Abstract
This paper investigates the nexus of military expenditure, income inequality, and profit rate, applying the non-parametric technique of Partial Least Squares Path Modeling (PLS-PM) to 21 countries for 1988–2008. The findings suggest that military expenditure has a positive effect on income inequality while income inequality has a positive impact on profit rate. In contrast, military expenditure has a (relatively small) positive effect on profit rate. However, these results change significantly once unobserved heterogeneity is considered. Accordingly, based on four segments, although the positive effect of income inequality on profit rate remains the same for each segment, for some segments, the effect of military expenditure on income inequality and profit rate become negative.
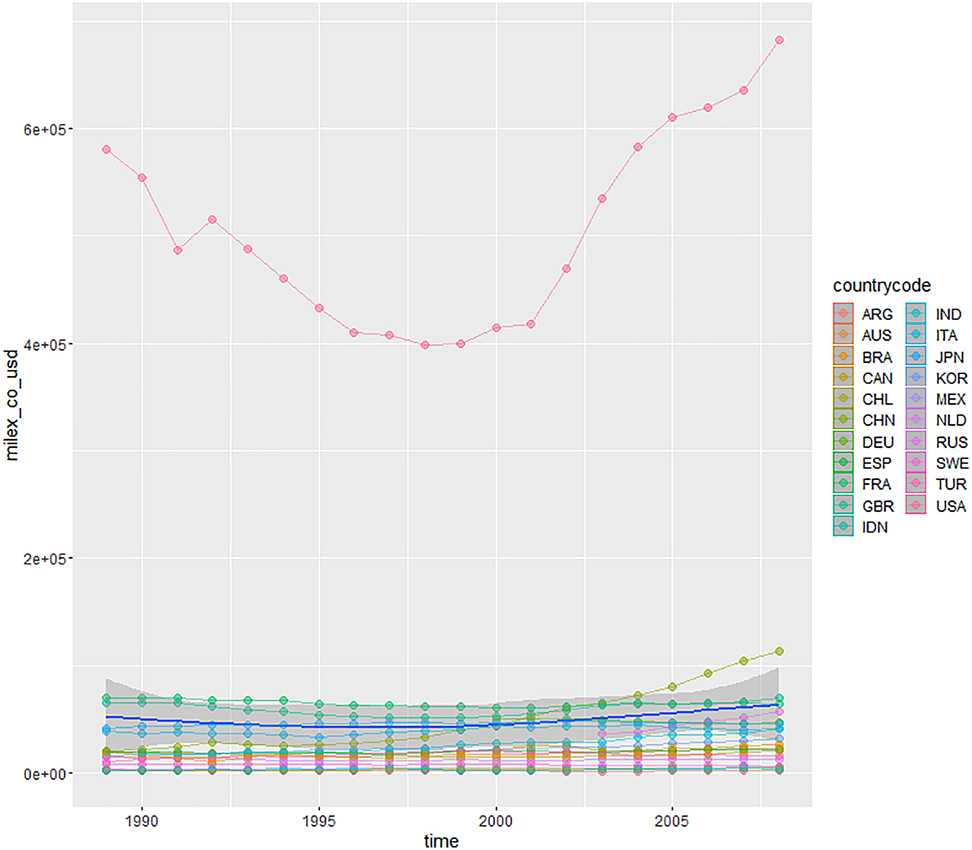
Military expenditure at constant price.
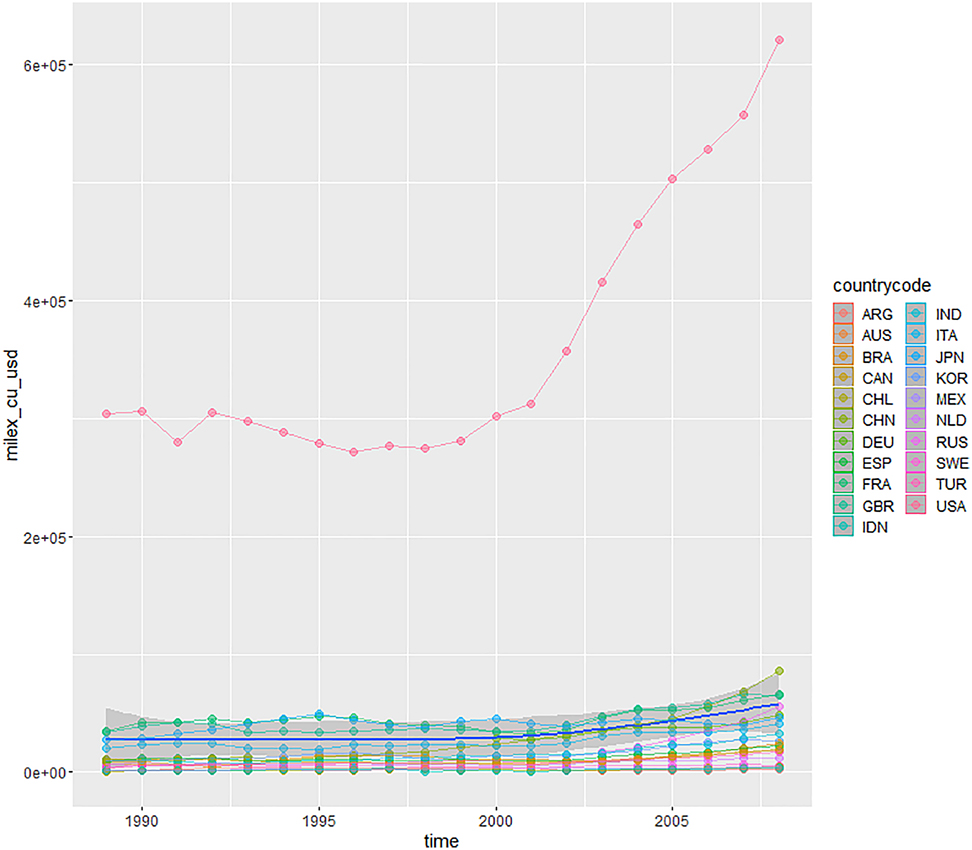
Military expenditure at current price.
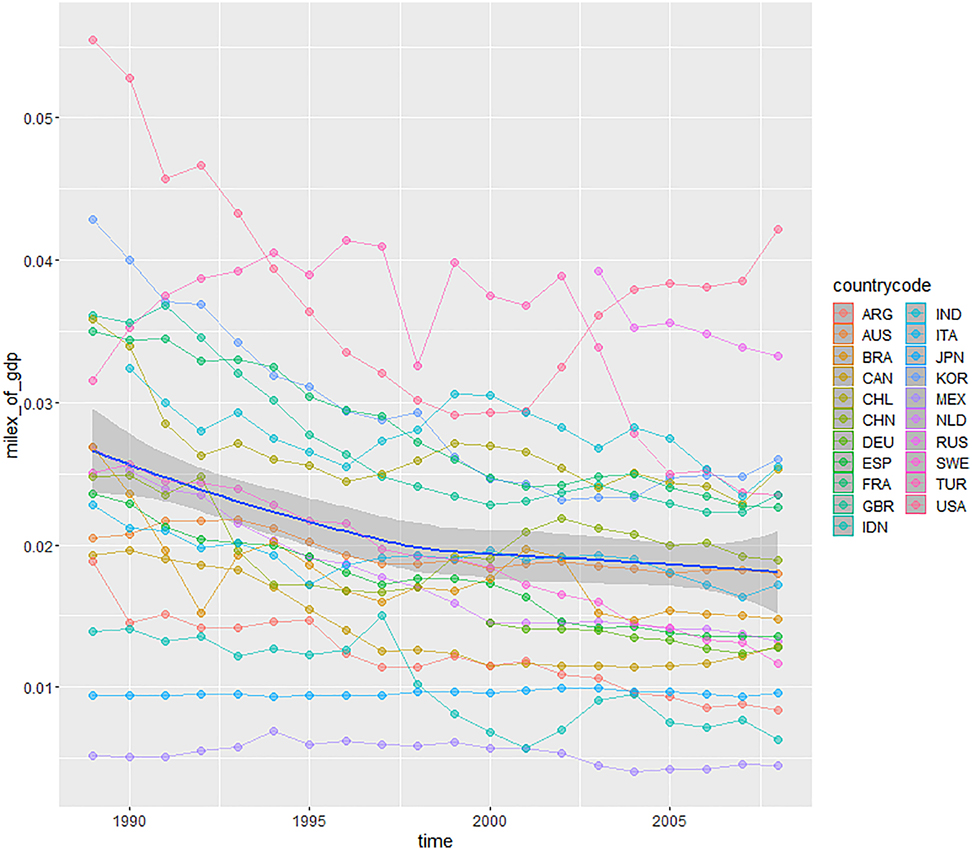
Military expenditure as a share of GDP.
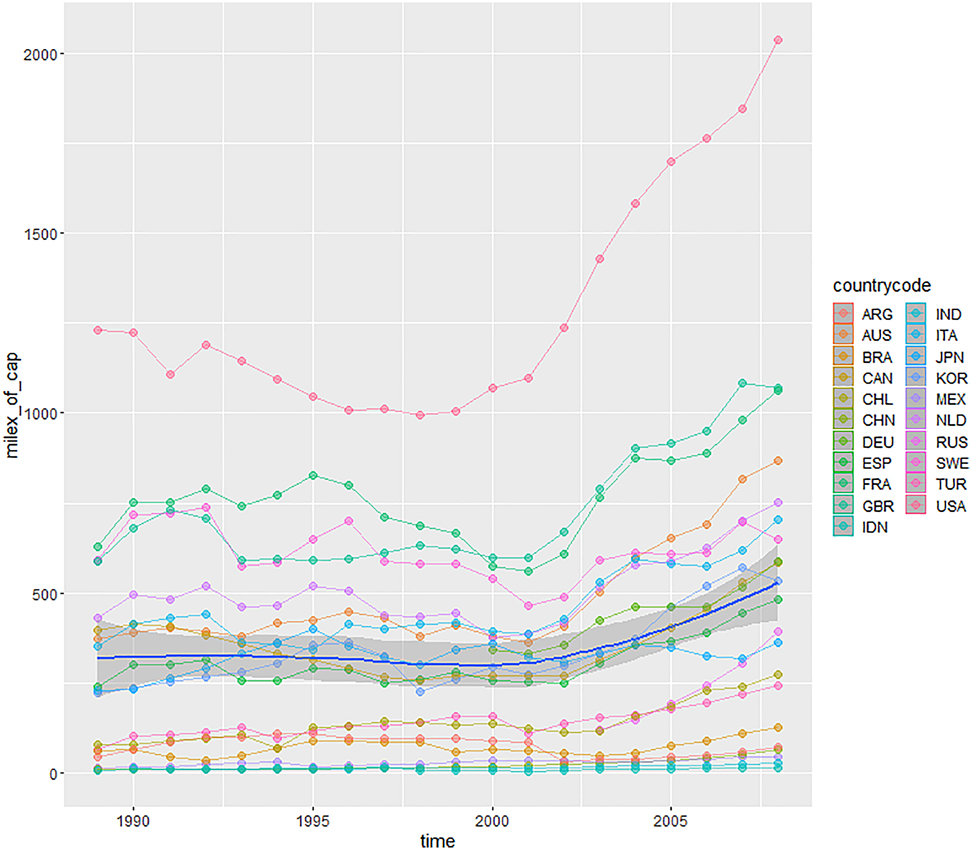
Military expenditure per capita.
References
Ali, H. E. 2007. “Military Expenditures and Inequality: Empirical Evidence from Global Data.” Defence and Peace Economics 18 (6): 519–35, https://doi.org/10.1080/10242690701331501.Search in Google Scholar
Ali, H. E. 2012. “Military Expenditure and Inequality in the Middle East and North Africa: A Panel Analysis.” Defence and Peace Economics 23 (6): 575–89, https://doi.org/10.1080/10242694.2012.663578.Search in Google Scholar
Alptekin, A., and P. Levine. 2012. “Military Expenditure and Economic Growth: A Meta-Analysis.” European Journal of Political Economy 28 (4): 636–50, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpoleco.2012.07.002.Search in Google Scholar
Ansari, S. 2018. “US Fiscal Policy, Manufacturing Stagnation, and the Shift to Financialization in the Era of Globalization: An Econometric Analysis, 1973–2015.” Review of Political Economy 30 (4): 595–614, https://doi.org/10.1080/09538259.2018.1504388.Search in Google Scholar
Biscione, A., and R. Caruso. 2019. “Military Expenditures and Income Inequality Evidence from a Panel of Transition Countries (1990-2015).” Defence and Peace Economics, https://doi.org/10.1080/10242694.2019.1661218.Search in Google Scholar
Dijkstra, T. K. 2010. “Latent Variables and Indices: Herman Wold’s Basic Design and Partial Least Squares.” In Handbook of partial least squares: Concepts, methods and applications, Vol. 2, edited by V. Esposito Vinzi, W. W. Chin, J. Henseler, and H. Wang, 23–46. Heidelberg: Springer: Springer Handbooks of Computational Statistics Series.10.1007/978-3-540-32827-8_2Search in Google Scholar
Dixon, W. J., and B. E. Moon. 1986. “The Military Burden and Basic Human Needs.” The Journal of Conflict Resolution 30 (4): 660–84.10.1177/0022002786030004004Search in Google Scholar
Dunne, J. P., L. Pieroni, and G. d’Agostino. 2013. Military Spending and the Falling Rate of Profit in the US. Also available at http://www.sipri.org/research/armaments/milex/ICES2013/papers/archive/dunne-pieroni-agostino-milex-falling-rate-of-profit-in-usa.Search in Google Scholar
Dunne, P., and N. Tian. 2015. “Military Expenditure, Economic Growth and Heterogeneity.” Defence and Peace Economics 26 (1): 15–31, https://doi.org/10.1080/10242694.2013.848575.Search in Google Scholar
Dunne, P., R. Smith, and D. Willenbockel. 2005. “Models of Military Expenditure and Growth: A Critical Review.” Defence and Peace Economics 16 (6): 449–61, https://doi.org/10.1080/10242690500167791.Search in Google Scholar
Elgin, C., and O. Öztunalı. 2012. “Shadow Economies Around the World: Model Based Estimates.” Bogazici University Department of Economics Working Papers 5, 1–48.Search in Google Scholar
Elveren, A. Y. 2019. The Economics of Military Spending: A Marxist Perspective. New York and London: Routledge.10.4324/9780429430947Search in Google Scholar
Elveren, A. Y. 2020. “Military Spending and Profit Rate: A Circuit of Capital Model with a Military Sector.” Defence and Peace Economics, https://doi.org/10.1080/10242694.2020.1832394.Search in Google Scholar
Elveren, A. Y., and S. Hsu. 2016. “Military Expenditures and Profit Rates: Evidence from OECD Countries.” Metroeconomica 67 (3): 551–77, https://doi.org/10.1111/meca.12111.Search in Google Scholar
Elveren, A. Y., and S. Hsu. 2018. “The Effect of Military Expenditure on Profit Rates: Evidence from Major Countries.” World Journal of Applied Economics 4 (2): 75–94, https://doi.org/10.22440/wjae.4.2.2.Search in Google Scholar
Elveren, A. Y., and G. Özgür. 2018. The Effect of Military Expenditures on the Profit Rates in Turkey. MPRA No: 88848. Also available at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/88848/1/MPRA_paper_88848.pdf.Search in Google Scholar
Galbraith, J. K., J. Lu, and W. A. Darity. 1999. “Measuring the Evolution of Inequality in the Global Economy.” UTIP Working Paper No. 7, January 31.10.1017/CBO9781139175210.009Search in Google Scholar
Georgiou, G. 1983. “The Political Economy of Military Expenditures.” Capital & Class 7: 183–205, https://doi.org/10.1177/030981688301900108.Search in Google Scholar
Georgiou, G. 1992. “Military Expenditure and the Rate of Profit: Some Empirical Results.” International Review of Applied Economics 16 (3): 344–61.10.1080/758534266Search in Google Scholar
Henseler, J., G. S. Hubona, and A. R. Pauline. 2016. “Using PLS Path Modeling in New Technology Research: Updated Guidelines.” Industrial Management & Data Systems 116 (1): 2–20, https://doi.org/10.1108/imds-09-2015-0382.Search in Google Scholar
Kentor, J., A. Jorgenson, and E. Kick. 2012. “The “New” Military and Income Inequality: A Cross National Analysis.” Social Science Research 41: 514–26.10.1016/j.ssresearch.2011.12.005Search in Google Scholar
Kollias, C., and T. Maniatis. 2003. “Military Expenditure and the Profit Rate in Greece.” Defence and Peace Economics 14 (2): 117–27, https://doi.org/10.1080/10242690302920.Search in Google Scholar
Lin, E. S., and H. E. Ali. 2009. “Military Spending and Inequality: Panel Granger Causality Test.” Journal of Peace Research 46 (5): 671–85, https://doi.org/10.1177/0022343309339247.Search in Google Scholar
Lin, E. S., H. E. Ali, and Y-L. Lu. 2015. “Does Military Spending Crowd Out Social Welfare Expenditures? Evidence from a Panel of OECD Countries.” Defence and Peace Economics 26 (1): 33–48, https://doi.org/10.1080/10242694.2013.848576.Search in Google Scholar
Michael, C., and R. Stelios. 2018. “The Effect of Military Spending on Income Inequality: Evidence from NATO Countries.” Empirical Economics 58: 1305–37.10.1007/s00181-018-1576-7Search in Google Scholar
Richter, N. F., G. Cepeda, J. L. Roldán, and C. M. Ringle. 2016. “European Management Research Using Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM).” European Management Journal 34 (6): 589–97, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2016.08.001.Search in Google Scholar
Rigdon, E. E. 2016. “Choosing PLS Path Modeling as Analytical Method in European Management Research: A Realist Perspective.” European Management Journal 34 (6): 598–605, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2016.05.006.Search in Google Scholar
Sanchez, G. 2013. PLS Path Modeling with R Trowchez Editions. Berkeley, 2013. Also available at http://www.gastonsanchez.com/PLSPathModelingwithR.pdf.Search in Google Scholar
Sarstedt, M., J. F. Hair, C. M. Ringle, K. O. Thiele, and S. P. Gudergan. 2016. “Estimation Issues with PLS and CBSEM: Where the Bias Lies!.” Journal of Business Research 69 (10): 3998–4010, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.06.007.Search in Google Scholar
SIPRI (Stockholm International Peace Research Institute). 2020. Also available at www.sipri.org.Search in Google Scholar
Theil, H. 1972. Statistical Decomposition Analysis: With Applications in the Social and Administrative Sciences. Amsterdam-London: North Holland Publishing Company.Search in Google Scholar
Töngür, Ü., and A. Y. Elveren. 2015. “Military Expenditures, Income Inequality, and Welfare and Political Regimes: A Dynamic Panel Data Analysis.” Defence and Peace Economics 26 (1): 49–74, https://doi.org/10.1080/10242694.2013.848577.Search in Google Scholar
Töngür, Ü., and A. Y. Elveren. 2017. “The Nexus of Economic Growth, Military Expenditures, and Income Inequality.” Quality and Quantity 51: 1821–42, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-016-0368-4.Search in Google Scholar
Töngür, Ü., S. Hsu, and A. Y. Elveren. 2015. “Military Expenditures and Political Regimes: Evidence from Global Data, 1963-2000.” Economic Modelling 44: 68–79, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2014.10.004.Search in Google Scholar
Vasudevan, R. 2016. “Financialization, Distribution and Accumulation: A Circuit of Capital Model with A Managerial Class.” Metroeconomica 67: 397–428, https://doi.org/10.1111/meca.12106.Search in Google Scholar
Wold, H. 1975. “PLS Path Models with Latent Variables: The Nipals Approach.” In Quantitative Sociology: International Perspectives on Mathematical and Statistical Modeling, edited by H. M. Blalock, A. Aganbegian, F. M. Borodkin, R. Boudon, and V. Cappecchi. New York: Academic Press.10.1016/B978-0-12-103950-9.50017-4Search in Google Scholar
Wolff, E. N. 2015. “Inequality and Rising Profitability in the United States, 1947–2012.” International Review of Applied Economics 29 (6): 741–69, https://doi.org/10.1080/02692171.2014.956704.Search in Google Scholar
World Bank, the, World Development Indicator. 2020. Also available at https://datacatalog.worldbank.org/dataset/world-development-indicators.Search in Google Scholar
Zhang, Y., L. Xiaoxing, X. Jiaxin, and ve. R. Wang. 2017. “Does Military Spending Promote Social Welfare? A Comparative Analysis of the BRICS and G7 Countries.” Defence and Peace Economics 28 (6): 686–702, https://doi.org/10.1080/10242694.2016.1144899.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin/Boston
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Research Articles
- The Fatal Conceit of Foreign Intervention: Evidence from the Afghanistan Papers
- The Effects of Agricultural Income Shocks on Forced Migration: Evidence from Colombia
- Three is a Crowd: Using Reciprocity to Explain Involvement in Ongoing Disputes
- The Effects of Military Expenditures on Economic Growth and Inflation: Evidence from Turkey
- Soft Modeling of Military Expenditure, Income Inequality, and Profit Rate, 1988–2008
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Research Articles
- The Fatal Conceit of Foreign Intervention: Evidence from the Afghanistan Papers
- The Effects of Agricultural Income Shocks on Forced Migration: Evidence from Colombia
- Three is a Crowd: Using Reciprocity to Explain Involvement in Ongoing Disputes
- The Effects of Military Expenditures on Economic Growth and Inflation: Evidence from Turkey
- Soft Modeling of Military Expenditure, Income Inequality, and Profit Rate, 1988–2008

