Abstract
C18H16N2O3S2, Monoclinic, P21 (no. 4), a = 12.3018(15) Å, b = 5.8113(6) Å, c = 12.7380(12) Å, β = 107.735(4)∘, V = 867.36(16) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0491, wR ref (F2) = 0.1055 T = 273.15 K.
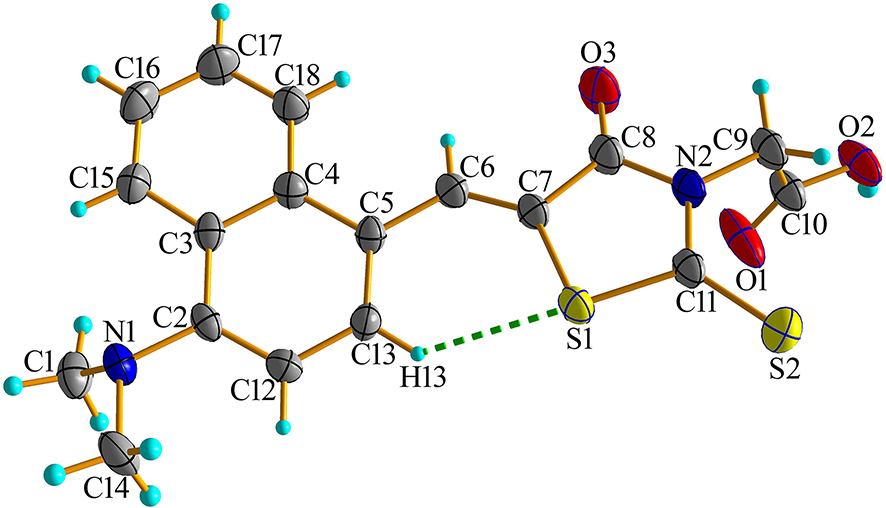
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data. The list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
1 Source of materials
Weigh 4-(dimethylamino)-1-napthaldehyde (0.80 g, 4 mmol) and 2-(4-oxo-2-thiothiazolidin-3-yl) acetic acid (0.76 g, 4 mmol) into a 100 mL round bottomed flask, add 60 mL ethanol, 5 drops of piperidine as catalyst, heat and reflux for 24 h, stop heating, cool to room temperature, precipitate red solid, filter, wash with ethanol for six times to obtain 1.1 g of red solid, with a yield of 75 %. A small amount of the target compound was dissolved in the mixed solvent of dichloromethane and methanol, and then volatilized slowly for 5 days to precipitate crystals suitable for X-ray-single crystal diffraction.
2 Experimental details
Using Olex2, 1 the structure was solved using Charge Flipping and refined with the ShelXL 2 refinement. All hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically, with d (C–H) = 0.97 – 0.99 Å, Uiso (H) = 1.2 times Ueq (C) and Uiso (H) = 1.5 times Ueq (O).
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | RED BLOCK |
| Size: | 0.13 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: μ: |
Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) 0.33 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: θmax, completeness: |
Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω scans 28.3°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 8641, 4105, 0.048 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3503 |
| N(param)refined: | 229 |
| Programs: | Olex2, 1 Bruker, 3 SHELX 2 |
3 Comment
In recent years, compounds with electron donor (D) – electron acceptor (A) structure have been widely used in the research of solar cells, 4 photodynamic antitumor 5 and photodynamic antibacterial. 6 By adjusting the structure of donor and acceptor to reduce the energy difference of HOMO–LUMO and reduce the energy gap of the lowest excited singlet state (S1) → excited triplet state (T1), the cross-over efficiency of photosensitizer can be improved, so as to improve the photosensitive efficiency. 7 The 2-thio-4-oxo-3-thiazolidine acetic acid is a special heterocyclic compound. This ring structure has strong polarity and electron absorption ability, making it an ideal electron withdrawing group. It is often used by researchers as an electron acceptor to construct compounds with D–A structure. 8 Moreover, the presence of these double bond atoms and other functional groups leads to extremely high density of polar interactions and hydrogen bond binding sites, which makes derivatives based on 2-thio-4-oxo-3-thiazolidine acetic acid have certain antibacterial activity. 9 , 10 , 11 Here, we report the crystal structure of (z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino) sodium-1-yl) methyl)-4-oxo-2-thiothiazolidin-3-yl) acid. The bond angles and bond lengths of the target compound were in the normal range. The title compound was obtained by the reaction of 4-(dimethylamino)-1-naphthaldehyde and 2-(4-oxo-2-thiothiazolidin-3-yl) acid. The crystal structure showed that the aldehyde group had Knoevenagel condensation with methylene to form a compound with D–A structure. The dihedral angle between the naphthalene ring and thiazole was 16.11°, and there was C13–H13⋯S1 intramolecular hydrogen bond in the molecule. The 1D chain structure was formed between molecules through O2–H2⋯N1 hydrogen bonds.
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341.10.1107/S0021889808042726Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Bruker. APEX2, Saint and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
4. Mao, J. J.; He, N. N.; Ning, Z. J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, F. L.; Chen, L.; Wu, W. J.; Hua, J. L.; Tian, H. Stable Dyes Containing Double Acceptors without COOH as Anchors for Highly Efficient Dye–Sensitized Solar Cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9873–9876; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201204948.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Shen, L. Y.; Zhang, Q. L.; Yao, Y. C.; Huang, Y. L.; Zheng, Z. C.; Li, M.; Xu, H.; Tan, L.; Liao, X. K.; Xia, B. Y.; Li, L.; Redshaw, C.; Bai, Y.; Yang, C. L. Alkyl Chain Length-Regulated In Situ Intelligent Nano-Assemblies with AIE-Active Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 19, 100967; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2024.100967.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Peng, S. L.; Song, J. Y.; Wu, S. T.; Wang, Q.; Shen, L. Y.; Li, D. M.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Q. L.; Yang, X. J.; Xu, H.; Redshaw, C.; Li, Y. Aggregation–Induced Emission Photosensitizer with Ag(I)-π Interaction–Enhanced Reactive Oxygen Species for Eliminating Multidrug Resistant Bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 30915–30928; https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c05202.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Kornman, C. T.; Li, L.; Weldeab, A. O.; Ghiviriga, I.; Abboud, K. A.; Castellano, R. K. Photoisomerization of Dicyanorhodaninefunctionalized Thiophenes. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 10190–10197; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0sc04409a.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Thamaraiselvi, P.; Duraipandy, N.; Kiran, M. S.; Easwaramoorthi, S. Triarylamine Rhodanine Derivatives as Red Emissive Sensor for Discriminative Detection of Ag+ and Hg+ Ions in Buffer–free Aqueous Solutions. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9865–9874; https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b00417.Search in Google Scholar
9. Song, M. X.; Zheng, C. J.; Deng, X. Q.; Sun, L. P.; Wu, Y.; Hong, L.; Li, Y. J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Z. Y.; Jin, M. J.; Piao, H. R. Synthesis and Antibacterial Evaluation of Rhodanine-Based 5-aryloxy Pyrazoles against Selected Methicillin Resistant and Quinoloneresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA and QRSA). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 60, 376e385; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.12.007.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Żesławska, E.; Tejchman, W.; Kincses, A.; Spengler, G.; Nitek, W.; Żuchowski, G.; Szymańska, E. 5-Arylidenerhodanines as P-gp Modulators: An Interesting Effect of the Carboxyl Group on ABCB1 Function in Multidrug-Resistant Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10812; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810812.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Stawoska, I.; Tejchman, W.; Mazuryk, O.; Lyčka, A.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Żesławska, E.; Nitek, W.; Kania, A. Spectral Characteristic and Preliminary Anticancer Activity in vitro of Selected Rhodanine-3-Carboxylic Acids Derivatives. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2017, 54, 2889; https://doi.org/10.1002/jhet.2897.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O

