Mathematical modeling of submerged membrane adsorption hybrid system and parameter estimation for adsorption of cesium from radioactive wastewater implementing eco-friendly adsorbent
-
Talib M. Albayati
, Wasan A. Muslim
Abstract
This study presents a comprehensive mathematical modeling and experimental investigation of a submerged membrane adsorption hybrid system (SMAHS) for the removal of cesium (Cs(I)) from radioactive wastewater. An eco-friendly adsorbent was synthesized and characterized for its adsorption performance. The homogeneous surface diffusion model (HSDM) model integrates surface diffusion as the dominant mass transfer mechanism and estimates key parameters, including the external mass transfer coefficient (K), surface diffusion coefficient (Ds), and membrane correlation coefficient (MCC). The pore and surface diffusion model (PSDM) is a comprehensive diffusion-based model that accounts for all diffusion processes in the solid phase. Experiments identified optimal operational conditions: pH 6.5, adsorbent dose 1.5 g/L, and contact time of 90 min, achieving over 95 % cesium removal. Ion selectivity tests demonstrated preferential adsorption of cesium in the presence of competing metal ions such as Na+, K+, and Ca2+. Regeneration studies showed that the adsorbent maintained over 85 % removal efficiency after five adsorption-desorption cycles, indicating cost-effectiveness. Model validation against experimental data exhibited strong agreement (R2 = 0.98), confirming the model’s suitability for design and scale-up of hybrid treatment systems. This work provides new insights into adsorption kinetics, hybrid system optimization, and eco-friendly adsorbent applications for radionuclide wastewater remediation.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the scientific support of the Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Technology-Iraq; Iraqi Atomic Energy Commission (IAEC)/Radiation and Nuclear Safety Directorate, Baghdad, Iraq, and to the Iraqi Geological Survey/Ministry of Industry and Minerals.
-
Research ethics: Not applicable.
-
Informed consent: Not applicable.
-
Author contributions: W.A.M. and T.M.A.; methodology, S.K.A.; validation, W.A.M. and A.S.A.; investigation; resources, A.S.A. and I.K.S.; writ-ing—original draft preparation, S.K.A. and T.M.A.; writing review and editing, T.M.N., W.A.M. and I.K.S..; visualization, T.M.A., and S.K.A; supervision, K.T.R..; project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
-
Use of Large Language Models, AI and Machine Learning Tools: Not applicable.
-
Declaration of AI Technology usage: We declare that no Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies or AI-assisted tools were utilized in any capacity during the writing and preparation of this article.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflict interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
-
Research funding: None declared.
-
Data availability: All relevant data and material are presented in the main paper.
Sample of calculation for K, MCC, Dₛ for mathematical model.
The values of K are estimated by the inclination of the curve C/C 0 versus t.
The data of batch adsorption kinetic study of bentonite can be used by the plotting of C/C₀ vs t as shown in the figure below:
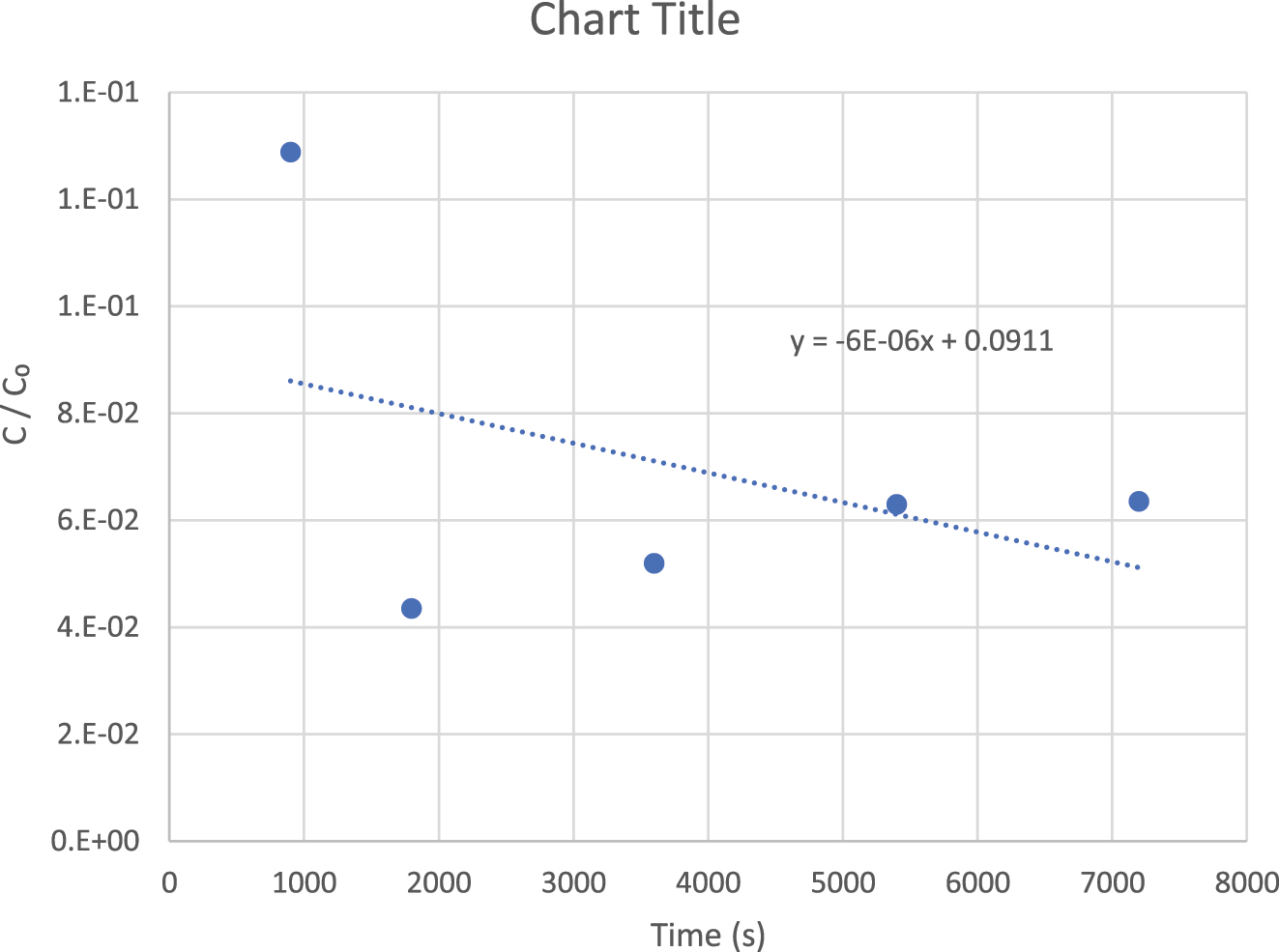
The slope of the curve of C/C₀ vs t from the figure = −6 × 10⁻⁶ s⁻¹
From eq 2.27:
m (adsorbent amount) in g = 0.25 g
S (surface area of adsorbent) = 77.7 m²/g
V (volume of solution) = 200 ml = 0.0002 m³
The values of MCC are estimated from eq 2.29:
The values of Dₛ are estimated from eq 2.30:
Where
References
1. Paranhos Gazineu, MH, de Araújo, AA, Brandão, YB, Hazin, CA, de, O, Godoy, JM. Radioactivity concentration in liquid and solid phases of scale and sludge generated in the petroleum industry. J Environ Radioact 2005;81:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2004.11.003.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
2. Muslim, WA, Albayati, TM, Al-Nasri, SK. Decontamination of actual radioactive wastewater containing 137Cs using bentonite as a natural adsorbent: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Sci Rep 2022;12:13837. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-18202-y.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Muslim, WA, Al-Nasri, SK, Albayati, TM. Evaluation of bentonite, attapulgite, and kaolinite as eco-friendly adsorbents in the treatment of real radioactive wastewater containing Cs-137. Prog Nucl Energy 2023:104730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2023.104730.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Muslim, W, Al-Nasri, S, Albayati, TM, Salih, I. Attapulgite as an eco-friendly adsorbent in the treatment of real radioactive wastewater. Water Pract Technol 2023;18:2068. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2023.131.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Muslim, WA, Al-Nasri, SK, Albayati, TM, Majdi, HS. Treatment of actual radioactive wastewater containing Cs-137 using kaolinite clay minerals as eco-friendly adsorbents. Desalination Water Treat 2023;307:162–70. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2023.29908.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Muslim, WA, Al-Nasri, SK, Albayati, TM, Salih, IK. Investigation of bentonite clay minerals as a natural adsorbent for Cs-137 real radioactive wastewater treatment. Desalination Water Treat 2024;317:100121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dwt.2024.100121.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Zhang, X, Ma, F, Dai, Z, Wang, J, Chen, L, Ling, H, et al.. Radionuclide transport in multi-scale fractured rocks: a review. J Hazard Mater 2022;424:127550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127550.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Khandaker, S, Kuba, T, Kamida, S, Uchikawa, Y. Adsorption of cesium from aqueous solution by raw and concentrated nitric acid-modified bamboo charcoal [internet]. J Environ Chem Eng 2017;5:1456–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.02.014.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Gabr, SS, Fayad, E, Binjawhar, DN, Mohamed, K, El Sayed, IE-T, Moghny, TA, et al.. RSM-CCD optimized adsorptive removal of p-Nitrophenol using eco-friendly magnetic activated carbon thin film. Inorg Chem Commun 2025;178:114471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2025.114471.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Al-Ani, T, Sarapää, O. Clay and clay mineralogy, physical – chemical properties and industrial uses. Geochemical survey of finland; 2008:1–94 pp.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Murray, HH. Applied clay mineralogy. Occurrences, processing and application of kaolins, bentonite, palygorskitesepiolite, and common clays, 1st ed. Clays Clay Miner. Oxford, UK: Elsevier B.V.; 2007.10.1016/S1572-4352(06)02001-0Suche in Google Scholar
12. Yuan, GD, Theng, BKG, Churchman, GJ, Gates, WP. Clays and Clay Minerals for Pollution Control [Internet]. 2nd ed. Dev Clay Sci. Copyright © 2013, 2006 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.; 2013. Available from. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-098259-5.00021-4.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Park, SM, Lee, J, Jeon, EK, Kang, S, Alam, MS, Tsang, DCW, et al.. Adsorption characteristics of cesium on the clay minerals: structural change under wetting and drying condition. Geoderma [Internet] 2019;340:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.12.002.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Zabulonov, Y, Kadoshnikov, V, Zadvernyuk, H, Melnychenko, T, Molochko, V. Effect of the surface hydration of clay minerals on the adsorption of cesium and strontium from dilute solutions. Adsorption [Internet] 2021;27:41–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-020-00263-y.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Zakrzewska-Trznadel, G, Harasimowicz, M, Chmielewski, AG. Membrane processes in nuclear technology-application for liquid radioactive waste treatment. Sep Purif Technol 2001;22–23:617–25.10.1016/S1383-5866(00)00167-2Suche in Google Scholar
16. al-Salmi, AF, Fayad, E, Mubarak, MF, & Hemdan, M. Dual removal of thallium (Tl+) and auramine O using alginate-coated iron oxide nanocomposites for sustainable wastewater treatment. Int J Environ Anal Chem 2025;1–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2025.2522259.Suche in Google Scholar
17. Saad Gabr, S, Fayad, E, Nasser Binjawhar, D, Mohamed, K, El-Tantawy El Sayed, I, Abdel Moghny, T, et al.. RSM-CCD optimized adsorptive removal of p-Nitrophenol using eco-friendly magnetic activated carbon thin film. Inorg Chem Commun 2025;178:114471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2025.114471.Suche in Google Scholar
18. Fang, X, Xu, Z, Luo, Y, Ren, L, Hua, W. Removal of radionuclides from laundry wastewater containing organics and suspended solids using inorganic ion exchanger. Procedia Environ Sci [Internet] 2016;31:375–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.02.053.Suche in Google Scholar
19. Awual, MR, Miyazaki, Y, Taguchi, T, Shiwaku, H, Yaita, T. Encapsulation of cesium from contaminated water with highly selective facial organic-inorganic mesoporous hybrid adsorbent. Chem Eng J [Internet] 2016;291:128–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.01.109.Suche in Google Scholar
20. Al-Alawy, IT, Mzher, OA. Radiological characterization of the irt-5000(14-Tammuz) research nuclear reactor at Al-Tuwaitha nuclear center in Iraq. Environ Earth Sci 2019;78:229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8122-6.Suche in Google Scholar
21. Albayati, TM, Doyle, AM. Shape-selective adsorption of substituted aniline pollutants from wastewater. Adsorpt Sci Technol 2013;31:459–68. https://doi.org/10.1260/0263-6174.31.5.459.Suche in Google Scholar
22. Talib, M. Albayati, application of nanoporous material MCM-41 in a membrane adsorption reactor (MAR) as a hybrid process for removal of methyl orange. Desalination Water Treat 2019;151:138–44. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23878.Suche in Google Scholar
23. Qusay, FA, Albyati, TM, Zablouk, MA. A study of the effect of operating conditions on reverse osmosis membrane performance with and without air sparging technique. Chem Eng Commun 2013;200:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2012.685529.Suche in Google Scholar
24. Usman, M, Katsoyiannis, I, Rodrigues, JH, Ernst, M. Arsenate removal from drinking water using by-products from conventional iron oxyhydroxides production as adsorbents coupled with submerged microfiltration unit. Environ Sci Pollut Control Ser 2021;28:59063–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08327-w.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
25. Kalaruban, M, Loganathan, P, Kandasamy, J, Vigneswaran, S. Submerged membrane adsorption hybrid system using four adsorbents to remove nitrate from water. Environ Sci Pollut Control Ser 2018;25:20328–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8905-9.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
26. Vigneswaran, S, Chaudhary, DS, Ngo, HH, Shim, WG, Moon, H. Application of a PAC-membrane hybrid system for removal of organics from secondary sewage effluent: experiments and modelling. Sep Sci Technol 2003;38:2183–99. https://doi.org/10.1081/ss-120021619.Suche in Google Scholar
27. Hilbrandt, I, Shemer, H, Ruhl, AS, Semiat, R, Jekel, M. Comparing fine particulate iron hydroxide adsorbents for the removal of phosphate in a hybrid adsorption/ultrafiltration system. Sep Purif Technol 2019;221:23–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.03.044.Suche in Google Scholar
28. Stylianou, S, Simeonidis, K, Mitrakas, M, Zouboulis, A, Ernst, M, Katsoyiannis, IA. Reductive precipitation and removal of Cr(VI) from groundwaters by pipe flocculation-microfiltration. Environ Sci Pollut Control Ser 2018;25:12256–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9967-4.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
29. Choi, B-B, Choi, Y-J, Choi, J-S, Lee, S, Oh, H-J. Energy management in submerged microfiltration systems by optimum control of aeration. Desalination 2009;247:233–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.12.027.Suche in Google Scholar
30. Shanmuganathan, S, Nguyen, TV, Shim, WG, Kandasamy, J, Vigneswaran, S. Performance of submerged membrane – ion exchange hybrid system with purolite A502PS in treating reverse osmosis feed. Sep Purif Technol [Internet] 2014;122:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.10.039.Suche in Google Scholar
31. Johir, MAH, Pradhan, M, Loganathan, P, Kandasamy, J, Vigneswaran, S. Phosphate adsorption from wastewater using zirconium (IV) hydroxide: kinetics, thermodynamics and membrane filtration adsorption hybrid system studies. J Environ Manage 2016;167:167–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.11.048.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
32. Johir, MAH, Nguyen, TT, Mahatheva, K, Pradhan, M, Ngo, HH, Guo, W, et al.. Removal of phosphorus by a high rate membrane adsorption hybrid system. Bioresour Technol 2016;201:365–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.11.045.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
33. Muslim, WA, Albayati, TM, Al-Nasri, SK, Rashid, KT, Salih, IK, Al-Nasri, AS. A hybrid adsorption/ultrafiltration membrane process for removal of Cs-137 from radioactive wastewater using natural clay adsorbent. Chem Eng Res Des 2024;208:853–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2024.07.036.Suche in Google Scholar
34. Inglezakis, VJ, Fyrillas, MM, Park, J. Variable diffusivity homogeneous surface diffusion model and analysis of merits and fallacies of simplified adsorption kinetics equations. J Hazard Mater 2019:224–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.023.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
35. Adaileh, A, Ragab, AH, Taher, MA, Gumaah, NF, Ahmad, IAA, Selim, H, et al.. Development of Cu-ZnO ZrO2 based polyacrylonitrile polymer composites for removing pharmaceutical pollutants and heavy metals from wastewater. Sci Rep 2025;15:22250. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-95736-x.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
36. Najm, IN. Mathematical modeling of PAC: adsorption processes: easy-to-use models for PAC adsorption processes are presented. J Am Water Works Assoc 1996;88:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1551-8833.1996.tb06631.x.Suche in Google Scholar
37. Ocampo-Perez, R, Leyva-Ramos, R, Mendoza-Barron, J, Guerrero-Coronado, RM. Adsorption rate of phenol from aqueous solution onto organobentonite: surface diffusion and kinetic models. J Colloid Interface Sci 2011;364:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.08.032.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
38. Behboudi, A, Jafarzadeh, Y, Yegani, R. Preparation and characterization of TiO2 embedded PVC ultrafiltration membranes. Chemical Engineering Research and Design [Internet] 2016;114:96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2016.07.027.Suche in Google Scholar
39. Mubarak, MF, Ragab, AH, Hosny, R, Ahmed, IA, Ahmed, HA, El-Bahy, SM, et al.. Enhanced performance of chitosan via a novel quaternary magnetic nanocomposite chitosan/grafted Halloysitenanotubes@ZnγFe3O4 for uptake of Cr (III), Fe (III), and Mn (II) from wastewater. Polymers 2021, 13, 2714. Polymers 2025, 17, 1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131759.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin/Boston


