Abstract
C33H23N4O4ClPb, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 11.0932(8) Å, b = 16.7331(10) Å, c = 16.1349(10) Å, β = 107.018(2)°, V = 2863.9(3) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0364, wRref(F2) = 0.0870, T = 293(2) K.
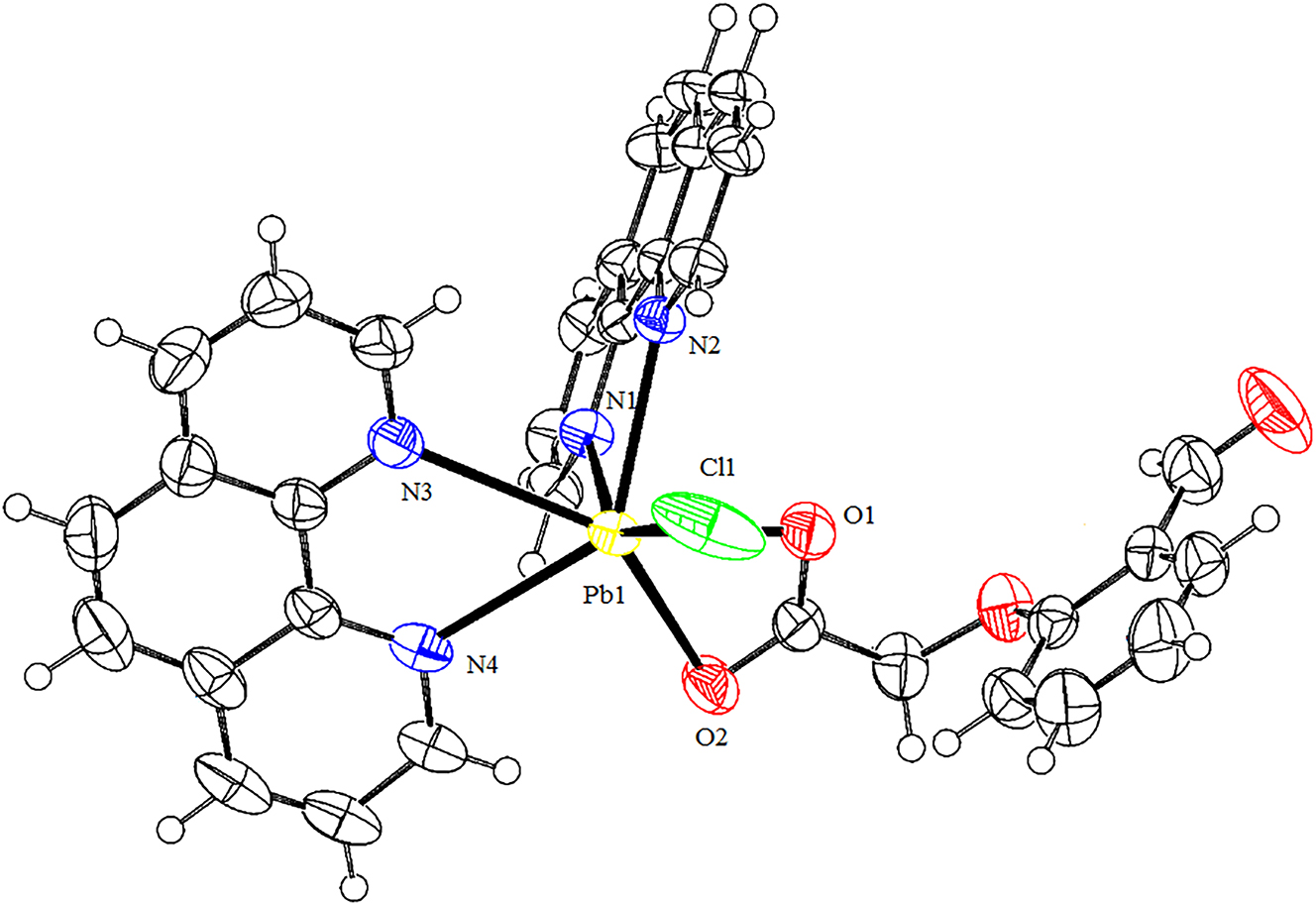
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data. The list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Block, colourless |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 6.03 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8, φ and ω-scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.5°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 78022, 6505, 0.093 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 5367 |
| N(param)refined: | 388 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs 1 , OLEX2 2 , SHELX 3 , DIAMOND 4 |
1 Source of materials
Adding 0.2781 g PbCl2 (1.0 mmol) to 30 ml ethanol-water (v:v = 1:1) solution containing 0.1802 g 2-formylphenoxyacetic acid (1.0 mmol), 0.1982 g 1,10-phenantroline (1.0 mmol) and 0.040 g sodium hydroxide (1.0 mmol) at room temperature. Then the aforementioned mixture was heated at 81 °C for 3 h with stirring. After cooling to room temperature the mixture was filtered. The colorless block crystals were received from the filtrate after 25 days.
2 Experimental details
Coordinates of hydrogen atoms were refined without any constraints or restraints. The hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically. Their Uiso values were set to 1.2 Ueq of the parent atoms.
3 Comment
The synthesis and characterization of lead(II) complexes has been one of the interests of coordination chemistry, as they exhibited novel structure 5 , 6 , 7 and properties such as luminescent property, 8 selective potentiometric microsensor, 9 iodine capture and dye removel, 10 and so on. In this work, a new Pb(II) complex has been synthesized by the assembly of PbCl2, 2-formylphenoxyacetic acid, 1,10-phenantroline and sodium hydroxide. The molecular structure of the title complex is shown in Figure 1. The single crystal X-ray diffraction shows that the Pb(II) complex is made up of one Pb(II) cation, two 1,10-phenantroline molecules, one 2-formylphenoxyacetate ligand, and one chloride ion. The Pb(II) ion is coordinated with four N atoms (N1, N2, N3, and N4) of two 1,10-phenantroline ligands, two O atoms (O1 and O2) of one coordinated H2O molecules, and two N atoms (N1, N2) of one 2-formylphenoxyacetate ligand, and one chloride ion, which forms a seven-coordinated distorted pentagonal bipyramid coordination geometry (Figure 1). Both 1,10-phenantroline and 2-formylphenoxyacetate ligands are in a bidentate coordination mode. The bond angles of N–Pb1–N, N–Pb–O, O–Pb–O, O–Pb–Cl, and N–Pb–Cl are in the range of 59.30(12)–129.61(12)°, 73.68(13)–151.33(13)°, 49.80(10)°, 94.53(10)–117.41(10)°, and 83.98(9)–148.55(9)°. The lengths of Pb–O bonds, Pb–N bonds, and Pb–Cl bond are in the range of 2.501(4)–2.710(4) Å, 2.531(4)–2.774(4) Å, and 2.9471(17) Å, respectively which are agreement with those in refs. 11 and 12. The dihedral angle of two phenantroline rings is 86.53°. The Pb(II) complex molecules form 1D chained structure by π–π interactions.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Henan Academy of Sciences (20253808001) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21171132, https://doi.org/10.13039/501100001809).
References
1. Bruker. Saint and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2000.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg, K. Diamond. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 3.2; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2012.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Darious, R. S.; Evangeline, H. G.; Perdih, F.; Vedha, S. A. Role of Tetrel Bonds in the Supramolecular Architecture of Tetranuclear Pb(ii)[LL-Thiophene Carboxylate] Complexes C an Experimental and Computational Study. CrystEngComm 2024, 26, 4098–4106. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ce00466c.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Song, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Y. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of a Novel 2D Supramolecular Lead Coordination Polymer with Phenanthroline Derivate and Adipic Acid. Main Group Met. Chem. 2021, 44, 239–242. https://doi.org/10.1515/mgmc-2021-0025.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Zhang, L. L.; Tang, S. L.; Li, D. J.; Cheng, Y. Z.; Zhang, L. P. Synthesis and Crystal Structure of One New Pb(II) Complex Constructed by 1,10-Phenanthroline and Two Carboxylate Ligands. Main Group Met. Chem. 2021, 44, 157–164. https://doi.org/10.1515/mgmc-2021-0019.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Cheng, M. L.; Yang, B. X.; Tang, L. Z. P.; Qin, M. N.; Liu, Q.; Tang, X. Y. Pb(II) Coordination Complexes Based on 5-Methyl-1H-Pyrazole-3-Carboxylic Acid: Syntheses, Structures and Luminescent Properties. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 35, 687–694.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Çıtlakoğlu, M.; Yolcu, Z. Dinuclear Pb(II) Monomer Complex: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of Pb(II) Ion-Imprinted Polymer as a Selective Potentiometric Microsensor. Polyhedron 2023, 243, 116539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2023.116539.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Kamal, S.; Khalid, M.; Khan, M. S.; Shahid, M.; Ahmas, M. A Bifunctionalised Pb-Based MOF for Iodine Capture and Dye Removel. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 4501–4516. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3dt00237c.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Wang, L. H.; Tai, H. W.; Li, Q. S.; Xia, Y. P.; Tai, X. S. The Crystal Structure of Tetrakis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate- κ2N,O)-bis(μ2-6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2O:O′)-bis(μ2-6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O:O)tetralead(II), C48H32N4O8Pb2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 1113–1116.10.1515/ncrs-2022-0378Suche in Google Scholar
12. Tai, X. S.; Liang, L.; Li, X. T.; Cao, S. H.; Wang, L. H. Crystal Structure of Diaqua-bis(μ2-6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O:O)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)lead(II)-N,N-dimethylformamide-water (1/2/4), C54H58N6O16Pb2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 1199–1201. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2021-0277.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of (1Z, 2Z)-3-phenyl-2-propenal 2-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)hydrazone, C15H12BrFN2
- Refinement of crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-1 H -inden-1-ylidene)-1 H -indene-1,3(2 H )-dione C18H10O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-fluoro-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-2-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C22H18FNO3
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear copper(II) complex bis(μ2-2,2′ -{[1,3-phenylenebis-(methylene)]bis(oxy)}dibenzoaot-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(dimethylformamide-κ1O)dicopper(II), C50H44Cu2N2O14
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(μ9-biphenyl-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylic-κ8 O,O:O,O′: O,O″:O,O‴)samarium(III)sodium(I)], C16H12NaSmO11
- The crystal structure of 5-benzyl-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-((4-fluorobenzyl)oxy)-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrol-2-one, C25H21F2NO2
- The crystal structure of diammonium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate, C8H12N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C21H19N3O4
- Crystal structure of poly[oktakis(μ2-oxido-κ2O:O)-tetrakis(oxido-κ1O)-bis(μ2-1,1′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]di(1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′))-tetravanadium(V)-dizinc(II)] monohydrate, C28H30Zn2N8O13V4
- Crystal structure of acotiamide hydrochloride dimethylacetamide solvate (1/1), C25H40ClN5O6S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[monoaqua (u2-(3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic-k4O:O′:O″:N)zinc(II))] monohydrate, C15H11NO10Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido{2,6-bis(3,5-diisopropyl-N-pyrazolyl)pyridine}zinc(II), C23H33Cl2N5Zn
- Crystal structure of nitrato-κ2O,O′-[hydridotris(3,5-diethylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″]copper(II), C21H34BCuN7O3
- Crystal structure of 2,7-bis(3,5-diethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-tetrone, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chlorophenyl)benzothiazole, C13H8ClNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure (3R,4′S)-4′-(3,5-dibromophenyl)-1′-methyl-2H-dispiro [benzofuran-3,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,2″-indene]-1″,2,3″-trione, C26H17Br2NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(((3a,7a-dihydro-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)methyl) triphenylphosphonium) tetrachloridomanganate(II), C50H42Cl4MnN6P2
- The crystal structure of 4,9-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-bis(2-cyanobenzyl)-2,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-2,7,5-(epiprop[2]ene[1,1,3]triyl)pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3,10-dicarbonitrile, C40H26Cl2N6
- The crystal structure of poly((μ2-3-(3-nitro-4-carboxylphenyl)benzoate-κ3O, O′:O″)-μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′-cadmium(II)), C26H17N5O6Cd
- The crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7(6H)-dione monohydrate, C7H6N2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-((cyclohexylsulfonyl)methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo [4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C18H24N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(2,4-di(fluorine)-1-phenylpyridine-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate–dichloromethane (1/1), C47H30Cl2F10IrN4P
- Crystal structure of (4-(1-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid, C19H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)arsonic acid, C12H11AsN2O3
- The crystal structure of N(benzyl(phenyl)carbomothioyl)benzamide, C21H18N2OS
- The crystal structure of bis(2-picolinium) hexachlorostannate dichloromethane monosolvate, C13H18Cl8N2Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-3–1-(carboxylatomethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylato)-κ4O:O′,O″,N)zinc(II)], C5H7N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide – 2-(nitrophenyl)methanol (1/1), C6H6N2O·C7H7NO3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-fluorobenzoate hydrate, C23H25F2N3O6
- Crystal structure of [diaqua-{1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′}magnesium(II)] C18H14MgN4O10
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (2-iodo-5-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C20H20INO5
- The crystal structure of 3,7,11-trimethylbenzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3,4-kl]phenothiazine 5,5,9,9-tetraoxide, C21H17NO4S2
- Crystal structure of tris(piperazine-1,4-diium)bis(2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propane-tricarboxylate) pentahydrate, C24H56N6O19
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-5-((5-isopropyl-2-methylphenoxy)methyl)pyridine, C16H18ClNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)benzylidene)-6,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydrobenzo[(b)]oxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzohydrazide, C17H16Cl2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3- dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-8-methylchroman-4-one, C17H16O5
- Crystal structure of bis[(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium]di-μ2-bromido-dibromidodicopper(I)
- Crystal structure of bis [(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidodicopper(I), C22H22Br2CuO2P
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid], C12H8N2O5
- The crystal structure of one-dimensional cooridnation polymer bis(thiocyanato)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis(1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine κ2N:N)iron(II), (C30H28N10S2Fe)n
- Crystal structure of ((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-l-alanine, C11H14N2O5S
- Crystal structure of [(1-naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), [C29H24P]+[CuCl2]−
- RbTm3S5: the first rubidium lanthanoid(III) sulfide with CsEr3Se5-type crystal structure
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(methylammoniumdiyl))bis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) diiodido-tris(μ2-iodido-κ2I:I)dicopper(II) chloride dihydrate, C16H30Cu2I6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-ethoxy-1-methoxy-4-(2-(methylsulfonyl)vinyl)benzene, C12H16O4S
- Crystal structure of potassium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanesulfonate, C8H4O3F13SK
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-(quinolin-8-yloxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)morpholine, C15H14O2N4S
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,5-dimethylbenzene, C10H12Br2
- The crystal structure of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]diazepine-4,6,8-triamine methanol solvate, C7H11N7O
- The crystal structure of chlorido-bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-(2-formylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O) lead(II), C33H23N4O4ClPb
- Crystal structure of pyridinium tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentadionato-κ2O,O′)yttrium(III) C20F12H16YO8C5H6N


