Abstract
C17H17AgN6O3, monoclinic, P21/c, a = 9.7281(3) Å, b = 18.8761(6) Å, c = 9.6289(3) Å, β = 99.548(3)∘, Z = 4, V = 1743.65(10) Å3, R gt (F) = 0.0465, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1193, T = 293 K.
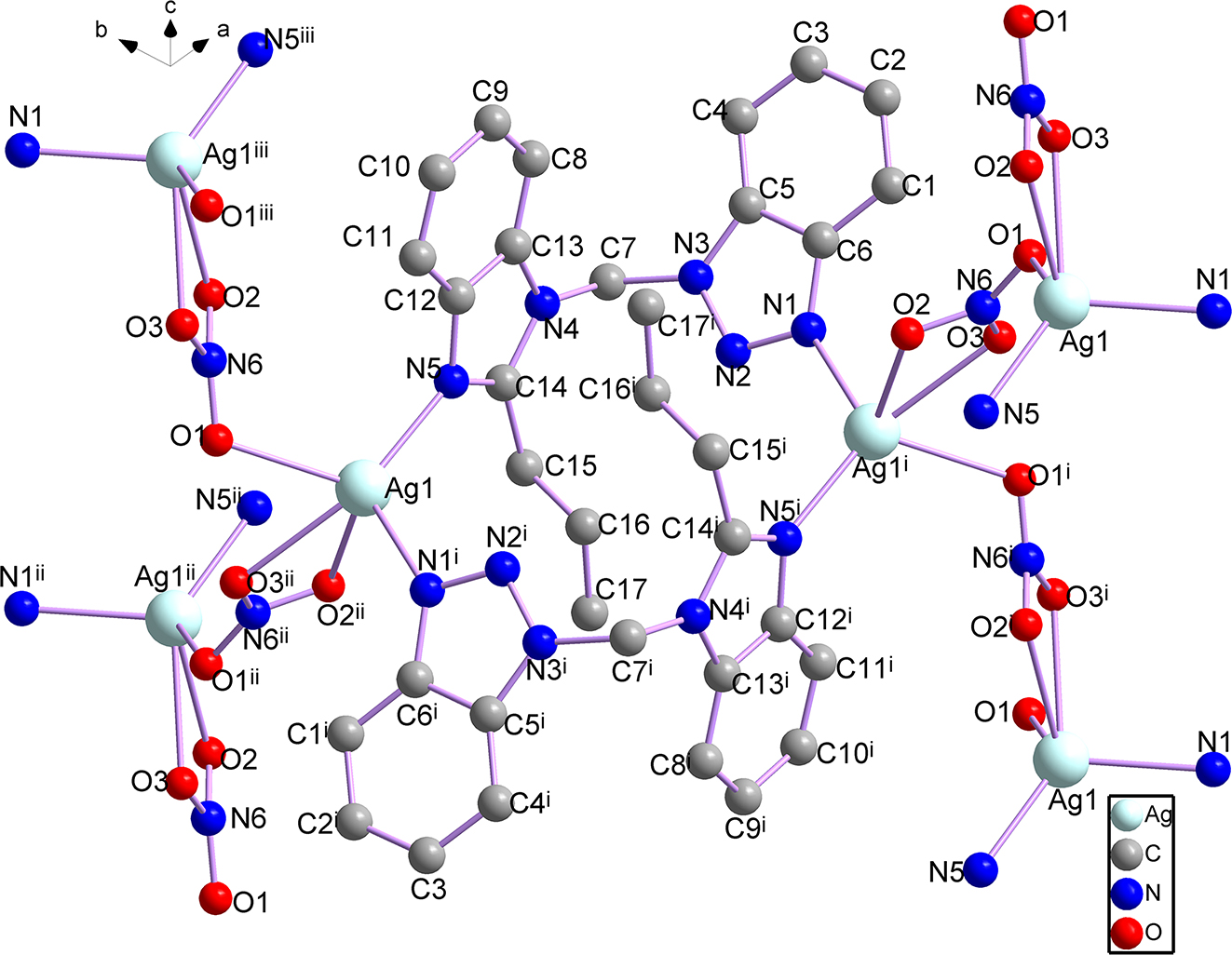
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data. The list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: μ: |
Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) 9.56 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: θ max, completeness: |
Oxford Xcalibur, Eos, ω scans 67.1°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 6625, 3120, 0.045 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2462 |
| N(param)refined: | 269 |
| Programs: | Oxford, 1 SHELX 2 |
1 Source of materials
All starting materials are commercially available without further purification. 1-[(2-propyl-1H-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole (pbmb) was prepared according to the literature method with some modifications. 2 The ligand 1-[(2-propyl-1H-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole (0.04 mmol, 0.0117 g) was dissolved in 2 mL of methanol solution and the solution was slowly added to 2 ml of AgNO3 (0.04 mmol, 0.0068 g) of methanol solution. The prepared solution was placed at room temperature and avoid light. Colorless crystals were obtained after five days.
2 Experimental details
H atoms were generated geometrically and treated as riding atoms with C–H = 0.93 Å and U iso(H) = 1.2 times U eq(C) for aromatic H atoms, with C–H = 0.97 Å and U iso(H) = 1.2 times U eq(C) for methylene H atoms, and with C–H = 0.96 Å and U iso(H) = 1.5 times U eq(C) for methyl H atoms.
3 Comment
Nitrogen heterocyclic compounds, as key products of carbon nitrogen bonding reactions, play important roles in drug synthesis, environmental protection, organic catalytic processes, 3 and biosensing signal detection. 4 In addition, nitrogen-containing heterocyclic metal complexes not only combine the characteristics of metal compounds and nitrogen-containing compounds, but also receive attention due to their unique heterocyclic structure. For example, the Jyothi R team synthesized metal complexes such as Co2+, Zn2+, Cu2+ using flavonoid derivatives, and studied the inhibitory activity of the complexes against various pathogenic bacteria and a-glucosidase. 5 Furthermore, our research group also synthesized two Cu (II) metal complexes based on benzotriazole derivatives, and found that the hypoglycemic activity of Cu (II) metal complexes was much higher than that of single ligands. 6 Silver has been used to treat burn infections for a hundred years, and nitrogen-containing heterocyclic complexes synthesized with silver ions as metal centers have good antibacterial effects. 7 De Menezes Pereira, G team synthesized a novel silver(I) complex of uracil isomer and found good inhibitory activity against Gram positive and Gram negative bacterial strains. 8
X-ray crystallographic analysis shows that the title complex has a two-dimensional structure with dual core Ag (II) as the central symmetric unit, and crystallizes in the monoclinic P21/c space group. As shown in Figure. The central atom Ag(II) is bonded to three O atoms (O1, O2ii, and O3ii) and two N atoms (N1i and N5 in the pbmb ligand), respectively. The lengths of the Ag–O and Ag–N bonds around Ag1 are: Ag1–O1:2.516(14) Å; Ag1–O2ii: 2.540(18) Å; Ag1–O3ii: 2.532(13) Å; Ag1–N1i: 2.335(4) Å; Ag1–N5: 2.231(4) Å. The range of bond angles around the metal center Ag(II) is 42.9(5)°-140.2(3)°. The smallest bond angle is O3ii–Ag1–O2ii, the largest is N5–Ag1–O3ii. In each pbmb ligand, the dihedral angle between the benzotriazole ring and the benzimidazole ring is 83.8°; and the two adjacent silver (II) ions are linked by nitrate ions to form a chain structure. The chain is connected by two pbmb ligands, forming a binucleate structure in a bidentate bridging coordination mode, and extending into a two-dimensional fish network structure.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Key Scientific and Research Projects of the Education Department of Henan Province (No. 21A430024).
References
1. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
2. Katritzky, A.-R.; Drewniak–Deyrup, M.; Lan, X.-F.; Brunner, F. Chemistry of Ben Zotriazole. Preparation, Lithiation and Transformation of N-(benzotriazol-1-ylmethyl) Heterocycles. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1989, 26, 829–836.10.1002/jhet.5570260359Search in Google Scholar
3. Dwivedi, K. C.; Sabharwal, G.; Kote, B. S.; Balakrishna, M. S. NiII, PdII and PtII Pincer Complexes of 2-(diphenylphosphanyl)–N-(2-(diphenyl-Phosphanyl)benzyl) Benzamide: Synthesis, Reactivity and Catalytic Studies. Dalton Trans. 2024, 53, 18321–18329; https://doi.org/10.1039/d4dt02611j.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Xu, Y.; Ma, J.; Dai, C.; Mao, Z.; Zhou, Y. CRISPR/Cas12a-drived Electrochemiluminescence and Fluorescence Dual-Mode Magnetic Biosensor for Sensitive Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Based on Iridium(III) Complex as Luminophore. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 264, 116678; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2024.116678.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Jyothi, R.; Vincent, S.; Joseph, J. Synthesis, Structural Characterization, Catalytic, Biological and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Studies of Metal Complexes with Flavone Derivatives. Alinteri J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 36, 265–276; https://doi.org/10.47059/alinteri/v36i1/ajas21040.Search in Google Scholar
6. Wang, X.; Ling, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, D.; Yang, H. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Biological Properties of Two Cu(II) Complexes Based on 1-(benzotriazole-1-Methyl)-1-(2-Ethylimidazole). J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1193, 348–356; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.05.036.Search in Google Scholar
7. Ceramella, J.; Catalano, A.; Mariconda, A.; D’Amato, A.; Aquila, S.; Saturnino, C.; Rosano, C.; Sinicropi, M. S.; Longo, P. Silver N–Heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Complexes as Antimicrobial and/or Anticancer Agents. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2024, 18, 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010009.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. De Menezes Pereira, G.; Bormio Nunes, J. H.; Macedo, V. S.; Pereira, D. H.; Buglio, K. E.; Affonso, D. D.; Ruiz, A. L. T. G.; de Carvalho, J. E.; Frajácomo, S. C. L.; Lustri, W. R.; Lima, C. S. P.; Bergamini, F. R. G.; Cuin, A.; Masciocchi, N.; Corbi, P. P. Antibacterial Profile and Antiproliferative Activities over Human Tumor Cells of New Silver(I) Complexes Containing Two Distinct Trifluoromethyl Uracil Isomers. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2023, 262, 112752; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2024.112752.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structure of [K3:N1:N2:N4-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazole] binuclear Ni(II) complex[Ni2(C7H5N4)2(C7H4ClO2)2]
- The crystal structure of di(thiocyanato-κ1N)-bis(methanol)-di(1,3-bis((pyridin-4-ylthio)methyl)benzene)-iron(II), C40H40FeN6O2S6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 3 O,O′:O″)-(μ 4-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 4 O,O′,O″,O‴)-dicadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C47H30Cd2F8N3O12
- The crystal structure of a 3d-4f complex based on 2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-6-methoxyphenol C31H27N4O13S2CoEr
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-yl)benzene-k 2 N:N′)(μ 4-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-k 4 O,O,O,O)dizinc(II)] dihydrate, C40H28Zn2N8O9
- The crystal structure of 4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, C11H13Cl2NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of-(10S,13S,16R,Z) −17-ethylidene-16-hydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3 H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one, C21H32O2
- The crystal structure of catena-((μ 2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ 2 N:N′)-bis(4-fluorobenzoato-κ1O)-copper(II)), C24H16F2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(ethylenediamine-κ2 N,N′)-μ-tetraoxomolybdato(VI) zinc(II)], C2H8MoN2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid, C4H3ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of bepotastine besilate, C27H31ClN2O6S
- The crystal structure of (η 6-p-cymene)benzyldiphenylphosphine-diiodido-ruthenium(II) dichloromethane solvate
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4- (imidazol-1′-yl-methyl)benzene κ 2 N:N′)-(μ 2-3-nitrobenzene -1,2-dicarboxylato-k4,O,O′:O′′,O′′′]zinc(II)-κ 2, C21H15N5O6Zn
- The crystal structure of (2R,4S)-5-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-2-methyl pentanoic acid, C23H29NO4
- The crystal strucure of [2,2′-{1,2-phenylenebis [(azanylylidene)methanylylidene]}bis(4-fluorophenolato)-κ4 N,N′,O,O′] nickel(II) N, N-dimethylformamide solvate, C23H19F2N3NiO3
- The structure of (E)-6-(cyclopropylmethyl)-11-(2,2-difluoropropylidene)-2-methyl-6, 11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C21H21F2NO2S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-(2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzyl)-1H-imidazole κ2N:N′)- (μ 2-cyclohexane-1,2-dicarboxylato κ2O,O′)cobalt(II) monohydrate]
- The crystal structure of 3,5,7-trinitro-1,3,5,7-oxatriazocane
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ3 O,O′:O′′)(μ2-1-[(2-propyl-1H-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-k2 N:N′)silver(I)], C17H17AgN6O3
- The crystal structure of (5-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)-2-sulfanylidene-1,3,4-oxadiazol-3(2H)-yl)(3-methylphenyl)methanone, C18H14N2O4S
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O]-cobalt(II), C11H11Co0.5N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-N-(4-morpholinophenyl)propanamide, C24H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of sodium methylsulfonate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(isothiocyanate κ 1 N)-(μ 2-3,3ʹ-methylenebis(1-methyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazole-2-thione)-κ 2 S:S′)-cobalt(II)], C11H12CoN6S4
- The crystal structure of {hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ 1N)nickel(II)} (μ 2-oxo)-hexaoxido-di-molybdenum(VI)─1-methyl-1H-imidazole (1/2), C32H48NiMo2N16O7
- 6-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3′,6′-tris(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C62H38N5O4P
- The crystal structure of R-2′-amino-N-methyl-N-(1-phenylethyl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxamide, C22H22N2O
- The crystal structure of bis{tetrakis(n-butyl)(μ-hydroxy)(2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoate) (μ 3 -oxo)ditin(IV)}
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ 2(3,4-dimethylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O:O′)-(3,6-bis(4′-pyridyl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine-κ 1 N)zinc(II)], C22H16N6O5S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-5-cyano–N-(5-(cyanomethyl)quinolin-8-yl)pentanamide, C19H15BrN4O
- The crystal structure of bis(tetramethylammonium) (di-μ2-aqua)hexaaqua-dibarium(II)) decavanadate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(bis(μ 2-chlorido)- (μ 2-4′-(pyridin-4-yl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine–N′, N″, N‴:N″″) -chlorido-dicopper(I,II)) monohydrate, C20H16N4OCl3Cu2
- Crystal structure of spiropachysine, C31H46N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 2 N: O)-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 3-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 2-nitrite-κ 3 O: O′: O″)dicadmium(II) monohydrate], C19H12Br3Cd2N3O9
- The crystal structure of 2-acetylpyridine-ortho-fluoro-phenylhydrazone, C14H12FN3O
- The crystal structure of poly(triaqua-(m 2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 2 O:O′)-bis(m 2-2-2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 4 O,O′:O″:O‴)dierbium(III)) hydrate, C36H26Er2N6O16
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(phenazine-5,10-diyl)bis(heptan-1-one), C26H34N2O2
- The crystal structure of (4-([2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridin]-4′-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C21H16BN3O2
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazine-5,7(6H)-dione, C6H3N3O3
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide ethanol solvate, C23H30N2O4
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis[1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-K2 O,O′]lutetium(III) C20F12H16LuO8C5H6N
- Crystal structure of dichlorido–tetrakis{3-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylpentan-3-ol-k 1N}cobalt(II), C64H88O4N12Cl6Co
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(4-allyl-2-methoxyphenyl nicotinato-k 1 N)bis(thiocyanato-k 1 N)cobalt(II)
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H21Cl2NO3
- The crystal structure of (E)–N-(4-chlorobenzylidene)(4-chlorophenyl)methanamine, C14H11Cl2N
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-ethylbenzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H22O4
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C4H2N3O4⋅C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of-(1S,4aR,5S)-5,6,7-trihydroxy-8-isopropyl-1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5,10,11,11a-octahydro-4a,1-(epoxymethano)dibenzo[a,d][7]annulen-13-one C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 7,9-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4-propylbenzo[f]isoquinolin-5-yl 4-bromobenzoate, C26H24BrNO4
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylbutanaminium)tridecathiotrimolybdate(2−), (BuMe3N)2[Mo3S13]
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-methylpiperazine-1-carbothioamide, C16H27N3S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2,2′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylenesulfanediyl)]dibenzoato-κ 4 O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ 2-1,1′-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-benzimidazole)-κ 2 N:N′)cadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C51H41N5O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,2′-pyran]-3-one, C19H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-cyanobenzyl)-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C20H15N3
- Crystal structure of (1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C22H22BrO2P
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrachloridomanganese(II)
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxyphenyl)-4,6-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine, C33H39N3O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(5-carboxypyridine-2-carboxylate-κ 2N,O)(2,5-pyridine-dicarboxylate-κ 4O,O′:N:O″)bismuth(III)], C14H9BiN2O9
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-fluoro-4-(2-(phenylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C14H11FO2S
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-amino-3-chloro-4-methoxybenzoate, C9H10ClNO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structure of [K3:N1:N2:N4-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-triazole] binuclear Ni(II) complex[Ni2(C7H5N4)2(C7H4ClO2)2]
- The crystal structure of di(thiocyanato-κ1N)-bis(methanol)-di(1,3-bis((pyridin-4-ylthio)methyl)benzene)-iron(II), C40H40FeN6O2S6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 3 O,O′:O″)-(μ 4-3,3″,5,5″-tetrafluoro-(1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl)-4,4″-dicarboxylate-κ 4 O,O′,O″,O‴)-dicadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C47H30Cd2F8N3O12
- The crystal structure of a 3d-4f complex based on 2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-6-methoxyphenol C31H27N4O13S2CoEr
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-yl)benzene-k 2 N:N′)(μ 4-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-k 4 O,O,O,O)dizinc(II)] dihydrate, C40H28Zn2N8O9
- The crystal structure of 4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, C11H13Cl2NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of-(10S,13S,16R,Z) −17-ethylidene-16-hydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3 H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one, C21H32O2
- The crystal structure of catena-((μ 2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ 2 N:N′)-bis(4-fluorobenzoato-κ1O)-copper(II)), C24H16F2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(ethylenediamine-κ2 N,N′)-μ-tetraoxomolybdato(VI) zinc(II)], C2H8MoN2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid, C4H3ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of bepotastine besilate, C27H31ClN2O6S
- The crystal structure of (η 6-p-cymene)benzyldiphenylphosphine-diiodido-ruthenium(II) dichloromethane solvate
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4- (imidazol-1′-yl-methyl)benzene κ 2 N:N′)-(μ 2-3-nitrobenzene -1,2-dicarboxylato-k4,O,O′:O′′,O′′′]zinc(II)-κ 2, C21H15N5O6Zn
- The crystal structure of (2R,4S)-5-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-2-methyl pentanoic acid, C23H29NO4
- The crystal strucure of [2,2′-{1,2-phenylenebis [(azanylylidene)methanylylidene]}bis(4-fluorophenolato)-κ4 N,N′,O,O′] nickel(II) N, N-dimethylformamide solvate, C23H19F2N3NiO3
- The structure of (E)-6-(cyclopropylmethyl)-11-(2,2-difluoropropylidene)-2-methyl-6, 11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C21H21F2NO2S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-(2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzyl)-1H-imidazole κ2N:N′)- (μ 2-cyclohexane-1,2-dicarboxylato κ2O,O′)cobalt(II) monohydrate]
- The crystal structure of 3,5,7-trinitro-1,3,5,7-oxatriazocane
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato-κ3 O,O′:O′′)(μ2-1-[(2-propyl-1H-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-k2 N:N′)silver(I)], C17H17AgN6O3
- The crystal structure of (5-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)-2-sulfanylidene-1,3,4-oxadiazol-3(2H)-yl)(3-methylphenyl)methanone, C18H14N2O4S
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O]-cobalt(II), C11H11Co0.5N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)-N-(4-morpholinophenyl)propanamide, C24H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of sodium methylsulfonate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(isothiocyanate κ 1 N)-(μ 2-3,3ʹ-methylenebis(1-methyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazole-2-thione)-κ 2 S:S′)-cobalt(II)], C11H12CoN6S4
- The crystal structure of {hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ 1N)nickel(II)} (μ 2-oxo)-hexaoxido-di-molybdenum(VI)─1-methyl-1H-imidazole (1/2), C32H48NiMo2N16O7
- 6-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3′,6′-tris(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C62H38N5O4P
- The crystal structure of R-2′-amino-N-methyl-N-(1-phenylethyl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxamide, C22H22N2O
- The crystal structure of bis{tetrakis(n-butyl)(μ-hydroxy)(2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoate) (μ 3 -oxo)ditin(IV)}
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ 2(3,4-dimethylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O:O′)-(3,6-bis(4′-pyridyl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine-κ 1 N)zinc(II)], C22H16N6O5S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-5-cyano–N-(5-(cyanomethyl)quinolin-8-yl)pentanamide, C19H15BrN4O
- The crystal structure of bis(tetramethylammonium) (di-μ2-aqua)hexaaqua-dibarium(II)) decavanadate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(bis(μ 2-chlorido)- (μ 2-4′-(pyridin-4-yl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine–N′, N″, N‴:N″″) -chlorido-dicopper(I,II)) monohydrate, C20H16N4OCl3Cu2
- Crystal structure of spiropachysine, C31H46N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 2 N: O)-(μ 2-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 3-3-bromoisonicotinato-κ 3 N: O: O′)-(μ 2-nitrite-κ 3 O: O′: O″)dicadmium(II) monohydrate], C19H12Br3Cd2N3O9
- The crystal structure of 2-acetylpyridine-ortho-fluoro-phenylhydrazone, C14H12FN3O
- The crystal structure of poly(triaqua-(m 2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 2 O:O′)-bis(m 2-2-2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-K 4 O,O′:O″:O‴)dierbium(III)) hydrate, C36H26Er2N6O16
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(phenazine-5,10-diyl)bis(heptan-1-one), C26H34N2O2
- The crystal structure of (4-([2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridin]-4′-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C21H16BN3O2
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazine-5,7(6H)-dione, C6H3N3O3
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide ethanol solvate, C23H30N2O4
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis[1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-K2 O,O′]lutetium(III) C20F12H16LuO8C5H6N
- Crystal structure of dichlorido–tetrakis{3-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylpentan-3-ol-k 1N}cobalt(II), C64H88O4N12Cl6Co
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(4-allyl-2-methoxyphenyl nicotinato-k 1 N)bis(thiocyanato-k 1 N)cobalt(II)
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H21Cl2NO3
- The crystal structure of (E)–N-(4-chlorobenzylidene)(4-chlorophenyl)methanamine, C14H11Cl2N
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-ethylbenzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H22O4
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-3-nitro-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylic acid dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C4H2N3O4⋅C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of-(1S,4aR,5S)-5,6,7-trihydroxy-8-isopropyl-1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5,10,11,11a-octahydro-4a,1-(epoxymethano)dibenzo[a,d][7]annulen-13-one C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 7,9-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4-propylbenzo[f]isoquinolin-5-yl 4-bromobenzoate, C26H24BrNO4
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylbutanaminium)tridecathiotrimolybdate(2−), (BuMe3N)2[Mo3S13]
- Crystal structure of N-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-methylpiperazine-1-carbothioamide, C16H27N3S
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2,2′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylenesulfanediyl)]dibenzoato-κ 4 O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ 2-1,1′-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-benzimidazole)-κ 2 N:N′)cadmium(II)]dimethylformamide solvate, C51H41N5O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,2′-pyran]-3-one, C19H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-cyanobenzyl)-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C20H15N3
- Crystal structure of (1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C22H22BrO2P
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrachloridomanganese(II)
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxyphenyl)-4,6-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine, C33H39N3O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(5-carboxypyridine-2-carboxylate-κ 2N,O)(2,5-pyridine-dicarboxylate-κ 4O,O′:N:O″)bismuth(III)], C14H9BiN2O9
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-fluoro-4-(2-(phenylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C14H11FO2S
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-amino-3-chloro-4-methoxybenzoate, C9H10ClNO3

