Abstract
Internet-of-Things (IoT) creates a significant impact in spectrum sensing, information retrieval, medical analysis, traffic management, etc. These applications require continuous information to perform a specific task. At the time, various intermediate attacks such as jamming, priority violation attacks, and spectrum poisoning attacks affect communication because of the open nature of wireless communication. These attacks create security and privacy issues while making data communication. Therefore, a new method autoencoder deep neural network (AENN) is developed by considering exploratory, evasion, causative, and priority violation attack. The created method classifies the transmission outcomes used to predict the transmission state, whether it is jam data transmission or sensing data. After that, the sensing data is applied for network training that predicts the intermediate attacks. In addition to this, the channel access algorithm is used to validate the channel for every access that minimizes unauthorized access. After validating the channel according to the neural network, data have been transmitted over the network. The defined process is implemented, and the system minimizes different attacks on various levels of energy consumption. The effectiveness of the system is implemented using TensorFlow, and the system ensures the 99.02% of detection rate when compared with other techniques.
1 Introduction
All manuscripts must be in English. These guidelines include complete descriptions of the fonts, spacing, and related information for producing your proceedings manuscripts.
Nowadays, the Internet-of-Things (IoT) [1,2,3] is one of the effective growing internet-enabled devices that utilized fitness trackers to smart health care systems. The IoT devices are integrating with different services [4] such as driverless cars, smart cities, smart brushing, smart farming, etc. These devices are worked along with the emerging techniques such as Artificial Intelligence because it is a fragment of the fourth industrial revolution. From the report of McKinsey, around a quarter of the business process [5] uses the IoT techniques, and it has been gradually increased in 2025. The IoT devices create a great impact in every industry and research application, but they can be misused and create risk because of privacy and security issues [6,7]. Generally, a greater number of IoT devices are interconnected to make the information transmission that time cybersecurity needs to be considered. The data transmission is hacked by malicious hackers [8] and creates thousands of attacks to access the private information, channel access, crippling infrastructure, and unsecured device access. Hence, the IoT devices are developed by withstanding the vulnerability and security issues. By considering these vulnerabilities, industries are planning to create IoT devices without having their firmware, software, and password details. Then, the devices are continuously changing their username and password at the time of installation; the created passwords are unique to every IoT device [9,10]. Finally, the firmware and software are the latest version that helps to mitigate the vulnerabilities.
Although the industries provide enough security measures to IoT devices, connectivity of IoT devices creates a specific set of security-related issues [11,12]. The IoT devices handle heterogeneity, scale, latency, proximity, interconnectivity, cost, structure (network attacks), dynamic configurations, and privacy-related issues. These IoT complexities created numerous impressions while transferring data from one location to another. Therefore, the Machine learning (ML) technique [13] is pragmatic in IoT security because it was able to adapt to changing parameters and also adjust changing environments successfully. Moreover, the ML technique’s ability to detect intermediate attacks and unknown malicious activities [14] is predicted by using the learning process. Along with this, known attacks like Distributed Denial of Services (DDoS) [15] are detected from learned patterns with maximum accuracy. From the various ML techniques, deep learning (DL) approaches [16] are highly utilized in this field to identify the attack in IoT. The DL concept is able to extract the features automatically by scanning data. Moreover, this concept has a fast learning process that correlates the extracted features effectively. These advantages are the main reason to utilize the DL network to predict intermediate attacks and unauthorized access.
Although the DL network works perfectly, few research works fail to concentrate on various attacks such as priority violation, jamming, and spectrum position attacks. The network characteristics and channel status are considered less priority, which create complexity and latency issues while transmitting data over a network. To overcome these issues, an autoencoder deep neural network (AENN) along with a channel access algorithm is implemented to manage the security in the IoT environment. During this process, the system analyzes different attack characteristics that are used to predict attacks in the IoT environment. The discussed system was implemented using TensorFlow, and the effectiveness of the system was evaluated using different metrics such as precision, recall, accuracy, detection rate, false alarm rate, and error rate. Then, the rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 analyzes the different researcher’s opinions about IoT security, Section 3 discusses the autoencoder DL technique-based data security, and the effectiveness of the system is evaluated in Section 4. Conclusion is discussed in Section 5.
2 Related works
Ullah et al. [17] apply DL techniques in IoT-based communication for detecting security threats. Here, TensorFlow deep network approach is used to analyze the pirated software and malware-infected files over the network. This process aims to identify the malicious activities with maximum prediction accuracy. During the analysis, system uses the Google Code Jam dataset information, which is utilized to investigate the malware samples from the malign dataset.
Tsogbaatar et al. [18] discovered anomaly activities in the IoT using a deep ensembling learning algorithm (DEL). This system aims to resolve the data heterogeneity, data imbalance issues while predicting anomaly activities in the IoT environment. This goal is achieved by integrating the software-defined networking in IoT to handle the various network features. The introduced system predicts the device status whether it is a normal or abnormal one.
Balasundaram et al. [19] detected intrusion activities using the bat extreme learning approach (BEL) in smart IoT environment. The system aims to design a scalable system to predict the security-related activities. This process use the data analyzer mechanism to examine the IoT network characteristics to predict malicious activities and attackers. This system is implemented using the API NDNOMNet smart automation tool. This system predicts the reply, spoofing, man-in-the-middle, and DDoS attacks effectively.
Basati et al. [20] detected intrusion activities in IoT environment using asymmetric parallel auto-encoder approach. This network uses the three layers of convolution filters that are used to extract the local features from input. The channel attention module is applied in the convolution layer to identify the intrusion activities. The discussed system is implemented using CICIDS2017, UNSW-NB15, and KDDCup99 dataset, and the system predicts the intrusion activity.
Swarna Priya et al. [21] detected intrusions on the Internet-of-Medical Things environment using gray wolf optimization along with DL network. This system examines the input, and various features are extracted according to the principal component analysis approach. With the help of the features, abnormal activities are detected, which improves the overall data security accuracy.
Hafeez et al. [22] introduced fuzzy C-means clustering with fuzzy interpolation techniques to predict malicious activities in an IoT environment. This process examines the user inputs and the similar activities are clustered, and abnormal activities are predicted with a minimum false positive rate. The successful determination of network access conditions helps to improve the overall prediction accuracy.
Fortino et al. [23] resilient framework is introduced in IoT to predict malicious activities. The system aims to minimize the delay and enhance trustworthiness while transmitting data in the network. This system uses the reputation model that provides effective solutions to identify attackers in the IoT environment.
Ullah and Mahmoud [24] detecting anomalous activities in IoT network using two-level flow approach. This system uses the flow-based approach to inspect the packet headers while transmitting data over the network. After that, a decision tree classifier is applied to predict the IoT Botnet attacks with high detection accuracy. The effectiveness of the system was evaluated using a cross-fold validation approach.
According to the above research activities, DL and ML techniques are utilized to investigate intermediate access and attacks effectively. By considering their opinion, in this work neural networks and channel access algorithms examine the intermediate access effectively. The detailed working process of the introduced system is discussed in the following section.
3 Proposed deep neural network for IoT network security
As discussed earlier, the ML techniques especially neural networks played a vital role in maintaining IoT network security. The IoT devices continuously transmit information from one location to another. During this time, intermediate attackers are aimed to access the network and transmitted packets to reduce the quality of the transferred data. This causes changes in data and creates complexity while making further data analytics.
The authorized access of the data minimizes the trust between the user and service provider in a network environment. Therefore, several ML techniques are incorporated with this IoT data transmission process but they are consuming time, high parameters are required to identify the threat patterns; latency and reliability are one of the serious problems. To overcome these issues, in this work, AENN is utilized. The network predicts the intermediate attacks by considering the behavior of evasion, exploratory, priority violation, and causative attacks. The created AENN approach investigated the packet or information transmission behavior to predict the attacks and unauthorized activities. This process directly indicates that the system cannot utilize the input samples to predict the intrusions in IoT. This process overcomes the data overfitting and unwanted data analysis time, because the input samples may contain noisy samples that differ from original data. Moreover, the information is transmitted by examining the channel status (busy or idle) then only the network receives the output (“No AcK” or “AcK”) status. The autoencoding neural network decides the intermediate attacks based on how the data transmission is performed in the single that considers the channel characteristics. The network effectively works in the unsupervised environment which means it is able to predict the unknown attack patterns using the learning parameters.
The AENN approach utilizing few general settings to identify the Internet mediate attacks in the IoT-wireless communication process. The
Here, the AENN network predicts the intermediate access in three phases such as sensing, transmission, and feedback phase.
According to the discussion, this paper investigates the

Three-phase of AENN IoT data transmission process.
In the sensing phase, the autoencoder network is utilized for sensing the channel using sample attributes and network behavior for making data transmission. The autoencoder is one of the effective neural networks that has efficient coding-based learning mechanism that helps to predict the patterns for unlabeled data. The encoding process regenerates the input patterns by performing the encoding process. During this process noise data, irrelevant information is eliminated to improve the overall channel status identification process. The network has two phases such as encoder and decoder; the encoder process maps the given input to the coding and the decoder process regenerates the input from coding. This process helps to maintain the input quality because it aims to preserve the data quality while making data transmission. The network has three layers similar to the multi-layer perceptron but the number of nodes in the input layer is similar to the output layer. Here, the aim is to identify the status of the channel but maintaining the input similarity. During the reconstruction process, the input
The deviation of
This computation deviation helps to reduce the latency difficulties while predicting the channel status (idle/busy) and attacker prediction process. The input x in
The mapping process defined in equation (4) is represented as
Here, h autoencoder mapping is reconstruction x′ of input x which is done by using the decoder weight (W′), bias (b′), and activation function (σ′). During this process, the variations are minimized according to equation (6).
Based on the above process, the network behavior decision is handled for every sample trying to send in the network. As discussed, sample S i has a different number of features {f i1, f i2, f i3,…,f iM}. These features are classified according to above-defined procedures; the class label C(S i ) is given for a specific sample. These labels help to identify the testing features related patterns, and the deviation between the computed and predicted labels are estimated using error probability value n error/n test. Based on the above process, channel idle and busy state have been identified. If the channel is in an idle state, the data have been transferred to the network. During the data transmission process, the labeled data helps to identify the characteristics of data. Suppose the network characteristics are changed that are treated as intermediate attacks, then the data transmission is eliminated in the earlier stage.
Further, the unauthorized access is eliminated by validating users using the channel access algorithm. The data have been transmitted from one station to another in wireless communication. Assume the IoT-based collected data consists of a number of stations information system (IS) which has upper boundary U, the transmitted data length has normalized to 1 which is denoted as
Channel access algorithm
|
Initialize:
|
| For every slot |
|
If Buffer (B)
|
| Realize the data generate backoff value following g(x) [0,1] |
|
Examine the channel at time
|
|
If carrier
|
| Data transmission immediately. |
| Else |
| Cancel the data transmission in that slot. |
| End |
| End |
| If not transmission then |
| Check slot for collision |
| If Collison occur then |
| The busy tone will ring |
| End |
| End |
| If packet = transmission then |
| No busy not ring and delete the packet from buffer |
| End |
| End |
| End |
According to the autoencoder, the network-based network validation and channel status examination process help to identify unauthorized activities effectively. The neural network utilizes the attack behaviors and characteristics while examining the network during the data transmission process. The created system effectiveness is evaluated using experimental results and discussion.
4 Results and discussion
This section examines the effectiveness of the AENN and channel access algorithm-based data transmission in an IoT environment. The introduced method reduces the security issues with minimum latency and reliability. Moreover, the system is able to consider the different attacks and their behavior, which is used to eliminate the intermediate and unauthorized access. The effectiveness of the system was evaluated using various metrics such as precision, recall, error rate, and mean-square-error rate. The AENN network uses the input samples and respective features to evaluate the network status. The identified status helps to predict the channel’s current position. The current status is used to predict the time of data transmission. For every data, it has a specific time to transmit from one place to another. If the network consumes more time to transmit specific data, then the system is considered as something such as collision, intermediate access, and unauthorized activities are happening in the network. In addition to this, the system uses the channel access algorithm that verifies channel status for every transmission which leads to improving the overall network precision and recall value. The obtained value is illustrated in Figure 2.
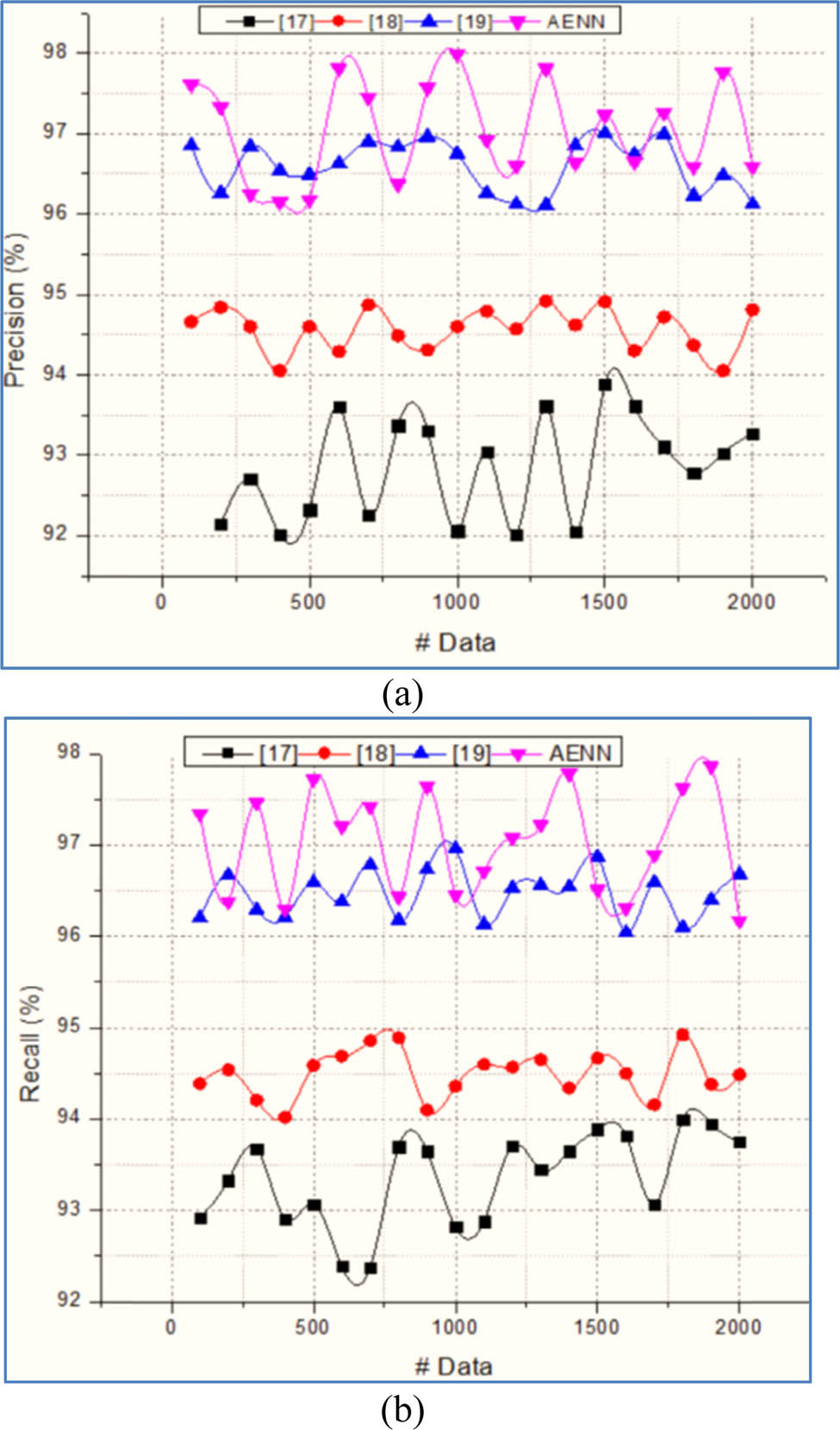
(a) Precision and (b) recall.
The successful formulation and reconstruction of inputs in the encoding process help to identify the channel state correctly. This process helps to minimize the deviation of output with respect to the input
Overall efficiency
| Attacks | Misdetection (%) | False alarm rate (%) | Normalized throughput (%) | Detection accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No attack | 2.18 | 1.01 | 97.89 | 98.39 |
| Jamming attack | 2.02 | 1.03 | 98.23 | 98.76 |
| Poisoning attack | 2.13 | 1.24 | 97.3 | 97.9 |
| Priority violation attack | 2.04 | 1.06 | 98.12 | 98.45 |
Table 2 clearly indicates that the AENN approach recognizes the various attacks such as jamming, poisoning, priority violation attacks with high detection rate, minimum misdetection, and minimum false alarm rate. The obtained system effectiveness is further evaluated with existing techniques, and the obtained results are illustrated in Table 3.
Attack detection rate
| S. No | Methods | Accuracy | Detection rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DL [17] | 95.57 | 96.13 |
| 2 | DEL [18] | 96.24 | 96.98 |
| 3 | BEL [19] | 97.48 | 97.46 |
| 4 | AENN | 99.18 | 99.02 |
Table 2 depicted that the AENN and channel access algorithm recognizes the attacks and authorizes the channel with a maximum detection rate (99.02%). In addition to this, the method predicts the channel condition such as idle and busy with high recognition accuracy (99.18%). Thus, the system improves the overall IoT security with minimum latency, false error rate, deviation, and high detection accuracy.
5 Conclusion
Thus, the paper analyzes the AENN with channel access algorithm to improve security in IoT-based data transmission. The network examines the data transmission channel using three layers of autoencoder neural network. The network maps and reconstructs data using a coding process. This approach continuously updates the network parameters using backpropagation learning that helps to minimize the deviations and reduce the false alarm rate. The learning process improves the overall channel status identification accuracy because it uses the various attacks related parameters and characteristics. Here, the channel access algorithm also utilizes that investigates the data transmission network in terms of their characteristics and collision status. According to the network information, channel status has been checked and authenticated for every data transmission slot. Then, the effectiveness of the system implemented using TensorFlow and the system ensures the 99.02% of detection rate when compared with other techniques. In the future, the effectiveness of the system improved using an optimized classifier for reducing the computation complexity.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dijlah University College for funding this research.
-
Funding information: This research was supported by the Dijlah University College l [grant number G2021-1].
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Hasan M, Islam MM, Zarif MI, Hashem MM. Attack and anomaly detection in IoT sensors in IoT sites using machine learning approaches. Internet Things. 2019;7:100059.10.1016/j.iot.2019.100059Search in Google Scholar
[2] Hussain F, Abbas SG, Shah GA, Pires IM, Fayyaz UU, Shahzad F, et al. A framework for malicious traffic detection in IoT healthcare environment. Sensors. 2021;21(9):3025.10.3390/s21093025Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Hafeez I, Ding AY, Antikainen M, Tarkoma S. Real-time IoT device activity detection in edge networks. In International Conference on Network and System Security. Cham: Springer; 2018. p. 221–36.10.1007/978-3-030-02744-5_17Search in Google Scholar
[4] Dian FJ, Vahidnia R, Rahmati A. Wearables and the internet of things (IoT), applications, opportunities, and challenges: a survey. IEEE Access. 2020;8:69200–11.10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2986329Search in Google Scholar
[5] Bughin J, Chui M, Manyika J. Clouds, big data, and smart assets: Ten tech-enabled business trends to watch. McKinsey Q. 2010;56(1):75–86.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Alfandi O, Khanji S, Ahmad L, Khattak A. A survey on boosting IoT security and privacy through blockchain. Clust Comput. 2020;24(1):1–19.10.1007/s10586-020-03137-8Search in Google Scholar
[7] Mohanta BK, Jena D, Ramasubbareddy S, Daneshmand M, Gandomi AH. Addressing security and privacy issues of IoT using blockchain technology. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020;8(2):881–8.10.1109/JIOT.2020.3008906Search in Google Scholar
[8] Reddy YB, Latifi S. Trust and access controls in IoT to avoid malicious activity. In: Cloud Network Management. London, UK: Chapman and Hall/CRC; 2020. p. 87–103.10.1201/9780429288630-6Search in Google Scholar
[9] Bhatt P, Bhatt S, Ko M. Poster: IoT SENTINEL-An ABAC approach against cyber-warfare in organizations. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM Symposium on Access Control Models and Technologies; 2020. p. 223–5.10.1145/3381991.3396227Search in Google Scholar
[10] Islam MR, Aktheruzzaman KM. An analysis of cybersecurity attacks against internet of things and security solutions. J Computer Commun 2020;8(4):11–25.10.4236/jcc.2020.84002Search in Google Scholar
[11] Fan R, Pan J, Huang S. ARM-AFL: coverage-guided fuzzing framework for ARM-based IoT devices. In: International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security. Cham: Springer; 2020. p. 239–54.10.1007/978-3-030-61638-0_14Search in Google Scholar
[12] Alferidah DK, Jhanjhi NZ. A review on security and privacy issues and challenges in internet of things. Int J Computer Sci Netw Security IJCSNS. 2020;20(4):263–86.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Waheed N, He X, Ikram M, Usman M, Hashmi SS, Usman M. Security and privacy in IoT using machine learning and blockchain: threats and countermeasures. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR). 2020;53(6):1–37.10.1145/3417987Search in Google Scholar
[14] Chanal PM, Kakkasageri MS. Security and privacy in IOT: a survey. Wirel Personal Commun. 2020;115(2):1667–93.10.1007/s11277-020-07649-9Search in Google Scholar
[15] Chen YW, Sheu JP, Kuo YC, Van Cuong N. Design and implementation of IoT DDoS attacks detection system based on machine learning. In: 2020 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC). United States: IEEE; 2020. p. 122–7.10.1109/EuCNC48522.2020.9200909Search in Google Scholar
[16] Ujjan RM, Pervez Z, Dahal K, Bashir AK, Mumtaz R, González J. Towards flow and adaptive polling sampling for deep learning based DDoS detection in SDN. Future Gener Computer Syst. 2020;111:763–79.10.1016/j.future.2019.10.015Search in Google Scholar
[17] Ullah F, Naeem H, Jabbar S, Khalid S, Latif MA, Al-Turjman F, et al. Cyber security threats detection in internet of things using deep learning approach. IEEE Access. 2019;7:124379–89. 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2937347.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Tsogbaatar E, Bhuyan MH, Taenaka Y, Fall D, Gonchigsumlaa K, Elmroth E, et al. DeL-IoT: a deep ensemble learning approach to uncover anomalies in IoT. Internet Things. 2021;14:100391.10.1016/j.iot.2021.100391Search in Google Scholar
[19] Balasundaram J. A novel optimized bat extreme learning intrusion detection system for smart Internet of things networks. Int J Commun Syst. 2021;34(7):e4729.10.1002/dac.4729Search in Google Scholar
[20] Basati A, Faghih MM. APAE: an IoT intrusion detection system using asymmetric parallel auto-encoder. Neural Comput Applic. 2021;2021:1–21. 10.1007/s00521-021-06011-9.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Swarna Priya RM, Maddikunta PK, Parimala M, Koppu S, Gadekallu TR, Chowdhary CL, et al. An effective feature engineering for DNN using hybrid PCA-GWO for intrusion detection in IoMT architecture. Comput Commun. 2020;160:139–49.10.1016/j.comcom.2020.05.048Search in Google Scholar
[22] Hafeez I, Antikainen M, Ding AY, Tarkoma S. IoT-KEEPER: detecting malicious IoT network activity using online traffic analysis at the edge. IEEE Trans Netw Serv Manag. 2020;17(1):45–59.10.1109/TNSM.2020.2966951Search in Google Scholar
[23] Fortino G, Messina F, Rosaci D, Sarnè GM. ResIoT: an IoT social framework resilient to malicious activities. IEEE/CAA J Automatica Sin. 2020;7(5):1263–78.10.1109/JAS.2020.1003330Search in Google Scholar
[24] Ullah I, Mahmoud QH. A two-level flow-based anomalous activity detection system for IoT networks. Electronics. 2020;9(3):530.10.3390/electronics9030530Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 Saif Mohammed Ali et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Construction of 3D model of knee joint motion based on MRI image registration
- Evaluation of several initialization methods on arithmetic optimization algorithm performance
- Application of visual elements in product paper packaging design: An example of the “squirrel” pattern
- Deep learning approach to text analysis for human emotion detection from big data
- Cognitive prediction of obstacle's movement for reinforcement learning pedestrian interacting model
- The application of neural network algorithm and embedded system in computer distance teach system
- Machine translation of English speech: Comparison of multiple algorithms
- Automatic control of computer application data processing system based on artificial intelligence
- A secure framework for IoT-based smart climate agriculture system: Toward blockchain and edge computing
- Application of mining algorithm in personalized Internet marketing strategy in massive data environment
- On the correction of errors in English grammar by deep learning
- Research on intelligent interactive music information based on visualization technology
- Extractive summarization of Malayalam documents using latent Dirichlet allocation: An experience
- Conception and realization of an IoT-enabled deep CNN decision support system for automated arrhythmia classification
- Masking and noise reduction processing of music signals in reverberant music
- Cat swarm optimization algorithm based on the information interaction of subgroup and the top-N learning strategy
- State feedback based on grey wolf optimizer controller for two-wheeled self-balancing robot
- Research on an English translation method based on an improved transformer model
- Short-term prediction of parking availability in an open parking lot
- PUC: parallel mining of high-utility itemsets with load balancing on spark
- Image retrieval based on weighted nearest neighbor tag prediction
- A comparative study of different neural networks in predicting gross domestic product
- A study of an intelligent algorithm combining semantic environments for the translation of complex English sentences
- IoT-enabled edge computing model for smart irrigation system
- A study on automatic correction of English grammar errors based on deep learning
- A novel fingerprint recognition method based on a Siamese neural network
- A hidden Markov optimization model for processing and recognition of English speech feature signals
- Crime reporting and police controlling: Mobile and web-based approach for information-sharing in Iraq
- Convex optimization for additive noise reduction in quantitative complex object wave retrieval using compressive off-axis digital holographic imaging
- CRNet: Context feature and refined network for multi-person pose estimation
- Improving the efficiency of intrusion detection in information systems
- Research on reform and breakthrough of news, film, and television media based on artificial intelligence
- An optimized solution to the course scheduling problem in universities under an improved genetic algorithm
- An adaptive RNN algorithm to detect shilling attacks for online products in hybrid recommender system
- Computing the inverse of cardinal direction relations between regions
- Human-centered artificial intelligence-based ice hockey sports classification system with web 4.0
- Construction of an IoT customer operation analysis system based on big data analysis and human-centered artificial intelligence for web 4.0
- An improved Jaya optimization algorithm with ring topology and population size reduction
- Review Articles
- A review on voice pathology: Taxonomy, diagnosis, medical procedures and detection techniques, open challenges, limitations, and recommendations for future directions
- An extensive review of state-of-the-art transfer learning techniques used in medical imaging: Open issues and challenges
- Special Issue: Explainable Artificial Intelligence and Intelligent Systems in Analysis For Complex Problems and Systems
- Tree-based machine learning algorithms in the Internet of Things environment for multivariate flood status prediction
- Evaluating OADM network simulation and an overview based metropolitan application
- Radiography image analysis using cat swarm optimized deep belief networks
- Comparative analysis of blockchain technology to support digital transformation in ports and shipping
- IoT network security using autoencoder deep neural network and channel access algorithm
- Large-scale timetabling problems with adaptive tabu search
- Eurasian oystercatcher optimiser: New meta-heuristic algorithm
- Trip generation modeling for a selected sector in Baghdad city using the artificial neural network
- Trainable watershed-based model for cornea endothelial cell segmentation
- Hessenberg factorization and firework algorithms for optimized data hiding in digital images
- The application of an artificial neural network for 2D coordinate transformation
- A novel method to find the best path in SDN using firefly algorithm
- Systematic review for lung cancer detection and lung nodule classification: Taxonomy, challenges, and recommendation future works
- Special Issue on International Conference on Computing Communication & Informatics
- Edge detail enhancement algorithm for high-dynamic range images
- Suitability evaluation method of urban and rural spatial planning based on artificial intelligence
- Writing assistant scoring system for English second language learners based on machine learning
- Dynamic evaluation of college English writing ability based on AI technology
- Image denoising algorithm of social network based on multifeature fusion
- Automatic recognition method of installation errors of metallurgical machinery parts based on neural network
- An FCM clustering algorithm based on the identification of accounting statement whitewashing behavior in universities
- Emotional information transmission of color in image oil painting
- College music teaching and ideological and political education integration mode based on deep learning
- Behavior feature extraction method of college students’ social network in sports field based on clustering algorithm
- Evaluation model of multimedia-aided teaching effect of physical education course based on random forest algorithm
- Venture financing risk assessment and risk control algorithm for small and medium-sized enterprises in the era of big data
- Interactive 3D reconstruction method of fuzzy static images in social media
- The impact of public health emergency governance based on artificial intelligence
- Optimal loading method of multi type railway flatcars based on improved genetic algorithm
- Special Issue: Evolution of Smart Cities and Societies using Emerging Technologies
- Data mining applications in university information management system development
- Implementation of network information security monitoring system based on adaptive deep detection
- Face recognition algorithm based on stack denoising and self-encoding LBP
- Research on data mining method of network security situation awareness based on cloud computing
- Topology optimization of computer communication network based on improved genetic algorithm
- Implementation of the Spark technique in a matrix distributed computing algorithm
- Construction of a financial default risk prediction model based on the LightGBM algorithm
- Application of embedded Linux in the design of Internet of Things gateway
- Research on computer static software defect detection system based on big data technology
- Study on data mining method of network security situation perception based on cloud computing
- Modeling and PID control of quadrotor UAV based on machine learning
- Simulation design of automobile automatic clutch based on mechatronics
- Research on the application of search algorithm in computer communication network
- Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence based Techniques and Applications for Intelligent IoT Systems
- Personalized recommendation system based on social tags in the era of Internet of Things
- Supervision method of indoor construction engineering quality acceptance based on cloud computing
- Intelligent terminal security technology of power grid sensing layer based upon information entropy data mining
- Deep learning technology of Internet of Things Blockchain in distribution network faults
- Optimization of shared bike paths considering faulty vehicle recovery during dispatch
- The application of graphic language in animation visual guidance system under intelligent environment
- Iot-based power detection equipment management and control system
- Estimation and application of matrix eigenvalues based on deep neural network
- Brand image innovation design based on the era of 5G internet of things
- Special Issue: Cognitive Cyber-Physical System with Artificial Intelligence for Healthcare 4.0.
- Auxiliary diagnosis study of integrated electronic medical record text and CT images
- A hybrid particle swarm optimization with multi-objective clustering for dermatologic diseases diagnosis
- An efficient recurrent neural network with ensemble classifier-based weighted model for disease prediction
- Design of metaheuristic rough set-based feature selection and rule-based medical data classification model on MapReduce framework
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Construction of 3D model of knee joint motion based on MRI image registration
- Evaluation of several initialization methods on arithmetic optimization algorithm performance
- Application of visual elements in product paper packaging design: An example of the “squirrel” pattern
- Deep learning approach to text analysis for human emotion detection from big data
- Cognitive prediction of obstacle's movement for reinforcement learning pedestrian interacting model
- The application of neural network algorithm and embedded system in computer distance teach system
- Machine translation of English speech: Comparison of multiple algorithms
- Automatic control of computer application data processing system based on artificial intelligence
- A secure framework for IoT-based smart climate agriculture system: Toward blockchain and edge computing
- Application of mining algorithm in personalized Internet marketing strategy in massive data environment
- On the correction of errors in English grammar by deep learning
- Research on intelligent interactive music information based on visualization technology
- Extractive summarization of Malayalam documents using latent Dirichlet allocation: An experience
- Conception and realization of an IoT-enabled deep CNN decision support system for automated arrhythmia classification
- Masking and noise reduction processing of music signals in reverberant music
- Cat swarm optimization algorithm based on the information interaction of subgroup and the top-N learning strategy
- State feedback based on grey wolf optimizer controller for two-wheeled self-balancing robot
- Research on an English translation method based on an improved transformer model
- Short-term prediction of parking availability in an open parking lot
- PUC: parallel mining of high-utility itemsets with load balancing on spark
- Image retrieval based on weighted nearest neighbor tag prediction
- A comparative study of different neural networks in predicting gross domestic product
- A study of an intelligent algorithm combining semantic environments for the translation of complex English sentences
- IoT-enabled edge computing model for smart irrigation system
- A study on automatic correction of English grammar errors based on deep learning
- A novel fingerprint recognition method based on a Siamese neural network
- A hidden Markov optimization model for processing and recognition of English speech feature signals
- Crime reporting and police controlling: Mobile and web-based approach for information-sharing in Iraq
- Convex optimization for additive noise reduction in quantitative complex object wave retrieval using compressive off-axis digital holographic imaging
- CRNet: Context feature and refined network for multi-person pose estimation
- Improving the efficiency of intrusion detection in information systems
- Research on reform and breakthrough of news, film, and television media based on artificial intelligence
- An optimized solution to the course scheduling problem in universities under an improved genetic algorithm
- An adaptive RNN algorithm to detect shilling attacks for online products in hybrid recommender system
- Computing the inverse of cardinal direction relations between regions
- Human-centered artificial intelligence-based ice hockey sports classification system with web 4.0
- Construction of an IoT customer operation analysis system based on big data analysis and human-centered artificial intelligence for web 4.0
- An improved Jaya optimization algorithm with ring topology and population size reduction
- Review Articles
- A review on voice pathology: Taxonomy, diagnosis, medical procedures and detection techniques, open challenges, limitations, and recommendations for future directions
- An extensive review of state-of-the-art transfer learning techniques used in medical imaging: Open issues and challenges
- Special Issue: Explainable Artificial Intelligence and Intelligent Systems in Analysis For Complex Problems and Systems
- Tree-based machine learning algorithms in the Internet of Things environment for multivariate flood status prediction
- Evaluating OADM network simulation and an overview based metropolitan application
- Radiography image analysis using cat swarm optimized deep belief networks
- Comparative analysis of blockchain technology to support digital transformation in ports and shipping
- IoT network security using autoencoder deep neural network and channel access algorithm
- Large-scale timetabling problems with adaptive tabu search
- Eurasian oystercatcher optimiser: New meta-heuristic algorithm
- Trip generation modeling for a selected sector in Baghdad city using the artificial neural network
- Trainable watershed-based model for cornea endothelial cell segmentation
- Hessenberg factorization and firework algorithms for optimized data hiding in digital images
- The application of an artificial neural network for 2D coordinate transformation
- A novel method to find the best path in SDN using firefly algorithm
- Systematic review for lung cancer detection and lung nodule classification: Taxonomy, challenges, and recommendation future works
- Special Issue on International Conference on Computing Communication & Informatics
- Edge detail enhancement algorithm for high-dynamic range images
- Suitability evaluation method of urban and rural spatial planning based on artificial intelligence
- Writing assistant scoring system for English second language learners based on machine learning
- Dynamic evaluation of college English writing ability based on AI technology
- Image denoising algorithm of social network based on multifeature fusion
- Automatic recognition method of installation errors of metallurgical machinery parts based on neural network
- An FCM clustering algorithm based on the identification of accounting statement whitewashing behavior in universities
- Emotional information transmission of color in image oil painting
- College music teaching and ideological and political education integration mode based on deep learning
- Behavior feature extraction method of college students’ social network in sports field based on clustering algorithm
- Evaluation model of multimedia-aided teaching effect of physical education course based on random forest algorithm
- Venture financing risk assessment and risk control algorithm for small and medium-sized enterprises in the era of big data
- Interactive 3D reconstruction method of fuzzy static images in social media
- The impact of public health emergency governance based on artificial intelligence
- Optimal loading method of multi type railway flatcars based on improved genetic algorithm
- Special Issue: Evolution of Smart Cities and Societies using Emerging Technologies
- Data mining applications in university information management system development
- Implementation of network information security monitoring system based on adaptive deep detection
- Face recognition algorithm based on stack denoising and self-encoding LBP
- Research on data mining method of network security situation awareness based on cloud computing
- Topology optimization of computer communication network based on improved genetic algorithm
- Implementation of the Spark technique in a matrix distributed computing algorithm
- Construction of a financial default risk prediction model based on the LightGBM algorithm
- Application of embedded Linux in the design of Internet of Things gateway
- Research on computer static software defect detection system based on big data technology
- Study on data mining method of network security situation perception based on cloud computing
- Modeling and PID control of quadrotor UAV based on machine learning
- Simulation design of automobile automatic clutch based on mechatronics
- Research on the application of search algorithm in computer communication network
- Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence based Techniques and Applications for Intelligent IoT Systems
- Personalized recommendation system based on social tags in the era of Internet of Things
- Supervision method of indoor construction engineering quality acceptance based on cloud computing
- Intelligent terminal security technology of power grid sensing layer based upon information entropy data mining
- Deep learning technology of Internet of Things Blockchain in distribution network faults
- Optimization of shared bike paths considering faulty vehicle recovery during dispatch
- The application of graphic language in animation visual guidance system under intelligent environment
- Iot-based power detection equipment management and control system
- Estimation and application of matrix eigenvalues based on deep neural network
- Brand image innovation design based on the era of 5G internet of things
- Special Issue: Cognitive Cyber-Physical System with Artificial Intelligence for Healthcare 4.0.
- Auxiliary diagnosis study of integrated electronic medical record text and CT images
- A hybrid particle swarm optimization with multi-objective clustering for dermatologic diseases diagnosis
- An efficient recurrent neural network with ensemble classifier-based weighted model for disease prediction
- Design of metaheuristic rough set-based feature selection and rule-based medical data classification model on MapReduce framework

