Abstract
This study aims to analyze and explore whether tumor biological three-dimensional printing (3DP) models can serve as reliable preclinical model research tools and assist in the personalized treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) patients. Ten GIST cases admitted to our hospital from May 2024 to September 2024 were included in the personalized treatment group. Patient-derived GIST 3DP models were established, and treatment plans were selected based on the results of drug sensitivity tests. The progression-free survival (PFS) of the personalized treatment group was compared with that of GIST patients who had progressed after first-line treatment and were admitted to our hospital before the study. Treatment safety was also assessed. Immunofluorescence staining technology was used to observe tumor markers in the 3DP tumor models and their corresponding parent tumor tissues, revealing a high degree of consistency, which indicates that the 3DP tumor models highly retain the histological characteristics of the parent tumor tissues. The median PFS of patients in the personalized treatment group was 6.1 months, compared to 5.3 months in the previous treatment group, with a statistically significant difference (P-value <0.05). The individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology, used for the personalized treatment of GIST patients who have progressed after first-line treatment, can benefit patients.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common malignant mesenchymal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. According to the National Cancer Institute in the United States, the incidence rate of GIST is approximately 1.5 per 100,000 people per year. Globally, GIST accounts for 1–2% of all gastrointestinal malignancies. In Europe, the incidence of GIST is estimated to be around 10 to 15 cases per million people per year [1]. In recent years, as our understanding of GIST has improved, diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for GIST have also been continuously refined.
GIST is highly resistant to conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy. As human understanding of GIST has improved, tumor treatment is gradually shifting from standard protocols to precision medicine. Currently, in clinical practice, individualized and precise treatment plans can significantly improve patient prognosis. Compared to tumors such as gastric cancer and colorectal cancer, which involve multiple gene and pathway mutations, the mutation targets of GIST are relatively singular, mainly focusing on mutations in tyrosine protein kinase (c-KIT) (80%) and platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) (10%), with the rest classified as wild-type [2]. Since the application of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib in the treatment of GIST, targeted therapy for GIST has achieved great success. For the first-line treatment of newly diagnosed GIST, a definite correlation has been established between the efficacy of imatinib and the primary gene mutations of GIST [3,4]. KIT mutations are mainly located in exon 11, with some mutations also present in exon 9. It has been clarified that for patients with KIT exon 11 mutations, imatinib can achieve an efficacy of over 90%; however, for patients with KIT exon 9 mutations, the treatment with imatinib needs to be intensified, and the prognosis is relatively worse compared to those with KIT exon 11 mutations. Additionally, patients with KIT exon 11 deletions and insertions have a worse prognosis than those with simple point mutations [5]. PDGFRA exon 18 mutations are typically D842V point mutations, and patients with this mutation are primarily resistant to imatinib, but avapritinib can achieve an efficacy close to 100% [6]. For wild-type patients without the aforementioned mutations, there are currently no clearly effective drugs in the first-line treatment.
With the rapid development of 3D bioprinting technology in recent years, 3D-bioprinted organ models have a broad prospect in the medical field. Currently, 3D-bioprinted tumor models have been widely applied in various solid tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer, and neuroblastoma. In a study by Sun et al., it was confirmed through genomic and histological analyses that colorectal cancer/colorectal cancer liver metastasis (CRC/CRLM) can effectively retain the parental tumor biomarkers and mutation spectra in 3D-bioprinted (3DP) tumor models. There is a significant correlation between the drug response in the CRLM biological three-dimensional printing (3DP) model and the clinical results of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. These findings suggest that patient-derived 3DP cancer models have great potential for the precise chemotherapy prediction and preclinical research in CRC/CRLM [7]. In terms of drug discovery, integrating intelligent cell culture systems and biosensors into 3D-bioprinted models can provide highly detailed and functional organ models for drug screening. By addressing current challenges in vascularization, electrophysiological control, and scalability, researchers can obtain more reliable and accurate drug development data, thereby reducing the risk of drug failure during clinical trials [8].
In patients with advanced GIST, most will develop secondary resistance to imatinib after approximately 2 years of first-line treatment. Currently, imatinib is the standard first-line treatment for GIST patients. However, once patients develop resistance to imatinib, the efficacy of second-line drugs available in the clinic is significantly lower than that of first-line treatment. In a previous retrospective study of 52 GIST patients who had progressed after first-line treatment at our hospital, the progression-free survival (PFS) time was only 4–6 months. Therefore, in the current treatment landscape for GIST, optimizing second-line treatment strategies and selecting sensitive second-line drugs as early as possible based on individualized drug sensitivity testing results are of paramount importance for achieving better prognosis. From an application perspective, 3D bioprinting technology holds higher clinical value, offering more efficient and diverse drug screening options and bringing better choices to clinical practice. Thus, we anticipate making clinically significant progress in the selection of second-line drugs after establishing 3D bioprinting models for GIST, aiming to identify effective treatment plans for patients that reduce treatment costs and alleviate adverse reactions. We currently report as follows:
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Establishment of patient inclusion criteria and primary cell isolation and culture
This study included GIST patients who progressed after first-line treatment with tumor reduction surgery or localization puncture (percutaneous or ultrasound-guided endoscopic puncture) at our hospital. Inclusion criteria: 1) GIST patients who progressed after first-line treatment with tumor reduction surgery or localization puncture; 2) age ≥ 18 years, regardless of gender; 3) surgical resection or localization puncture to obtain at least one tumor sample with a volume greater than 0.5 cm3; 4) good general condition, expected to receive subsequent adjuvant therapy; 5) voluntarily signed informed consent. Exclusion criteria: 1) patients with poor general condition, expected to be intolerant to systemic treatment; 2) unable to obtain tumor samples through tumor reduction surgery or localization puncture; 3) poor patient compliance; 4) history of other malignant tumors.
Collect surgical tumor specimens from GIST patients who progressed after first-line treatment: 1) preoperative preparation: patients were evaluated through clinical examination, imaging studies (computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging), and laboratory tests to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the tumor; 2) Surgical procedure: tumor resection was performed by experienced surgeons. The surgical approach was chosen based on the location, size, and extent of the tumor. For patients with localized tumors, complete resection with negative margins was attempted. For patients with metastatic or recurrent tumors, debulking surgery was performed to obtain sufficient tumor tissue for analysis. 3) Tissue sampling: during surgery, multiple samples were collected from different parts of the tumor to ensure that heterogeneity was captured. Each sample was approximately 0.5 cm3 in volume. Tissue samples were immediately placed in sterile containers with cold transport medium (Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium [DMEM] supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS)) and transported to the laboratory within 30 min. 4) Postoperative handling: tissue samples were processed within 1 h of arrival in the laboratory. The samples were washed with sterile PBS to remove excess blood and debris. Tumor tissue was minced into small pieces (1–2 mm3) using sterile scalpels. The minced tissue was then digested with a mixture of collagenase type I (1 mg/mL) and DNase I (0.1 mg/mL) in DMEM at 37°C for 1–2 h with gentle agitation.
Cell isolation and culture: After digestion, the tissue suspension was passed through a 70 µm cell strainer to obtain a single-cell suspension. The cell suspension was centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 5 min, and the pellet was resuspended in complete culture medium (DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% penicillin–streptomycin, and 1% l-glutamine). Cells were cultured in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2. Cell viability was assessed using the trypan blue exclusion method, and only samples with viability >90% were used for further experiments.
-
Informed consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to human use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations and institutional policies and in accordance with the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and has been approved by the authors’ institutional review board or equivalent committee.
1.2 Establishment of patient-derived GIST 3DP models
After successfully isolating and counting primary tumor cells, they were directly resuspended in bio-ink (Bio-ink composition: Printing material: GelMA (GelMA30, EFL). Final cell concentration: 1.0 × 10⁷ cells/mL in 7.5% (w/v) GelMA30 (with 0.1% (w/v) lithium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate as a photoinitiator. Printing parameters: Nozzle diameter: 23G needle, printing speed 4.8 mm/s, extrusion speed 1.05 mm3/s, crosslinking under 405 nm light of 15 mW/cm² for 18 seconds; model parameters: grid structure, 6 mm × 6 mm × 0.92 mm, 4 layers, layer height 0.23 mm, line distance 0.99 mm; printing temperature: nozzle 23°C, bed 10°C) for bioprinting and cultured in GIST 3DP culture medium. Cell viability was tested on days 1, 3, 7, 14, and 28 to confirm that primary tumor cells can survive long-term in the 3D printing culture system.
1.3 Confirmation of the tumor 3D printing model retaining histological characteristics of parent tumor
The GIST biomarkers in the GIST-3DP model were detected to confirm that the tumor 3DP model highly retains the histological characteristics of the parent tumor.
1.4 This study investigates the efficacy and safety of personalized treatment for GIST patients who progressed a fter first-line imatinib, comparing their survival outcomes with those of a historical cohort
This study plans to include 10 cases of GIST patients who progressed after first-line treatment with imatinib and from whom tumor specimens can be obtained, forming a personalized treatment group. Patients in the personalized treatment group will select treatment plans based on drug sensitivity test results, and the drugs included in the selection will all be within the indications for that tumor, with controllable treatment risks. A retrospective statistical analysis of the progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of 52 GIST patients who progressed after first-line treatment at our hospital from January 2020 to April 2024 will be conducted. The PFS of the personalized treatment group will be compared with that of corresponding patients with GIST who progressed after first-line treatment admitted to our hospital during the earlier phase of the study, and treatment safety will be assessed.
1.5 Analysis of the correlation between the targeted drug response of GIST-3DP/GIST-3DMP models and the clinical response to targeted therapy in corresponding patients after first-line treatment progression
(1) collection of patient clinical data: Collect clinical data from patients, including their clinical response to targeted therapy. (2) Correlation analysis: conduct a correlation analysis between the drug response results from the 3DP models and the clinical response to targeted therapy in corresponding patients after first-line treatment progression.
2 Result
Flowchart illustrates the criteria for sample selection and the process of surgical specimen collection, cell isolation, 3D printing model construction, and drug sensitivity testing (Figure 1).
We established the process of creating patient-derived 3DP tumor models (Figure 2).
We used immunofluorescence staining technology to observe the tumor markers in the 3DP tumor models and their corresponding parent tumor tissues separately. We found a high degree of consistency between the two, indicating that the 3DP tumor models highly retain the histological characteristics of the parent tumor tissues (Figure 4).
We retrospectively analyzed and calculated the PFS and OS of GIST patients who progressed after first-line treatment and were admitted to our hospital from January 2020 to April 2024 (a total of 52 cases), and performed survival analysis (Figure 5).
The correlation analysis between the drug response of the 3DP tumor model and the clinical response to targeted therapy in patients is as follows:
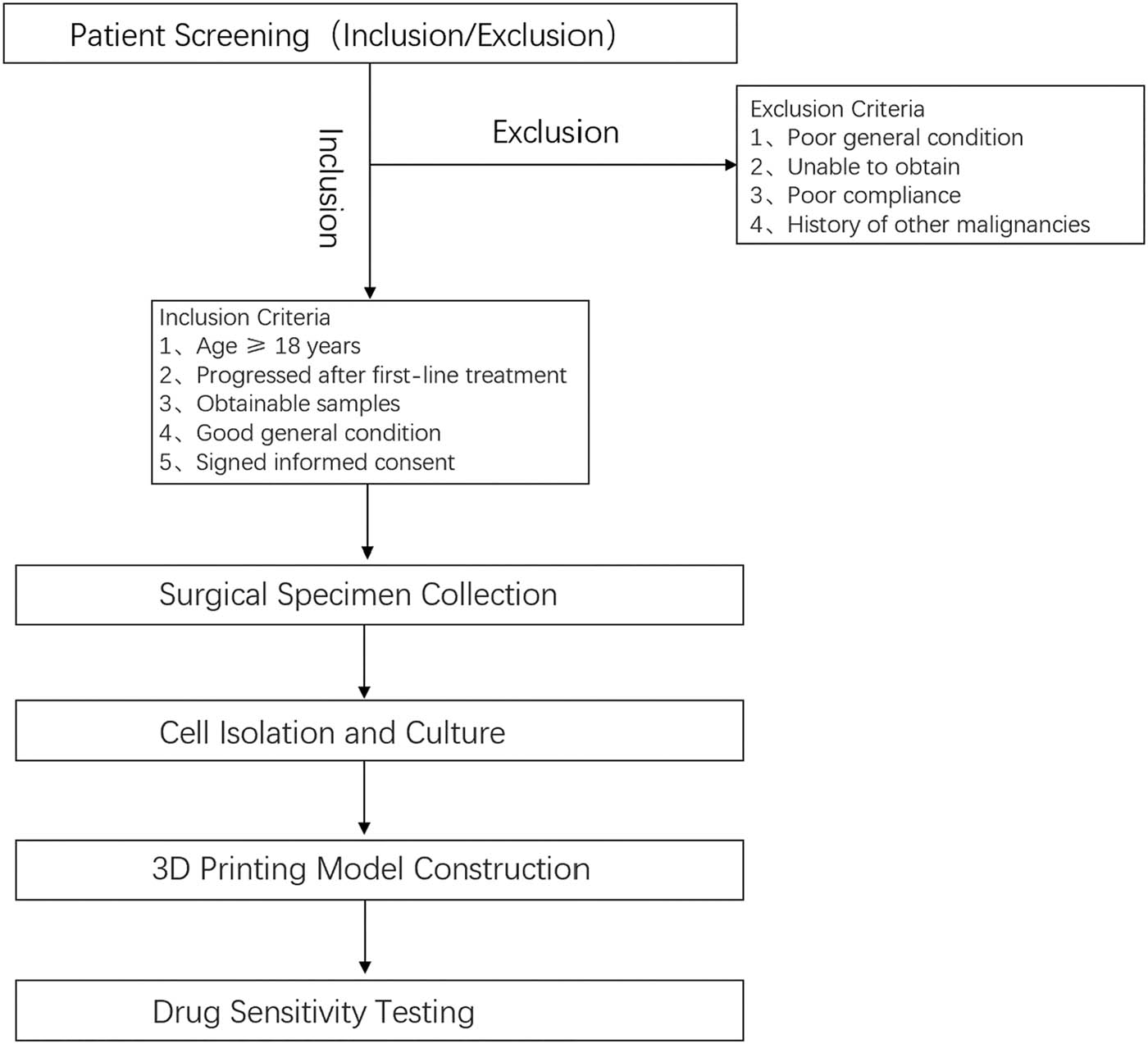
Flowchart of sample selection and processing.
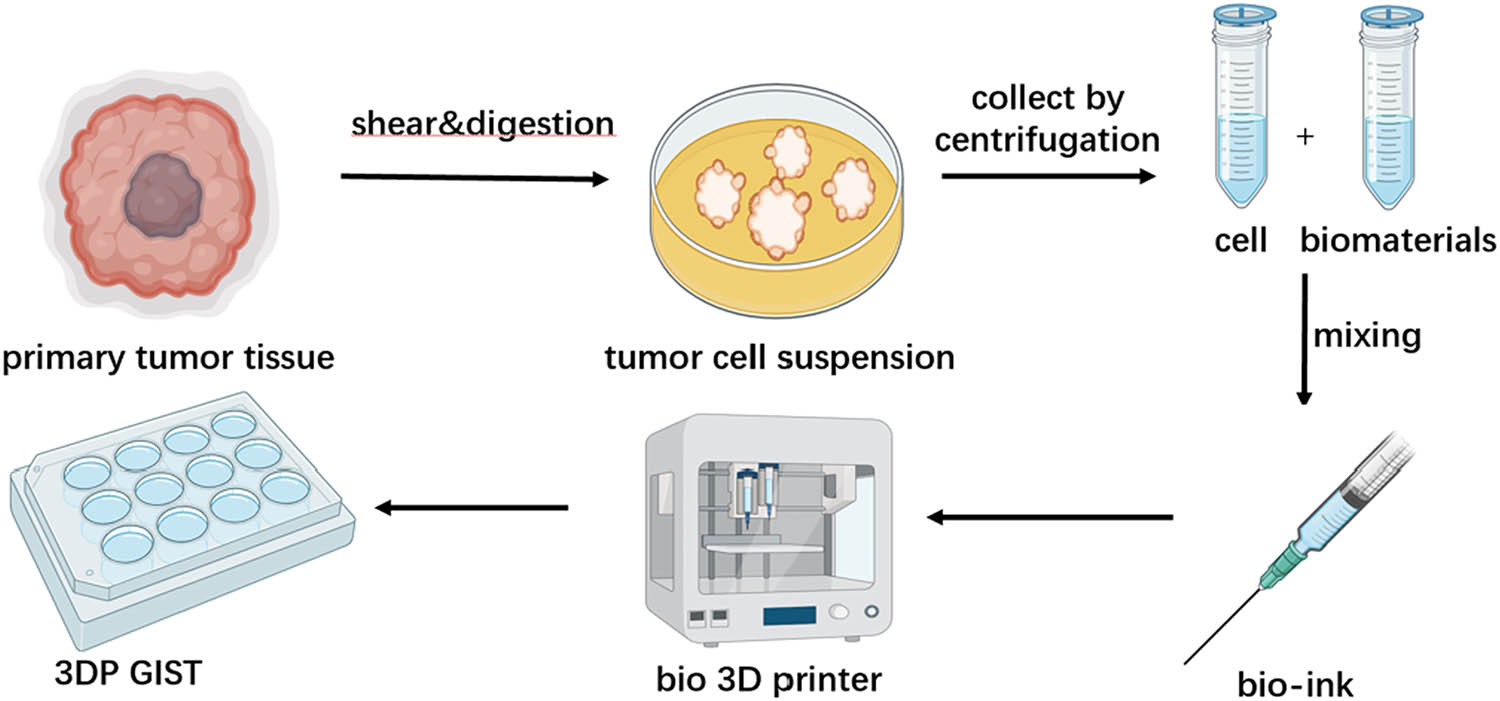
Flowchart of the establishment of 3DP tumor mode.
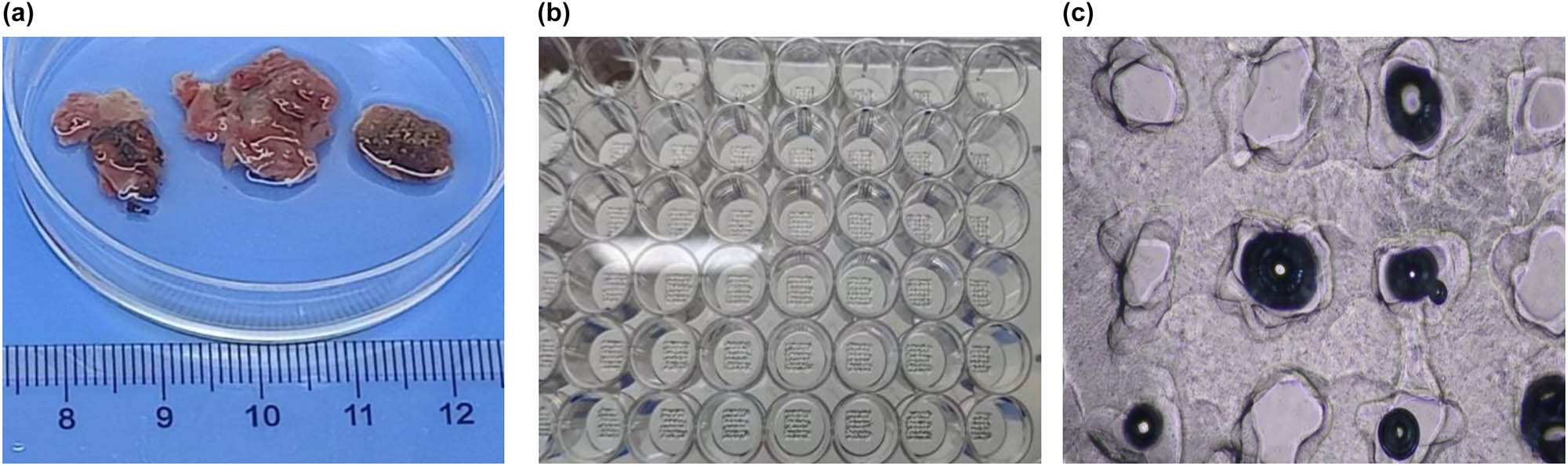
Fabrication of 3DP tumor models. Photographs of freshly resected tumor specimens (a), GIST 3DP models in 48-well plate (b), and bright field image of 3DP tumor models (c).
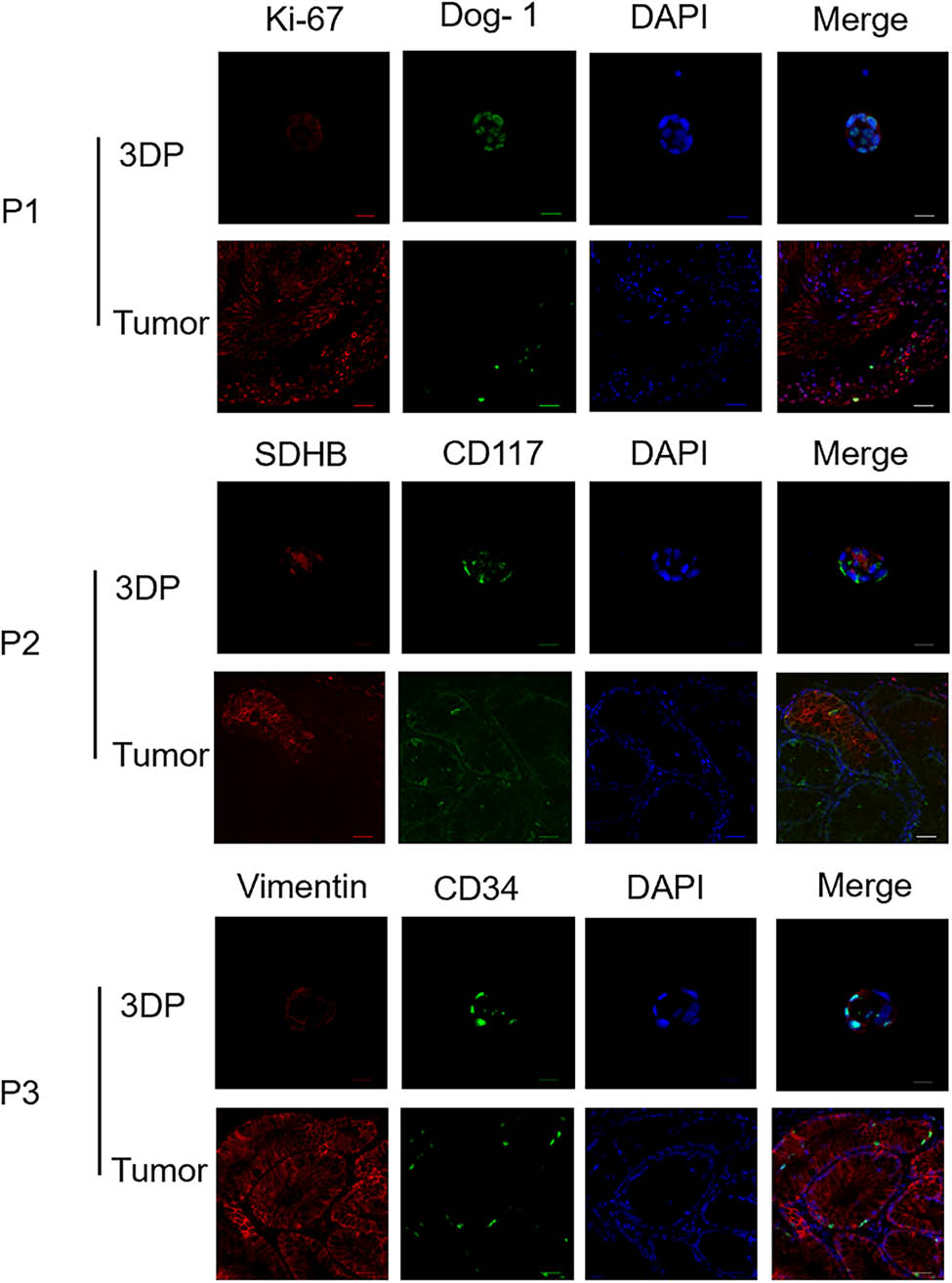
Immunofluorescence of 3DP tumor models and primary tumor tissues.
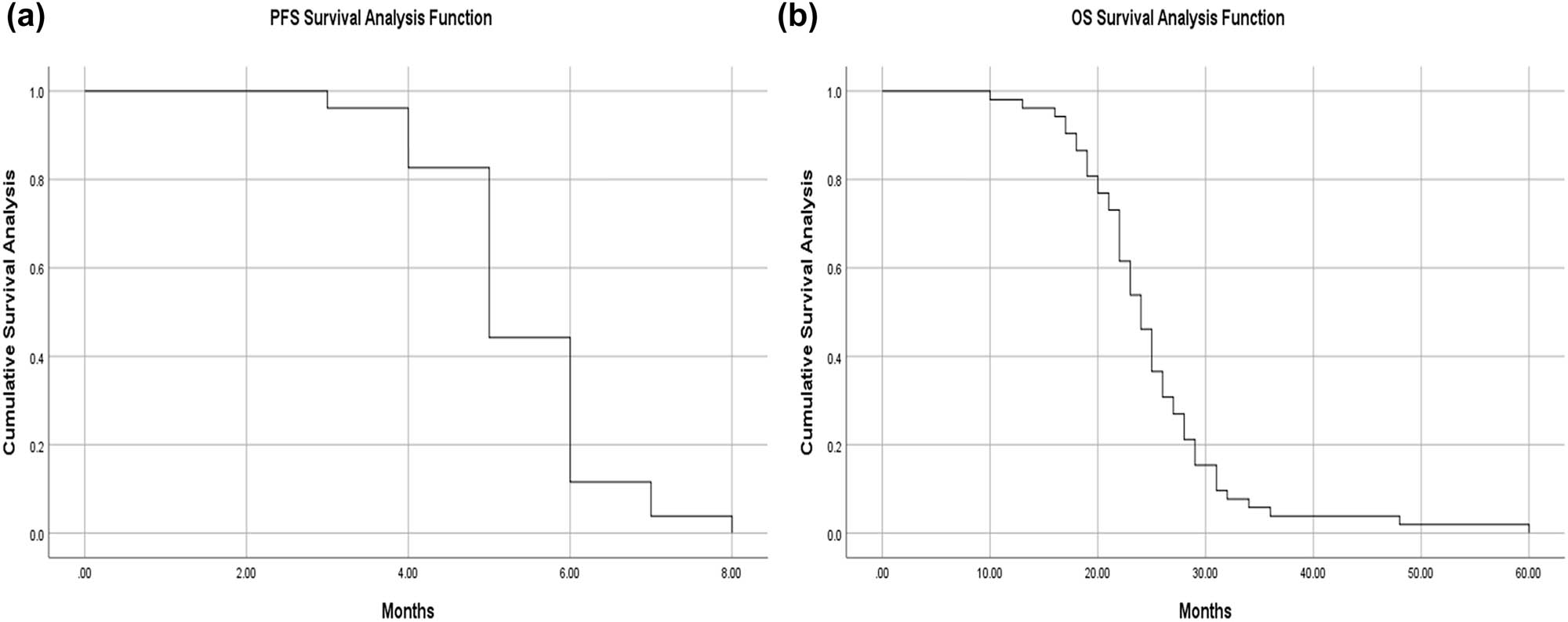
Survival analysis of PFS in patients with GIST in the pretreatment group (a) and survival analysis of OS in patients with GIST in the pretreatment group (b).
Clinical baseline information of GIST patients
| Age | Gender | Tumor type | Gene testing | Drug sensitivity test results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imatinib | Sunitinib | Regorafenib | Ripretinib | ||||
| 42 | Man | Intestinal stromal tumor with liver metastasis | KIT p.K558_D572del mutation | Insensitive | Intermediate | Intermediate | Sensitive |
| 47 | Man | Recurrent gastric stromal tumor after surgery | KIT p.W557_K558del mutation | Intermediate | Intermediate | Intermediate | Sensitive |
| 69 | Female | Recurrent intestinal stromal tumor | KIT exon 9 non-synonymous insertion mutation | Insensitive | Sensitive | Sensitive | Insensitive |
| 68 | Man | Recurrent gastric stromal tumor after surgery | KIT p.k550_K557delinsiR mutation | Insensitive | Sensitive | Sensitive | Sensitive |
| 62 | Man | Recurrent gastric stromal tumor after surgery | KIT exon 11 mutation positive, exon 17 mutation positive | Insensitive | Intermediate | Sensitive | Insensitive |
| 36 | Female | Recurrent gastric stromal tumor after surgery | No mutations found in KIT and PDGFRA genes | Insensitive | Insensitive | Insensitive | Sensitive |
| 61 | Female | Recurrent gastric stromal tumor after surgery | KIT exon 11 small fragment insertion mutation | Insensitive | Insensitive | Intermediate | Insensitive |
| 35 | Man | Recurrent gastric stromal tumor after surgery | KIT gene exon 11 mutation | Insensitive | Insensitive | Intermediate | Intermediate |
| 70 | Man | Recurrent intestinal stromal tumor after surgery | KIT exon 11 mutation positive | Insensitive | Insensitive | Sensitive | Insensitive |
| 54 | Female | Recurrent gastric stromal tumor after surgery | KIT exon 9 mutation positive | Insensitive | Sensitive | Intermediate | Insensitive |
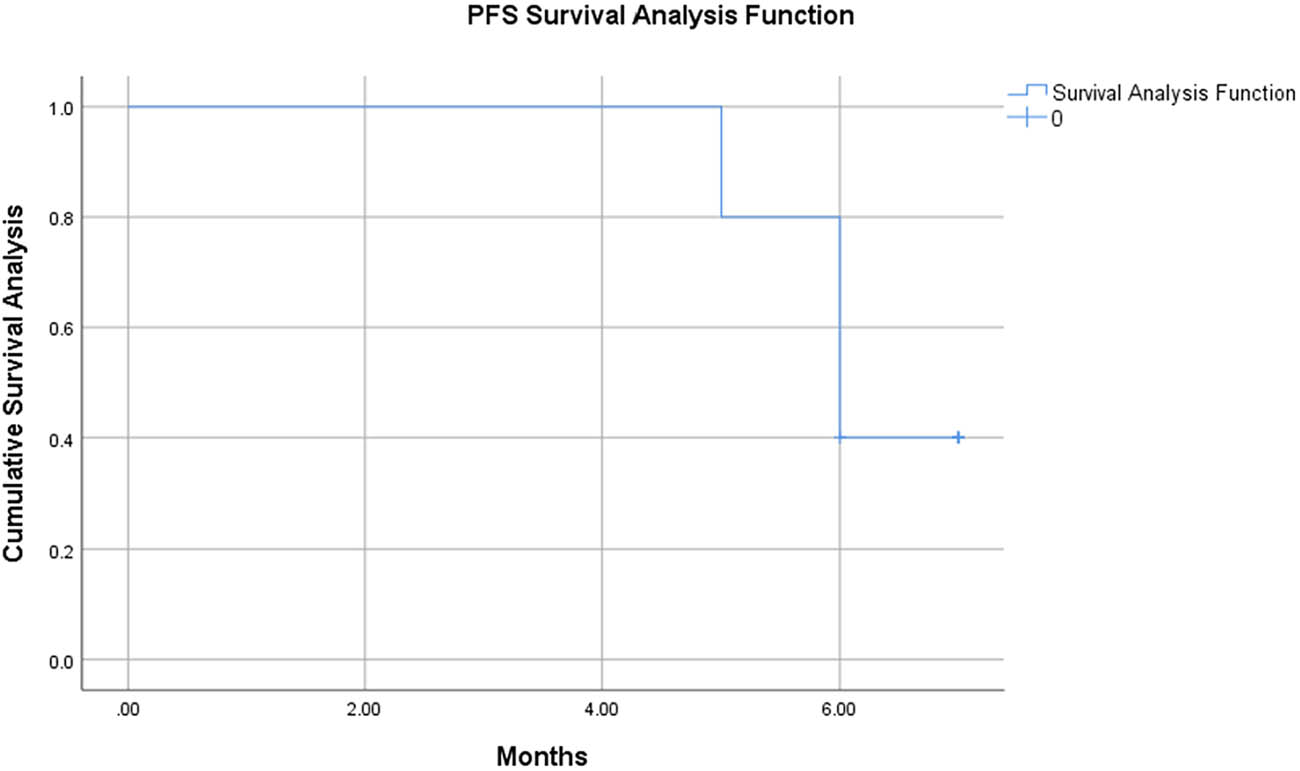
Survival analysis of PFS in patients with GIST in the individualized treatment group.
PFS of previous treatment group and personalized treatment group
| Group | Total number of cases | Median PFS | t-value | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous treatment group | 52 | 5.3 | −2.019 | <0.05 |
| Personalized treatment group | 10 | 6.1 |
Analysis of the clinical response to targeted therapy in a case of GIST patient admitted earlier is as follows: the patient had a recurrence of small intestine stromal tumor and underwent multiple surgeries. The genetic testing report showed that the primary gene mutation was a c-KIT exon 9 mutation. The treatment process was as follows: Gleevec prophylactic medication – increased dosage after progression – surgery after further progression – developed high fever after switching to Sutent – could not tolerate third-line treatment – progressed on fourth-line medication – received second-line treatment again (partial progression, partial effectiveness).
The clinical response to targeted therapy in the patient was highly consistent with the drug response of the 3DP tumor model. Moreover, the drug sensitivity test found that the single targeted drugs, imatinib and ripretinib, were not sensitive (consistent with the clinical presentation of this patient). However, when these two drugs were used in combination, they were found to be effective. This finding provides an explanation for the clinical phenomenon that the combination of targeted drugs is effective in some patients.
3 Discussion
Currently, two-dimensional (2D) culture is an important model for drug screening and has been widely applied in the medical field. Although it has the advantages of simplicity, reproducibility, and technical maturity, the planar 2D structure is significantly different from the three-dimensional (3D) spatial structure of the human or animal body. Antitumor drugs that show significant tumor-suppressing effects in 2D culture models may not have good pharmacological effects when applied to the human body [9]. In 2D cell line drug sensitivity tests, the fourth-line drug ripretinib has inhibitory effects on all secondary gene mutations except for the PDGFA D842V mutation. In actual clinical use, in head-to-head comparisons of drugs after first-line treatment progression, ripretinib did not show an advantage over sunitinib [10]. This to some extent also indicates the inconsistency between 2D cell line drug sensitivity tests and actual clinical situations. Therefore, its benefits to clinical practice are limited. Therefore, in recent years, the dynamics and complexity of the tumor microenvironment (TME) have been the main cause of this clinical dilemma. The TME consists of tumor cells, stromal cells, extracellular matrix, and various cytokines secreted by cells, which endow tumors with innate chemoresistance [11]. Studies have found that the TME plays an important role in tumor proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and the formation of drug resistance [12,13]. The individualized drug sensitivity detection platform based on bio-3D printing technology has extremely excellent precision, feasibility, and efficiency, giving this method an unbeatable advantage in establishing the required models, and it can efficiently and truly reflect the TME [14,15]. From past experience, tumor models constructed based on 3D bioprinting technology are structurally stable, have high success rates, low heterogeneity, and high consistency with tumors in the patient’s body. Combined with clinical practice, it shows that the results of drug sensitivity tests are highly reliable [16,17,18]. In particular, this detection platform can provide drug sensitivity test results in about 1 week, making it the only solution that can provide a test report before the clinical decision on the patient’s adjuvant treatment plan. The model construction success rate is close to 100%, which is significantly higher than other tumor models.
At present, in the realm of first-line treatment, the genotyping of GIST has successfully established a clear correlation with the application of targeted drugs. It can be said that for newly diagnosed GIST patients, individualized treatment based on tumor gene testing results is now possible. However, for patients who have progressed after first-line treatment, the specific medication and especially how to use medication based on gene testing results, although some progress has been made in clinical and research settings, it is still not clear. In particular, for the drug selection after first-line treatment progression in advanced GIST patients, the current guidelines suggest using drugs in a stepwise manner, and after fourth-line progression, it is recommended to participate in clinical trials or switch to previously effective drugs. A considerable number of experts have proposed that for GIST patients who have progressed after first-line treatment, the choice of second-line drugs should be based on gene testing results, but this view is still in question. Especially in the selection of second-line drugs, the controversy is more concentrated at present. Moreover, there are still many problems with the use of targeted drugs in the second-line clinical practice of GIST patients. First, in different historical periods or different centers, the acquisition of gene mutation data in advanced GIST patients is not consistent. The secondary mutations found in tissue samples and the secondary mutations found in blood circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) are used as variables, and when comparing the efficacy of the third-line drug regorafenib, significant differences were found [19]. In addition, in advanced GISTs, there is significant heterogeneity between different recurrence foci, which also limits the clinical significance of local sample gene testing [20]. The positive results of blood circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) mutation tests also show significant temporal heterogeneity with the use of sensitive targeted drugs [21].
Our study included 10 cases of GIST in the personalized treatment group and compared them with the 52 cases of GIST that progressed after first-line treatment and were admitted to our hospital in the past. It was found that the median progression-free survival (mPFS) of patients in the personalized treatment group was 6.1 months, which was higher than the mPFS of 5.3 months in the previous treatment group, and there was a statistical difference. Due to the insufficient follow-up time, it is not possible to compare the OS of patients. The findings of our study align with several other studies that have explored the potential of 3D bioprinting technology in the context of GIST treatment. For example, a study by Sun et al. [7] demonstrated that 3D-bioprinted colorectal cancer models effectively retained the histological and genetic characteristics of the parent tumors, showing a strong correlation between drug responses in the 3D models and clinical outcomes. This supports our observation that 3D-bioprinted GIST models can accurately reflect the TME and provide reliable drug sensitivity data. Moreover, the work by Bauer et al. [10] highlighted the limitations of traditional 2D cell line models in predicting clinical outcomes for GIST patients, particularly in the context of drug resistance. This further underscores the need for more advanced models like 3D bioprinting to better understand the complex interactions within the TME. Our study’s results, which show a higher PFS in the personalized treatment group using 3D bioprinting, provide additional evidence for the potential benefits of this technology. In addition, recent advancements in the understanding of GIST’s genetic landscape, as reported by several studies [19,20,21], highlight the challenges associated with genetic heterogeneity and the limitations of current gene testing methods. Our study addresses these challenges by using 3D bioprinting to create patient-specific models that can provide more accurate and personalized drug sensitivity data, potentially overcoming the limitations of traditional genetic testing.
4 Conclusion
Therefore, we have reason to believe that the 3DP model can be a powerful tool to participate in achieving personalized precision treatment as an in vitro tumor model that truly simulates the TME in the body, providing drug references for patients in a short time, selecting the optimal treatment plan, and strive to secure treatment time for patients, achieving the medical purpose of “surrogate drug testing.” We will include more cases and extend the patient follow-up time in the future to make the trial results more reliable. We look forward to making clinically significant progress in the selection of second-line drugs after the establishment of 3D bioprinting models for GIST.
Acknowledgments
We thank ChangDu BioEng. and Therapy Co., Ltd. for their invaluable support in the development of 3D-bioprinted GIST models and conducting in vitro drug sensitivity test, and all of the investigators and participants who contributed to these studies.
-
Funding information: The research has been supported by the Zhejiang Province Medical and Health Science and Technology Project (2025KY1277).
-
Author contributions: Data collection and manuscript writing were completed by Yang-yang Tu; data organization was done by Zhong-ting Huang, Zhi-yong Zhang and Dong-liang Liu; data organization and funding support were provided by Hai-long Qian.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in collaboration with ChangDu BioEng. and Therapy Co., Ltd. The company provided the bio-3D printing technology and related materials used in the study. However, the study design, data collection, analysis, and interpretation were independently conducted by the research team. ChangDu BioEng. and Therapy Co., Ltd. did not have any influence on the data interpretation or the presentation of the results. The final decision regarding the conclusions and the manuscript content was made solely by the authors.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Christos V, Panagiotis S, Anastasios K, Evangelos K, Stamatios T, Athanasios GP, et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs): novel therapeutic strategies with immunotherapy and small molecules. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):493.10.3390/ijms22020493Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Kelly CM, Gutierrez Sainz L, Chi P. The management of metastatic GIST: current standard and investigational therapeutics. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):2.10.1186/s13045-020-01026-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Demetri GD, Von Mehren M, Blanke CD, Van den Abbeele AD, Eisenberg B, Roberts PJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(7):472–80.10.1056/NEJMoa020461Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Rubin BP, Heinrich MC, Corless CL. Gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Lancet. 2007;369(9574):1731–41.10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60780-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Blanke CD, Rankin C, Demetri GD, Ryan CW, von-Mehren M, Benjamin RS, et al. Phase III randomized, intergroup trial assessing imatinib mesylate at two dose levels in patients with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors expressing the kit receptor tyrosine kinase: S0033. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(4):626–32.10.1200/JCO.2007.13.4452Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Heinrich MC, Jones RL, von-Mehren M, Schöffski P, Serrano C, Kang YK, et al. Avapritinib in advanced PDGFRA D842V-mutant gastrointestinal stromal tumour (NAVIGATOR): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(7):935–46.10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30269-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Sun H, Sun LJ, Ke XD, Liu LJ, Li CC, Jin B, et al. Prediction of clinical precision chemotherapy by patient-derived 3D bioprinting models of colorectal cancer and its liver metastases. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(2):e2304460.10.1002/advs.202304460Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Juraski AC, Sharma S, Sparnese S, da Silva VA, Wong J, Laksman Z, et al. 3D bioprinting for organ and organoid models and disease modeling. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2023;18(9):1043–59.10.1080/17460441.2023.2234280Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Rouwkema J, Khademhosseini A. Vascularization and angiogenesis in tissue engineering: beyond creating static networks. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34(9):733–45.10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.03.002Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Bauer S, Jones RL, Blay JY, Gelderblom H, George S, Schöffski P, et al. Ripretinib versus sunitinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor after treatment with imatinib (INTRIGUE): a randomized, open-label, phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(34):3918–28.10.1200/JCO.22.00294Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Ravid S, Teppei M, Kevin S, Michal BR, Qian ZR, Du JY, et al. Tumour micro-environment elicits innate resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion. Nature. 2012;487(7408):500–4.10.1038/nature11183Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Jackstadt R, van-Hooff SR, Leach JD, Cortes-Lavaud X, Lohuis JO, Ridgway RA, et al. Epithelial NOTCH signaling rewires the tumor microenvironment of colorectal cancer to drive poor-prognosis subtypes and metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2019;36(3):319–36.10.1016/j.ccell.2019.08.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Xu M, Xu X, Pan B, Chen XX, Lin K, Zeng KX, et al. LncRNA SATB2-AS1 inhibits tumor metastasis and affects the tumor immune cell microenvironment in colorectal cancer by regulating SATB2. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):135.10.1186/s12943-019-1063-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Bagrat G, Samantha JP, Corbett DC, Sazer DW, Fortin CL, Zaita AJ, et al. Multivascular networks and functional intravascular topologies within biocompatible hydrogels. Science. 2019;364(6439):458–64.10.1126/science.aav9750Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Kelly BE, Bhattacharya I, Heidari H, Shusteff M, Spadaccini CM, Taylor HK. Volumetric additive manufacturing via tomographic reconstruction. Science. 2019;363(6431):1075–9.10.1126/science.aau7114Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Xie FH, Sun LJ, Pang Y, Xu G, Jin B, Xu HF, et al. Three-dimensional bio-printing of primary human hepatocellular carcinoma for personalized medicine. Biomaterials. 2021;265:120416.10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120416Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Zhang J, Yang H, Yang H. Highlights of constructing liver-relevant models with 3D bioprinting. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2022;11(6):896–8.10.21037/hbsn-22-486Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Yang H, Sun L, Pang Y, Hu D, Xu H, Mao S, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinted hepatorganoids prolong survival of mice with liver failure. Gut. 2021;70(3):567–74.10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319960Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Xu H, Chen L, Shao Y, Zhu D, Zhi X, Zhang Q, et al. Clinical application of circulating tumor DNA in the genetic analysis of patients with advanced GIST. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018;17(1):290–6.10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0436Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Heinrich MC, Jones RL, George S, Gelderblom H, Schöffski P, von Mehren M, et al. Ripretinib versus sunitinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumor: ctDNA biomarker analysis of the phase 3 INTRIGUE trial. Nat Med. 2024;30(2):498–506.10.1038/s41591-023-02734-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Ko TK, Lee E, Ng CC, Yang VS, Farid M, Teh BT, et al. Circulating tumor DNA mutations in progressive gastrointestinal stromal tumors identify biomarkers of treatment resistance and uncover potential therapeutic strategies. Front Oncol. 2022;12:840843.10.3389/fonc.2022.840843Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- 10.1515/biol-2025-1168
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- 10.1515/biol-2025-1168
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”

