Abstract
C27H19NiN3O5, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 11.082(1) Å, b = 10.480(1) Å, c = 22.719(2) Å, β = 117.76(4)°, V = 2334.9(9) Å3, Z = 4, R gt(F) = 0.0489, wR ref(F 2 ) = 0.1271, T = 293 K.
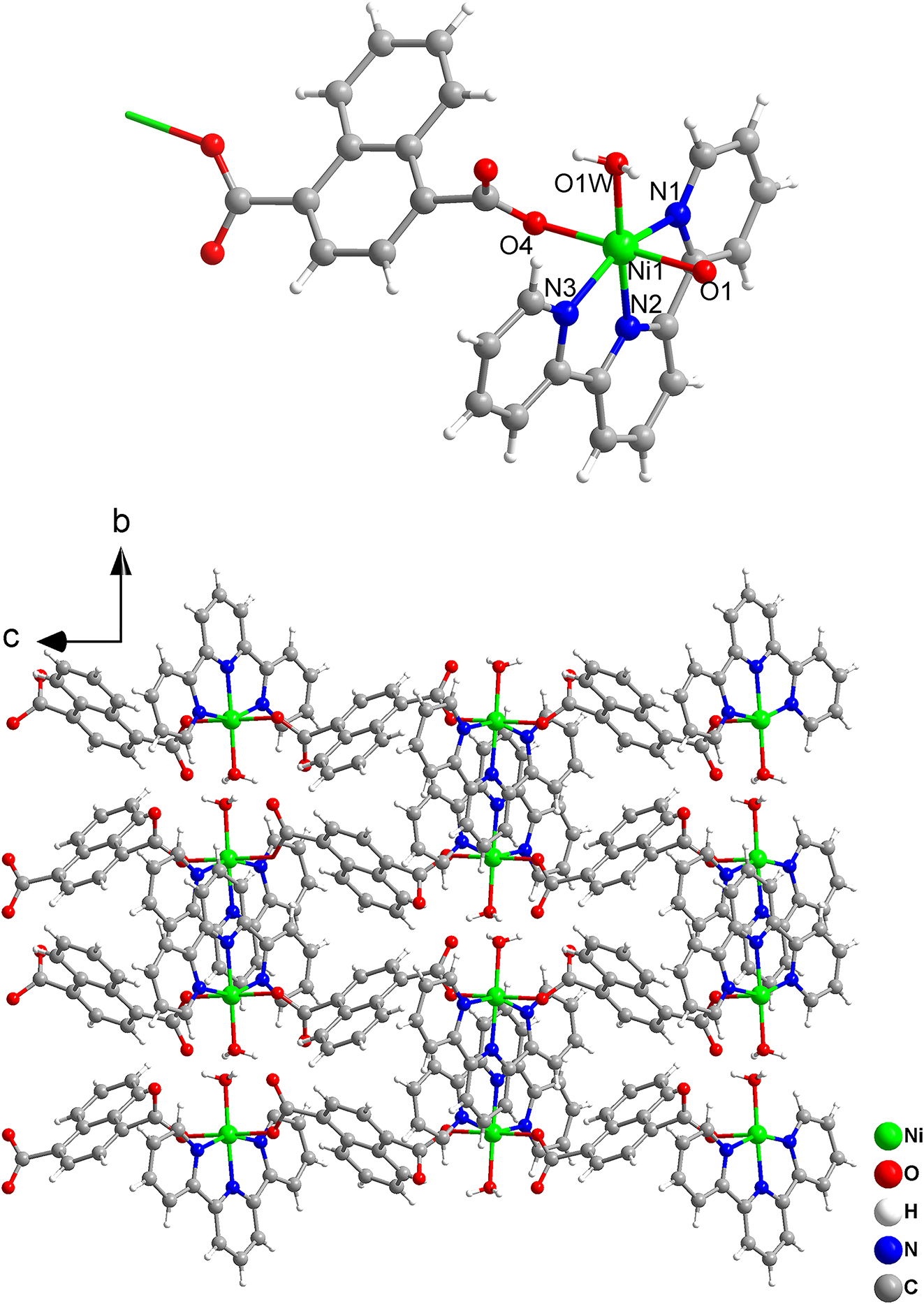
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Blue block |
| Size: | 0.28 × 0.25 × 0.23 mm |
| Wavelength: | MoKα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.88 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.0°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 11150, 4110, 0.066 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2277 |
| N(param)refined: | 331 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Shelx [2,3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni1 | 0.24604 (5) | 0.74730 (4) | 0.50314 (2) | 0.03551 (18) |
| O1 | 0.2657 (3) | 0.7541 (2) | 0.41827 (12) | 0.0437 (7) |
| O2 | 0.3552 (3) | 0.9456 (3) | 0.41881 (14) | 0.0618 (9) |
| O3 | 0.3557 (3) | 0.5876 (3) | 0.14226 (13) | 0.0613 (9) |
| O4 | 0.2290 (3) | 0.7605 (2) | 0.09019 (12) | 0.0424 (7) |
| O1W | 0.2595 (3) | 0.9451 (3) | 0.50864 (13) | 0.0512 (8) |
| H1WA | 0.310 (4) | 0.968 (2) | 0.4912 (18) | 0.061* |
| H1WB | 0.296 (4) | 0.967 (2) | 0.5472 (10) | 0.061* |
| N1 | 0.0315 (4) | 0.7207 (3) | 0.44215 (15) | 0.0424 (9) |
| N2 | 0.2291 (3) | 0.5552 (3) | 0.49480 (14) | 0.0345 (8) |
| N3 | 0.4501 (3) | 0.6906 (3) | 0.56143 (15) | 0.0393 (8) |
| C1 | −0.0647 (5) | 0.8114 (4) | 0.4157 (2) | 0.0526 (12) |
| H1 | −0.039845 | 0.895349 | 0.429010 | 0.063* |
| C2 | −0.1967 (5) | 0.7875 (5) | 0.3704 (2) | 0.0657 (14) |
| H2 | −0.259836 | 0.853340 | 0.352583 | 0.079* |
| C3 | −0.2338 (5) | 0.6613 (5) | 0.3518 (2) | 0.0715 (15) |
| H3 | −0.322938 | 0.641686 | 0.320975 | 0.086* |
| C4 | −0.1387 (5) | 0.5653 (4) | 0.3790 (2) | 0.0522 (12) |
| H4 | −0.163214 | 0.480625 | 0.367387 | 0.063* |
| C5 | −0.0059 (4) | 0.5973 (4) | 0.42406 (18) | 0.0414 (10) |
| C6 | 0.1080 (4) | 0.5032 (4) | 0.45552 (18) | 0.0392 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0943 (5) | 0.3709 (4) | 0.4469 (2) | 0.0511 (12) |
| H7 | 0.009996 | 0.334073 | 0.419803 | 0.061* |
| C8 | 0.2098 (5) | 0.2961 (4) | 0.4800 (2) | 0.0604 (14) |
| H8 | 0.203049 | 0.207807 | 0.475281 | 0.072* |
| C9 | 0.3366 (5) | 0.3521 (4) | 0.5204 (2) | 0.0532 (12) |
| H9 | 0.414689 | 0.302535 | 0.542007 | 0.064* |
| C10 | 0.3424 (4) | 0.4854 (4) | 0.52722 (18) | 0.0387 (10) |
| C11 | 0.4662 (5) | 0.5611 (4) | 0.5696 (2) | 0.0457 (10) |
| C12 | 0.5884 (5) | 0.5084 (4) | 0.6141 (2) | 0.0683 (13) |
| H12 | 0.597889 | 0.420204 | 0.618637 | 0.082* |
| C13 | 0.6975 (5) | 0.5872 (5) | 0.6523 (3) | 0.0849 (15) |
| H13 | 0.780159 | 0.552357 | 0.683075 | 0.102* |
| C14 | 0.6829 (5) | 0.7162 (4) | 0.6444 (2) | 0.0716 (13) |
| H14 | 0.755280 | 0.770489 | 0.669369 | 0.086* |
| C15 | 0.5576 (5) | 0.7646 (4) | 0.5984 (2) | 0.0513 (10) |
| H15 | 0.547866 | 0.852566 | 0.592885 | 0.062* |
| C16 | 0.3041 (4) | 0.8416 (4) | 0.39196 (18) | 0.0402 (10) |
| C17 | 0.2892 (4) | 0.8109 (3) | 0.32329 (17) | 0.0338 (10) |
| C18 | 0.3854 (4) | 0.8572 (4) | 0.30657 (18) | 0.0424 (11) |
| H18 | 0.450554 | 0.914354 | 0.335131 | 0.051* |
| C19 | 0.3883 (4) | 0.8204 (4) | 0.24705 (19) | 0.0448 (11) |
| H19 | 0.454438 | 0.853751 | 0.237096 | 0.054* |
| C20 | 0.2931 (4) | 0.7351 (4) | 0.20397 (17) | 0.0384 (10) |
| C21 | 0.2950 (5) | 0.6893 (4) | 0.14130 (18) | 0.0423 (11) |
| C22 | 0.1883 (4) | 0.6892 (3) | 0.21801 (17) | 0.0356 (10) |
| C23 | 0.1829 (4) | 0.7272 (3) | 0.27743 (17) | 0.0352 (10) |
| C24 | 0.0739 (4) | 0.6801 (4) | 0.28778 (19) | 0.0442 (11) |
| H24 | 0.066406 | 0.705943 | 0.325097 | 0.053* |
| C25 | −0.0205 (5) | 0.5968 (4) | 0.2433 (2) | 0.0553 (12) |
| H25 | −0.089081 | 0.564932 | 0.251900 | 0.066* |
| C26 | −0.0155 (5) | 0.5589 (4) | 0.1850 (2) | 0.0561 (12) |
| H26 | −0.080411 | 0.503017 | 0.155205 | 0.067* |
| C27 | 0.0859 (5) | 0.6051 (4) | 0.17273 (19) | 0.0479 (11) |
| H27 | 0.088185 | 0.581197 | 0.133849 | 0.058* |
1 Source of materials
An ethanol solution (30 mL) of 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine[2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine], (0.233 g, 1 mmol) was added to an aqueous solution (30 mL) containing nickel sulfate hexahydrate (0.263 g, 1 mmol) and sodium 1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylate (0.262 g, 1 mmol) under continuous stirring at 55 °C for 12 h. Then the resulting solution was allowed to stand at room temperature in the darkness. After 7 days, blue block crystals of the title nickel(II) complex (yield: 61 %) suitable for X-ray structure determination were deposited.
2 Experimental details
The H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms. All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically. The C-bond H atoms were geometrically placed d(C–H) = 0.98 Å and (U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C)).
3 Comment
2,2′:6′,2″-tripyridine[2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine] and its derivatives with NNN-tridentate structure have been used to construct a large number of novel complexes [4], [5], [6], [7]. The complexes formed by nickel(II) with 2,2′:6′,2″-tripyridine and its derivatives have potential application prospects in many fields, such as catalysis [8], [9], [10], anti-proliferative activity and biomolecular interactions [11], effective separation of C2H4 from C2H2/C2H4 mixtures [12], magnetic properties [13], [14]. The molecular structure of the title nickel(II) complex asymmetric unit is composed of a nickel(II) ion, a 1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylate ligand, a 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine ligand and a coordinated water molecule. The central nickel(II) ion in the complex is six-coordinated in a slightly distorted octahedral environment by three N atoms and three O atoms. The nickel(II) ion in asymmetric unit is chelated by three nitrogen atoms (N1, N2, N3) from a 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine ligand, two O atoms (O1, O4) from two 1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylate ligands and an O atom from a coordinated water molecule. The adjacent nickel(II) ions are connected by two 1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylate ligands to form a 1-D chain structure. The bond lengths of Ni1–N1, Ni1–N2 and Ni1–N3 are 2.139, 2.023 and 2.104 Å, respectively [15]. The bond length of Ni1–O1 and Ni1–O4 are 2.040 and 2.073 Å, respectively [16, 17].
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This project was supported by the Key Projects of Natural Science Research in Universities of Anhui Province (No. KJ2021A0921), the Science and Technology Major Project of Anhui Province of China (No. 201903a07020003), Hefei Normal University 2022 Scientific Research Launch Fund for Introducing High level Talents (No. 2022rcjj26, 2022rcjj35 and 2022rcjj42), The Science and Technology Major Project of Fuyang of Anhui Province of China (FK20208018).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. Saint, Apex2 and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXS-97. Program for the Solution of Crystal Structures; University of Göttingen: Germany, 1997.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8, https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Andres, P. R., Schubert, U. S. New functional polymers and materials based on 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine metal complexes. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1043–1068, https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200306518.Search in Google Scholar
5. Edwin, C. C. Expanded ligands – an assembly principle for supramolecular chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 842–855; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2007.10.020.Search in Google Scholar
6. Foerster, C., Dorn, M., Reuter, T., Otto, S., Davarci, G., Reich, T., Carrella, L., Rentschler, E., Heinze, K. Ddpd as expanded terpyridine: dramatic effects of symmetry and electronic properties in first row transition metal complexes. Inorganics 2018, 6, 86–122; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6030086.Search in Google Scholar
7. He, H. D., Zhang, S. R., Chen, Z., Wang, H., Yu, X. J., Li, X. P. Molecular complexes, supramolecular architectures and metallo-polymers based on chiral terpene-fused 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridines. Chem. Lett. 2023, 52, 370–380; https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.230088.Search in Google Scholar
8. Winter, A., Newkome, G. R., Schubert, U. S. Catalytic applications of terpyridines and their transition metal complexes. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 1384–1406; https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201100118.Search in Google Scholar
9. Ahmad, E., Rai, S., Padhi, S. K. Proton reduction by a Ni(II) catalyst and foot-of-the wave analysis for H2 evolution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 16467–16477; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.04.236.Search in Google Scholar
10. Winter, A., Schubert, U. S. Metal-terpyridine complexes in catalytic application - a spotlight on the last decade. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 2890–2941; https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201902290.Search in Google Scholar
11. Wang, B. W., Sun, D. M., Wang, S. H., Chen, M., Liu, H. M., Zhou, Y. L., Chen, H. L., Ma, Z. Nickel chloride complexes with substituted 4′-phenyl-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine ligands: synthesis, characterization, anti-proliferation activity and biomolecule interactions. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 28, 627–641, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-023-02011-3.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Wang, H. H., Liu, Q. Y., Li, L. B., Krishna, R., Wang, Y. L., Peng, X. W., He, C. T., Lin, R. B., Chen, B. L. Nickel-4′-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-2,2′,6′,2″-terpyridine framework: efficient separation of ethylene from acetylene/ethylene mixtures with a high productivity. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 9489–9494; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01479.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Gorczynski, A., Walesa-Chorab, M., Kubicki, M., Korabik, M., Patroniak, V. New complexes of 6,6″-dimethyl-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine with Ni(II) ions: synthesis, structure and magnetic properties. Polyhedron 2014, 77, 17–23, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2014.03.058.Search in Google Scholar
14. Fortea-Pérez, F. R., Vallejo, J., Mastropietro, T. F., De Munno, G., Rabelo, R., Cano, J., Julve, M. Field-induced single-ion magnet behavior in nickel(II) complexes with functionalized 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine derivatives: preparation and magneto-structural study. Molecules 2023, 28, 4423–4439, https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114423.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
15. Cortes, R., Arriortua, M. I., Rojo, T., Solans, X., Beltran, D. Synthesis and crystal structure of a new nickel(II) terpyridine complex: [Ni(terpy)(NO2)(ONO)(H2O)]. Polyhedron 1986, 5, 1987–1990; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0277-5387(00)87127-2.Search in Google Scholar
16. Sahoo, R., Chand, S., Mondal, M., Pal, A., Pal, S. C., Rana, M. K., Das, M. C. A thermodynamically stable 2D nickel metal–organic framework over a wide pH range with scalable preparation for efficient C2s over C1 hydrocarbon separations. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 12624–12631; https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202001611.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
17. Mei, C.-Z., Shan, W.-W., Liu, B.-T. Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of a nickel(II) coordination polymer with 1,1′-biphenyl-2,2′- dicarboxylato-6,6′-dicarboxylic acid and 2,2′:6,2″-terpyridine ligands. Z. Naturforsch. B: Chem. Sci. 2011, 66, 654–658, https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-2011-0616.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3

