Abstract
The health target is still considered one of the most challenging goals for most Middle East and North African (MENA) Countries. Using Panel Least Square with Regional Dummies (LSDV) for 20 MENA countries over the period 2000–2009, the study concludes that with less than 5 years for the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) to be concluded, a significant acceleration in economic growth is required for the MENA countries to achieve their goals on reducing the under-five infant mortality rates (UFMR) and the maternal mortality rates (MMR) if these countries depended solely on economic growth. As a policy implication, MENA governments need to concentrate on developing and improving many areas including social and physical infrastructure as well as legal and financial institutions.
Appendix
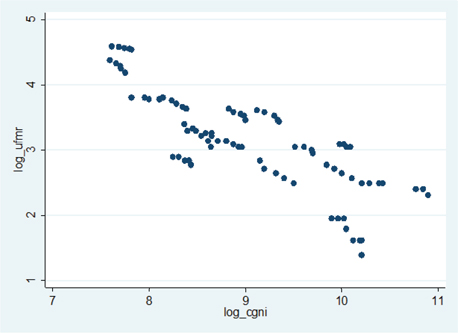
Log of under-five mortality rate vs. log of per capita GNI
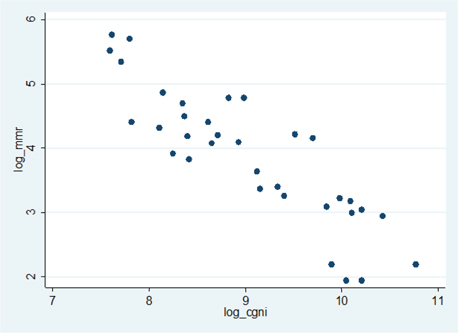
Log of MMR vs. log of per capita GNI
Country code
| Number | Country |
| 1 | Algeria |
| 2 | Bahrain |
| 3 | Djibouti |
| 4 | Egypt |
| 5 | Iran |
| 6 | Iraq |
| 7 | Israel |
| 8 | Jordan |
| 9 | Kuwait |
| 10 | Lebanon |
| 11 | Libya |
| 12 | Malta |
| 13 | Morocco |
| 14 | Oman |
| 15 | Qatar |
| 16 | Saudi Arabia |
| 17 | Syria |
| 18 | Tunisia |
| 19 | United Arab Emirates |
| 20 | Yemen |
Correlation between independent variables
| Per capita GNI | Female primary school completion rate | Access to improved sanitation facilities | Access to clean water | Measles immunization rate | Health expenditure | |
| Per capita GNI | 1.000 | |||||
| Female primary school completion rate | 0.5890 | 1.000 | ||||
| Access to improved sanitation facilities | 0.7119 | 0.8413 | 1.000 | |||
| Access to clean water | 0.4865 | 0.4549 | 0.7252 | 1.000 | ||
| Measles immunization rate | 0.5914 | 0.7840 | 0.7457 | 0.6825 | 1.000 | |
| Health expenditure | −0.1296 | −0.0335 | 0.0937 | 0.3179 | 0.1367 | 1.000 |
Computing growth using semi-log tend function of eq. [3] where
| # | Country | a | b |
| 1 | Algeria | 8.65 | 0.01 |
| 2 | Bahrain | 9.91 | 0.10 |
| 3 | Djibouti | 7.42 | 0.09 |
| 4 | Egypt | 8.10 | −0.01 |
| 5 | Iran | 8.91 | −0.06 |
| 6 | Iraq | 7.55 | −0.92 |
| 7 | Israel | 9.91 | −0.02 |
| 8 | Jordan | 8.15 | 0.02 |
| 9 | Kuwait | 10.52 | 0.08 |
| 10 | Lebanon | 8.77 | 0.03 |
| 11 | Libya | 9.36 | −0.14 |
| 12 | Malta | 9.64 | 0.03 |
| 13 | Morocco | 7.93 | 0.00 |
| 14 | Oman | 9.50 | −0.08 |
| 15 | Qatar | 8.01 | −0.05 |
| 16 | Saudi Arabia | 9.84 | −0.01 |
| 17 | Syria | 8.07 | 0.06 |
| 18 | Tunisia | 8.48 | 0.01 |
| 19 | United Arab Emirates | 9.01 | 0.06 |
| 20 | Yemen | 7.46 | 0.02 |
Under-five mortality rate gap analysis based on income elasticity
| Country | MDG Latest Year(1) | MDG Latest Value(2) | 2015 MDG Target(3) | Years Left to 2015(4) | MDG Required Growth “r”(5) | 2015 MDG Projection(6) | MDG Gap 2015(7) | Required Per-capita GDP (%)(8) | Actual Per-capita GDP “b”(9) | Per-capita GDP Gap(10) |
| Algeria | 2009 | 32 | 20 | 6 | −0.08 | 30.30 | −10.30 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.10 |
| Bahrain | 2009 | 12 | 5 | 6 | −0.14 | 7.72 | −2.72 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Djibouti | 2009 | 94 | 41 | 6 | −0.13 | 64.50 | −23.50 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| Egypt | 2009 | 21 | 30 | 6 | 0.06 | 20.02 | 9.98 | −0.09 | −0.01 | −0.08 |
| Iran | 2009 | 31 | 24 | 6 | −0.04 | 23.88 | 0.12 | 0.06 | −0.06 | 0.12 |
| Israel | 2009 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 0.00 | 3.68 | 0.32 | 0.00 | −0.02 | 0.02 |
| Jordan | 2009 | 25 | 13 | 6 | −0.10 | 22.88 | −9.88 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.13 |
| Kuwait | 2009 | 10 | 6 | 6 | −0.08 | 7.20 | −1.20 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.04 |
| Lebanon | 2009 | 12 | 13 | 6 | 0.01 | 10.58 | 2.42 | −0.02 | 0.03 | −0.05 |
| Libya | 2009 | 19 | 12 | 6 | −0.07 | 10.52 | 1.48 | 0.11 | −0.14 | 0.25 |
| Morocco | 2009 | 38 | 30 | 6 | −0.04 | 38.19 | −8.19 | 0.06 | −0.001 | 0.06 |
| Oman | 2009 | 13 | 16 | 6 | 0.04 | 9.35 | 6.65 | −0.05 | −0.08 | −0.03 |
| Qatar | 2009 | 11 | 6 | 6 | −0.10 | 8.80 | −2.80 | 0.14 | −0.05 | 0.15 |
| Saudi Arabia | 2009 | 21 | 14 | 6 | −0.07 | 20.27 | −6.27 | 0.10 | −0.01 | 0.11 |
| Syria | 2009 | 16 | 12 | 6 | −0.05 | 12.33 | −0.33 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| Tunisia | 2009 | 21 | 17 | 6 | −0.03 | 20.33 | −3.33 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| United Arab Emirates | 2009 | 8 | 6 | 6 | −0.05 | 6.11 | −0.11 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| Yemen | 2009 | 66 | 42 | 6 | −0.07 | 61.85 | −19.85 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.09 |
MMR gap analysis based on income elasticity
| Country | MDG Latest Year(1) | MDG Latest Value(2) | 2015 MDG Target(3) | Years Left to 2015(4) | MDG Required Growth “r”(5) | 2015 MDG Projection(6) | MDG Gap 2015(7) | Required Per-capita GDP (%)(8) | Actual Per-capita GDP “b”(9) | Per-capita GDP Gap(10) |
| Algeria | 2008 | 120 | 63 | 7 | –0.09 | 107.53 | –44.53 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.06 |
| Bahrain | 2008 | 19 | 6 | 7 | –0.15 | 7.65 | –1.65 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.03 |
| Djibouti | 2008 | 300 | 93 | 7 | –0.15 | 138.28 | –45.28 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.04 |
| Egypt | 2008 | 82 | 55 | 7 | –0.06 | 74.51 | –19.51 | 0.05 | –0.01 | 0.06 |
| Iran | 2008 | 30 | 38 | 7 | 0.03 | 17.61 | 20.39 | –0.03 | –0.06 | –0.03 |
| Israel | 2008 | 7 | 3 | 7 | –0.11 | 5.91 | –2.91 | 0.10 | –0.02 | 0.12 |
| Jordan | 2008 | 59 | 28 | 7 | –0.10 | 49.35 | –21.35 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| Kuwait | 2008 | 9 | 3 | 7 | –0.15 | 4.59 | –1.59 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.05 |
| Lebanon | 2008 | 26 | 13 | 7 | –0.09 | 20.17 | –7.17 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| Libya | 2008 | 64 | 25 | 7 | –0.13 | 18.66 | 6.34 | 0.11 | –0.14 | –0.25 |
| Morocco | 2008 | 110 | 68 | 7 | –0.07 | 111.11 | –43.11 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.14 |
| Oman | 2008 | 20 | 12 | 7 | –0.07 | 10.18 | 1.82 | 0.06 | –0.08 | –0.11 |
| Qatar | 2008 | 8 | 4 | 7 | –0.09 | 5.08 | –1.08 | 0.08 | –0.05 | 0.13 |
| Saudi Arabia | 2008 | 24 | 10 | 7 | –0.12 | 22.35 | –12.35 | 0.10 | –0.01 | 0.11 |
| Syria | 2008 | 46 | 30 | 7 | –0.06 | 27.04 | 2.96 | 0.05 | 0.06 | –0.04 |
| Tunisia | 2008 | 60 | 33 | 7 | –0.08 | 56.19 | –23.19 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.06 |
| United Arab Emirates | 2008 | 10 | 7 | 7 | –0.05 | 5.78 | 1.22 | 0.04 | 0.06 | –0.03 |
| Yemen | 2008 | 210 | 135 | 7 | –0.06 | 184.25 | –49.25 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
References
Akinkugbe, O.2007. “Health Care Spending as a Determinant of Health Status: A Panel Data Analysis of SSA and MENA.” University of Botswana, unpublished.Suche in Google Scholar
Bourguignon, F., A.Bénassy-Quéré, S.Dercon, A.Estache, J. W.Gunning, R.Kanbur, S.Klasen, S.Maxwell, J.-P.Platteau, and A.Spadaro. 2008. “Millennium Development Goals at Midpoint: Where Do We Stand and Where Do We Need to Go?” Research paper for the European Commission, International Development (DFID), UK. http://www.eadi.org/fileadmin/MDG_2015_Publications/Bourguignon_et_al__PAPER.pdf.Suche in Google Scholar
Chatterjee, S.2006. “Growth and MDG Attainments: A Technical Note Based Oncross-Country Data.” Asian Development Bank, 14 (1), Manila.Suche in Google Scholar
Deribew, A., F.Tessema, and B.Girma. 2007. “Determinants of Under-Five Mortality in Gilgel Gibe Field Research Center, Southwest Ethiopia .” Ethiopian Journal of Health Development21(2):117–24.10.4314/ejhd.v21i2.10038Suche in Google Scholar
Emara, N. forthcoming, 2014. “Income Elasticity and the Gender Gap: A Challenging MDG for the MENA Countries .” Review and Resubmit to the Review of Middle East Economics and Finance.10.1515/rmeef-2012-0034Suche in Google Scholar
Enders, C. K. 2003. “Using the Expectation Maximization Algorithm to Estimate Coefficient Alpha for Scales with Item-Level Missing Data .” Psychological Methods8(3):322–37. doi:10.1037/1082-989X.8.3.322Suche in Google Scholar
Gyimah-Brempong, K., and M.Wilson. 2004. “Health Human Capital and Economic Growth in Sub-Saharan African and OECD Countries .” The Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance44(2):296–320.10.1016/j.qref.2003.07.002Suche in Google Scholar
Haddad, L. 2003. “Reducing Child Malnutrition: How Far Does Income Growth Take Us? ” World Bank Economic Review17(1):107–31.10.1093/wber/lhg012Suche in Google Scholar
Houweling, T. A. J., et al. 2005. “Determinants of Under-5 Mortality among the Poor and the Rich: A Cross-National Analysis of 43 Developing Countries .” International Journal of Epidemiology34(6):1257–65. doi:10.1093/ije/dyi190Suche in Google Scholar
Kamaly, A.2007. “On the Determinants of Selected Health and Education Outcomes in Sub-Saharan Countries: A Quantitative Analysis.” unpublished.Suche in Google Scholar
Kamiya, Y. 2010. “Determinants of Health in Developing Countries: Cross-Country Evidence .” Osaka School of International Public Policy DP-2010-E-009.Suche in Google Scholar
Melamed, C., K.Higgins, and A.Summer. 2010. “Economic Growth and the MDGs .” Overseas Development Institute, Policy Brief, UK, June 2010.Suche in Google Scholar
Panda, M., and A.Ganesh-Kumar. 2007. “Impact of Economic Growth on Achieving MDGs.” Report submitted to the UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and Pacific (ESCAP), Bangkok.Suche in Google Scholar
Peng, C. Y. J., M.Harwell, S. M.Liou, and L. H.Ehman. 2006. “Advances in Missing Data Methods and Implications for Educational Research.” In Real Data Analysis, edited by S. S.Sawilowsky, 31–78. Charlotte, NC: Information Age Pub.Suche in Google Scholar
Ram, R. 2006. “Growth Elasticity of Poverty: Alternative Estimates and a Note of Caution .” Kyklos59(4):601–10.10.1111/j.1467-6435.2006.00351.xSuche in Google Scholar
Ravallion, M. 2007. “Inequality Is Bad for the Poor.” In Inequality and Poverty Re-Examined, edited by S.Jenkins and J.Micklewright. Oxford: Oxford University Press.Suche in Google Scholar
Sanchez, L.2013. “Egypt Leads North Africa in Achieving Millennium Development Goals .” Daily News (Egypt), May 27.Suche in Google Scholar
UNICEF. September 2010. “Narrowing the Gaps to Meet the Goals.” The Convention on The Right For Children. http://www.unicef.org/media/files/Narrowing_the_Gaps_to_Meet_the_Goals_090310_2a.pdfSuche in Google Scholar
Wagstaff, A., M.Claeson, R.Hecht, P.Gottret, and Q.Fang. 2006. “Millennium Development Goals for Health: What Will It Take to Accelerate Progress?” In Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries, edited by D. T.Jamison, J. G.Breman, A. R.Measham, et al., 2nd ed. Washington, DC: World Bank.Suche in Google Scholar
World Bank. 2005. Pro-Poor Growth in the 1990s: Lessons and Insights from 14 Countries. Washington, DC: World Bank.Suche in Google Scholar
World Health Organization. 2009. “Measles .” Fact sheet N286, December 2009. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs286/en/Suche in Google Scholar
World Health Organization. 2010. “Millennium Development Goals: Progress Towards the Health-Related Millennium Development Goals .” Fact sheet N290, May 2010. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs290/en/index.htmlSuche in Google Scholar
- 1
d = 1 Algeria, Malta, Morocco, Tunisia. d = 2 Egypt, Libya. d = 3 Israel, Jordan, Lebanon. d = 4 Syria, Iran, Iraq. d = 5 Bahrain, Kuwait, Qatar, Saudi Arabia. d = 6 Djibouti, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Yemen.
©2014 by Walter de Gruyter Berlin / Boston
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Effect of Corruption on Tax Revenues in the Middle East
- The Real Exchange Rate and External Competitiveness in Egypt, Morocco and Tunisia
- Effect of Income Elasticity on MDG Health Indicators: The Case of MENA Countries
- Corporate Governance, Capital Structure and Corporate Performance: Evidence from GCC Countries
- Book Review
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Effect of Corruption on Tax Revenues in the Middle East
- The Real Exchange Rate and External Competitiveness in Egypt, Morocco and Tunisia
- Effect of Income Elasticity on MDG Health Indicators: The Case of MENA Countries
- Corporate Governance, Capital Structure and Corporate Performance: Evidence from GCC Countries
- Book Review


