Abstract
C23H25FN2O, triclinic,
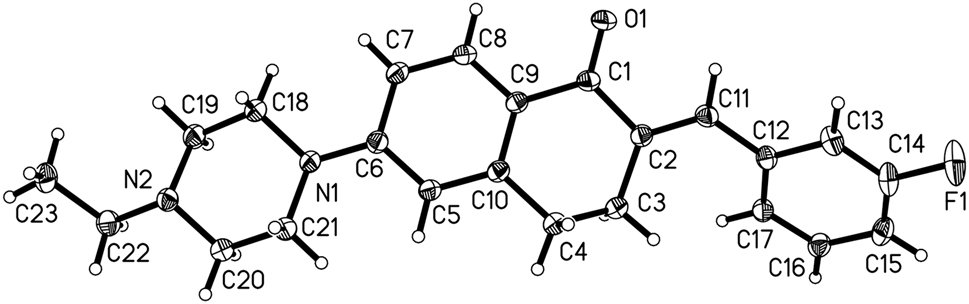
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30 % probability level. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.13 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54178 Å) |
| μ: | 0.69 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova |
| θ max, completeness: | 73.8°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 14,800, 3721, 0.024 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 3395 |
| N(param)refined: | 245 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2, 3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1.1192 (2) | 0.22187 (14) | 0.09765 (11) | 0.0367 (3) |
| C2 | 0.91358 (19) | 0.17804 (12) | 0.02154 (10) | 0.0333 (3) |
| C3 | 0.7120 (2) | 0.17249 (14) | 0.06413 (10) | 0.0377 (3) |
| H3A | 0.596591 | 0.115287 | 0.009579 | 0.045* |
| H3B | 0.678803 | 0.257850 | 0.087683 | 0.045* |
| C4 | 0.7299 (2) | 0.12527 (14) | 0.15274 (10) | 0.0391 (3) |
| H4A | 0.603104 | 0.132011 | 0.182304 | 0.047* |
| H4B | 0.739950 | 0.035066 | 0.126926 | 0.047* |
| C5 | 0.9158 (2) | 0.22839 (12) | 0.33858 (10) | 0.0332 (3) |
| H5 | 0.789688 | 0.201500 | 0.356809 | 0.040* |
| C6 | 1.0955 (2) | 0.29448 (12) | 0.41698 (10) | 0.0325 (3) |
| C7 | 1.2853 (2) | 0.32830 (13) | 0.38452 (10) | 0.0365 (3) |
| H7 | 1.409173 | 0.368293 | 0.433309 | 0.044* |
| C8 | 1.2896 (2) | 0.30316 (13) | 0.28254 (10) | 0.0362 (3) |
| H8 | 1.416403 | 0.327773 | 0.263856 | 0.043* |
| C9 | 1.10892 (19) | 0.24154 (12) | 0.20552 (10) | 0.0314 (3) |
| C10 | 0.92115 (19) | 0.20228 (12) | 0.23548 (10) | 0.0315 (3) |
| C11 | 0.9237 (2) | 0.15400 (13) | −0.07730 (10) | 0.0351 (3) |
| H11 | 1.058834 | 0.158119 | −0.092789 | 0.042* |
| C12 | 0.7489 (2) | 0.12184 (12) | −0.16484 (10) | 0.0330 (3) |
| C13 | 0.7657 (2) | 0.03678 (14) | −0.26175 (11) | 0.0414 (3) |
| H13 | 0.884262 | −0.000233 | −0.270254 | 0.050* |
| C14 | 0.6048 (3) | 0.00868 (14) | −0.34410 (11) | 0.0454 (4) |
| C15 | 0.4289 (2) | 0.06224 (14) | −0.33743 (11) | 0.0436 (3) |
| H15 | 0.323100 | 0.041018 | −0.394981 | 0.052* |
| C16 | 0.4133 (2) | 0.14883 (14) | −0.24257 (11) | 0.0393 (3) |
| H16 | 0.296638 | 0.187975 | −0.236045 | 0.047* |
| C17 | 0.5705 (2) | 0.17773 (13) | −0.15700 (10) | 0.0350 (3) |
| H17 | 0.556929 | 0.235234 | −0.093399 | 0.042* |
| C18 | 1.2817 (2) | 0.36874 (16) | 0.59737 (11) | 0.0431 (3) |
| H18A | 1.387071 | 0.421999 | 0.578309 | 0.052* |
| H18B | 1.336297 | 0.293655 | 0.598829 | 0.052* |
| C19 | 1.2444 (2) | 0.44441 (14) | 0.70348 (11) | 0.0417 (3) |
| H19A | 1.375352 | 0.467765 | 0.753162 | 0.050* |
| H19B | 1.201972 | 0.523421 | 0.703566 | 0.050* |
| C20 | 0.8866 (2) | 0.33917 (15) | 0.65923 (11) | 0.0409 (3) |
| H20A | 0.845014 | 0.418449 | 0.659484 | 0.049* |
| H20B | 0.774742 | 0.291008 | 0.678877 | 0.049* |
| C21 | 0.9130 (2) | 0.26050 (15) | 0.55183 (11) | 0.0435 (3) |
| H21A | 0.941764 | 0.177807 | 0.550021 | 0.052* |
| H21B | 0.782283 | 0.244486 | 0.503628 | 0.052* |
| C22 | 1.0481 (2) | 0.44190 (14) | 0.83798 (10) | 0.0412 (3) |
| H22A | 0.925817 | 0.394120 | 0.851295 | 0.049* |
| H22B | 1.016742 | 0.524341 | 0.840573 | 0.049* |
| C23 | 1.2364 (3) | 0.46564 (16) | 0.92225 (11) | 0.0502 (4) |
| H23A | 1.269932 | 0.384601 | 0.919697 | 0.075* |
| H23B | 1.202438 | 0.509687 | 0.988194 | 0.075* |
| H23C | 1.355975 | 0.517684 | 0.912241 | 0.075* |
| F1 | 0.6224 (2) | −0.07580 (10) | −0.43747 (7) | 0.0724 (4) |
| N1 | 1.08606 (17) | 0.32706 (11) | 0.52014 (9) | 0.0369 (3) |
| N2 | 1.08151 (17) | 0.37027 (10) | 0.73407 (8) | 0.0334 (3) |
| O1 | 1.28790 (16) | 0.24587 (15) | 0.07123 (9) | 0.0617 (4) |
1 Source of material
Based on literature synthetic techniques [4, 5], N-ethylpiperazine (18.27 g, 0.16 mol) and potassium carbonate (27.64 g, 0.2 mol) have been delivered to N,N-dimethylformamide (2 mL), and after stirring at 313 K overnight, 6-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one (3.28 g, 0.02 mol) and N,N-dimethylformamide (0.5 mL) had been combined and introduced dropwise to the response gadget and the temperature of mixture was adjusted to 373 K. The reaction lasted for 5.5 h. It used to be monitored via thin-layer chromatography (TLC, dichloromethane:methyl alcohol = 10:1, v:v). The product was filtered and the filtrate used to be washed with dichloromethane. The solvent was once eliminated by using attention underneath decreased pressure. Separation and purification used to be carried out by way of a silica gel column with the use of dichloromethane:methyl alcohol (20:1, v:v) as eluent. Intermediates have been obtained. Using 25 % sodium hydroxide solution (5.0 mL) as a catalyst, 6-(4-ethylpiperazinyl)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one (0.26 g, 1.00 mmol) used to be blended with 3-fluorobenzaldehyde (0.274 g, 2 mmol) in 10 mL of methanol for 12 h at room temperature below nitrogen atmosphere. The filter residue was once dissolved using dichloromethane and washed with distilled water. The accumulated natural segment used to be dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent used to be eliminated by way of awareness underneath decreased pressure. The received product is soluble in a combination of dichloromethane (2 mL) and methyl alcohol (2 mL), and slowly evaporated at room temperature to achieve appropriate colourless crystals, (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one.
2 Experimental details
The H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with d(C–H) = 0.96 Å (methyl), U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C), and d(C–H) = 0.97 Å (methylene), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C), and d(C–H) = 0.93 Å (aromatic), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C).
3 Comment
3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one is a potential active fragment of anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory compounds [4, 6]. In latest years, some active compounds, such as (2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one) [7], (E)-7-bromo-2-(4-(4-methylpiperazin)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthhalen-1(2H)-one [8] and (E)-7-bromo-2-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one [9] were reported. Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds have accurate organic activity, are noticeably secure in the human body, and have excessive operational efficiency. They are convenient to have interaction with DNA through hydrogen bonds [10]. So we use N-ethylpiperazine for substitution in this study. The substitution of benzylidene can decorate anti-inflammatory activity [11]. The introduction of α,β-unsaturated ketone can make 3,4-dihydronaphthalene-1(2H)-one have two pharmacophores and minimize cytotoxicity, as proven by our group [12, 13]. Some 3,4-dihydronaphthalene-1(2H)-one derivatives substituted by way of electron withdrawing businesses have been proven to have anti-neuroinflammatory effects [4]. Therefore, we are changing benzaldehyde with electron withdrawing fluorophenyl group, which can amplify the lipophilicity of drugs [14]. In this study, N-ethylpiperazine and 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one were used to shape an intermediate through nucleophilic addition, further to generate the title compound, (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin)-2-(3-fluorobenzidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthhalen-1(2H)-one, through Claisen–Schmidt condensation with 3-fluorobenzaldehyde.
Single-crystal structure analysis reveals that the title compound crystallizes in the triclinic system
Funding source: Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation
Award Identifier / Grant number: (Nos. ZR2022MH159 and ZR2023MH190)
Funding source: Shandong Province Science and Technology-based Small and Medium-sized Enterprises Innovation Capacity Enhancement Project
Award Identifier / Grant number: (No. 2023TSGC0870)
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Nos. ZR2022MH159 and ZR2023MH190) and Shandong Province Science and Technology-based Small and Medium-sized Enterprises Innovation Capacity Enhancement Project (No. 2023TSGC0870).
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku, O. D. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England, 2017.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Sun, Y., Zhou, Y. Q., Liu, Y. K., Zhang, H. Q., Hou, G. G., Meng, Q. G., Hou, Y. Potential anti-neuroinflammatory NF-κB inhibitors based on 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one derivative. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1631–1640; https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2020.1804899.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Luan, M. Z., Wang, H. Y., Zhang, M., Song, J., Hou, G. G., Zhao, F. L., Meng, Q. G. Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl) benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H14F6O2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 61–63; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0446.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Barlow, J. W., Zhang, T., Woods, O., Adam, J., John, J. W. Novel mast cell-stabilising amine derivatives of 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one and 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[7]annulen-5-one. Med. Chem. 2011, 7, 213–223; https://doi.org/10.2174/157340611795564222.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Li, Y. L., Meng, Q. G., Hou, G. G., Geng, Z. K. Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy- 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H16F4O3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 1157–1159; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0373.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Qi, Q. B., Li, W. X., Hou, G. G., Li, C. B. Crystal structure of (E)-7-bromo-2-(4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H23BrN2O. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 235–237; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0590.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Zhang, Y. L., Liu, S. L., Hou, G. G., Zhang, X. F., Wang, L., Xin, W. Y. Crystal structure of (E)-7-bromo-2-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H15BrO2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 945–947; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0315.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Ozkay, Y., Işikdaǧ, I., Incesu, Z., Akalin, G. Synthesis of 2-substituted-N-[4-(1-methyl-4,5-diphenyl-1H-imidazole-2-yl)phenyl]acetamide derivatives and evaluation of their anticancer activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3320–3328; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.04.015.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Gao, C. L., Hou, G. G., Liu, J., Ru, T., Xu, Y. Z., Zhao, S. Y., Ye, H., Zhang, L. Y., Chen, K. X., Guo, Y. W., Pang, T., Li, X. W. Synthesis and target identification of benzoxepane derivatives as potential anti-neuroinflammatory agents for ischemic stroke. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2429–2439; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201912489.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Zhang, X. F., Luan, M. Z., Yan, W. B., Zhao, F. L., Hou, Y., Hou, G. G., Meng, Q. G. Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of novel 5,6-dihydrobenzo [h]quinazolin-2-amine derivatives in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 235, 114322; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114322.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Luan, M. Z., Zhang, X. F., Yang, Y., Meng, Q. G., Hou, G. G. Anti-inflammatory activity of fluorine-substituted benzo[h]quinazoline-2-amine derivatives as NF-κB inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 132, 106360; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106360.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
14. Swallow, S. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry. Prog. Med. Chem. 2015, 54, 65–133; https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmch.2014.11.001.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
15. Yuan, X. Q., Zhao, L. H., Zhang, J. J., Hou, G. G. Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H23NO3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 363–365; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0578.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3

