Abstract
The data with the advancement of information technology are increasing on daily basis. The data mining technique has been applied to various fields. The complexity and execution time are the major factors viewed in existing data mining techniques. With the rapid development of database technology, many data storage increases, and data mining technology has become more and more important and expanded to various fields in recent years. Association rule mining is the most active research technique of data mining. Data mining technology is used for potentially useful information extraction and knowledge from big data sets. The results demonstrate that the precision ratio of the presented technique is high comparable to other existing techniques with the same recall rate, i.e., the R-tree algorithm. The proposed technique by the mining effectively controls the noise data, and the precision rate is also kept very high, which indicates the highest accuracy of the technique. This article makes a systematic and detailed analysis of data mining technology by using the Apriori algorithm.
1 Introduction
After decades of research and practice, data mining technique has absorbed many disciplines results and formed a unique research branch. Undoubtedly, the research and application of data mining are very challenging. Data mining has to go through concept presentation, concept acceptance, extensive research and exploration, gradual application, and mass application stages like developing other new technologies. Most scholars believe that data mining research is still in the stage of extensive research and exploration from the current situation. On the one hand, the concept of data mining has been widely accepted. In theory, several challenging and prospective questions are being asked that are attracting more and more researchers. Since the concept of data mining was put forward in the 1980s, its economic value has emerged, and it has been advocated by many commercial manufacturers, forming a preliminary market [1].
Because the association rule find the relationship between items that cannot be found by traditional artificial intelligence and statistical methods, it has an important research value. At the same time, it satisfies people’s urgent need to acquire knowledge from large-scale data storage. Currently, the research institutions of the world’s famous universities and the major IT companies’ research departments have invested much energy in their research and achieved many research results. It includes many advanced mining algorithms. Users who do not need to have advanced statistical knowledge and training can use it to dig out, including sequential patterns, classification, and so on the many types of knowledge. The system can run on various platforms, and many mainstream database systems (such as SQL-Server and Oracle) are closely combined. Simultaneously, online analysis and mining technology are also introduced so that the system can analyze advantages of data warehouses [1].
The computational procedure of expansive data sets’ examples disclosure is included in data mining. The data are concentrated from the dataset, which further utilizes for the reasonable structure. Data mining is about taking care of issues by dissecting data in databases [2]. The organizations make proactive knowledge-driven decisions, and these tools predict future trends [3]. The knowledge discovery in database (KDD) is the basic step in the data mining techniques, and the data mining is referred to as KDD [4]. For since word alternatives, data mining utilized in KDD are care-of [5]. Figure 1 shows the data mining steps in knowledge discovery in database.

Basic diagram of data mining steps in database.
Data mining and association rules have attracted great attention in the information industry. Research institutions have carried out research and exploration on data mining technology.
The organization of this article is as follows. Section 2 provides a summary of the exhaustive literature survey followed by a methodology adopted in Section 3. A detailed discussion and analysis of the Apriori algorithm are given in Section 4. Section 5 provides detailed information that shows the improvement of the Apriori algorithm and details the mining data results. Finally, concluding remarks are provided in Section 6.
2 Literature review
Data mining can find out useful information that traditional analysis methods cannot find. Many famous universities in the world of the major research institutions and IT companies in the research department have spent a lot of energy to study and obtained many research results. For example, Stanford University developed a DMMiner mining system, which includes many advanced mining algorithms, mining the type of knowledge (AssociationRules) from association rules, and sequential patterns (sequence pattern) to find the classification of the drive (Discovery – Driver), and the system can run on multiple platforms, with many mainstream database systems closely. IBM’s Almaden lab’s Quest project contains sequential patterns of association rules, classification, and clustering of the time series (TimeSeriesClustering) research. The representative products are DB2IntelligentMinerforData. Canada SimonFraser OBMiner was developed at the university. The system design aims to find the relationship between database and data mining integration based on the attribute-oriented concept of multistage found all kinds of knowledge. Many university research institutions and scholars made a great contribution to the development in this field. For example, Simon Fraster University in Canada and the University of Helsinki, Belgium, are famous in the world in data mining research. Moreover, there are numerous research works in this area. Cho et al. proposed the famous Apriori algorithm to improve the efficiency of mining association rules, and many new technologies were also generated [6].
Many authors have worked on data mining techniques. The traditional algorithms have been unable to meet data mining requirements in the aspect of efficiency [7]. The parallelization based on the Hadoop framework algorithm is realized. The existing data mining algorithms are highly complex, and the execution time is too long. In this article, the authors detail and analyze the association rules in the data mining technology and their merits and demerits [8]. The obtained results showed that the proposed algorithm is superior to the existing techniques. The authors in this article proposed a new data mining algorithm that is based on an association rule algorithm [9]. The K-means clustering algorithm is used for the clustering analysis of new mining results. The authors provide a relative study on a percentage of the most widely data mining algorithms that are used in commercial business and normal life [10]. Different systems, tools, and software’s are used for relative data extraction from a specific group of data. The authors reviewed many data mining techniques [11] and recommend the products to the user based on the transaction history of other users who have the same characteristics as this user [12]. Hence, details such as age, gender, education, marital status, and salary are collected. So, data mining techniques such as clustering are required. The general Apriori Algorithm is used in the study. The authors explained the E-commerce businesses using tools of implicit rule algorithm in the data mining [13]. The experimental results obtained from the proposed techniques show that the processing time is improved.
2.1 Contribution
Different data mining existing technologies have some complexities in terms of time, computation, and efficiency. This article provides a systematic, in-depth, comprehensive research on the data mining technology. The data mining association rules are deeply analyzed by using the Apriori algorithm because it is an efficient algorithm from other state-of-the-art techniques. The results obtained from the improved Apriori mining algorithm show that it is not only simpler but also more efficient technique compared to other existing techniques.
3 Research on data mining technology
With the developed database techniques and the application of database management systems, the data storage in the world has increased rapidly. However, the current database system has not discovered the hidden knowledge behind the data and cannot predict the future trend of the development according to the data. The lack of technology and means for in-depth data analysis lead to the phenomenon of “rich data but poor knowledge” [14]. In the face of this challenge, data mining and knowledge discovery DM&KD technology emerged and developed rapidly.
3.1 Definition of data mining
The data forms knowledge like regard concepts, rules, patterns, and constraints. The hidden patterns that may exist in large databases are searched. The patterns and correlations between patterns are discovered by the data mining scans through large datasets. The data analysis and prediction are included in the data mining along with the collection and managing the data. The data are represented in quantitative, textual, or multimedia forms that can be performed on data mining. The data are examined by the variety of parameters used by the data mining applications [15]. Defining the problem, data preparation and exploration, building models, model exploration, and validation are the basic steps that can be defined. Researchers from different fields, especially in the database, artificial intelligence, machine learning, statistics, pattern recognition, data visualization, and other aspects of scholars and engineers, have been brought together to devote themselves to the emerging research field of data mining, forming a new technical hotspot [16].
However, compared with the traditional data analysis, the differences between data mining tools and traditional analysis tools are presented in Table 1.
Differences between data mining tools and traditional analysis tools
| Data analysis tools | Data mining tool | |
|---|---|---|
| Characteristics of tool | Retrospectives, validations | Predictive, discoverable |
| Analysis of the key | What has happened | Predict the future |
| Analysis purposes | List the largest customers from the most recent sales documents | Lock in future potential customers to reduce future sales costs |
| Data set size | The data dimension and the data in the dimension are small | The data dimension and the number of attributes in the dimension are huge |
| Start the way | Business manager, systems analyst, management consultant startup and control | Data with system startup, minimal personnel guidance |
| Technical conditions | Mature | Statistical analysis tools are being developed |
3.2 Data mining technology
Data mining technology covers a wide range, mainly including database system, artificial intelligence, machine learning, data visualization, and other fields. There are also many technologies used in data mining. Figure 2 shows the structure diagram of the data mining technique. In data mining, we rarely use one tool or technique. For a given problem, the nature of the data itself affects how the technology is chosen, so we should use various techniques or tools to find the best model. The following is a brief introduction and analysis of the techniques often used in data mining.
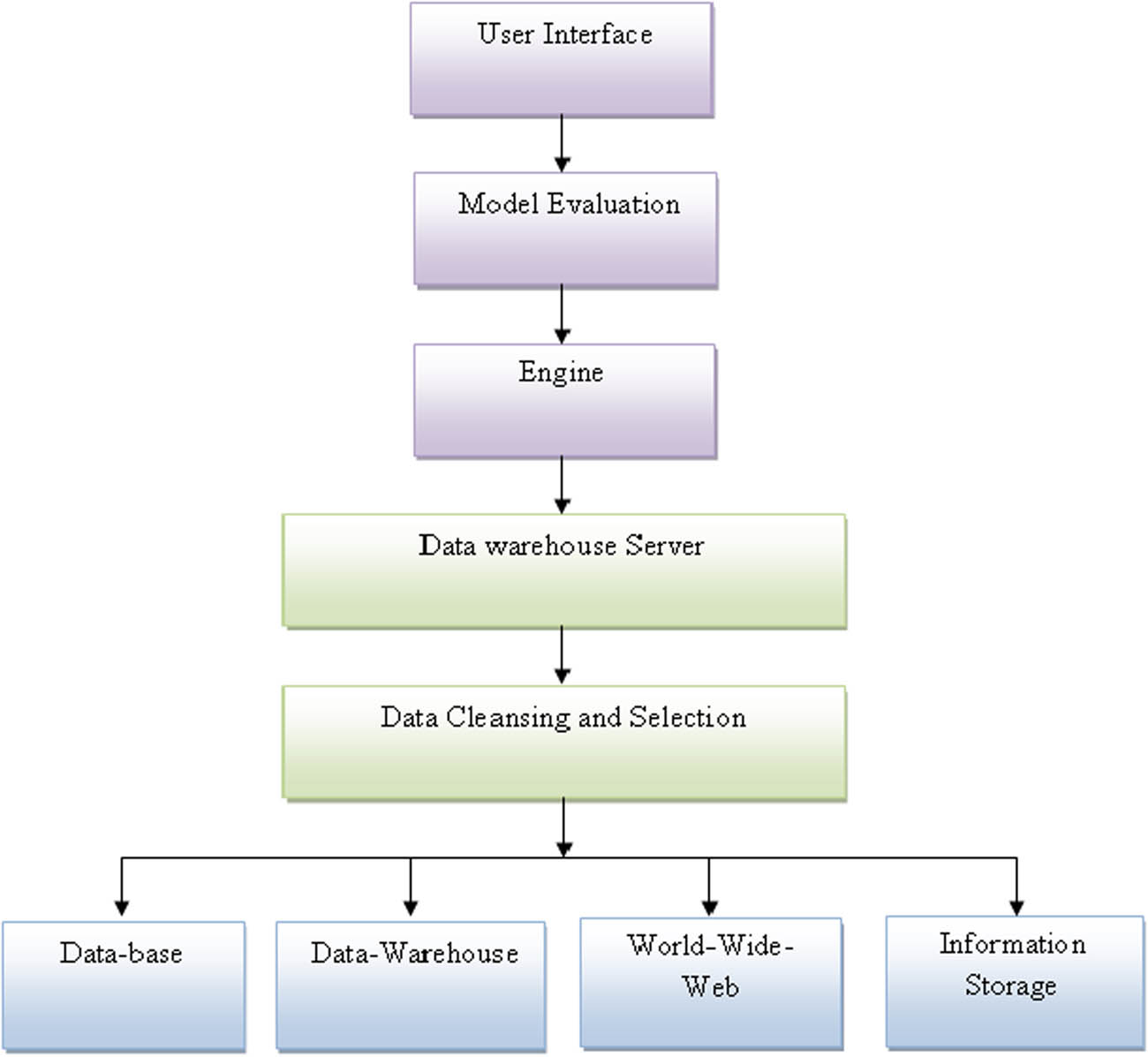
Technical structure of data mining.
The user interface in the starting provides the human computer interaction and communication. Model evaluation is an integral part of the model development process. It helps to find the best model that represents our data and how well the chosen model will work in the future. All the tools and software employed in the system are included in the engine to gain knowledge from the data warehouses. The data ware house compiled and organized all the data from the big data in the database. All the noisy data are removed from the database and to correct the inconsistencies in the data cleaning and selection process.
Neural network
The artificial neural network image simulates human intuition thinking based on the characteristics of the biological neuron and neural network, by simplifying, inducing, and summarizing a class of parallel processing network. Neural networks for large-scale and complex problems containing hundreds of interactions between the independent variables can be effectively used for model, and hence, people are very interested in the neural network [17]. It can be used to solve classification problems in data mining (output variables are discrete) and regression problems (output variables are continuous).
The decision tree
The data records are classified by the tree structure, and a record set is represented by a leaf node under a certain condition, and branches of the tree are established according to different values of record fields [18]. A decision tree is a way of deriving a class of values from a set of rules.
Genetic algorithm
Genetic algorithms, by themselves, are not utilized to discover patterns but used to guide the learning process. Genetic technique guide is followed for finding good models and pattern of biological evolution, passing on their characteristics from generation to generation until they find the best model [19]. The information inherited is called a gene, which contains the parameters of the model established.
Visualization technology
Data visualization techniques are often used in conjunction with other data mining techniques to analyze data effectively, and their importance cannot be underestimated [20]. For example, the multidimensional data in the database is changed into a variety of graphics, which play a great role in revealing the distribution of data. Visualization of the data mining process and man–machine interaction can improve the data mining effectiveness [21]. There are rough sets, regression analysis, discrimination analysis, and other techniques in addition to the aforementioned techniques.
3.3 The flow of data mining
The process of data mining includes problem definition, data preparation, data mining, result analysis, and knowledge application, as shown in Figure 3.
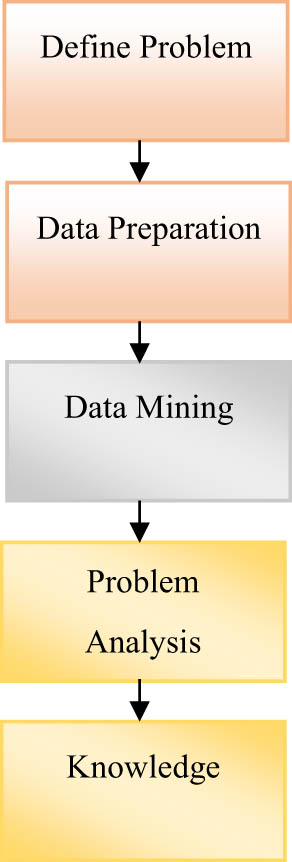
Data-mining flowchart.
First, the problem that to be solved is defined and then, the data relevant are decided and retrieved from the data collection for the analysis [22]. The transformation of the selected data into the forms of mining procedure is done. Data mining is a very important and a major step in which extract patterns are potentially extracted by clever techniques. The problem is then analyzed correctly [23]. The representation of the discovered knowledge is presented visually to the user, which is the final step for knowledge representation.
4 Classical association rule mining algorithm
Association mining algorithm is the active research area of data mining. The following algorithms, such as Apriori and partition, are briefly introduced.
4.1 Apriori algorithm
In 1994, Agrawal et al. designed a fundamental technique, Apriori, which is the influential and classical algorithm for mining one-dimensional, single-layer, and Boolean association rules.
Design idea of Apriori algorithm
This algorithm is based on the idea of a two-stage frequent item set to obtain the method of finding the frequent item set:
Frequent items with a growth rate of 1 are recorded as L[1].
The candidate item set C[k+L] is generated, which is L[k] based, and the candidate’s subsets are required to be frequent item sets.
The transaction D database is scanned, and each candidate item set is calculated, if it is greater than minsup, then attach to L[k+1].
If L[k+L] is a void set, it ends, and the desired outcome is L[1] union L[2] union. Otherwise, continue by turning 2.
Figure 4 provides the flow chart of the Apriori algorithm.
Apriori algorithm description
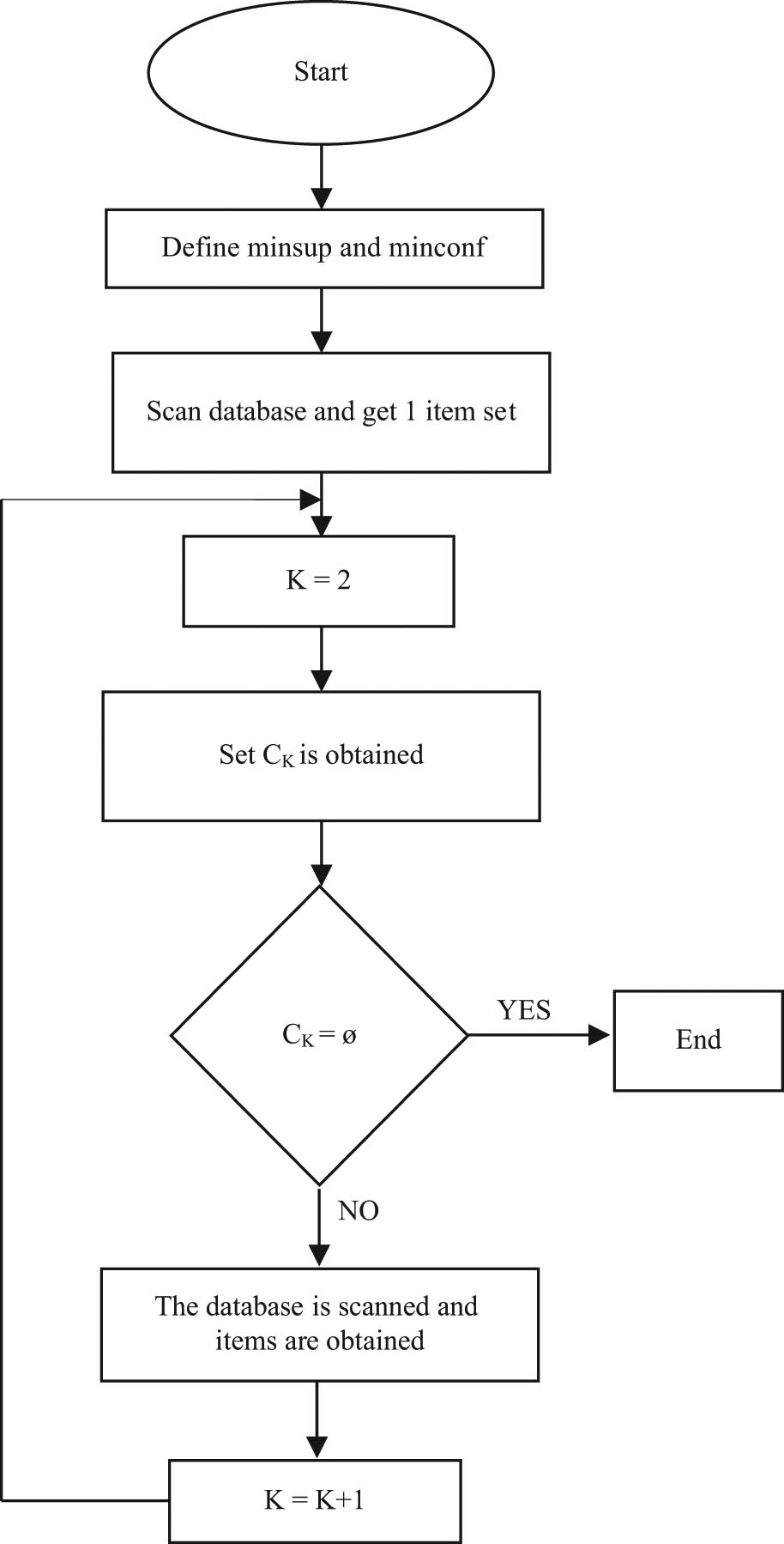
Flow chart of the Apriori algorithm.
A test method is utilized by the Apriori algorithm called layered iteration, k-item set for exploring (k+1) [24]. First, the set L1 of frequent 1-item sets is found. The set L2 is found by the L1 of frequent two-item sets, and L2 is used to find the set L3, and so on. A database scan is required for finding each Lk [25].
By definition, if the minimum support threshold is not met by the item set I, then I is not frequent, that is, support (I). If item A is added to I, the resulting item set (that is, IUA) cannot happen more commonly compared to I. Therefore, IUA is not frequent, that is, support (I).
The special classification called anti-monotone means that if a set is not passed the test, then all the supersets cannot pass the same test. It is called anti-monotone because it is monotone in the sense of not passing the test.
The Apriori algorithm is described as follows: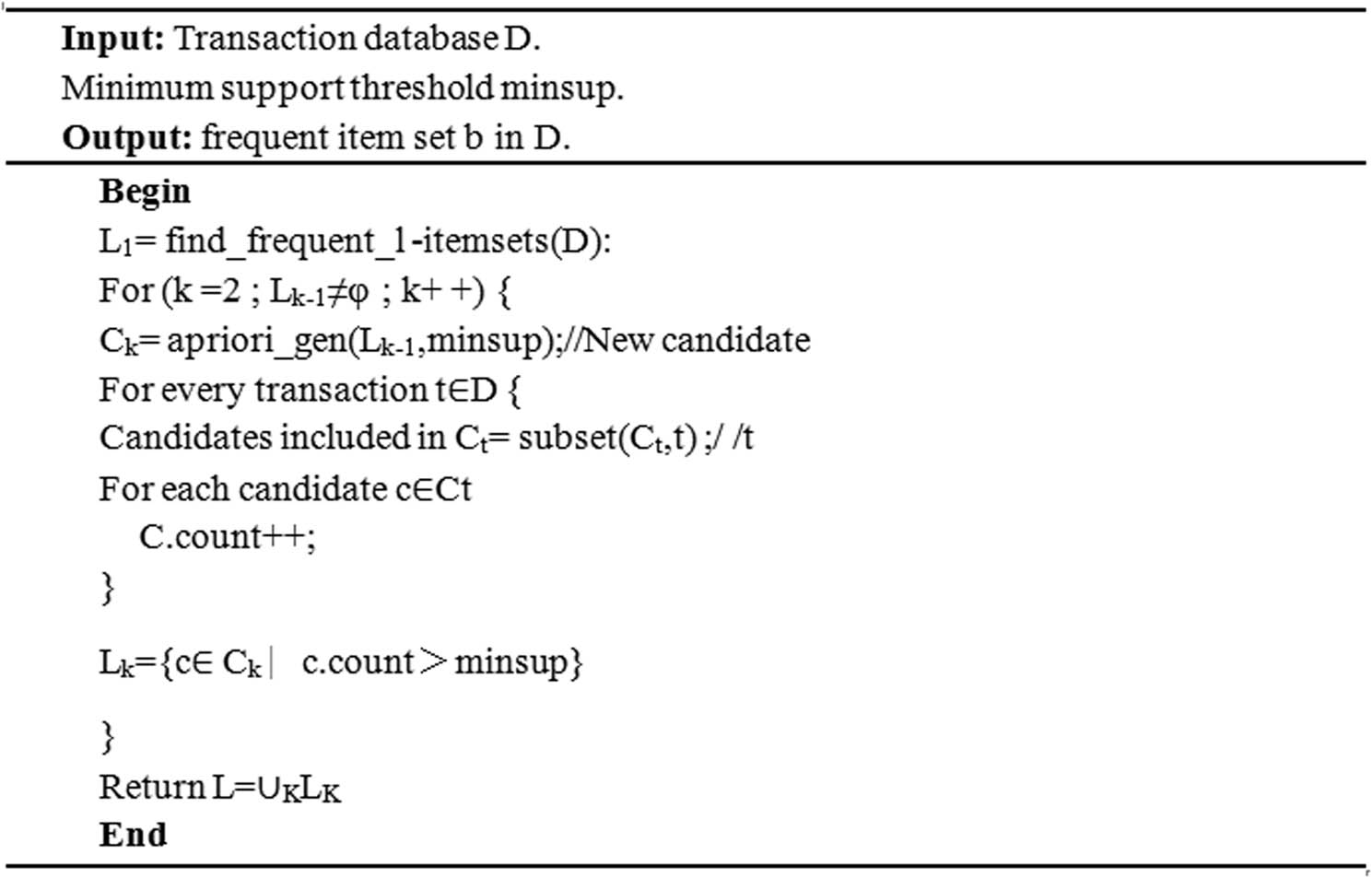
Among them, apriori_gen is a frequent item set and Lk−1 is connection candidate item set of Ck generation. The specific description process is as follows:
The frequent item sets must be frequent according to the Apriori property, and the layer-by-layer search technique is utilized by this algorithm. Given k-item sets, check (k−1) – subsets whether they are frequent. The frequent item sets must be frequent according to the Apriori property and layer-by-layer search technique is utilized.
4.2 Key technologies of Apriori algorithm
The Apriori property is applied in the Lk−1 finding process of the algorithm, which is composed of connection and pruning [26].
Connection step: Lk is found by connecting Lk−1 with itself for k-item candidate set generation. The item sets are referred to as Ck [27]. Let l1 and l2 be the item set in Lk−1. The notation Li[j] represents the JTH item of Li and, for convenience, assumes that the items in the item set are arranged in the lexicographical order [28].
Pruning step: All k-frequent item sets are included in Ck and Ck is the superset of Lk, which may or may not be frequent [29]. To compress Ck, the Apriori property is utilized: any infrequent (k−1)-item set cannot be a subset of the frequent k-item set. The candidate is not frequent and can therefore be deleted from Ck [30].
5 Results and discussion
The features and the results obtained by the presented technique are discussed briefly in this section. The comparative analysis of the proposed technique with the state-of-the art techniques is also performed and discussed.
5.1 Features of Apriori algorithm
The algorithm explores the (k+1) item set according to the k-item set using a method called layer-by-layer iteration of candidate generation tests.
Apriori algorithm is a hierarchical iterative algorithm
First, a set of frequent 1-item sets is found, which is denoted as L1, then L1 gets L2, L2 gets L3, and so on, until the frequent k-item set cannot be found [31]. Apriori algorithm mining produces all frequent items with no less than minimum support of minsup.
Data are organized in a transactional manner
The association is that the data are organized in the form of {Id,Item}, that is, {trans. number, Item set}.
Mining association rules applicable to transaction database.
5.2 Improvement of Apriori algorithm
To reduce the impact of existing problems in Apriori algorithm and improve the effectiveness of Apriori, many scholars have conducted a lot of research based on it and proposed some improved algorithms. These improved algorithms based on Apriori are usually called Apriori-like algorithms. The following is an introduction to several typical improvement methods [34].
Hashing-based Optimization method
The optimization method based on hashing is utilized to compress the size of the (k ≥ 2) set of the candidate k-item set Ck. When the transaction database is scan, produced by the candidate k – itemsets, at the same time, it produce each transaction (k+l) subset and increase thecount barrels in the next candidate item sets (k+1) [35,36,37,38]. This technique is particularly effective when k = 2. The key is to construct a valid hash function.
Optimization method based on transaction compression
The transaction-based optimization method reduces the scanned transaction database size by reduction of unnecessary transactions, so as to improve the efficiency of mining [33]. We can delete these transactions because they are no longer needed when scanning the database to produce (k+1) item sets [39,40].
Dynamic item set counting-based optimization method
The dynamic set counting-based optimization method divides the database into blocks. The algorithm can add a new set of waiting options at any starting point [40,41,42,43]. This technique dynamically evaluates the support of all item sets that have been counted. This algorithm has fewer times of scanning database than Apriori algorithm.
5.3 Data mining result verification in parallel
Data mining results are obtained and demonstrated by comparing serial and parallel programs of data mining. The parallel program is considered reliable if the results of the data parallel program are consistent with the serial data program. The data mining results of serial and parallel for 150 and 250 M file are tabulated in Tables 2 and 3, respectively. The FIM used in the table represents the frequent item sets.
Data mining results of serial and parallel for 150 M files
| Algorithm | Serial | Parallel |
|---|---|---|
| FIM1 | 21 | 21 |
| FIM2 | 67 | 67 |
| FIM3 | 45 | 45 |
| FIM4 | 28 | 28 |
Data mining results of serial and parallel for 250 M files
| Algorithm | Serial | Parallel |
|---|---|---|
| FIM1 | 19 | 19 |
| FIM2 | 67 | 67 |
| FIM3 | 45 | 45 |
| FIM4 | 28 | 28 |
By the parallel algorithms, there is a consistency in the serial algorithm with the varying item sets. The results from one sets to four sets are compared, but these are all consistent. The parallel technique is better in terms of reliability and accuracy and the frequent item sets are excavated accurately in which minimum support is satisfied. From the results, no such advantage of mining efficiency of the parallel algorithm was observed because of the work schedule overhead. The parallel algorithms is advantageous as it gradually emerges and the use less mining time than the serial algorithm. The proposed algorithm is also utilized for small-capacity database, and the time, the acceleration ratio, and the speed are presented in Table 4.
The mining time, mining acceleration ratio, and mining speed are obtained
| Proposed technique | |
|---|---|
| Mining time (s) | 40.34 |
| Mining acceleration | 15.76 |
| Mining speed | 4.98 |
The parameters obtained by the presented technique is highly controlled and accurate. There system is highly reliable in terms of time, speed, and acceleration.
The presented method is compared with the existing techniques in terms of accuracy at the level of recall rate. The obtained results are tabulated in Table 5 and graphically represented in Figure 5. Graphical representation gives the better visualization of the values, and better analysis is done by the graphical form of values.
Comparison of the proposed technique in terms of accuracy at the level of recall rate
| Recall ratio (%) | R-tree (%) | Dynamic (%) | The proposed technique (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 80.7 | 81.1 | 82.4 |
| 20 | 62.2 | 65.3 | 68.2 |
| 30 | 50.4 | 52.6 | 55.3 |
| 40 | 32.6 | 41.5 | 44.7 |
| 50 | 27.8 | 36.2 | 38.9 |
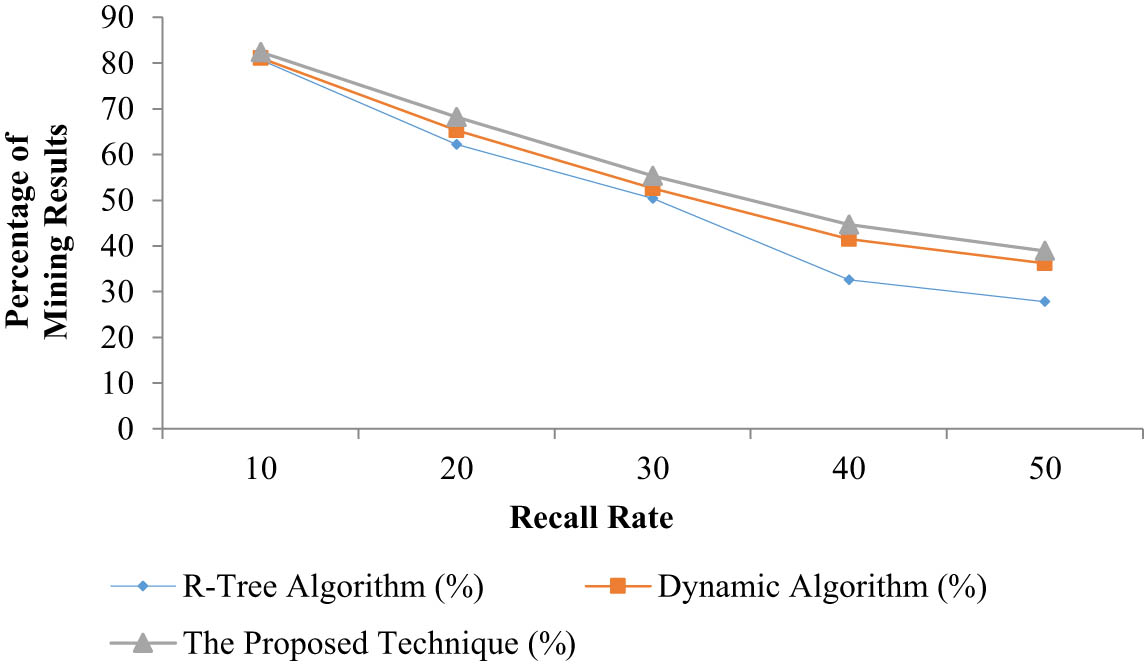
Comparison of the proposed technique in terms of accuracy at the level of recall rate.
It is clear from the comparison results that the precision ratio of the presented technique is high compared to other existing techniques with the same recall rate, i.e., R-tree algorithm. The noise data are effectively controlled by the proposed technique by controlling the mining time, speed, and the acceleration. The precision rate is also kept high, which indicates the highest accuracy of the technique.
6 Conclusion
The mining of association rules in large databases always requires more resources such as memory and CPU and expensive I/O costs, so improving efficiency is a work with high application value. The Apriori algorithm for association rules and the improved Apriori mining algorithm are further concluded that the algorithm is not only simple but also greatly reduces the number of candidate frequent item sets and has the advantages of fast search speed, which not only saves the calculation cost but also improves the efficiency of the algorithm. The results obtained from the improved Apriori mining algorithm show that it is not only simpler but also more efficient technique compared to the existing techniques.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Balaji BV , Rao VV . Improved classification based association rule mining. Int J Adv Res Comput Commun Eng. 2013;2(5):2211–21.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Hand DJ . Data mining: statistics and more? Am Stat. 1998;52(2):112–8.10.1080/00031305.1998.10480549Search in Google Scholar
[3] De Clercq PA , Hasman A , Blom JA , Korsten HH . Design and implementation of a framework to support the development of clinical guidelines. Int J Med Inform. 2001;64(2–3):285–318.10.1016/S1386-5056(01)00189-7Search in Google Scholar
[4] Miller HJ , Han J . (Eds.). Geographic data mining and knowledge discovery. CRC press; 2009.10.1201/9781420073980Search in Google Scholar
[5] Bose I , Mahapatra RK . Business data mining – a machine learning perspective. Inf Manag. 2001;39(3):211–25.10.1016/S0378-7206(01)00091-XSearch in Google Scholar
[6] Cho YH , Kim JK , Kim SH . A personalized recommender system based on web usage mining and decision tree induction. Expert Syst Appl. 2002;23(3):329–42.10.1016/S0957-4174(02)00052-0Search in Google Scholar
[7] Fu C , Wang X , Zhang L , Qiao L . Mining algorithm for association rules in big data based on Hadoop. AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol. 1955, no. 1. AIP Publishing LLC; 2018 April. p. 040035.10.1063/1.5033699Search in Google Scholar
[8] Xu Y . Research of association rules algorithm in data mining. Int J Datab Theor Appl. 2016;9(6):119–30.10.14257/ijdta.2016.9.6.12Search in Google Scholar
[9] Zhang G , Liu C , Men T . Research on data mining technology based on association rules algorithm. 2019 IEEE 8th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC). IEEE; 2019 May. p. 526–30.10.1109/ITAIC.2019.8785788Search in Google Scholar
[10] Baker RSJD . Data mining for education. Int Encycl Educ. 2010;7(3):112–8.10.1016/B978-0-08-044894-7.01318-XSearch in Google Scholar
[11] Altaf W , Shahbaz M , Guergachi A . Applications of association rule mining in health informatics: a survey. Artif Intell Rev. 2017;47(3):313–40.10.1007/s10462-016-9483-9Search in Google Scholar
[12] Yabing J . Research of an improved apriori algorithm in data mining association rules. Int J Comput Commun Eng. 2013;2(1):25.10.7763/IJCCE.2013.V2.128Search in Google Scholar
[13] Jha J , Ragha L . Educational data mining using improved apriori algorithm. Int J Inf Comput Technol. 2013;3(5):411–8.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Liu H , Gegov A , Cocea M . Rule based networks: an efficient and interpretable representation of computational models. J Artif Intell Soft Comput Res. 2017;7.10.1515/jaiscr-2017-0008Search in Google Scholar
[15] Chandaka Babi D , Rao MV , Rao VV . Study of association rule mining for discovery of frequent item sets on big data sets. Int J Appl Eng Res. 2017;12(22):12169–75.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Hussain S , Dahan NA , Ba-Alwib FM , Ribata N . Educational data mining and analysis of students’ academic performance using WEKA. Indones J Electr Eng Comput Sci. 2018;9(2):447–59.10.11591/ijeecs.v9.i2.pp447-459Search in Google Scholar
[17] Masud M . Collaborative e-learning systems using semantic data interoperability. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;61:127–35.10.1016/j.chb.2016.02.094Search in Google Scholar
[18] Ramasamy S , Nirmala K . Disease prediction in data mining using association rule mining and keyword based clustering algorithms. Int J Comput Appl. 2020;42(1):1–8.10.1080/1206212X.2017.1396415Search in Google Scholar
[19] Liu H , Gegov A , Cocea M . Network based rule representation for knowledge discovery and predictive modelling. In 2015 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE). IEEE; 2015 August. p. 1–8.10.1109/FUZZ-IEEE.2015.7337807Search in Google Scholar
[20] García E , Romero C , Ventura S , De Castro C . A collaborative educational association rule mining tool. Internet High Educ. 2011;14(2):77–88.10.1016/j.iheduc.2010.07.006Search in Google Scholar
[21] Nicholson S . The basis for bibliomining: Frameworks for bringing together usage-based data mining and bibliometrics through data warehousing in digital library services. Inf Process Manag. 2006;42(3):785–804.10.1016/j.ipm.2005.05.008Search in Google Scholar
[22] Shi GR , Yang XS . Optimization and data mining for fracture prediction in geosciences. Proc Comput Sci. 2010;1(1):1359–66.10.1016/j.procs.2010.04.151Search in Google Scholar
[23] Liu Y . Research on association rules mining algorithm based on large data. Inf Technol. 2017;40(1):192–4.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Roobaea A . An empirical combination of machine learning models to enhance author profiling performance. Int J Adv Trends Comput Sci Eng. 2020;9:2.10.30534/ijatcse/2020/187922020Search in Google Scholar
[25] Sharma A , Kumar R . A framework for pre-computated multi-constrained quickest qos path algorithm. J Telecommun Electron Computer Eng. 2017;9(3–6):73–7.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Feng H , Liao R , Liu F , Wang Y , Zhu X . Optimization algorithm improvement of association rule mining based on particle swarm optimization. In 2018 10th International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA). IEEE; 2018. p. 524–9 10.1109/ICMTMA.2018.00132Search in Google Scholar
[27] Rizvi SJ , Haritsa JR . Maintaining data privacy in association rule mining. VLDB'02: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Very Large Databases. Morgan Kaufmann; 2002 January. p. 682–93.10.1016/B978-155860869-6/50066-4Search in Google Scholar
[28] Afzali GA , Mohammadi S . Privacy preserving big data mining: association rule hiding using fuzzy logic approach. IET Inf Secur. 2017;12(1):15–24.10.1049/iet-ifs.2015.0545Search in Google Scholar
[29] Guangpeng L , Peng C . Research on reliability modeling of cnc system based on association rule mining. Proc Manuf. 2017;11:1162–9.10.1016/j.promfg.2017.07.240Search in Google Scholar
[30] Pannu A . Artificial intelligence and its application in different areas. Artif Intell. 2015;4(10):79–84.Search in Google Scholar
[31] Hamzaoui A , Malluhi Q , Clifton C , Riley R . Association rule mining on fragmented database. Data privacy management, autonomous spontaneous security, and security assurance. Cham: Springer; 2014. p. 335–42.10.1007/978-3-319-17016-9_23Search in Google Scholar
[32] Jiang P , Liu XS . Big data mining yields novel insights on cancer. Nat Genet. 2015;47(2):103–4.10.1038/ng.3205Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Weng CH . Identifying association rules of specific later-marketed products. Appl Soft Comput. 2016;38:518–29.10.1016/j.asoc.2015.09.047Search in Google Scholar
[34] Kaushik M , Gupta SH , Balyan V . Power optimization of invivo sensor node operating at terahertz band using PSO. Optik. 2020;202:163530.10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163530Search in Google Scholar
[35] Kaushik M , Gupta SH , Balyan V . Evaluating threshold distance by using eigen values and analyzing its impact on the performance of WBAN. In 2019 6th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN). IEEE; 2019 March. p. 864–7.10.1109/SPIN.2019.8711666Search in Google Scholar
[36] Masud M , Gaba GS , Alqahtani S , Muhammad G , Gupta BB , Kumar P , et al. A Lightweight and robust secure key establishment protocol for internet of medical things in COVID-19 patients care. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020 1–9 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3047662Search in Google Scholar
[37] Masud M , Alazab M , Choudhary K , Gaba GS . 3P-SAKE: privacy-preserving and physically secured authenticated key establishment protocol for wireless industrial networks. Comput Commun. 2021;82–90.10.1016/j.comcom.2021.04.021Search in Google Scholar
[38] Rathee G , Sharma A , Iqbal R , Aloqaily M , Jaglan N , Kumar R . A blockchain framework for securing connected and autonomous vehicles. Sensors. 2019;19(14):3165.10.3390/s19143165Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Masud M , Gaba GS , Choudhary K , Alroobaea R , Hossain MS . A robust and lightweight secure access scheme for cloud based E-healthcare services. Peer-to-Peer Netw Appl. 2021;1–15. 10.1007/s12083-021-01162-x Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] Poongodi M , Sharma A , Vijayakumar V , Bhardwaj V , Parkash Sharma A , Iqbal R , et al. Prediction of the price of Ethereum blockchain cryptocurrency in an industrial finance system. Comput Electr Eng. 2020;81:106527.10.1016/j.compeleceng.2019.106527Search in Google Scholar
[41] Gaba GS , Kumar G , Monga H , Kim TH , Kumar P . Robust and lightweight mutual authentication scheme in distributed smart environments. IEEE Access. 2020;8:69722–33.10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2986480Search in Google Scholar
[42] Rathee G , Sharma A , Kumar R , Ahmad F , Iqbal R . A trust management scheme to secure mobile information centric networks. Comput Commun. 2020;151:66–75.10.1016/j.comcom.2019.12.024Search in Google Scholar
[43] Gaba GS , Kumar G , Monga H , Kim TH , Liyanage M , Kumar P . Robust and lightweight key exchange (LKE) protocol for industry 4.0. IEEE Access. 2020;8:132808–24.10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3010302Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Zhenyi Zhao et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Best Polynomial Harmony Search with Best β-Hill Climbing Algorithm
- Face Recognition in Complex Unconstrained Environment with An Enhanced WWN Algorithm
- Performance Modeling of Load Balancing Techniques in Cloud: Some of the Recent Competitive Swarm Artificial Intelligence-based
- Automatic Generation and Optimization of Test case using Hybrid Cuckoo Search and Bee Colony Algorithm
- Hyperbolic Feature-based Sarcasm Detection in Telugu Conversation Sentences
- A Modified Binary Pigeon-Inspired Algorithm for Solving the Multi-dimensional Knapsack Problem
- Improving Grey Prediction Model and Its Application in Predicting the Number of Users of a Public Road Transportation System
- A Deep Level Tagger for Malayalam, a Morphologically Rich Language
- Identification of Biomarker on Biological and Gene Expression data using Fuzzy Preference Based Rough Set
- Variable Search Space Converging Genetic Algorithm for Solving System of Non-linear Equations
- Discriminatively trained continuous Hindi speech recognition using integrated acoustic features and recurrent neural network language modeling
- Crowd counting via Multi-Scale Adversarial Convolutional Neural Networks
- Google Play Content Scraping and Knowledge Engineering using Natural Language Processing Techniques with the Analysis of User Reviews
- Simulation of Human Ear Recognition Sound Direction Based on Convolutional Neural Network
- Kinect Controlled NAO Robot for Telerehabilitation
- Robust Gaussian Noise Detection and Removal in Color Images using Modified Fuzzy Set Filter
- Aircraft Gearbox Fault Diagnosis System: An Approach based on Deep Learning Techniques
- Land Use Land Cover map segmentation using Remote Sensing: A Case study of Ajoy river watershed, India
- Towards Developing a Comprehensive Tag Set for the Arabic Language
- A Novel Dual Image Watermarking Technique Using Homomorphic Transform and DWT
- Soft computing based compressive sensing techniques in signal processing: A comprehensive review
- Data Anonymization through Collaborative Multi-view Microaggregation
- Model for High Dynamic Range Imaging System Using Hybrid Feature Based Exposure Fusion
- Characteristic Analysis of Flight Delayed Time Series
- Pruning and repopulating a lexical taxonomy: experiments in Spanish, English and French
- Deep Bidirectional LSTM Network Learning-Based Sentiment Analysis for Arabic Text
- MAPSOFT: A Multi-Agent based Particle Swarm Optimization Framework for Travelling Salesman Problem
- Research on target feature extraction and location positioning with machine learning algorithm
- Swarm Intelligence Optimization: An Exploration and Application of Machine Learning Technology
- Research on parallel data processing of data mining platform in the background of cloud computing
- Student Performance Prediction with Optimum Multilabel Ensemble Model
- Bangla hate speech detection on social media using attention-based recurrent neural network
- On characterizing solution for multi-objective fractional two-stage solid transportation problem under fuzzy environment
- Deep Large Margin Nearest Neighbor for Gait Recognition
- Metaheuristic algorithms for one-dimensional bin-packing problems: A survey of recent advances and applications
- Intellectualization of the urban and rural bus: The arrival time prediction method
- Unsupervised collaborative learning based on Optimal Transport theory
- Design of tourism package with paper and the detection and recognition of surface defects – taking the paper package of red wine as an example
- Automated system for dispatching the movement of unmanned aerial vehicles with a distributed survey of flight tasks
- Intelligent decision support system approach for predicting the performance of students based on three-level machine learning technique
- A comparative study of keyword extraction algorithms for English texts
- Translation correction of English phrases based on optimized GLR algorithm
- Application of portrait recognition system for emergency evacuation in mass emergencies
- An intelligent algorithm to reduce and eliminate coverage holes in the mobile network
- Flight schedule adjustment for hub airports using multi-objective optimization
- Machine translation of English content: A comparative study of different methods
- Research on the emotional tendency of web texts based on long short-term memory network
- Design and analysis of quantum powered support vector machines for malignant breast cancer diagnosis
- Application of clustering algorithm in complex landscape farmland synthetic aperture radar image segmentation
- Circular convolution-based feature extraction algorithm for classification of high-dimensional datasets
- Construction design based on particle group optimization algorithm
- Complementary frequency selective surface pair-based intelligent spatial filters for 5G wireless systems
- Special Issue: Recent Trends in Information and Communication Technologies
- An Improved Adaptive Weighted Mean Filtering Approach for Metallographic Image Processing
- Optimized LMS algorithm for system identification and noise cancellation
- Improvement of substation Monitoring aimed to improve its efficiency with the help of Big Data Analysis**
- 3D modelling and visualization for Vision-based Vibration Signal Processing and Measurement
- Online Monitoring Technology of Power Transformer based on Vibration Analysis
- An empirical study on vulnerability assessment and penetration detection for highly sensitive networks
- Application of data mining technology in detecting network intrusion and security maintenance
- Research on transformer vibration monitoring and diagnosis based on Internet of things
- An improved association rule mining algorithm for large data
- Design of intelligent acquisition system for moving object trajectory data under cloud computing
- Design of English hierarchical online test system based on machine learning
- Research on QR image code recognition system based on artificial intelligence algorithm
- Accent labeling algorithm based on morphological rules and machine learning in English conversion system
- Instance Reduction for Avoiding Overfitting in Decision Trees
- Special section on Recent Trends in Information and Communication Technologies
- Special Issue: Intelligent Systems and Computational Methods in Medical and Healthcare Solutions
- Arabic sentiment analysis about online learning to mitigate covid-19
- Void-hole aware and reliable data forwarding strategy for underwater wireless sensor networks
- Adaptive intelligent learning approach based on visual anti-spam email model for multi-natural language
- An optimization of color halftone visual cryptography scheme based on Bat algorithm
- Identification of efficient COVID-19 diagnostic test through artificial neural networks approach − substantiated by modeling and simulation
- Toward agent-based LSB image steganography system
- A general framework of multiple coordinative data fusion modules for real-time and heterogeneous data sources
- An online COVID-19 self-assessment framework supported by IoMT technology
- Intelligent systems and computational methods in medical and healthcare solutions with their challenges during COVID-19 pandemic
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Best Polynomial Harmony Search with Best β-Hill Climbing Algorithm
- Face Recognition in Complex Unconstrained Environment with An Enhanced WWN Algorithm
- Performance Modeling of Load Balancing Techniques in Cloud: Some of the Recent Competitive Swarm Artificial Intelligence-based
- Automatic Generation and Optimization of Test case using Hybrid Cuckoo Search and Bee Colony Algorithm
- Hyperbolic Feature-based Sarcasm Detection in Telugu Conversation Sentences
- A Modified Binary Pigeon-Inspired Algorithm for Solving the Multi-dimensional Knapsack Problem
- Improving Grey Prediction Model and Its Application in Predicting the Number of Users of a Public Road Transportation System
- A Deep Level Tagger for Malayalam, a Morphologically Rich Language
- Identification of Biomarker on Biological and Gene Expression data using Fuzzy Preference Based Rough Set
- Variable Search Space Converging Genetic Algorithm for Solving System of Non-linear Equations
- Discriminatively trained continuous Hindi speech recognition using integrated acoustic features and recurrent neural network language modeling
- Crowd counting via Multi-Scale Adversarial Convolutional Neural Networks
- Google Play Content Scraping and Knowledge Engineering using Natural Language Processing Techniques with the Analysis of User Reviews
- Simulation of Human Ear Recognition Sound Direction Based on Convolutional Neural Network
- Kinect Controlled NAO Robot for Telerehabilitation
- Robust Gaussian Noise Detection and Removal in Color Images using Modified Fuzzy Set Filter
- Aircraft Gearbox Fault Diagnosis System: An Approach based on Deep Learning Techniques
- Land Use Land Cover map segmentation using Remote Sensing: A Case study of Ajoy river watershed, India
- Towards Developing a Comprehensive Tag Set for the Arabic Language
- A Novel Dual Image Watermarking Technique Using Homomorphic Transform and DWT
- Soft computing based compressive sensing techniques in signal processing: A comprehensive review
- Data Anonymization through Collaborative Multi-view Microaggregation
- Model for High Dynamic Range Imaging System Using Hybrid Feature Based Exposure Fusion
- Characteristic Analysis of Flight Delayed Time Series
- Pruning and repopulating a lexical taxonomy: experiments in Spanish, English and French
- Deep Bidirectional LSTM Network Learning-Based Sentiment Analysis for Arabic Text
- MAPSOFT: A Multi-Agent based Particle Swarm Optimization Framework for Travelling Salesman Problem
- Research on target feature extraction and location positioning with machine learning algorithm
- Swarm Intelligence Optimization: An Exploration and Application of Machine Learning Technology
- Research on parallel data processing of data mining platform in the background of cloud computing
- Student Performance Prediction with Optimum Multilabel Ensemble Model
- Bangla hate speech detection on social media using attention-based recurrent neural network
- On characterizing solution for multi-objective fractional two-stage solid transportation problem under fuzzy environment
- Deep Large Margin Nearest Neighbor for Gait Recognition
- Metaheuristic algorithms for one-dimensional bin-packing problems: A survey of recent advances and applications
- Intellectualization of the urban and rural bus: The arrival time prediction method
- Unsupervised collaborative learning based on Optimal Transport theory
- Design of tourism package with paper and the detection and recognition of surface defects – taking the paper package of red wine as an example
- Automated system for dispatching the movement of unmanned aerial vehicles with a distributed survey of flight tasks
- Intelligent decision support system approach for predicting the performance of students based on three-level machine learning technique
- A comparative study of keyword extraction algorithms for English texts
- Translation correction of English phrases based on optimized GLR algorithm
- Application of portrait recognition system for emergency evacuation in mass emergencies
- An intelligent algorithm to reduce and eliminate coverage holes in the mobile network
- Flight schedule adjustment for hub airports using multi-objective optimization
- Machine translation of English content: A comparative study of different methods
- Research on the emotional tendency of web texts based on long short-term memory network
- Design and analysis of quantum powered support vector machines for malignant breast cancer diagnosis
- Application of clustering algorithm in complex landscape farmland synthetic aperture radar image segmentation
- Circular convolution-based feature extraction algorithm for classification of high-dimensional datasets
- Construction design based on particle group optimization algorithm
- Complementary frequency selective surface pair-based intelligent spatial filters for 5G wireless systems
- Special Issue: Recent Trends in Information and Communication Technologies
- An Improved Adaptive Weighted Mean Filtering Approach for Metallographic Image Processing
- Optimized LMS algorithm for system identification and noise cancellation
- Improvement of substation Monitoring aimed to improve its efficiency with the help of Big Data Analysis**
- 3D modelling and visualization for Vision-based Vibration Signal Processing and Measurement
- Online Monitoring Technology of Power Transformer based on Vibration Analysis
- An empirical study on vulnerability assessment and penetration detection for highly sensitive networks
- Application of data mining technology in detecting network intrusion and security maintenance
- Research on transformer vibration monitoring and diagnosis based on Internet of things
- An improved association rule mining algorithm for large data
- Design of intelligent acquisition system for moving object trajectory data under cloud computing
- Design of English hierarchical online test system based on machine learning
- Research on QR image code recognition system based on artificial intelligence algorithm
- Accent labeling algorithm based on morphological rules and machine learning in English conversion system
- Instance Reduction for Avoiding Overfitting in Decision Trees
- Special section on Recent Trends in Information and Communication Technologies
- Special Issue: Intelligent Systems and Computational Methods in Medical and Healthcare Solutions
- Arabic sentiment analysis about online learning to mitigate covid-19
- Void-hole aware and reliable data forwarding strategy for underwater wireless sensor networks
- Adaptive intelligent learning approach based on visual anti-spam email model for multi-natural language
- An optimization of color halftone visual cryptography scheme based on Bat algorithm
- Identification of efficient COVID-19 diagnostic test through artificial neural networks approach − substantiated by modeling and simulation
- Toward agent-based LSB image steganography system
- A general framework of multiple coordinative data fusion modules for real-time and heterogeneous data sources
- An online COVID-19 self-assessment framework supported by IoMT technology
- Intelligent systems and computational methods in medical and healthcare solutions with their challenges during COVID-19 pandemic


