Abstract
This article presents a model of political insulation of bureaucracies. Political influence can harm competence because it lowers the incentives of bureaucrats to invest in competence. Politicians then want to adopt institutions that insulate the bureaucracy because this establishes a commitment to reward competence. Political leaders insulate the bureaucracy if public good provision is important compared to rent extraction or when political competition forces the political elite to internalize the welfare loss caused by patronage. Through this channel political reforms can lead to reforms of the bureaucracy. The theoretical findings are illustrated with existing empirical studies and data on central bank independence.
1 Introduction
The question of what determines effective government is central to development economics and political economy. Some progress has been made in the study of certain political institutions but there is still little consensus on which institutions determine good governance more generally and how they should be measured.[1] One reason is that there is no agreed way to categorize and measure bureaucratic institutions.[2]
Possible avenues are the institutions that regulate the selection and promotion of bureaucrats. We call the selection by political leaders patronage.[3] In this setup bureaucrats can be hired, promoted and fired by the political leadership without institutional restrictions. However, in most developed countries the bureaucracy is (at least partially) insulated from political influence. Institutions like state examinations for entry, objective standards for promotion, firing restrictions guarded by a civil service commission all hinder political involvement with the declared aim of maximizing bureaucratic competence. The institutions that guard central bank independence (CBI) in many countries are an example of insulation.
This article provides a theoretical model of political insulation to explain why it, firstly, might raise bureaucratic efficiency compared to patronage and, secondly, why political leaders (politicians) choose to insulate the bureaucracy. We start with the assumption that when politicians are able to select bureaucrats they face a trade-off between rent extraction and public good provision. Our model shows that this trade-off can hinder effective competition for bureaucratic posts and leads to an underinvestment in competence under patronage. Political insulation raises efficiency because it changes career incentives. Politicians introduce insulation if the lost rents can be compensated by the increase in bureaucratic efficiency. This is the case if the benefit of public good provision compared to rent extraction is high or if shared political power forces politicians to internalize the loss in efficiency that patronage entails.
We show that patronage is abolished if political power is shared among different groups in society. An increase in political competition can therefore raise bureaucratic efficiency. Put differently, our model points to a spillover from competitive political institutions to efficient bureaucratic institutions. This finding stands in contrast to theoretical work which argues that political competition can lead to an increase in the use of patronage and rising inefficiency.[4] In order to support our theory we therefore discuss existing evidence on political insulation. We also show that changes in bureaucratic independence, measured as the political independence of the central bank CEO, seem to follow changes in political competition in a large cross section of countries.
One of the main motivations is to try to understand why politicians give up control over the selection of bureaucrats. We postulate that political insulation is introduced if politicians want to commit future governments not to meddle in selection. A key element in our argument is that political selection leads to a bias in recruitment and promotion of bureaucrats which harms bureaucratic efficiency. We illustrate and support this argument with a discussion of civil service reforms in the UK and a review of the empirical literature.
Our model suggests that the benefits of rent extraction relative to public good provision (polarization) play an important role in insulation. High levels of polarization lead to the adoption of bureaucratic institutions that allow for political influence and lower bureaucratic efficiency. This finding is in line with the long-term effects of ethnic fractionalization, civil wars and resource abundance. The possibility that changes in the political system spill over into bureaucratic institutions also implies that an empirical measure of insulation could explain some of the variation in the performance of political institutions.[5]
We provide two extensions to the basic model. In the first extension we assume that specialization in competence is costly. We show that, somewhat surprisingly, patronage can now lead to higher competence than insulation if political competition is absent. However, it is only in the combination between patronage and strong incumbent power that patronage performs well. With strong political competition patronage is always less efficient than insulation.
In a second extension we endogenize political power in a simple voting model with vested interest. We show that if the incumbent can mobilize powerful vested interests, patronage is adopted to allow the incumbent to stay in power. If the incumbent has very strong vested interests against himself he can use bureaucratic insulation to dissipate political resistance. Insulation dissipates opposition because it ensures that bureaucratic decisions are not affected by the political leadership. This highlights a surprising mechanism in which bureaucratic reforms fill in for political reform.
The following section discusses the related literature. Section 3 presents the basic model. This model is then extended in Section 4. Section 5 discusses new and existing empirical evidence in support of the theoretical findings. The last section discusses the results and caveats.
2 Related Literature
Civil service institutions insulate the bureaucracy from the influence of politicians. Central pillars of this insulation are institutions that restrict hiring and firing of bureaucrats. From the point of view of classic incentive theory this seems to be a bad idea. Insulation harms the provision of sharp incentives. Not surprisingly, the arising moral hazard problem has provided a main motivation for research on bureaucracy.[6]
Accordingly, there is a large literature on why political insulation is adopted nonetheless. One of the main arguments is provided by Moe (1989) who posits that incumbents face uncertainty about their own grip on political power in the future. This will prompt them to favor structures that insulate their achievements from politics. Strong opposition in this framework will impose structures that subvert effective performance and politicize agency decisions. Stephenson (2008) argues formally that bureaucratic insulation works as an insurance for the median voter against political uncertainty induced by elections. Lavertu (2013) builds on these works and shows that there is issue-specific variation in the degree of political insulation of the bureaucracy. Relatively conflict-ridden and volatile issue areas are politically uncertain and the bureaucracy is therefore insulated. We deviate from this viewpoint in that we argue that insulation enhances welfare, i.e. the opposition favors insulation compared to politicization. Changes in the political institutions toward more competitiveness, like an expansion of the franchise, will therefore tend to increase insulation and bureaucratic efficiency.
In our framework insulation is adopted in order to guarantee an investment in expertise. Many scholars have stressed the importance of this investment.[7] Our work is most closely related to work on discretion by Gailmard and Patty (2007) who model the decision of bureaucrats to invest in costly expertise. They show that, in order to ensure competence, it can be rational to grant discretion to bureaucrats despite the fact that bureaucrats with a political bias will select into the bureaucracy.[8] We focus on the selection of bureaucrats under the assumption that bureaucrats enjoy discretion once selected. In our focus on selection we are in line with theoretical work which argues that promotions can be used to solve incentive problems within organizations.[9]Alesina and Tabellini (2007), for example, argue that bureaucrats are motivated by career incentives and contrast this to the re-election incentives for politicians. We add to this literature by analyzing the incentives of politicians to manipulate bureaucratic careers. In this way we are able to analyze the impact of political institutions on the choice of bureaucratic institutions and, hence, bureaucratic efficiency.
We argue that the existence of a commitment problem not to meddle in the selection of bureaucrats is the reason for why political insulation is so common in developed states. While direct references to civil service institutions are rare, there are several theoretical works that relate to this argument. Aghion and Tirole (1997) argue that a commitment by the principal to follow an agent’s advice will boost the latter’s incentives to gather information for this decision. Their ideas are similar to Max Weber’s vision of a bureaucracy in which formal authority is given to those with expertise. Konrad and Torsvik (1997) show that a politician who plays a repeated contracting game with a bureaucrat might want to commit not to learn about bureaucrat’s type because this boosts the incentives for the bureaucrat to reveal information in the earlier period of the game. They argue that the existence of term limits for politicians might be explained with this commitment problem. Maskin and Tirole (2004) show that accountability of public decision makers can lead to a welfare loss if it makes them pander to public opinion. In their model the public uses the institution of a judge to commit not to fire a decision-maker that takes actions against the public’s prior.
But if bureaucratic institutions are to solve a commitment problem they have to be hard to reverse. Our model treats bureaucratic institutions as state variables that cannot be changed immediately. This assumption is common in the literature on institutions. Acemoglu and Robinson (2005), for example, explain democratization through a commitment problem that can only be solved through an institutionalized transfer of political power. In their model, democratic institutions are a (political) state variable. A main difference of our work to the existing literature on state variables is that political insulation improves efficiency.[10] In that sense civil service reform can be regarded as a beneficial investment in the competence of the bureaucracy.[11] This puts our theory in line with Besley and Persson (2009) who argue that the capacity of the state is due to an investment in this capacity.
In the empirical section we show that political changes toward more competition indeed coincide with an institutional insulation of the central bank.[12] This finding is in line with findings in De Haan and Van’t Hag (1995) who show that measures of political instability correlate with CBI in the cross section. Bernhard (1998) argues that CBI is adopted to solve policy conflicts between government ministers and backbench legislators. He uses cross-country data to show that CBI is adopted if government ministers, party legislators and coalition partners have different monetary policy incentives and if government ministers fear that party legislators and coalition partners will withdraw their support over a policy dispute. We add to this in two ways. First, our argument applies also to non-democracies. Second, we exploit changes across time in both political institutions and institutions that determine CBI. In this way we reduce concerns of omitted variable bias.[13]Dreher et al. (2010) use a panel dataset on turnover of central bank governors for the years 1970–2005 as a proxy for CBI. Among other things, they show that turnover decreases with a higher the level of political instability, i.e. the more often governments are being replaced. We focus instead on changes in the institutions that govern the recruitment of the governor. Given the commitment power of institutions this is an important distinction.
In our main model we assume political power to be exogenous. This stands in stark contrast to work by Acemoglu, Ticchi, and Vindigni (2010) who show that if politicians have the power to provide jobs in government then political competition can create stronger incentives to do so. Their model predicts more inefficiency from patronage with more political competition. This finding is in line with other work that features endogenous political power like the study of dictatorships presented in Debs (2010) or Guriev and Sonin (2009). Both studies argue, in different contexts, that a strong dictator will promote better inferiors than a weak dictator as he is less worried about a loss of political power. A crucial difference to this literature is that our findings suggest a positive correlation between bureaucratic efficiency and political competition.[14]
The assumption of politically motivated bureaucrats links our work to theoretical work that analyzes the role of intrinsic motivation in public sector performance.[15] One key difference is, however, that bureaucrats here are driven by group-specific policy preferences not unlike the policy preference in models of politicians or special interest groups. The main advantage of this assumption from a modeling perspective is that the impact of political recruitment bias under patronage is relatively robust to an expansion in the number of bureaucrats who compete for a post.
3 Basic Model
3.1 Setup
Society consists of two groups of equal size identified by the parameter
The politician of type A (incumbent) is assumed to be in power in period 1. He remains in power with probability
At the beginning of period 1 the incumbent chooses the bureaucratic institutions,
Given S and p the two bureaucrats compete by specializing in one of two policy dimensions – public good provision or rent extraction. If a bureaucrat specialized on a policy dimension in period 1 she is able to provide a successful policy on that dimension with probability
A bureaucrat is defined as competent if she specialized on the dimension of public good provision in period 1. Denote the level of competence by
The expected utility for all individuals (including the bureaucrat) of group t from a bureaucrat of type t and competence
where the first term represents the expected benefit from public good provision and the second term the expected benefit from rent extraction. Analogously, the expected utility for group t from a bureaucrat of type
Equation [2] shows that the expected utility provided by a bureaucrat from the opposition is always increasing in her competence. This is because both increased public good provision and decreasing rent extraction by a bureaucrat of type
The variable h is a measure for the level of specialization in public good provision and rent extraction. For h close to
To end the description of the model, the sequencing of the actions is as follows. The incumbent first chooses the bureaucratic system S. Then, given S, the two bureaucrats simultaneously decide on their specialization
3.2 Bureaucratic Efficiency
A discussion of bureaucratic performance is most useful in the light of the first best. We assume that public goods are non-excludable, i.e. the politician does not internalize the overall benefits of public good provision. This drives a wedge between the politician’s utility in eqs [1] and [2] and overall welfare. Given that both groups in society are of equal size, a social planner who maximizes welfare would always want to select a competent bureaucrat in period 2 (
Political insulation is assumed to give all recruitment powers to a neutral commission that is only interested in competence. Assume that the commission chooses the candidate with the highest level of competence,
Patronage gives the right of selecting the bureaucrat to the politician in power in period 2. Clearly, politicians have an incentive to recruit a bureaucrat of their own type because she will distribute rents toward their group. This group-specific interest can clash with the selection by competence.
Bureaucratic recruitment under patronage is politically biased if
Denote the level of competence of the two bureaucrats by
Insert
Lemma 1 explains why patronage can fail to recruit competent bureaucrats. The reason is that the politician might have to choose between a bureaucrat who would allocate rents to his group and a bureaucrat who is more competent. If rents are important (
An immediate effect of the bias described in Lemma 1 is that recruitment under patronage is fully determined by the type of politician in power. For all
Under patronage bureaucrats specialize in rent extraction (
See Appendix. ■
Proposition 1 gives a possible explanation for why political insulation is often regarded as the better bureaucratic system. Patronage can imply that the bureaucrats specialize in extracting rents from the political opposition if these rents exceed the benefit from public good provision. From a welfare perspective this creates a loss of resources due to bureaucratic incompetence.
The political bias discussed in Lemma 1 is at the heart of this failure of patronage. Given that patronage recruits by type and not by competence there is effectively no competition between bureaucrats of different types. Polarization creates a labor market monopsony for bureaucrats with the correct type and, hence, bureaucrats know that they do not compete against bureaucrats with different policy preferences.
In a politically insulated system, competence can prevent the competing candidate from taking the bureaucratic post and implementing rent extraction in her favor. As both bureaucrats compete on an equal footing, polarization now works as an incentive for a specialization in competence.
Note that if
This assumption implies two things. First, bureaucrats will specialize in rent extraction when left to their own devices. Second, politicians cannot commit to recruit by competence in period 2. As a result patronage is inefficient. We discuss the case of
Given that patronage leads to a specialization in rent extraction the question arises whether the incumbent might still choose it as bureaucratic system. The next section shows that the incumbent’s decision is closely related to the level of political competition p and polarization
3.3 Political Competition and Bureaucratic Institutions
In the first period the incumbent tries to affect outcomes in the second period by choosing the set of bureaucratic institutions,
His expected utility from political insulation is
Note first that under patronage both governments always recruit a bureaucrat of their own type in period 2. This implies that if group A is more powerful (higher p) then the likelihood that bureaucrat A gets the post in period 2 is also higher. As p increases the incumbent can therefore expect more rents to be distributed toward the group he represents. Under political insulation both bureaucrats are selected with probability
Assume
See Appendix. ■
Shared political power (lower p) makes political insulation more attractive. There is a unique level of political power
at which the incumbent is indifferent between political insulation and patronage. For all values of
Corollary 1 suggests a simple link between political and bureaucratic institutions (p and S, respectively). If political institutions exclude access to political power for the opposition (
A large potential for rent extraction compared to public good provision (high
Corollary 2 follows immediately from condition (5). Higher polarization leads to a lower likelihood of insulation. In other words, the adoption of inferior bureaucratic institutions is more likely with the rising importance of rents.
Note that Corollary 2 relies on assumption
Corollary 1 implies that changes in political institutions can lead to an increase in bureaucratic efficiency because they lead to changes in bureaucratic institutions. A lot of the debate around the economic effects of democratization ignores this second-order effect. However, Corollary 2 suggests that the association between democratization and bureaucratic efficiency will depend on whether the implied reduction in p can compensate for lost rents. Here the level of polarization can play for or against an impact of democratization. To see this note, for example, that
In summary, the model delivers a micro-foundation for the choice of inferior bureaucratic institutions and how this choice links to the political situation of a country. Absolutist political institutions and high potential for rent extraction lead to a choice of inefficient bureaucratic institutions which are geared toward the extraction of these rents. Political reforms can lead to an improvement of bureaucratic performance if they give a diverse set of groups access to political power. According to the model, political competition can imply that the political elite of a country adopts political insulation, bureaucratic efficiency increases and rent-extraction decreases.
4 Extensions
4.1 Costly Investment in Competence
There is a recent literature on dictators which argues that stronger dictators might improve bureaucratic efficiency.[21] One way to reconcile this view with our results is to assume that a specialization in competence is more costly than a specialization in rent extraction. This is particularly plausible where public good provision requires more expertise that is specific to the public sector.
Assume that competence costs the bureaucrat c regardless of whether she is selected for the post or not. Assume biased recruitment under patronage (
while candidate B invests in competence if
which illustrates the fact that the strength of the patron (p or
Under insulation investment incentives are independent of p. We show in the appendix that for a range
there are multiple equilibria in investment. There are two asymmetric equilibria in which only one of the candidates invests with certainty. In these equilibria insulation always dominates patronage in terms of welfare. However, there is a third equilibrium in which the two candidates play a mixed strategy and invest with probability
In this equilibrium patronage can dominate insulation.
Assume costly investments in competence at cost c. Without political competition (p close to 1), patronage can lead to higher competence than insulation if
and if c is in a range of costs
See Appendix. ■
We illustrate the proposition in Figures 1 and 2. Figure 1 shows the level of competence under insulation (solid line) and patronage (dashed line) for different values of c and a monopoly of power (
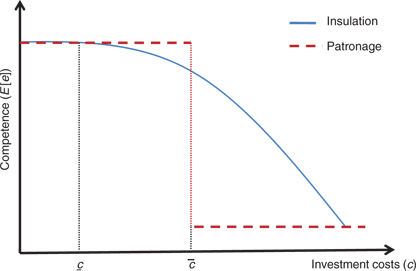
Competence with investment costs (no political competition).
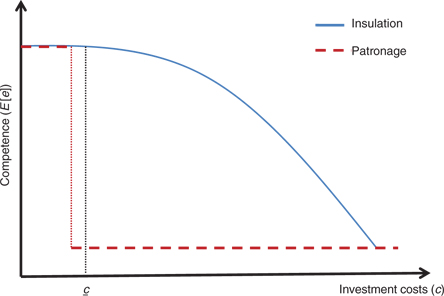
Competence with investment costs (strong political competition).
The situation of a weak incumbent (
The main intuition behind Proposition 3 is that since specialization in competence is costly, a bureaucrat will only invest in competence if she is sufficiently confident that this competence will be put to use. Under patronage, a lack of political competition can therefore work as a guarantee that the candidate’s investment will pay off. In this way patronage can welfare dominate insulation under
Proposition 3 is important because it reinforces the notion that political and bureaucratic institutions are complementary. An absolutist ruler can guarantee to hire his group and, thus, maximizes their incentives to invest into competence. This incentive can be so strong that welfare is higher under patronage than under insulation. However, if political power is shared, patrons are weak. Patronage then harms competence and insulation welfare dominates because it does not rely on the absence of political competition to provide investment incentives.
The incentives of the incumbent to adopt insulation are similar to the main model. Without political competition the incumbent always adopts patronage. If power is shared the incumbent always wants to insulate the bureaucracy. We discuss the adoption decision in more detail in the appendix.
4.2 Endogenous Political Power
Patronage is often referred to as the use of spoils to gather political support. Acemoglu, Ticchi, and Vindigni (2010), for example, use this view on patronage to provide a theory of inefficient states. This section incorporates this view by making p endogenous to the choice of bureaucratic system.
The political process is modeled as a voting game. There are three kinds of voters. The first kind is only interested in public good provision and votes for the politician that is expected to provide the highest benefit on that policy dimension. This group has a mass of
The second group of voters has a mass of
Uncertainty in the political process is modeled through a third group of noise voters whose votes lead to an aggregate shock of votes
The game structure is as follows. First, the incumbent chooses the bureaucratic system. Second, the first two voter types support their preferred candidate. Finally, bureaucrats specialize before the uncertainty introduced by the third voter type gets resolved. Indifferent voters are assumed to randomize their vote.
Under insulation the identity of the politician in the second stage has no impact on outcomes and all decisions are made as before. In particular, both bureaucrats always invest into competence by Proposition 1 regardless of which group is more powerful. The incumbent’s expected utility from
We maintain assumption
or
Given that
while under insulation it is
The following result follows immediately.
Assume
See Appendix. ■
The main novelty in Proposition 4 is that as spoils become more important for political outcomes (rising
Additional insights can be gained from the case in which
while it remains
There are two important cases that might be explained by this reverse causality argument – Prussia and Imperial China. It has been argued that Prussian feudalism might have survived so long because of a relatively insulated bureaucracy. The rising classes were less willing to stage revolution because they were able to reach relatively influential positions in the powerful bureaucracy.[23] Similarly, Northern Sung rulers chose civil service examinations to limit the development of alternative power centers by drawing into their government the sons of elites from newly emerging regions in South China.[24] In both cases autocrats introduced bureaucratic reforms to prevent political opposition.
5 Empirical Evidence
The model provides two main testable propositions. Proposition 1 predicts that patronage leads to bureaucratic inefficiency because it alters career incentives. Proposition 2 states that shared political power and decreasing polarization make insulation more likely. This section discusses the empirical evidence on these two sets of hypothesis separately.
5.1 Political Interference and Bureaucratic Performance
In the nineteenth century Great Britain introduced state exams and a civil service commission; both of these institutional features reduced political control over recruitment with the declared aim of increasing competence. The arguments surrounding these reforms are well documented and can therefore give an insight into the motivation behind actual civil service reforms.
At the beginning of the nineteenth century patronage was the norm in Great Britain while objective criteria hardly played any role in recruitment into the bureaucracy.[25] The struggle for the introduction of a merit system began in 1853 when Charles Trevelyan and Stafford Northcote were asked by the then Chancellor of the Exchequer, William Gladstone, to write a report on its recruitment and promotion.[26] The resulting report, published in 1854, urges for insulation with the following argument:
It may safely be asserted that, as matters now stand, the Government of the country could not be carried on without the aid of an efficient body of permanent officers, occupying a position duly subordinate to that of the Ministers who are directly responsible to the Crown and to Parliament, yet possessing sufficient independence, character, ability, and experience to be able to advise, assist, and to some extent, influence, those who are from time to time set over them.[27]
There is no doubt that Northcote and Trevelyan aimed at insulating the British bureaucracy from political influence. One of their contemporaries, John Stuart Mill, praised reforms in the East India Company as follows:[28]
A second great advantage of the present system is, that those who are sent out as candidates to rise by degrees are generally unconnected with the influential classes in the country, and out of the range of Parliamentary influence. The consequence is, that those who have the disposal of offices in India have little or no motive to put unfit persons into important situations [...][29]
Thus, not only were reformers in Great Britain aware of political incentives to promote unfit personal, they saw political independence as a way to improve performance in this context. Two recent empirical studies lend support for this mechanism. Iyer and Mani (2012) study transfers in the top layers of the Indian civil service between 1980 and 2004. They show first that the reallocation of posts in the Indian bureaucracy is correlated with political change – i.e. even in a system geared toward selection by merit politicians use the leverage they have to alter careers. The clearest division line for political interests in India is caste membership. Consistent with the idea that this political division creates a labor market monopoly for members of the “right” caste, Iyer and Mani found that officers are more likely to be appointed to important positions when they belong to the same caste as the Chief Minister’s party base.
What are the efficiency costs of this politicization? While direct evidence is difficult to establish, Iyer and Mani provide some evidence that career incentives are indeed altered by the political allocation of posts. They show that bureaucrats who can expect to have more politicized careers (i.e. careers that depend more on political change) invest less in expertise. Their study also lends some support for the fact that the performance of government agencies suffers from more politicization.
In addition to this detailed study there are several cross-sectional empirical studies that lend support for the idea that political insulation improves performance. Lewis (2007) uses the scores of an evaluation program initiated by the Bush administration in 2004 to measure program performance. He finds that politically appointed managers perform significantly worse than career civil servants.[30] He shows that the best proxy to explain this difference is the higher bureau experience that civil servants bring to the table. In a cross-country study Rauch and Evans (2000) find that meritocratic recruitment (recruitment by state exams) correlates closely and robustly with measures of bureaucratic performance.
5.2 When Do Politicians Introduce Insulation?
Our theory provides comparative statics regarding the effect of political competition on the use of patronage that are in conflict with existing theoretical work on the topic. In this section we therefore provide some evidence that political competition leads to insulation as Proposition 2 suggests. In addition, we relate our results on the role of polarization to recent discourses in the literature.
Barbara Gedde’s book Politician’s dilemma: Building state capacity in Latin America provides a detailed account of bureaucratic reforms in Latin America. She finds support for the idea that insulation was introduced in Latin America when new political groups gained access to political power. In Venezuela, for example, a civil service reform was drafted in 1960 after the dominant political party, Democratic Action (AD), had lost a large share of its seats in the Venezuelan chamber of deputies. Civil service reforms were implemented once the AD drew equal to its main political competitor in 1968,[31] but then reversed by presidential decree when the AD returned to its dominant role in 1973. Such a reversal is a good indicator that political competition can be an important factor for changes in bureaucratic institutions.[32]
Another example of the relationship between political and bureaucratic reform is the case of Great Britain discussed in the previous section. The Northcote and Trevelyan report was written at a time of radical political changes in the nineteenth century. The middle classes had gained the right to vote in the first reform act in 1832. In addition, the prerogative power of the crown had come to be increasingly taken over by ministers who could be held accountable by parliament. Thus, the executive had become more volatile in the interests it represented both because new groups had entered the political arena and because institutional changes facilitated their access to executive power. In 1854 Northcote and Trevelyan proposed to modify recruitment procedures through the introduction of an entry examination for all public servants, administered by an independent Board of Examiners. Reforms, however, did not take place because parliament resisted their implementation. State exams were not introduced until 1870 – in the middle of a wave of political reforms that would guarantee representatives of the working class access to parliament.[33] One interpretation of this timing of events is that the established members of parliament feared that the control over political recruitment could fall into the hands of the middle and working classes. As their political power was fading, the members of parliament preferred to transfer the power of bureaucratic recruitment to a neutral body.
In addition to these detailed accounts there is empirical evidence from within-country studies that indicate that politicians prefer to insulate if their political power is challenged. Hanssen (2004), for example, studies the institutions governing the appointment of judges in the United States between 1950 and 1990. He shows that institutions that increase judicial independence from politics tend to be implemented in states that feature competitive politics and confirms this pattern with time variation available in the data. Similarly, Ruhil and Camões (2003) show that electoral competition was a key predictor of insulation at the state level in the United States. One standard deviation in closeness of elections more than doubled the chance that a state adopted competitive state examinations between 1900 and 1939.
In order to test whether these patterns appear more generally we need measures of both political competition and bureaucratic institutions which are consistent across countries. Sadly, there is little available data that quantifies specific bureaucratic institutions for a large set of countries.[34] The most commonly used data on bureaucratic quality is provided by the Policy Risk Survey Group (PRSG) but the group does not state which institutions exactly are responsible for high bureaucratic quality. This makes the data less useful for testing the link between political competition and specific bureaucratic institutions.[35] The concern can be avoided with data on CBI provided by Cukierman, Webb, and Neyapti (1992) and Crowe and Meade (2008). Their measure of CBI contains a category which seeks to measure the independence of the Central Bank CEO from political interference on a 0–1 scale.[36] Most economists would agree that political selection might hinder efficiency in this bureaucratic post.
In order to show that political competition is related to bureaucratic independence it is important to find a relatively precise measure of the political institutions we have in mind.[37] The measure most closely related to our concept of political competition is the index of competitiveness of executive recruitment provided by the Polity IV project. According to the Polity IV manual “Competitiveness refers to the extent that prevailing modes of advancement give subordinates equal opportunities to become superordinates.”[38] The codebook distinguishes between fair elections of the chief executive (the top layer of government) and selection through hereditary succession, designation or rigged election. In Table 1, column (1) shows the correlation of CEO independence in 2003 with the average extent of political competition for the years 1998 till 2003.[39] The coefficient suggests that an increase of political competition by 1 standard deviation implies half a standard deviation increase in bureaucratic independence. Column (2) shows that this simple correlation is robust to controlling for GDP per capita and past inflation. Column (3) reveals that running the same regression for the 1980s yields identical results. Interestingly, the extent of political competition in this earlier period does not predict CEO independence in 2003 (column (4)). The underlying reason is considerable change both in political competitiveness and bureaucratic independence between the 1980s and 2003. Column (5) confirms that an increase in political competition within this relatively small period of time went hand in hand with insulation even when controlling for changes in GDP per capita. This suggests a link between competitiveness and bureaucratic independence in the direction suggested by our theory.
Political competition and political independence of the Central Bank Chief Executive Officer (CEO).
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| Variables Independence of Central Bank CEO (2003) | Independence of Central Bank CEO (2003) | Independence of Central Bank CEO (1980–1989) | Independence of Central Bank CEO (2003) | Change in CEO independence | |
| Political competition (1998-2003) | 0.0600** | 0.0832** | |||
| (0.0280) | (0.0335) | ||||
| GDP per capita (2002) | –1.09e-06 | ||||
| (2.00e-06) | |||||
| Average inflation | –6.48e-05 | ||||
| (0.000209) | |||||
| Political competition (1975–1985) | 0.0537** | 0.00298 | |||
| (0.0257) | (0.0227) | ||||
| Change in political competition | 0.0900** | ||||
| (0.0381) | |||||
| Difference in GDP pc | –0.0318 | ||||
| (0.0438) | |||||
| Observations | 82 | 71 | 64 | 81 | 55 |
| R2 | 0.054 | 0.085 | 0.066 | 0.000 | 0.107 |
Evidence on the connection between polarization and bureaucratic institutions is relatively sparse. While there is a wealth of work in development economics that studies the negative impact of variables like inequality, resource rents and ethnic divisions on economic outcomes our theory suggests that the effect should be coming through the capacity of the state to provide public goods as opposed to extracting rents. The most direct evidence here comes from Alesina, Baqir, and Easterly (1999) who study the impact of ethnic fractionalization on the provision of public goods in US cities, metropolitan areas and urban counties. They show that the share of spending on productive public goods declines with ethnic fractionalization and suggest that this might be driven by an increase in spending motivated by patronage in these jurisdictions.
Note that we modeled polarization as the benefits from rent extraction relative to the benefits of public goods provision. An intriguing application of this view is the military. To see this, note that the definition of polarization here captures the difference between external and internal wars. If an external war looms, all members of society would suffer a huge loss if national defense is not successful. Thus, the present government wants to recruit the military by merit because this maximizes defense (public good provision). In a civil war the government wants to recruit the military by patronage because it wants to be sure that the hired military is loyal, i.e. the group-specific control of rents is more important than maximizing the overall level of military competence. Here our theory closely relates to findings by Besley and Persson (2009) who show in a cross section of countries that measures of state capacity correlate positively with past external conflict but negatively with internal conflict.
Abundance of natural resources is another example of an environment with high rents. And indeed there are several case studies that link resource booms to increasing patronage. Robinson, Torvik, and Thierry (2006), for example, summarize several case studies to show how resource booms lead to politically motivated expansions of the public sector. A particularly revealing account comes from Ross (2001) who shows that countries in Southeast Asia dismantled existing forestry institutions (laws, regulations and departments) and increased patronage in the face of timber price shocks. He shows how institutions insulating the forestry bureaucracy from political pressures were dismantled in the Philippines and Malaysia by politicians in order to gain access to resource rents.
6 Discussion
This article stresses the importance of recruitment and promotion in the bureaucracy. Two sets of institutions, insulation and patronage, have been modeled with the aim to analyze their impact on economic welfare and their relationship with political institutions such as elections. The model shows that insulation performs better if patronage leads to a political bias in recruitment which hinders competition for bureaucratic posts by competence. If this gain in efficiency is important, politicians want to commit the future government to recruit by competence. Political insulation is then chosen as a commitment device.
The main finding in the model is that political institutions can have an important effect on the trade-off between political control and competence. If political competition threatens the power of the incumbent he will be more inclined to give up the power of controlling selection for a gain in competence. In this way political reform can trigger bureaucratic reforms. Using a dataset on CBI we have shown that changes in CBI indeed trace changes in political competition.
A crucial assumption in our model is that insulation binds the hands of future governments. There are several features of civil service institutions that justify this assumption. First, the transfer of power to an independent civil service commission and the promise to bureaucrats of a lifelong career by merit creates a vested interest in the survival of the system. Second, civil service institutions have an informational dimension. The entry by exam and promotion by tenure or merit keeps information about the bureaucrat’s preferences from politicians.[40] As the signal on types received by politicians is weak patronage is less attractive. Third, insulation is an investment that increases efficiency. This can strengthen incentives to maintain these institutions.
One drawback of the present model is that it takes political power as exogenously given. This drawback is partly alleviated in a second extension which analyzes the case where the choice of bureaucratic institutions feeds back to political support for the politician. The extension highlights the fact that bureaucratic systems can both increase and decrease political conflict. Patronage increases the stakes of the political game while insulation reduces them. Political mobilization can therefore become an additional incentive to implement inefficient patronage.
A possible criticism regarding the categorization of bureaucratic institutions is that political insulation and patronage could be combined to prevent a trade-off between political preference and competence.[41] In the presented model a pre-selection according to objective criteria followed by a choice by the political elite would perform as well as insulation in terms of welfare. However, the efficiency of political selection then relies on the fact that the two candidates have exactly the same level of competence. In reality, insulation will never lead to two candidates with exactly the same level of competence. The trade-off between competence and political preference will persist.
We argue that bureaucratic institutions of recruitment and promotion have an independent effect on the capacity of the state to provide public goods. A categorization and measurement of bureaucratic institutions might therefore provide a stepping stone in understanding state capacity.
Funding statement: Funding: The author acknowledges the financial support from the Ramon y Cajal program, Research Grant SGR 1064 by the Catalan Government and the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, through the Severo Ochoa Programme for Centres of Excellence in R&D (SEV-2011-0075). All mistakes are that of the author.
Appendix
Proof of Proposition 1
Note first that
which is the case if and only if
Under insulation there are two cases to be considered. Given that the candidate of type
or
And if the other candidate does not specialize in public good provision the candidate of type t wants to be competent if
or
Note that
Proof of Proposition 2
For values of
or
Proof of Proposition 3
The candidate of type A invests in competence if
while candidate B invests in competence if
Since
which is always satisfied for
Under insulation the investment decision of the candidates depends on the other candidate. Type t invests given that
or
while she invests given that the other candidate does not invest if
or
which implies that for a range
which implies that insulation always leads to a more competent bureaucracy in these two equilibria.
In addition, insulation always has a symmetric equilibrium in which both candidates
To compare the two institutions in terms of welfare it is sufficient to analyze the expected level of competence by the chosen bureaucrat. Expected competence under patronage is
and under insulation
which implies that there is no unique value of p below which insulation is adopted. We show this in the following section.
In order to illustrate the role of political competition we focus on two cases
or
It remains to be shown that patronage never leads to higher competence for
or
which is impossible by assumption
Institutional Choice with Investment Costs
As before focus on
which implies that the expected utility of the incumbent from adopting patronage is
and the expected utility from political insulation in the mixed strategy equilibrium is
which implies that due to discrete jumps in the utility, institutional choice is ambiguous. We illustrate this in Figures 3 and 4 in which we draw the two expected utility functions for
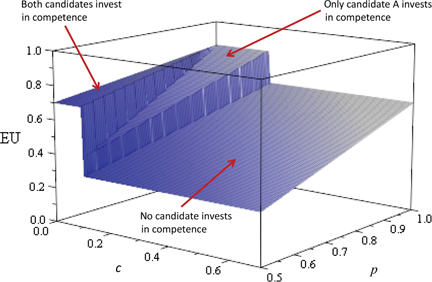
Incumbent utility from patronage with investment costs.
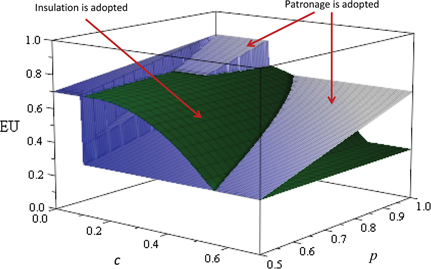
Adoption of insulation with investment costs.
and for the type B candidate stops to invest at
which are clearly visible as two triangular shapes in the space spanned by
In Figure 4 we add the expected utility from insulation (under the assumption of a mixed strategy equilibrium). The dark, smooth curved shape represents
Note that the choice of bureaucratic institution is now not necessarily monotone in p. As illustrated in Figure 4 there are values of c (around
However, the main comparative statics remain quite simple. At very low costs the incumbent prefers patronage as it comes at no cost in terms of competence. When costs increase, patronage leads to incompetence and insulation is preferred. When insulation also leads to incompetent bureaucrats because of prohibitive costs, patronage is preferred again. Note that these results are very much in line with the main model. As before, the incumbent adopts insulation for low values of p and only if insulation offers an advantage in terms of competence. He never adopts insulation for high values of
Proof of Proposition 4
Assume
or
which implies that insulation is introduced for
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Oriana Bandiera, Timothy Besley, Matthew Ellman, Paul Grout, Stephen Hansen, Rafael Hortala-Vallve, Kai Konrad, Gilat Levy, Rocco Macchiavello, Rajesh Ramachandran, Ronny Razin, Gerard Padró i Miquel, Torsten Persson and Daniel Sturm for their advice and comments. The paper benefitted from presentations at the London School of Economics, University of Warwick and the Institute for Economic Analysis.
References
Acemoglu, D., D. Ticchi, and A. Vindigni. 2010. “Emergence and Persistence of Inefficient States.” Journal of the European Economic Association 9: 177–369.10.3386/w12748Search in Google Scholar
Acemoglu, D. 2005. Constitutions, Politics and Economics: A Review Essay on Persson and Tabellini’s “The Economic Effect of Constitutions.” NBER Working Paper, 11235.10.3386/w11235Search in Google Scholar
Aghion, P., and J. Tirole. 1997. “Formal and Real Authority in Organizations.” Journal of Political Economy 105: 1–29.10.1086/262063Search in Google Scholar
Alesina, A., R. Baqir, and W. Easterly. 1999. “Public Goods and Ethnic Divisions.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 114: 1243–84.10.3386/w6009Search in Google Scholar
Alesina, A., and G. Tabellini. 2007. “Bureaucrats or Politicians? Part I: A Single Policy Task.” American Economic Review 97: 169–79.10.1257/aer.97.1.169Search in Google Scholar
Bai, Y., and R. Jiaz. 2014. Mobility and Revolution: The Impact of the Abolition of China’s Civil Service Exam System. Mimeo.Search in Google Scholar
Banerjee, A. 1997. “A Theory of Misgovernance.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 112: 1289–332.10.1162/003355300555484Search in Google Scholar
Bekke, H., and Van Der Meer, F., eds. 2000. Civil Service Systems in Western Europe. Cheltenham: Edward Elgar.Search in Google Scholar
Bernhard, W. 1998. “A Political Explanation of Variations in Central Bank Independence.” American Political Science Review 92: 311–327.10.2307/2585666Search in Google Scholar
Besley, T., and M. Ghatak. 2005. “Competition and Incentives with Motivated Agents.” American Economic Review 95: 616–36.10.1257/0002828054201413Search in Google Scholar
Besley, T., and M. Kudamatsu. 2008. “Making Autocracy Work.” In Institutions and Economic Performance, edited by E. Helpman, Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.10.2307/j.ctv21hrgnz.15Search in Google Scholar
Besley, T., and T. Persson. 2009. “The Origins of State Capacity: Property Rights, Taxation and Politics.” American Economic Review 99: 1218–44.10.3386/w13028Search in Google Scholar
Bubb, R., and P. Warren. 2014. “Optimal Agency Bias and Regulatory Review.” The Journal of Legal Studies 43: 95–135.10.1086/675258Search in Google Scholar
Clark, K. 1959. “statesmen in Disguise’: Reflexions on the History of the Neutrality of the Civil Service.” Historical Journal 2: 19–39.10.1017/S0018246X00021762Search in Google Scholar
Crowe, C., and E. Meade. 2008. “Central Bank Independence and Transparency: Evolution and Effectiveness.” IMF Working Paper WP/08/119.10.5089/9781451869798.001Search in Google Scholar
Cukierman, A., S. Webb, and B. Neyapti. 1992. “Measuring the Independence of Central Banks and Its Effect on Policy Outcomes.” The World Bank Economic Review 6: 353–423.10.1093/wber/6.3.353Search in Google Scholar
Debs, A. 2010. “Economic Theories of Dictatorship.” Economics of Peace and Security Journal 5: 11–17.10.15355/epsj.5.1.20Search in Google Scholar
De Figueiredo, R. 2002. “Electoral Competition, Political Uncertainty, and Policy Insulation.” American Political Science Review 96: 321–33.10.1017/S0003055402000199Search in Google Scholar
De Haan, J., and G. Van’t Hag. 1995. “Variation in Central Bank Independence across Countries: Some Provisional Empirical Evidence.” Public Choice 85: 335–51.10.1007/BF01048203Search in Google Scholar
Dewatripont, M., I. Jewitt, and J. Tirole. 1999. “The Economics of Career Concerns, Part I: Comparing Information Structures.” Review of Economic Studies 66: 183–198.10.1111/1467-937X.00084Search in Google Scholar
Dreher, A., J.-E. Sturm, and J. de Haan. 2010. “When is a Central Bank Governor Replaced? Evidence Based on a New Data Set.” Journal of Macroeconomics 32: 766–781.10.1016/j.jmacro.2010.04.001Search in Google Scholar
Eijffinger, S., and J. De Hann. 1996. “The Political Economy of Central Bank Independence.” Princeton Studies in International Economics 19.Search in Google Scholar
Elman, B. 1991. “Political, Social, and Cultural Reproduction via Civil Service Examinations in Late Imperial China.” Journal of Asian Studies 50: 7–28.10.2307/2057472Search in Google Scholar
Francois, P. 2000. “‘Public Service Motivation’ as an Argument for Government Provision.” Journal of Public Economics 78: 275–99.10.1016/S0047-2727(00)00075-XSearch in Google Scholar
Gailmard, S., and J. Patty. 2007. “Slackers and Zealots: Civil Service, Policy Discretion, and Bureaucratic Expertise.” American Journal of Political Science 51: 873–889.10.1111/j.1540-5907.2007.00286.xSearch in Google Scholar
Gailmar, S., and J. Patty. 2012. “Formal Models of Bureaucracy.” Annual Review of Political Science 15: 353–377.10.1146/annurev-polisci-031710-103314Search in Google Scholar
Geddes, B. 1994. Politician’s Dilemma: Building State Capacity in Latin America. Berkeley: University of California Press.10.1525/9780520918665Search in Google Scholar
Glazer, A. 1989. “Politics and the Choice of Durability.” American Economic Review 79: 1207–13.Search in Google Scholar
Greaves, H. 1947. The Civil Service in the Changing State: A Survey of Civil Service Reform and the Implications of a Planned Economy on Public Administration in England. London: Harrap.Search in Google Scholar
Guriev, S., and K. Sonin. 2009. “Dictators and Oligarchs: A Dynamic Theory of Contested Property Rights.” Journal of Public Economics 93: 1–13.10.1016/j.jpubeco.2008.07.003Search in Google Scholar
Haas, S. 2004. Die Kultur der Verwaltung. Frankfurt: Campus.Search in Google Scholar
Hanssen, A. 2004. “Is There a Politically Optimal Level of Judicial Independence?” American Economic Review 94: 712–29.10.1257/0002828041464470Search in Google Scholar
Iyer, L., and A. Mani. 2012. “Traveling Agents: Political Change and Bureaucratic Turnover in India.” Review of Economics and Statistics 94: 723–39.10.1162/REST_a_00183Search in Google Scholar
Justman, M., and M. Gradstein. 1999. “The Industrial Revolution, Political Transition, and the Subsequent Decline in Inequality in 19th-Century Britain.” Explorations in Economic History 36: 109–27.10.1006/exeh.1999.0713Search in Google Scholar
Keefer, P., and D. Stasavage. 2003. “The Limits of Delegation: Veto Players, Central Bank Independence, and the Credibility of Monetary Policy.” American Political Science Review 97: 407–23.10.1017/S0003055403000777Search in Google Scholar
Konrad, K., and G. Torsvik. 1997. “Dynamic Incentives and Term Limits in Bureaucracy Regulation.” European Journal of Political Economy 13: 261–79.10.1016/S0176-2680(97)00005-0Search in Google Scholar
Lavertu, S. 2013. “Issue-Specific Political Uncertainty and Policy Insulation in Federal Agencies.” Journal of Law, Economics, and Organization 29: 145–77.10.1093/jleo/ewr029Search in Google Scholar
Lazear, E., and S. Rosen. 1981. “Rank-Order Tournaments as Optimum Labor Contracts.” Journal of Political Economy 89: 841–64.10.3386/w0401Search in Google Scholar
Lewis, D. 2007. “Testing Pendleton’s Premise: Do Political Appointees Make Worse Bureaucrats?” Journal of Politics 69: 1073–88.10.1111/j.1468-2508.2007.00608.xSearch in Google Scholar
Kaufmann, D., A. Kraay, and M. Mastruzzi. 2010. “The Worldwide Governance Indicators: Methodology and Analytical Issues.” Policy Research Working Paper, 5430.Search in Google Scholar
Maskin, E., and J. Tirole. 2004. “The Politician and the Judge: Accountability in Government.” American Economic Review 94: 1034–54.10.1257/0002828042002606Search in Google Scholar
Moe, T. 1989. “The Politics of Bureaucratic Structure.” In Can the Government Govern, edited by J. E. Chubb and P. E. Peterson, Washington, DC: Brookings Institution.Search in Google Scholar
Niskanen, W. 1975. “Bureaucrats and Politicians.” Journal of Law and Economics 18: 617–43.10.1086/466829Search in Google Scholar
Northcote, S., and C. Trevelyan. 1954 (reprint). Northcote-Trevelyan Report. Public Administration, 32, 1–16.10.1111/j.1467-9299.1954.tb01719.xSearch in Google Scholar
Persson, T., and G. Tabellini. 2009. “Democratic Capital: The Nexus of Political and Economic Change.” American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics 1: 88–126.10.3386/w12175Search in Google Scholar
Persson, T., and G. Tabellini. 2000. Political Economics: Explaining Economic Policy. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.Search in Google Scholar
Prendergast, C. 2007. “The Motivation and Bias of Bureaucrats.” American Economic Review 97: 180–196.10.1257/aer.97.1.180Search in Google Scholar
Rauch, J., and P. Evans. 2000. “Bureaucratic Structure and Bureaucratic Performance in Less Developed Countries.” Journal of Public Economics 75: 49–71.10.1016/S0047-2727(99)00044-4Search in Google Scholar
Robinson, J., R. Torvik, and V. Thierry. 2006. “Political Foundations of the Resource Curse.” Journal of Development Economics 79 (2): 447–68.10.1016/j.jdeveco.2006.01.008Search in Google Scholar
Ruhil, A., and P. Camões. 2003. “What Lies Beneath: The Political Roots of State Merit Systems.” Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory 13: 27–42.10.1093/jopart/mug006Search in Google Scholar
Ross, M. 2001. Timber Booms and Institutional Breakdown in Southeast Asia. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.10.1017/CBO9780511510359Search in Google Scholar
Ryan, A. 1972. “Utilitarianism and Bureaucracy.” In Studies in the Growth of Nineteenth Century Government, edited by G. Sutherland, London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.Search in Google Scholar
Stephenson, M. 2008. “Optimal Political Control of the Bureaucracy.” Michigan Law Review 107: 53.Search in Google Scholar
Stephenson, M. 2011. “Information Acquisition and Institutional Design.” Harvard Law Review 124: 1422.Search in Google Scholar
©2015 by De Gruyter
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Advances
- Insulation or Patronage: Political Institutions and Bureaucratic Efficiency
- Rural Property Rights, Migration, and Welfare in Developing Countries
- The Impact of Voluntary Youth Service on Future Outcomes: Evidence from Teach For America
- Contributions
- Human Capital Formation and International Trade
- Racial Discrimination in the Labor Market for Recent College Graduates: Evidence from a Field Experiment
- Life Insurance and Suicide: Asymmetric Information Revisited
- The Impact of Immigration on Native Wages and Employment
- The Effect of Pharmacies’ Right to Negotiate Discounts on the Market Share of Parallel Imported Pharmaceuticals
- Vertical or Horizontal: Endogenous Merger Waves in Vertically Related Industries
- Violence in Illicit Markets: Unintended Consequences and the Search for Paradoxical Effects of Enforcement
- Topics
- The Effect of Alcohol Consumption on Labor Market Outcomes of Young Adults: Evidence from Minimum Legal Drinking Age Laws
- Impacts of FTA Utilization on Firm Performance
- Is There a Motherhood Wage Penalty for Highly Skilled Women?
- Developers’ Incentives and Open-Source Software Licensing: GPL vs BSD
- Noise or News? Learning about the Content of Test-Based School Achievement Measures
- Entrepreneurial Risk Choice and Credit Market Equilibria
- How Responsive Are EU Coal-Burning Plants to Changes in Energy Prices?
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Advances
- Insulation or Patronage: Political Institutions and Bureaucratic Efficiency
- Rural Property Rights, Migration, and Welfare in Developing Countries
- The Impact of Voluntary Youth Service on Future Outcomes: Evidence from Teach For America
- Contributions
- Human Capital Formation and International Trade
- Racial Discrimination in the Labor Market for Recent College Graduates: Evidence from a Field Experiment
- Life Insurance and Suicide: Asymmetric Information Revisited
- The Impact of Immigration on Native Wages and Employment
- The Effect of Pharmacies’ Right to Negotiate Discounts on the Market Share of Parallel Imported Pharmaceuticals
- Vertical or Horizontal: Endogenous Merger Waves in Vertically Related Industries
- Violence in Illicit Markets: Unintended Consequences and the Search for Paradoxical Effects of Enforcement
- Topics
- The Effect of Alcohol Consumption on Labor Market Outcomes of Young Adults: Evidence from Minimum Legal Drinking Age Laws
- Impacts of FTA Utilization on Firm Performance
- Is There a Motherhood Wage Penalty for Highly Skilled Women?
- Developers’ Incentives and Open-Source Software Licensing: GPL vs BSD
- Noise or News? Learning about the Content of Test-Based School Achievement Measures
- Entrepreneurial Risk Choice and Credit Market Equilibria
- How Responsive Are EU Coal-Burning Plants to Changes in Energy Prices?

