To the Editor,
Primary hyperparathyroidism (PHP), the excretion of abnormal amounts of parathyroid hormone (PTH) relative to serum calcium levels, is most often caused by parathyroid adenoma (80–85% of cases) [1]. When indicated, surgery remains the only curative intervention for PHP [2]. When performed by an experienced surgeon, cure rates are high and may approach 100% [3]. Intraoperative PTH measurements are a cornerstone in the surgical strategy for PHP [4]. Although multiple criteria for success have been defined (reviewed in [4]), fast PTH measurements are required for optimal use. This optimal use may not stem from patient outcome, as this is similar for fast and standard-length PTH assays in patients with monoglandular disease [5], but on reduced time in the operation theatre [6]. Also, one may hypothesise that patients suffering from causes other than monoglandular forms of hyperparathyroidism will benefit from fast turnaround times as the surgeon will be able to act faster to a lack of decrease in PTH.
Typically, decay in PTH is measured and timing is set to 10–20 min after resection. At this moment, only few marketed options are widely available [7]. Abbott’s Architect, Siemens Advia Centaur and Beckman’s Access intact PTH assays are available but have relatively long incubation times (time-to-result: 18 min). Also, these machines are commonly found in the core laboratory and thus necessitate sample transport. Shorter incubation times can be achieved using Roche’s Elecsys (time-to-result: 9) which is commonly found in the core laboratory and Future Diagnostics’ point-of-care IO-PTH package which can be brought up to the patient’s bedside (time-to-result: 8 min).
Here, we describe a modified intact PTH measurement protocol with shorter incubation times that can be implemented on IDS’s ISYS automated immunoassay platform (IDS, Boldon, UK). The standard incubation times (first, 26 min and s, 10 min) were shortened to 7 min and 3 min, respectively. This protocol was compared to the standard protocol in left-over samples from routine measurements (n=71) as well as samples collected during parathyroid surgery (n=51) of patients suffering from PHP. Ultimately, measurements of both the non-modified (IVD) and modified (LDT) assays were compared to results from a Future Diagnostics IO-PTH analyser (Future Diagnostics, Wijchen, The Netherlands) as well as a third-generation PTH assay on a Fujirebio Lumipulse G1200 analyser (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan).
Measurement variation of the LDT was CV 9.5% (mean 5.5 pM) and CV 6.7% (mean 105.5 pM), in 21 separate runs. This was comparable to the CV% found for other IO-PTH platforms [7]. Measurement uncertainty of the IVD assay was CV 6.7% at 6.5 pM and CV 8.0% at 119.0 pM. Long-term measurement uncertainty of the FD assay was not assessed by retrospective analysis as each kit comes with new controls. From the literature, it was derived that the intra-assay CV% is 23.5% for this platform [7]. Measurement uncertainty of the Lumipulse assay was CV 4.9% (mean 2.1 pM) and CV 6.7% (mean 40.4 pM), in 24 separate runs.
In leftover samples, a small proportional bias was found between IVD and LDT assays (β=97%, 95% CI 96–99%, Figure 1A). Also, a small absolute bias (α=0.3 pM, 95% CI 0.1–0.4 pM) was found. Both findings were most likely due to the fact that the IVD and LDT assays were run on different machines, and the magnitude of bias was deemed clinically irrelevant as it fell well within the intermediate precision of the IVD assay. In surgical patient samples, a similar proportional bias was seen (β=96%, 95% CI 92–99%, Figure 1B) in addition to a small absolute bias (α=−0.5 pM, 95% CI −0.8 to −0.1 pM). Together, these data show that the IDS-ISYS LDT can be used interchangeably with the IVD assay.

Parathyroid hormone (PTH) measured using IDS-ISYS employing the manufacturer provided protocol (X-axis) vs. an adapted protocol (Y-axis). Adaptation was based in shortening the incubation steps from 26 and 10 min to 7 and 3 min, respectively.
(A) PTH measured in left over samples of non-surgical patients. (B) PTH measured in left over samples of patients during parathyroid surgery.
Taking these data, we used the LDT as the standard and compared outcomes, both absolute and relative, to a dedicated IO-PTH platform (FD). When comparing absolute data, a significant proportional bias was seen (β=271%, 95% CI 234–308%, data not shown), which was expected from previous findings by others [8]. Also, we found an absolute bias (α=2.5 pM, –3.3 pM, data not shown). These data prevent the use of the IDS-ISYS LDT and FD assays interchangeably.
Based on these data, we tested whether the LDT would result in similar outcomes in terms of percentage decrease in PTH when compared to the IVD. As expected, when expressed as %decrease of PTH in time, the IVD and LDT produce similar results. The proportional bias was significant (β=101%, 95% CI 100–101%, Figure 2A) but deemed irrelevant given its magnitude. No absolute bias was found (α=2%, 95% CI 0–3%).
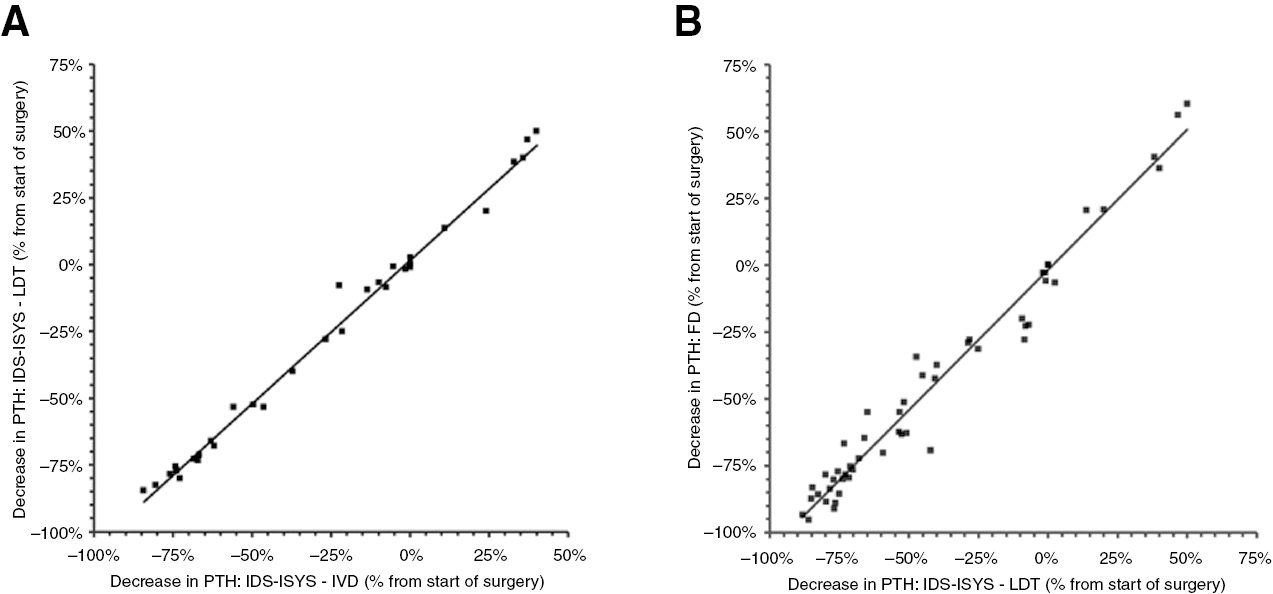
Decrease in parathyroid hormone (PTH) during parathyroid surgery.
(A) PTH was measured using IDS-ISYS employing the manufacturer provided protocol (X-axis) vs. an adapted protocol (Y-axis). (B) PTH was measured using IDS-ISYS employing the adapted protocol (X-axis) vs. measurement of PTH on a dedicated intra-operative PTH measurement platform (Future Diagnostics IO-PTH (Y-axis). Adaptation of the IDS-ISYS protocol was based in shortening the incubation steps from 26 and 10 min to 7 and 3 min, respectively.
Finally, we used the LDT to predict outcome of the FD assay. Although the absolute results of the assays were different, the results of the LDT and FD assay were similar in terms of %decrease in PTH. No proportional bias was found (β=105%, 95% CI 100–110%, Figure 2B). Also, no absolute bias was found (α=−2%, 95% CI −4% to 0%).
Given the nature of the disease and intervention performed, it is reduction in production of PTH and not reduction in circulating fragment concentration that causes the decrease in PTH concentration. This was confirmed by measuring PTH in all samples using a third-generation PTH assay which specifically measures PTH1-84, the mature hormone released by the parathyroid gland. As hypothesised, the decrease in PTH seen with the third-generation assay was similar to the decrease in the LDT; there was no proportional (β=102%, 95% CI 93–110%, data not shown) or absolute bias (α=−8%, 95% CI −11 to 3%, data not shown). We must, however, keep in mind that our study only included patients with PHP. Comparability of results between platforms may differ in patients with reduced kidney function and accompanied impairments of PTH fragments when using second- (but not third-) generation PTH assays [9].
Together, these data show that an incubation time-modified IDS-ISYS intact PTH can be used for intraoperative PTH measurements in patients suffering from PHP. The modified IDS assay had no bias when compared to the IDS IVD assay in samples collected randomly or during parathyroid surgery, and equal measurement uncertainty. Also, estimation of fractional decrease in PTH and thereby clinical interpretation of results during surgery were similar using the LDT when compared to both a dedicated STAT IO-PTH platform.
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
Research funding: None declared.
Employment or leadership: None declared.
Honorarium: None declared.
Competing interests: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
1. Parnell KE, Oltmann SC. The surgical management of primary hyperparathyroidism: an updated review. Int J Endocr Oncol 2018;5:IJE07.10.2217/ije-2017-0019Suche in Google Scholar
2. Bilezikian JP, Brandi ML, Eastell R, Silverberg SJ, Udelsman R, Marcocci C, et al. Guidelines for the management of asymptomatic primary hyperparathyroidism: summary statement from the fourth international workshop. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014;99:3561–9.10.1210/jc.2014-1413Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Udelsman R, Lin Z, Donovan P. The superiority of minimally invasive parathyroidectomy based on 1650 consecutive patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Ann Surg 2011;253:585–91.10.1097/SLA.0b013e318208fed9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Patel KN, Caso R. Intraoperative parathyroid hormone monitoring. Optimal utilization. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 2016;25:91–101.10.1016/j.soc.2015.08.005Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Sokoll LJ, Donovan PI, Udelsman R. The national academy of clinical biochemistry laboratory medicine practice guidelines for intraoperative parathyroid hormone. Point Care 2007;6:253–60.10.1097/poc.0b013e3181126ef1Suche in Google Scholar
6. Terris DJ, Weinberger PM, Farrag T, Seybt M, Oliver JE. Restoring point-of-care testing during parathyroidectomy with a newer parathyroid hormone assay. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011;145:557–60.10.1177/0194599811413718Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Chen L-S, Singh RJ. Niche point-of-care endocrine testing – Reviews of intraoperative parathyroid hormone and cortisol monitoring. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 2018;55:115–28.10.1080/10408363.2018.1425975Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Sturgeon CM, Sprague S, Almond A, Cavalier E, Fraser WD, Algeciras-Schimnich A, et al. Perspective and priorities for improvement of parathyroid hormone (PTH) measurement – A view from the IFCC Working Group for PTH. Clin Chim Acta 2017;467:42–7.10.1016/j.cca.2016.10.016Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Cavalier E, Schleck ML, Souberbielle JC. Spurious intraoperative PTH results observed with 2nd, but not with 3rd generation PTH assays. Clin Chim Acta 2018;477:72–3.10.1016/j.cca.2017.12.012Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
©2020 Sjoerd A.A. van den Berg et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Editorial
- Biotin interference in cardiac troponin immunoassay – where the wild things are?
- Review
- Laboratory-related issues in the measurement of cardiac troponins with highly sensitive assays
- Mini Review
- Chromatographic methods development for clinical practice: requirements and limitations
- Opinion Paper
- Harmonising EQA schemes the next frontier: challenging the status quo
- Genetics and Molecular Diagnostics
- Direct comparison study between droplet digital PCR and a combination of allele-specific PCR, asymmetric rapid PCR and melting curve analysis for the detection of BRAF V600E mutation in plasma from melanoma patients
- A novel mitochondrial m.14430A>G (MT-ND6, p.W82R) variant causes complex I deficiency and mitochondrial Leigh syndrome
- Obesity status modifies the association between rs7556897T>C in the intergenic region SLC19A3-CCL20 and blood pressure in French children
- General Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine
- Influence of reagent lots and multiple measuring systems on estimating the coefficient of variation from quality control data; implications for uncertainty estimation and interpretation of QC results
- Electrophoretic α1-globulin for screening of α1-antitrypsin deficient variants
- A continued method performance monitoring approach for the determination of pediatric renin samples – application within a European clinical trial
- Pilot study for cystic fibrosis neonatal screening: the Cuban experience
- Validation of the analytical performance of the NOVEOS™ System, a system which improves upon the third-generation in vitro allergy testing technology
- IgE cross-reactivity measurement of cashew nut, hazelnut and peanut using a novel IMMULITE inhibition method
- Sexual dimorphism in the cerebrospinal fluid total protein content
- Current state of the morphological assessment of urinary erythrocytes in The Netherlands: a nation-wide questionnaire
- Reference Values and Biological Variations
- Within-subject and between-subject biological variation of first morning void urine amino acids in 12 healthy subjects
- Proenkephalin as a new biomarker for pediatric acute kidney injury – reference values and performance in children under one year of age
- Hematology and Coagulation
- Quality performance for indirect Xa inhibitor monitoring in patients using international external quality data
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Clinical risk assessment of biotin interference with a high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T assay
- Short- and long-term biological variation of cardiac troponin I in healthy individuals, and patients with end-stage renal failure requiring haemodialysis or cardiomyopathy
- Infectious Diseases
- Monocyte distribution width (MDW) as a screening tool for sepsis in the Emergency Department
- Performance of a Toxo IgM prototype assay for the diagnosis of maternal and congenital Toxoplasma infections
- Letters to the Editors
- Evaluation of an ELISA for SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing: clinical performances and correlation with plaque reduction neutralization titer
- Preliminary evaluation of Roche Cobas Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 chemiluminescence immunoassay
- Hypoalbuminemia and elevated D-dimer in COVID-19 patients: a call for result harmonization
- Total pathway to method validation
- Derivation of performance specifications for uncertainty of serum C-reactive protein measurement according to the Milan model 3 (state of the art)
- FGF23 measurement in burosumab-treated patients: an emerging treatment may induce a new analytical interference
- Use of a modified IDS-ISYS intact PTH assay for intraoperative PTH measurements
- Agreement of dried blood spot lyso-Gb3 concentrations obtained from different laboratories in patients with Fabry disease
- Influence of delayed separation of plasma from whole blood and centrifugation protocol on Zn plasma concentration
- A survey of order of draw on inpatient wards and adherence to EFLM-COLABIOCLI recommendations
- Successful implementations of automated minimum re-test intervals to overcome ferritin over-requesting in a Spanish hospital laboratory
- Remarkable pseudoleucocytosis induced by mild cryoglobulinemia
- Massive hemolysis due to Clostridium perfringens: a laboratory’s perspective
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Editorial
- Biotin interference in cardiac troponin immunoassay – where the wild things are?
- Review
- Laboratory-related issues in the measurement of cardiac troponins with highly sensitive assays
- Mini Review
- Chromatographic methods development for clinical practice: requirements and limitations
- Opinion Paper
- Harmonising EQA schemes the next frontier: challenging the status quo
- Genetics and Molecular Diagnostics
- Direct comparison study between droplet digital PCR and a combination of allele-specific PCR, asymmetric rapid PCR and melting curve analysis for the detection of BRAF V600E mutation in plasma from melanoma patients
- A novel mitochondrial m.14430A>G (MT-ND6, p.W82R) variant causes complex I deficiency and mitochondrial Leigh syndrome
- Obesity status modifies the association between rs7556897T>C in the intergenic region SLC19A3-CCL20 and blood pressure in French children
- General Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine
- Influence of reagent lots and multiple measuring systems on estimating the coefficient of variation from quality control data; implications for uncertainty estimation and interpretation of QC results
- Electrophoretic α1-globulin for screening of α1-antitrypsin deficient variants
- A continued method performance monitoring approach for the determination of pediatric renin samples – application within a European clinical trial
- Pilot study for cystic fibrosis neonatal screening: the Cuban experience
- Validation of the analytical performance of the NOVEOS™ System, a system which improves upon the third-generation in vitro allergy testing technology
- IgE cross-reactivity measurement of cashew nut, hazelnut and peanut using a novel IMMULITE inhibition method
- Sexual dimorphism in the cerebrospinal fluid total protein content
- Current state of the morphological assessment of urinary erythrocytes in The Netherlands: a nation-wide questionnaire
- Reference Values and Biological Variations
- Within-subject and between-subject biological variation of first morning void urine amino acids in 12 healthy subjects
- Proenkephalin as a new biomarker for pediatric acute kidney injury – reference values and performance in children under one year of age
- Hematology and Coagulation
- Quality performance for indirect Xa inhibitor monitoring in patients using international external quality data
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Clinical risk assessment of biotin interference with a high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T assay
- Short- and long-term biological variation of cardiac troponin I in healthy individuals, and patients with end-stage renal failure requiring haemodialysis or cardiomyopathy
- Infectious Diseases
- Monocyte distribution width (MDW) as a screening tool for sepsis in the Emergency Department
- Performance of a Toxo IgM prototype assay for the diagnosis of maternal and congenital Toxoplasma infections
- Letters to the Editors
- Evaluation of an ELISA for SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing: clinical performances and correlation with plaque reduction neutralization titer
- Preliminary evaluation of Roche Cobas Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 chemiluminescence immunoassay
- Hypoalbuminemia and elevated D-dimer in COVID-19 patients: a call for result harmonization
- Total pathway to method validation
- Derivation of performance specifications for uncertainty of serum C-reactive protein measurement according to the Milan model 3 (state of the art)
- FGF23 measurement in burosumab-treated patients: an emerging treatment may induce a new analytical interference
- Use of a modified IDS-ISYS intact PTH assay for intraoperative PTH measurements
- Agreement of dried blood spot lyso-Gb3 concentrations obtained from different laboratories in patients with Fabry disease
- Influence of delayed separation of plasma from whole blood and centrifugation protocol on Zn plasma concentration
- A survey of order of draw on inpatient wards and adherence to EFLM-COLABIOCLI recommendations
- Successful implementations of automated minimum re-test intervals to overcome ferritin over-requesting in a Spanish hospital laboratory
- Remarkable pseudoleucocytosis induced by mild cryoglobulinemia
- Massive hemolysis due to Clostridium perfringens: a laboratory’s perspective


