Abstract
C13H19NO2, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 5.2692(3) Å, b = 13.8663(9) Å, c = 17.8020(13) Å, β = 93.323(6)°, V = 1298.50(15), Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0590, wRref(F2) = 0.1932, T = 293 K.
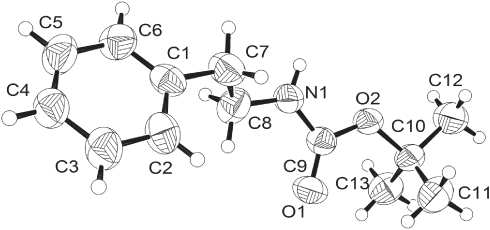
The asymmetric unit of the title structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless needle Size 0.57 × 0.18 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.8 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 59.8°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 6696, 3146, 0.022 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1985 |
| N(param)refined: | 186 |
| Programs: | SHELX [14], CrysAlisPRO [15], WinGX [16] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | −0.1282(3) | 0.15249(12) | −0.02887(9) | 0.0674(5) |
| O2 | 0.1718(2) | 0.24524(10) | 0.03205(8) | 0.0595(4) |
| C1a | 0.3832(2) | −0.01016(10) | −0.21915(8) | 0.056(2) |
| C2a | 0.1667(2) | −0.00308(10) | −0.26730(8) | 0.0677(17) |
| H2a | 0.0548 | 0.0481 | −0.2625 | 0.081* |
| C3a | 0.1176(2) | −0.07251(10) | −0.32257(8) | 0.0730(16) |
| H3a | −0.0272 | −0.0678 | −0.3548 | 0.088* |
| C4a | 0.2850(2) | −0.14901(10) | −0.32968(8) | 0.0682(17) |
| H4a | 0.2521 | −0.1955 | −0.3667 | 0.082* |
| C5a | 0.5015(2) | −0.15610(10) | −0.28153(8) | 0.0739(17) |
| H5a | 0.6134 | −0.2073 | −0.2863 | 0.089* |
| C6a | 0.5506(2) | −0.08667(10) | −0.22626(8) | 0.0676(17) |
| H6a | 0.6954 | −0.0914 | −0.1940 | 0.081* |
| C7a | 0.4229(17) | 0.0638(8) | −0.1572(5) | 0.070(3) |
| H7Aa | 0.6014 | 0.0643 | −0.1405 | 0.084* |
| H7Ba | 0.3815 | 0.1270 | −0.1777 | 0.084* |
| C8a | 0.2677(7) | 0.0468(3) | −0.0900(2) | 0.070(3) |
| H8Aa | 0.0906 | 0.0388 | −0.1068 | 0.084* |
| H8Ba | 0.3242 | −0.0121 | −0.0649 | 0.084* |
| C1Ab | 0.3508(7) | −0.0104(3) | −0.2191(2) | 0.055(3) |
| C2Ab | 0.1686(7) | −0.0229(3) | −0.2779(2) | 0.068(2) |
| H2Ab | 0.0330 | 0.0198 | −0.2839 | 0.082* |
| C3Ab | 0.1890(7) | −0.0994(3) | −0.3277(2) | 0.078(2) |
| H3Ab | 0.0671 | −0.1078 | −0.3670 | 0.093* |
| C4Ab | 0.3917(7) | −0.1633(3) | −0.3186(2) | 0.075(2) |
| H4Ab | 0.4053 | −0.2145 | −0.3519 | 0.090* |
| C5Ab | 0.5739(7) | −0.1508(3) | −0.2598(2) | 0.087(2) |
| H5Ab | 0.7095 | −0.1936 | −0.2538 | 0.105* |
| C6Ab | 0.5535(7) | −0.0743(3) | −0.2100(2) | 0.076(2) |
| H6Ab | 0.6754 | −0.0660 | −0.1707 | 0.091* |
| C7Ab | 0.349(2) | 0.0737(9) | −0.1667(6) | 0.064(3) |
| H7A1b | 0.5195 | 0.1005 | −0.1611 | 0.076* |
| H7A2b | 0.2380 | 0.1231 | −0.1887 | 0.076* |
| C8Ab | 0.2655(13) | 0.0486(4) | −0.0927(4) | 0.066(4) |
| H8A1b | 0.0885 | 0.0292 | −0.0980 | 0.080* |
| H8A2b | 0.3630 | −0.0064 | −0.0738 | 0.080* |
| C9 | 0.0918(4) | 0.17255(14) | −0.01289(11) | 0.0506(5) |
| C10 | −0.0073(4) | 0.30852(16) | 0.06855(12) | 0.0579(5) |
| C11 | −0.1721(5) | 0.36138(18) | 0.01000(16) | 0.0782(7) |
| H11A | −0.0665 | 0.3920 | −0.0251 | 0.117* |
| H11B | −0.2708 | 0.4093 | 0.0341 | 0.117* |
| H11C | −0.2840 | 0.3164 | −0.0162 | 0.117* |
| C12 | 0.1684(5) | 0.3775(2) | 0.11144(18) | 0.0922(10) |
| H12A | 0.2756 | 0.3423 | 0.1472 | 0.138* |
| H12B | 0.0698 | 0.4237 | 0.1374 | 0.138* |
| H12C | 0.2718 | 0.4105 | 0.0770 | 0.138* |
| C13 | −0.1626(5) | 0.25076(18) | 0.12148(14) | 0.0718(7) |
| H13A | −0.2796 | 0.2101 | 0.0928 | 0.108* |
| H13B | −0.2556 | 0.2939 | 0.1519 | 0.108* |
| H13C | −0.0514 | 0.2116 | 0.1533 | 0.108* |
| N1 | 0.2909(3) | 0.12580(13) | −0.03773(10) | 0.0613(5) |
| H1 | 0.4407 | 0.1437 | −0.0217 | 0.074* |
aOccupancy: 0.558(8); bOccupancy: 0.442(8).
Source of material
tert-Butyl 2-phenylethylcarbamate was synthesized from the reaction of 2-phenylethylamine with 1.2 equivalents of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate in the presence of 1.5 equivalents of triethylamine in dichloromethane at 0 °C for 15 minutes and then under reflux for 1 h. The crude product was purified by crystallization from hexane to give the title compound (90%) as colourless crystals, mp 56–57 °C (lit. 56.1–56.4 °C [1]; 54–55 °C [2]; 55–56 °C [3]).
Experimental details
The methylbenzene segment of the molecule is disordered and was refined with the occupancies 56(1)% and 44(1)%. The aromatic ring was constrained into a regular hexagon with C—C distances of 1.39 Å. All H atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined using a riding model. For the methyl groups, C—H bonds were fixed at 0.96 Å and Uiso(H) set to 1.5Ueq(C) with free rotation around the C—C bond. For the rest of the hydrogens, Uiso(H) was set to 1.2Ueq(C) with aromatic C—H and N—H distances of 0.93 and 0.86 Å, respectively.
Discussion
Various carbamate and thiocarbamate derivatives show antimicrobial activities [4], [5], [6] and various synthetic procedures have been reported for the production of carbamates. Convenient and efficient syntheses involve reactions of amino acids with Boc-benzotriazoles in the presence of triethylamine in aqueous acetonitrile at room temperature [7], of amines with phenyl 4,5-dichloro-6-oxopyridazine-1(6H)-carboxylate in tetrahydrofuran (THF) at room temperature [8], of nitriles with an excess of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate in the presence of a catalytic amount of nickel boride in methanol at room temperature [9], of aromatic carboxylic acids with di-tert-butyl dicarbonate in the presence of sodium azide, tetrabutylammonium bromide and zinc(II) trifluoromethanesulfonate in THF at 40 °C [10] and of nitro aromatics with excess chloroformates in the presence of zinc and ammonium chloride in aqueous THF at 0 °C [11]. High yields of substituted derivatives can be produced from regioselective lithiation of aryl carbamates using lithium reagents, at room temperature, followed by treatment of the lithium intermediates obtained in situ with electrophiles [12], [13].
The asymmetric unit of the title structure consists of one molecule with a disordered benzyl fragment. All bond lengths and angles are in the expected ranges. In the crystal structure, the amide group is involved in a N—H⋯O hydrogen bond (N⋯O distance = 3.078(2)Å, N—H⋯O angle = 153.3°) leading to the formation of C(4) chains along [100].
Acknowledgements:
The authors extend their appreciation to the College of Applied Medical Sciences Research Centre and the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for their funding of this research.
References
1. Hanada, S.; Yuasa, A.; Kuroiwa, H.; Motoyama, Y.; Nagashima, H.: Hydrosilanes are not always reducing agents for carbonyl compounds, II: Ruthenium-catalyzed deprotection of tert-butyl groups in carbamates, carbonates, esters, and ethers. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 6 (2010) 1021–1025.10.1002/ejoc.200901279Search in Google Scholar
2. Chong, P. Y.; Janicki, S. Z.; Petillo, P. A.: Multilevel selectivity in the mild and high-yielding chlorosilane-induced cleavage of carbamates to isocyanates. J. Org. Chem. 63 (1998) 8515–8521.10.1021/jo981816+Search in Google Scholar
3. Baumgarten, H. E.: Reactions of amines. XVIII. The oxidative rearrangement of amides with lead tetraacetate. J. Org. Chem. 40 (1975) 3554–35561.10.1021/jo00912a019Search in Google Scholar
4. Krátký, M.; Volková, M.; Novotná, E.; Trejtnar, E.; Stolaříková, J.; Vinšová, J.: Synthesis and biological activity of new salicylanilide N,N-disubstituted carbamates and thiocarbamates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 22 (2014) 4073–4082.10.1016/j.bmc.2014.05.064Search in Google Scholar
5. Blaser, A.; Palmer, B. D.; Sutherland, H. S.; Kmentova, I.; Franzblau, S. G.; Wan, B.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Thompson, A. M.; Denny, W. A.: Structure–activity relationships for amide-, carbamate-, and urea-linked analogues of the tuberculosis drug (6S)-2-nitro-6-{[4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzyl]oxy}-6,7-dihydro-5H-imidazo[2,1-b][1, 3]oxazine (PA-824). J. Med. Chem. 55 (2012) 312–326.10.1021/jm2012276Search in Google Scholar
6. Yang, Y. H.; Voak, A.; Wilkinson, S. R.; Hu, L. Q.: Design, synthesis, and evaluation of potential prodrugs of DFMO for reductive activation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 22 (2012) 6583–6586.10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.09.005Search in Google Scholar
7. Ibrahim, T. S.; Tala, S. R.; El-Feky, S. A.; Abdel-Samii, Z. K.; Katritzky, A. R.: Benzotriazole reagents for the syntheses of Fmoc-, Boc-, and Alloc-protected amino acids. Synlett. 14 (2011) 2013–2016.10.1055/s-0030-1261160Search in Google Scholar
8. Lee, H.-G.; Kim, M.-J.; Park, S.-E.; Kim, J.-J.; Lee, S.-G.; Yoon, Y.-J.: Phenyl 4,5-dichloro-6-oxopyridazine-1(6H)-carboxylate as carbonyl source: Facile and selective synthesis of carbamates and ureas under mild conditions. Synlett. 17 (2009) 2809–2814.10.1002/chin.201009081Search in Google Scholar
9. Caddick, S.; Judd, D. B.; Lewis, A. K. de K.; Reich, M. T.; Williams, M. R. V.: A generic approach for the catalytic reduction of nitriles. Tetrahedron 59 (2003) 5417–5423.10.1016/S0040-4020(03)00858-5Search in Google Scholar
10. Lebel, H.; Leogane, O.: Curtius rearrangement of aromatic carboxylic acids to access protected anilines and aromatic ureas. Org. Lett. 8 (2006) 5717–5720.10.1021/ol0622920Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Porzelle, A.; Woodrow, M. D.; Tomkinson, N. C. O.: Facile procedure for the synthesis of N-aryl-N-hydroxy carbamates. Synlett. 5 (2009) 798–802.10.1055/s-0028-1087943Search in Google Scholar
12. Smith, K.; El-Hiti, G. A.; Alshammari, M. B.: Directed lithiation of N′-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl)-N,N-dimethylurea and tert-butyl (2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl)carbamate. Synthesis 46 (2014) 394–402.10.1055/s-0033-1338570Search in Google Scholar
13. Smith, K.; El-Hiti, G. A.; Alshammari, M. B.: Variation in the site of lithiation of 2-(2-methylphenyl)ethanamine derivatives. J. Org. Chem. 77 (2012) 11210–11215.10.1021/jo3023445Search in Google Scholar PubMed
14. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
15. Agilent. CrysAlisPRO. Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England, 2014.Search in Google Scholar
16. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
©2016 Gamal A. El-Hiti et al., published by De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of the catena-poly-[bis(μ2-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl-κN)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] 5.5 hydrate, C32H44N6NiO11F2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-[(μ2-2-(2-((2,6-dimethylphenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2-(2-((2,6-dimethylphenyl)amino)phenyl)acetate-κ3O,O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C28H20N2Cl4O4Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(pyridin-4-yl)-isophthalate-κ2O, O′)cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C13H11NO5Cl2Cd
- Crystal structure of poly-{[μ2-(E)-1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)but-2-ene-κ2N:N′][μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′]nickel(II)}, C18H22N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of aqua (5,5′-dicarboxy-(1,1′-biphenyl)-2,3′-dicarboxylato-κO) bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)cadmium monohydrate, C40H28CdN4O10
- Crystal structure of 5-methoxy-N′-[(3Z)-5-chloro-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3-ylidene]-1H-indole-2-carbohydrazide-DMSO (1/1), C25H18ClFN4O3 · C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of 5-methoxy-N′-[(3Z)-1-benzyl-5-fluoro-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3-ylidene]-1H-indole-2-carbohydrazide-DMSO (1/1), C27H25FN4O4S
- Crystal structure of poly-[bis{μ2-N-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-N-phenylaniline-κ2N:N′)}-(μ2-naphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylato)-(μ4-naphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylato)dicadmium(II)], C36H25N5O4Cd
- Crystal structure of 1-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-(4-bromophenyl)thiourea, C17H21BrN2S
- Crystal structure of N′-[(1E)-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-methylidene]adamantane-1-carbohydrazide, C18H20Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-5′-([2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridin]-4′-yl)-[1,1′:3′,1′′-terphenyl]-4,4′′-dicarboxylate-κ3N,N′,N′′}zinc(II), C39H31Cl2N3O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,3,5,7-tetraoxo-3a,4,4a,5,7,7a,8,8a-octahydro-4,8-ethenopyrrolo [3,4-f]isoindole-2,6(1H,3H)-diyl)dibenzoic acid, C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-ethyl oxime, C17H16Cl2N2O2
- The crystal structure of diaqua-(N-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzyl)iminodiacetato-κ4-N,O,O′,O′′)chromium(III) based on synchrotron data, C11H13CrN2O9
- Crystal structure of ethyl 5-amino-3-(methylthio)-1-(1-phenyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C21H19N5O3S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C17H16Br2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dibromido μ-oxalato-κ2O,O′:κ2O′′,O′′′−η6-p-cymenediosmium(II), C22H28Br2O4Os2
- Crystal structure of 2-(bromomethyl)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-tosylpyrrolidine, C18H19BrClNO2S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione; C13H11FN2O3
- Crystal structure of diethylammonium 1,3-dimethyl-2,4,6-trioxohexahydropyrimidin-5-ide, C10H19N3O3
- Crystal structure of 1,1-dimethyl-3-(2-phenylethyl)urea, C11H16N2O
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-thiazolo[4,5-b]pyridine, C13H10N2OS
- Crystal structure of 3-tert-butyl-7-azadioxindole, C11H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-ferrocenyl-6-bromopyrene, C26H17BrFe
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carbothioamide, C16H13BrFN3S
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,5-ditrifluoromethylphenyl)-3-cyano-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4H-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyran, C20H16F6N2O2
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13N3O4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2, 4-dichlorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H12Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-chlorido)-bis(di-p-tolylhydroxyphosphine-κP)-bis(di-p-tolylphosphite-κP)dipalladium(II), C56H58Cl2O4P4Pd2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-methyl-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ2-O,N)cadmium(II) tetrahydrate, C12H22CdN4O14
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5-nitrosalicylato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II), C19H13CuN3O6
- Crystal structure of bis(4-(2-phenylpropan-2-yl)phenyl)amine, C30H31N
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16F2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H11F3N2O2
- Crystal structure of an isomeric bis[(η5:η1-6,6-di-p-tolylpentafulvene)(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)titanium(III)]-μ2,η1:η1-dinitrogen complex, C60H66N2Ti2
- Crystal structure of 3,4-dinitropyrazole, C3H2N4O4
- Crystal structure of (4-vinylpyridine-κN)triphenyl tin(IV) chloride, C25H22ClNSn
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl 2-phenylethylcarbamate, C13H19NO2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-((E)-(4-chlorobenzyli-dene)hydrazono)-1-p-tolylpyrrolidine-3-carbonitrile, C19H17ClN4
- Crystal structure of bis(biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)dizinc(II)2.5 hydrate, C62H57N6Zn2O16.5F2
- Crystal structure of dichloridobis{μ2-2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-chlorophenolato)-κ5O,N,N′,O′:O′}diiron(III), C32H24Cl6Fe2N4O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((4,4-dimethyl-2, 6-dioxocyclohexylidine)methylamino)-N-(3,4-dimethylisoxazol-5-yl)benzenesulfonamide, C20H23N3O5S
- Crystal structure of poly-[aqua-μ2-aqua-μ2-(4,4′-oxybis(benzoato)-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)], C14H12O7Cd
- Crystal structure of aqua(μ2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ3O,O′:O′′)-(μ2-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)cadmium(II) 1.5 hydrate, C62H60N6Cd2O19F2
- Crystal structure of dimethanolo-bis[μ-(2-(2-(5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)phenoxy)benzoato)-κ5O,O′,N:N′,N′′]dicopper(II) — methanol (1/2), C46H48Cu2N8O12
- Crystal structure of poly-[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-2,5-dibenzoyl-1,4-benzenedicarboxylato-κ4O1:O2:O3:O4)-μ2-2,5-dibenzoyl-1,4-benzenedicarboxylato-k4O5,O6: O5′,O6′-didysprosium(III)] tetrahydrate C33H26O13Dy
- Crystal structure of hexaaqua-bis(3-(3-pyridin-4-yl-[1,2,4]oxadiazol-5-yl) propionato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis(3-(3-pyridin-4-yl-[1,2,4]oxadiazol-5-yl)propionato-κO)-bis(3-(3-pyridin-4-yl-[1,2,4]oxadiazol-5-yl)propionato-κ2O,O′)dineodymium(III) octahydrate, C60H76N18O32Nd2
- Crystal structure of poly-[triaqua-(μ3-3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-1,2-phthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′,O′′′) (2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoato-κ2O,O′) praseodymium(III)], C15H7F8O9Pr
- The crystal structure of dichlorido (1,3-dimesityl-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(isoquinoline-κN)palladium(IV) – ethylacetate (1/1), C34H39Cl2N3O2Pd
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(1,3-bis(2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(isoquinolinyl)palladium(IV), C28H27Cl2N3Pd
- Crystal structure of 5-(4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium 7-carboxy-1,3-dioxo-1H,3H-benzo[de]isochromene-6-carboxylate monohydrate 4,5-anhydride, C24H16N6O8
- Crystal structure of poly-[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)thio)acetato-κ2N:O) cadmium(II)], C8H8CdN6O6S2
- Crystal Structure of (E)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2,3,4-tris(benzyloxy)-6-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C37H32O6
- Structure and photochromism of 1-(1,2-dimethylindol-3-yl)-2-[2-methyl-5-(3-fluorophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C26H18F7NS
- Crystal structure of two-dimensional coordination polymer poly-[μ2-azido-aqua-(μ2-pyrazine-2-carboxylato-κ3O,N:N′)nickel(II)], C5H5N5O3Ni
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-5-oxo-4-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4H,5H-pyrano [3,2-c]chromene-3-carbonitrile, C21H10F6N2O3
- Crystal structure of 4-(5-((2-methylbenzyl)thio)-4-phenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C21H18N4S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-N-ethyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carbothioamide, C18H16Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 4-(benzofuran-2-yl)-2-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3,3a,4,5-tetrahydro-2H-benzo[g]indazol-2-yl)thiazole, C28H20FN3OS
- Crystal structure of bis(dicyanamido-κ1N)-tetrakis[1-benzyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ1N]cobalt(II), CoC40H36N18
- Crystal structure of 1-benzyl-6-hydroxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C13H14N2O
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-7-methyl-4-(3,4-difluoro-phenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carbonitrile, C16H10F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 4-[(benzo[1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethylene)-amino]-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1,2-dihydro-pyrazol-3-one, C19H17N3O3
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dihydro-1-phenylchromeno[4,3-c]pyrazole, C16H12N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(5-((3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)sulfonyl)quinolin-8-yl)benzamide, C21H17N3O4S
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-9-methoxy-1-phenyl-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-((3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)amino)ethan-1-one, C23H20F3NO3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-3-carbonitrile – ethanol (1:1), C21H16N4O8
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-[(1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-ium-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate-κ2O,O′)-(μ2-4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)zinc(II)] hemihydrate, C31H27ZnFN3O9.5S
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C12H13BrO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-bromophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C13H15BrO4
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-((3-bromophenyl)amino)-6-(tert-butyl)-3-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)cinnolin-8-yl)-2-methylbut-3-yn-2-ol, C26H30BrN3O2
- Crystal structure poly-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazolyl-κ2NN1:N2N)-(μ3-2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)diacetato-κ5-O1,O2:O2:O3,O4)cadmium(II), C22H19CdN5O4
- Crystal structure of bis(1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxido-7-(piperazin-1-ium-1-yl)-1,8-naphthyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylate-κ2O,O′)copper(II) benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylate dihydrate, C38H42F2CuN8O12
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of potassium lithium molybdate monohydrate, KLiMoO4·H2O
- Crystal structure of [tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ3N](isonicotinate-κO) cobalt(II) [tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ3N](isonicotinic acid-κO) cobalt(II) triperchlorate, C60H51N16O16Cl3Co2
- The crystal structure of tris(μ2-1,3-bis(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-oxido-1-(oxo)but-2-en-1-yl)phenyl-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(1,2-dimethoxyethane-κ2O,O′)dicerium(III), C50H38F18O16Ce2
- Crystal structure of 8-isopropyl-8-aza-bicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-ol, C10H19NO
- Crystal structure of 2,4-dibenzoyl-N,N-dimethylbenzenamine, C22H19NO2
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6,8-diphenyl-4-(phenylamino)quinazoline — acetonitrile (1/1), C35H28N4O
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of the catena-poly-[bis(μ2-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl-κN)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] 5.5 hydrate, C32H44N6NiO11F2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-[(μ2-2-(2-((2,6-dimethylphenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2-(2-((2,6-dimethylphenyl)amino)phenyl)acetate-κ3O,O′:O′)cadmium(II)], C28H20N2Cl4O4Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-4-(pyridin-4-yl)-isophthalate-κ2O, O′)cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C13H11NO5Cl2Cd
- Crystal structure of poly-{[μ2-(E)-1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)but-2-ene-κ2N:N′][μ2-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′]nickel(II)}, C18H22N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of aqua (5,5′-dicarboxy-(1,1′-biphenyl)-2,3′-dicarboxylato-κO) bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)cadmium monohydrate, C40H28CdN4O10
- Crystal structure of 5-methoxy-N′-[(3Z)-5-chloro-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3-ylidene]-1H-indole-2-carbohydrazide-DMSO (1/1), C25H18ClFN4O3 · C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of 5-methoxy-N′-[(3Z)-1-benzyl-5-fluoro-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3-ylidene]-1H-indole-2-carbohydrazide-DMSO (1/1), C27H25FN4O4S
- Crystal structure of poly-[bis{μ2-N-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-N-phenylaniline-κ2N:N′)}-(μ2-naphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylato)-(μ4-naphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylato)dicadmium(II)], C36H25N5O4Cd
- Crystal structure of 1-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-(4-bromophenyl)thiourea, C17H21BrN2S
- Crystal structure of N′-[(1E)-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-methylidene]adamantane-1-carbohydrazide, C18H20Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-5′-([2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridin]-4′-yl)-[1,1′:3′,1′′-terphenyl]-4,4′′-dicarboxylate-κ3N,N′,N′′}zinc(II), C39H31Cl2N3O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,3,5,7-tetraoxo-3a,4,4a,5,7,7a,8,8a-octahydro-4,8-ethenopyrrolo [3,4-f]isoindole-2,6(1H,3H)-diyl)dibenzoic acid, C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-ethyl oxime, C17H16Cl2N2O2
- The crystal structure of diaqua-(N-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzyl)iminodiacetato-κ4-N,O,O′,O′′)chromium(III) based on synchrotron data, C11H13CrN2O9
- Crystal structure of ethyl 5-amino-3-(methylthio)-1-(1-phenyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate, C21H19N5O3S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C17H16Br2N2O2
- Crystal structure of dibromido μ-oxalato-κ2O,O′:κ2O′′,O′′′−η6-p-cymenediosmium(II), C22H28Br2O4Os2
- Crystal structure of 2-(bromomethyl)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-tosylpyrrolidine, C18H19BrClNO2S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione; C13H11FN2O3
- Crystal structure of diethylammonium 1,3-dimethyl-2,4,6-trioxohexahydropyrimidin-5-ide, C10H19N3O3
- Crystal structure of 1,1-dimethyl-3-(2-phenylethyl)urea, C11H16N2O
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-thiazolo[4,5-b]pyridine, C13H10N2OS
- Crystal structure of 3-tert-butyl-7-azadioxindole, C11H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-ferrocenyl-6-bromopyrene, C26H17BrFe
- Crystal structure of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carbothioamide, C16H13BrFN3S
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,5-ditrifluoromethylphenyl)-3-cyano-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4H-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyran, C20H16F6N2O2
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13N3O4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2, 4-dichlorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H12Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-chlorido)-bis(di-p-tolylhydroxyphosphine-κP)-bis(di-p-tolylphosphite-κP)dipalladium(II), C56H58Cl2O4P4Pd2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-methyl-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ2-O,N)cadmium(II) tetrahydrate, C12H22CdN4O14
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5-nitrosalicylato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II), C19H13CuN3O6
- Crystal structure of bis(4-(2-phenylpropan-2-yl)phenyl)amine, C30H31N
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C18H16F2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H11F3N2O2
- Crystal structure of an isomeric bis[(η5:η1-6,6-di-p-tolylpentafulvene)(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)titanium(III)]-μ2,η1:η1-dinitrogen complex, C60H66N2Ti2
- Crystal structure of 3,4-dinitropyrazole, C3H2N4O4
- Crystal structure of (4-vinylpyridine-κN)triphenyl tin(IV) chloride, C25H22ClNSn
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl 2-phenylethylcarbamate, C13H19NO2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-((E)-(4-chlorobenzyli-dene)hydrazono)-1-p-tolylpyrrolidine-3-carbonitrile, C19H17ClN4
- Crystal structure of bis(biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-bis(1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)dizinc(II)2.5 hydrate, C62H57N6Zn2O16.5F2
- Crystal structure of dichloridobis{μ2-2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-chlorophenolato)-κ5O,N,N′,O′:O′}diiron(III), C32H24Cl6Fe2N4O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((4,4-dimethyl-2, 6-dioxocyclohexylidine)methylamino)-N-(3,4-dimethylisoxazol-5-yl)benzenesulfonamide, C20H23N3O5S
- Crystal structure of poly-[aqua-μ2-aqua-μ2-(4,4′-oxybis(benzoato)-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)], C14H12O7Cd
- Crystal structure of aqua(μ2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato-κ3O,O′:O′′)-(μ2-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)cadmium(II) 1.5 hydrate, C62H60N6Cd2O19F2
- Crystal structure of dimethanolo-bis[μ-(2-(2-(5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)phenoxy)benzoato)-κ5O,O′,N:N′,N′′]dicopper(II) — methanol (1/2), C46H48Cu2N8O12
- Crystal structure of poly-[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-2,5-dibenzoyl-1,4-benzenedicarboxylato-κ4O1:O2:O3:O4)-μ2-2,5-dibenzoyl-1,4-benzenedicarboxylato-k4O5,O6: O5′,O6′-didysprosium(III)] tetrahydrate C33H26O13Dy
- Crystal structure of hexaaqua-bis(3-(3-pyridin-4-yl-[1,2,4]oxadiazol-5-yl) propionato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis(3-(3-pyridin-4-yl-[1,2,4]oxadiazol-5-yl)propionato-κO)-bis(3-(3-pyridin-4-yl-[1,2,4]oxadiazol-5-yl)propionato-κ2O,O′)dineodymium(III) octahydrate, C60H76N18O32Nd2
- Crystal structure of poly-[triaqua-(μ3-3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-1,2-phthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′,O′′′) (2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoato-κ2O,O′) praseodymium(III)], C15H7F8O9Pr
- The crystal structure of dichlorido (1,3-dimesityl-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(isoquinoline-κN)palladium(IV) – ethylacetate (1/1), C34H39Cl2N3O2Pd
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(1,3-bis(2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(isoquinolinyl)palladium(IV), C28H27Cl2N3Pd
- Crystal structure of 5-(4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium 7-carboxy-1,3-dioxo-1H,3H-benzo[de]isochromene-6-carboxylate monohydrate 4,5-anhydride, C24H16N6O8
- Crystal structure of poly-[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-((1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)thio)acetato-κ2N:O) cadmium(II)], C8H8CdN6O6S2
- Crystal Structure of (E)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2,3,4-tris(benzyloxy)-6-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C37H32O6
- Structure and photochromism of 1-(1,2-dimethylindol-3-yl)-2-[2-methyl-5-(3-fluorophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C26H18F7NS
- Crystal structure of two-dimensional coordination polymer poly-[μ2-azido-aqua-(μ2-pyrazine-2-carboxylato-κ3O,N:N′)nickel(II)], C5H5N5O3Ni
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-5-oxo-4-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4H,5H-pyrano [3,2-c]chromene-3-carbonitrile, C21H10F6N2O3
- Crystal structure of 4-(5-((2-methylbenzyl)thio)-4-phenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C21H18N4S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-N-ethyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carbothioamide, C18H16Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 4-(benzofuran-2-yl)-2-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3,3a,4,5-tetrahydro-2H-benzo[g]indazol-2-yl)thiazole, C28H20FN3OS
- Crystal structure of bis(dicyanamido-κ1N)-tetrakis[1-benzyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ1N]cobalt(II), CoC40H36N18
- Crystal structure of 1-benzyl-6-hydroxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C13H14N2O
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-7-methyl-4-(3,4-difluoro-phenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carbonitrile, C16H10F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 4-[(benzo[1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethylene)-amino]-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1,2-dihydro-pyrazol-3-one, C19H17N3O3
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dihydro-1-phenylchromeno[4,3-c]pyrazole, C16H12N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(5-((3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)sulfonyl)quinolin-8-yl)benzamide, C21H17N3O4S
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-9-methoxy-1-phenyl-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-((3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)amino)ethan-1-one, C23H20F3NO3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-3-carbonitrile – ethanol (1:1), C21H16N4O8
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-[(1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-ium-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate-κ2O,O′)-(μ2-4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)zinc(II)] hemihydrate, C31H27ZnFN3O9.5S
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C12H13BrO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-bromophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C13H15BrO4
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-((3-bromophenyl)amino)-6-(tert-butyl)-3-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)cinnolin-8-yl)-2-methylbut-3-yn-2-ol, C26H30BrN3O2
- Crystal structure poly-(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazolyl-κ2NN1:N2N)-(μ3-2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)diacetato-κ5-O1,O2:O2:O3,O4)cadmium(II), C22H19CdN5O4
- Crystal structure of bis(1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxido-7-(piperazin-1-ium-1-yl)-1,8-naphthyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylate-κ2O,O′)copper(II) benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylate dihydrate, C38H42F2CuN8O12
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of potassium lithium molybdate monohydrate, KLiMoO4·H2O
- Crystal structure of [tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ3N](isonicotinate-κO) cobalt(II) [tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ3N](isonicotinic acid-κO) cobalt(II) triperchlorate, C60H51N16O16Cl3Co2
- The crystal structure of tris(μ2-1,3-bis(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-oxido-1-(oxo)but-2-en-1-yl)phenyl-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(1,2-dimethoxyethane-κ2O,O′)dicerium(III), C50H38F18O16Ce2
- Crystal structure of 8-isopropyl-8-aza-bicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-ol, C10H19NO
- Crystal structure of 2,4-dibenzoyl-N,N-dimethylbenzenamine, C22H19NO2
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6,8-diphenyl-4-(phenylamino)quinazoline — acetonitrile (1/1), C35H28N4O

