Abstract
C19H23CuNO4, monoclinic, C2/c (no. 15), a = 16.1601(4) Å, b = 23.3298(7) Å, c = 12.8950(3) Å, β = 128.275(1)∘, V = 3816.6(2) Å3, Z = 8, R gt(F) = 0.0620, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1251, T = 296(2) K.
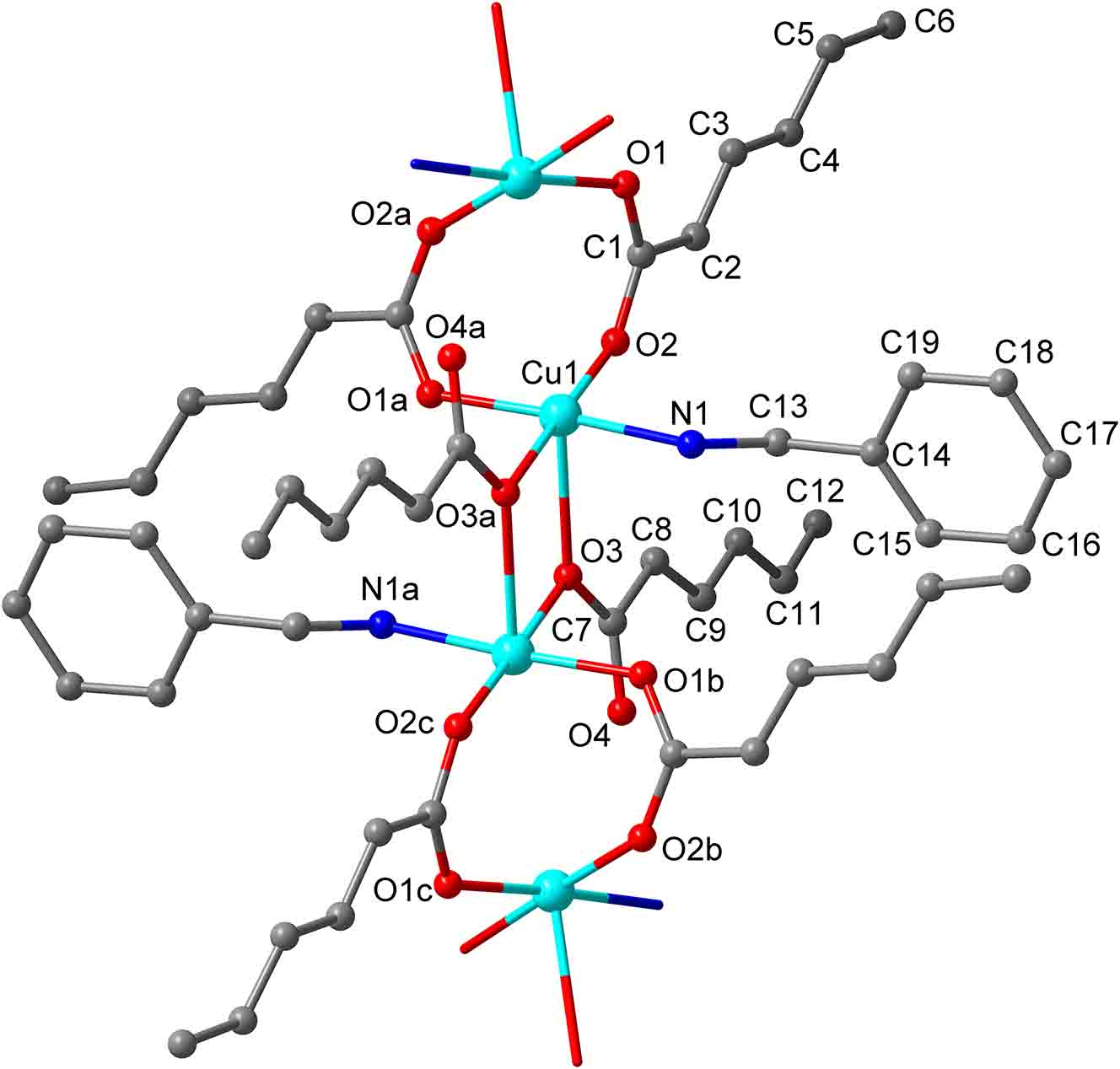
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Blue polyhedron |
| Size: | 0.28 × 0.25 × 0.19 mm |
| Wavelength: μ: |
Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) 1.17 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: θ max, completeness: |
Bruker P4, ω
28.3°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 24932, 4722, 0.145 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 2646 |
| N(param)refined: | 228 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2,3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1 | 0.36860 (3) | 0.26536 (2) | 0.14511 (4) | 0.03431 (16) |
| O1 | 0.4099 (2) | 0.31020 (11) | 0.0558 (2) | 0.0422 (7) |
| O2 | 0.42021 (19) | 0.32727 (11) | 0.2742 (3) | 0.0404 (7) |
| C1 | 0.4949 (3) | 0.33785 (16) | 0.1120 (4) | 0.0349 (9) |
| C2 | 0.4991 (3) | 0.38642 (17) | 0.0420 (4) | 0.0440 (10) |
| H2 | 0.561108 | 0.407615 | 0.086975 | 0.053* |
| C3 | 0.4213 (3) | 0.40163 (17) | −0.0792 (4) | 0.0465 (11) |
| H3 | 0.359005 | 0.380818 | −0.122096 | 0.056* |
| C4 | 0.4232 (4) | 0.4478 (2) | −0.1527 (5) | 0.0603 (13) |
| H4 | 0.483442 | 0.470496 | −0.108956 | 0.072* |
| C5 | 0.3455 (4) | 0.4601 (2) | −0.2774 (5) | 0.0694 (15) |
| H5 | 0.284827 | 0.437928 | −0.318749 | 0.083* |
| C6 | 0.3447 (5) | 0.5055 (2) | −0.3587 (6) | 0.101 (2) |
| H6A | 0.405135 | 0.529782 | −0.303092 | 0.151* |
| H6B | 0.281627 | 0.527976 | −0.401105 | 0.151* |
| H6C | 0.346737 | 0.488140 | −0.424603 | 0.151* |
| O3 | 0.31230 (19) | 0.20464 (11) | 0.0120 (2) | 0.0366 (6) |
| O4 | 0.4752 (2) | 0.17689 (13) | 0.1019 (3) | 0.0720 (11) |
| C7 | 0.3791 (3) | 0.17181 (17) | 0.0176 (4) | 0.0403 (10) |
| C8 | 0.3339 (3) | 0.12689 (16) | −0.0860 (4) | 0.0410 (10) |
| H8 | 0.260976 | 0.124972 | −0.149215 | 0.049* |
| C9 | 0.3920 (3) | 0.08925 (17) | −0.0933 (4) | 0.0460 (11) |
| H9 | 0.464811 | 0.093243 | −0.032918 | 0.055* |
| C10 | 0.3516 (4) | 0.04277 (17) | −0.1868 (4) | 0.0475 (11) |
| H10 | 0.278856 | 0.039062 | −0.249044 | 0.057* |
| C11 | 0.4112 (4) | 0.00508 (18) | −0.1900 (4) | 0.0541 (12) |
| H11 | 0.483799 | 0.010213 | −0.130794 | 0.065* |
| C12 | 0.3707 (4) | −0.0452 (2) | −0.2815 (5) | 0.0746 (16) |
| H12A | 0.401133 | −0.079774 | −0.230943 | 0.112* |
| H12B | 0.389766 | −0.041001 | −0.338428 | 0.112* |
| H12C | 0.295399 | −0.046976 | −0.333943 | 0.112* |
| N1 | 0.3191 (2) | 0.21851 (13) | 0.2272 (3) | 0.0377 (8) |
| H1A | 0.261187 | 0.200107 | 0.162156 | 0.045* |
| H1B | 0.368019 | 0.191957 | 0.277150 | 0.045* |
| C13 | 0.2956 (5) | 0.2459 (2) | 0.3076 (6) | 0.0802 (17) |
| H13A | 0.235316 | 0.270851 | 0.250948 | 0.096* |
| H13B | 0.355026 | 0.269946 | 0.372336 | 0.096* |
| C14 | 0.2724 (4) | 0.20676 (19) | 0.3799 (5) | 0.0543 (12) |
| C15 | 0.1742 (4) | 0.2027 (2) | 0.3446 (5) | 0.0619 (13) |
| H15 | 0.119044 | 0.222746 | 0.271164 | 0.074* |
| C16 | 0.1546 (5) | 0.1691 (2) | 0.4162 (6) | 0.0787 (16) |
| H16 | 0.086625 | 0.166663 | 0.390169 | 0.094* |
| C17 | 0.2340 (6) | 0.1400 (3) | 0.5236 (6) | 0.0814 (18) |
| H17 | 0.220845 | 0.118046 | 0.572185 | 0.098* |
| C18 | 0.3327 (5) | 0.1428 (2) | 0.5606 (6) | 0.0831 (18) |
| H18 | 0.387189 | 0.122438 | 0.634046 | 0.100* |
| C19 | 0.3525 (5) | 0.1759 (2) | 0.4893 (6) | 0.0748 (16) |
| H19 | 0.420464 | 0.177541 | 0.515035 | 0.090* |
1 Source of material
The mixture of CuCl (0.030 g, 0.3 mmol), benzylamine (0.033 mL, 0.3 mmol), sorbic acid (0.034 g, 0.3 mmol) in ethanol (1.0 mL) was sealed under vacuum in a Pyrex tube and heated to 70 °C for 68 h, then cooled to room temperature at 20 °C/h. The pH before the reaction was 6 and it remained unchanged after the reaction. The blue polyhedral crystals of the title compound were recovered by vacuum filtration. The product is stable in air.
2 Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined as riding model, and their positions and isotropic displacement parameters were refined. The Uiso value of the H atoms in sorbate and benzylamine were set to 1.2 Ueq except for the terminal methyl group (1.5 Ueq) in sorbate.
3 Comment
Many copper(II) complexes have been studied because of their interesting structural features followed by the metal center being able to adopt various coordination geometries such as square planar, square pyramidal, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral [5]. Specially, copper(II) carboxylates containing nitrogen donor ligands have been extensively studied due to their importance in biology and magnetism [6], [7], [8], [9]. In this study we report a 1D copper(II) coordination polymer containing monocarboxylic sorbate anion and benzylamine molecule.
One unique copper atom is coordinated by each one oxygen atoms of three sorbate anions (d(Cu–O) = 1.954(3), 1.958(2), 1.961(2) Å) and one nitrogen atom of benzylamine (d(Cu–N) = 2.001(3) Å) to form a square planar geometry. An additional sorbate oxygen atom is weakly coordinated to Cu in an apical position (d(Cu–O) = 2.409(2) Å), completing the slightly distorted square pyramidal arrangement, as evidenced by the τ value (angular structure parameter) of 0.02 [10]. The bond valence sum (BVS) calculation for Cu gives a value of +2.024 indicating an oxidation state of +2 [11]. The CuNO4 square pyramids share a common edge of weakly bonded oxygen (O3) atoms to form Cu2N2O6 dimeric units with the Cu⋯Cu distance of about 3.38 Å. The dinuclear Cu(II) unit is positioned around a center of inversion. The dimers are connected to each other by sorbate anions, forming a neutral Cu(benzylamine) (sorbate)2 chain in the [101] direction. The chains are further stabilized by the presence of intra-chain hydrogen bonds between the NH2 of benzylamine and non-coordinated carboxylate O atom [d(NH⋯O4) = 2.788(4) Å] or the coordinated carboxylate O atom [d(NH⋯O3) = 2.727(4) Å]. That is, of the two independent sorbates, only one sorbate weakly coordinated with Cu is involved in the hydrogen bonds. Adjacent chains are arranged so that the alkyl group of sorbates are partially interdigitated. The interchain distance between the sorbate groups is >3.78 Å, suggesting that van der Waals interactions predominate with only weak π–π stacking.
Funding source: (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT)
Award Identifier / Grant number: (No. 2021R1F1A1060277)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2021R1F1A1060277).
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government(MSIT) (No. 2021R1F1A1060277).
References
1. Bruker. SAINT, APEX2; Bruker Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2016.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Hubschle, C. B., Sheldrick, G. M., Dittrich, B. ShelXle: a Qt graphical user interface for SHELXL. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1281–1284; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889811043202.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Brandenburg, K.. DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Version 4.2.2; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2016.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Hathaway, B. J. Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry; Pergamon: Oxford, 1987.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Wang, Z., Kravtsov, V. C., Zaworotko, M. J. Ternary nets formed by self-assembly of triangles, squares, and tetrahedra. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2877–2880; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200500156.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Kato, M., Muto, Y. Factors affecting the magnetic properties of dimeric copper(II) complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1988, 92, 45–83; https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-8545(88)85005-7.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Ferrer, S., Lioret, F., Beertmenu, I., Alzuet, G., Borras, J., Garcia-Granda, S., Liu–Gonzales, M., Hassnoot, J. G. Cyclic trinuclear and chain of cyclic trinuclear copper(II) complexes containing a pyramidal Cu3O(H) core. Crystal structures and magnetic properties of [Cu3(μ3-OH)(aaat)3(H2O)3](NO3)2⋅H2O [aaat = 3-acetylamino-5-amino-1,2,4-triazolate] and {[Cu3(μ3-OH)(aat)3(μ3–SO4)]⋅6H2O [aat = 3-acetylamino-1,2,4-triazolate]: new cases of spin-frustrated systems. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 41, 5821–5830; https://doi.org/10.1021/ic020179+.10.1021/ic020179+Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Christou, G., Perlepes, S. P., Libby, E., Folting, K., Huffman, J. C., Webb, R. J., Hendrickson, D. N. Preparation and properties of the triply bridged, ferromagnetically coupled dinuclear copper(II) complexes [Cu2(OAc)3(bpy)2](ClO4) and [Cu2(OH)(H2O)(OAc)(bpy)2](ClO4)2. Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29, 3657–3666; https://doi.org/10.1021/ic00344a008.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Addison, W., Rao, T. N., Reedijk, J., van Rijn, J., Verschoor, G. C. Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of copper(II) compounds containing nitrogen-sulphur donor ligands; the crystal and molecular structure of aqua[1,7-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane]copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1984, 1349–1356; https://doi.org/10.1039/dt9840001349.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Brese, N. E., O’Keeffe, M. Bond-valence parameters for solids. Acta Crystallogr. 1991, B47, 192–197; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108768190011041.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3

