetrachloridocuprate(II) monohydrate, C24H24Cl4CuN4O5
- Crystal structure of cyclo-[octaaqua-tetrakis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)tetramagnesium(II)], C20H24N40O8Mg4
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative, 13-(4-Cl-pyrrole)-matrine, C18H26ClN4O
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)bis(2-chlorobenzyl-κC1)dichloridotin(IV), C28H26Cl4OSSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)(μ2-4-cyanobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-methanol-κ2O:O)copper(II)], C9H8CuN4O3
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-dibenzyl-3,3′-dicyano-1,1′,4,4′-tetrahydro-4,4′-bipyridine, C26H22N4
- Crystal structure of (2-bromobenzyl)((1-bromonaphthalen-2-yl)methyl)sulfane, C18H14Br2S
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-ammoniocyclohexyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)imidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-ium 2-[(2-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate dihydrate, [C18H22N4][C14H8O4S2] ⋅ 2H2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-((3R,5S,10S, 13S,14S,17S)-17-((S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl)-2-methylbut-2-enamide – water – methanol (1/1/1), C29H54N2O3
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(3-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C21H15F2N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ4-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato-κ5O1,O2:O3:O4:O5)-(μ2-5-(3-pyridyl)tetrazolato-κ2N1:N3)dizinc(II)], C15H13N5O9Zn2
- Crystal structure of N-(3-methylphenyl)(propan-2-yloxy)carbothioamide, C11H15NOS
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1,3-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)(nitrato-κ1O)cadmium(II)] — water (2/1), C28H32CdN10O7
- Crystal structure of 4-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C8H7N3S
- Crystal structure of benzyltrichloridobis(1H-pyrazole-κ2N)tin(IV), C13H15Cl3N4Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido-4-fluorobenzyl-bis(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)tin(IV), C27H22ClFN2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(O,O′-diisopropyldithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)zinc(II), C36H66N4O8P4S8Zn2
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium 4,4-oxydibenzoate – boric acid – water (1/2/6) C46H98B2N2O17
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[[tribenzyltin(IV)]-(μ2-pyridine-4-carboxylato-κ2N:O)], C27H25NO2Sn
- The synthysis and crystal structure of cyclohexyl 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C18H15N3Cl2F6O3S
- The crystal structure of 5,7-bis(2-hydroxyethoxy)-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one, C19H18O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (±)-Ethyl 5′-(difluoromethyl)-2-oxo-4′,5′-dihydrospiro[indoline-3,3′-pyrazole]-4′-carboxylate, C14H13F2N3O3

