Abstract
C24H18F2N2O3S, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 15.180(5) Å, b = 10.221(3) Å, c = 13.556(4) Å, β = 106.628(4)°, V = 2015.3(10) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0530, wRref(F2) = 0.1342, T = 173(2) K.
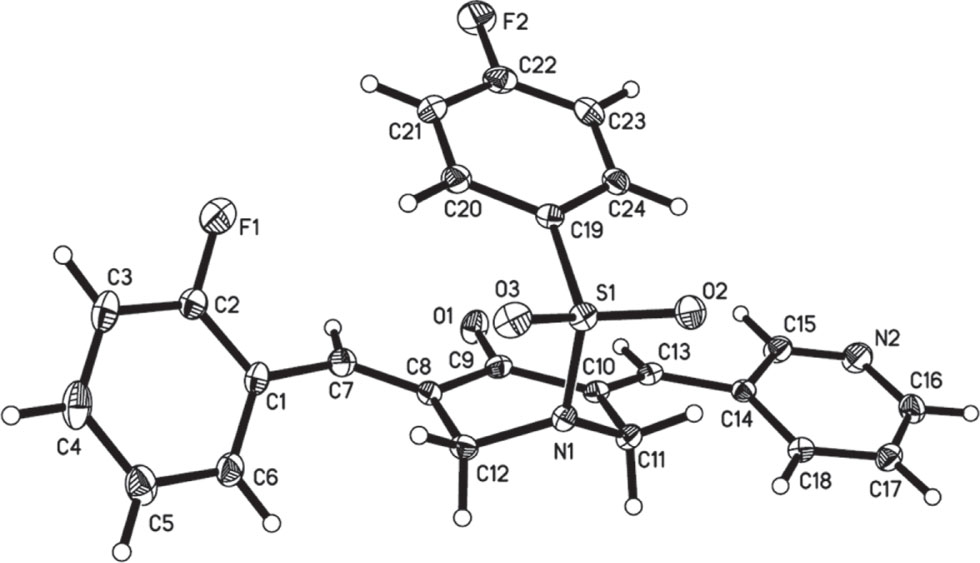
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow plan |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.09 × 0.08 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.21 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 10317, 3742, 0.045 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2780 |
| N(param)refined: | 289 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.44401(18) | 0.2070(3) | 0.3413(2) | 0.0278(6) |
| C2 | 0.51423(19) | 0.1209(3) | 0.3407(2) | 0.0327(7) |
| C3 | 0.58082(19) | 0.0816(3) | 0.4264(3) | 0.0382(8) |
| H3 | 0.626202 | 0.019801 | 0.421830 | 0.046* |
| C4 | 0.5804(2) | 0.1340(3) | 0.5196(3) | 0.0423(8) |
| H4 | 0.626994 | 0.110357 | 0.580308 | 0.051* |
| C5 | 0.51259(19) | 0.2209(3) | 0.5250(2) | 0.0408(8) |
| H5 | 0.512404 | 0.256750 | 0.589630 | 0.049* |
| C6 | 0.44521(19) | 0.2558(3) | 0.4375(2) | 0.0334(7) |
| H6 | 0.398329 | 0.314697 | 0.442806 | 0.040* |
| C7 | 0.37576(18) | 0.2454(3) | 0.2446(2) | 0.0278(6) |
| H7 | 0.398759 | 0.267018 | 0.188492 | 0.033* |
| C8 | 0.28470(17) | 0.2529(2) | 0.2278(2) | 0.0221(6) |
| C9 | 0.22800(18) | 0.2922(2) | 0.1219(2) | 0.0236(6) |
| C10 | 0.12574(17) | 0.2888(2) | 0.0985(2) | 0.0214(6) |
| C11 | 0.08420(18) | 0.2352(3) | 0.1792(2) | 0.0236(6) |
| H11A | 0.066488 | 0.309120 | 0.216715 | 0.028* |
| H11B | 0.027648 | 0.185937 | 0.144584 | 0.028* |
| C12 | 0.23502(17) | 0.2129(3) | 0.3046(2) | 0.0253(6) |
| H12A | 0.274109 | 0.151984 | 0.355409 | 0.030* |
| H12B | 0.223582 | 0.291211 | 0.342149 | 0.030* |
| C13 | 0.07662(18) | 0.3336(2) | 0.0060(2) | 0.0221(6) |
| H13 | 0.112493 | 0.361664 | −0.037160 | 0.027* |
| C14 | −0.02238(17) | 0.3466(2) | −0.0396(2) | 0.0214(6) |
| C15 | −0.0526(2) | 0.3715(3) | −0.1451(2) | 0.0322(7) |
| H15 | −0.007160 | 0.376180 | −0.180716 | 0.039* |
| C16 | −0.2023(2) | 0.3787(3) | −0.1481(2) | 0.0341(7) |
| H16 | −0.265331 | 0.385968 | −0.185665 | 0.041* |
| C17 | −0.18055(19) | 0.3579(3) | −0.0432(2) | 0.0290(7) |
| H17 | −0.227668 | 0.353563 | −0.009907 | 0.035* |
| C18 | −0.08969(18) | 0.3435(2) | 0.0125(2) | 0.0230(6) |
| H18 | −0.073047 | 0.331629 | 0.084999 | 0.028* |
| C19 | 0.19913(18) | −0.0289(2) | 0.1260(2) | 0.0225(6) |
| C20 | 0.29227(19) | −0.0544(3) | 0.1503(2) | 0.0297(7) |
| H20 | 0.327317 | −0.064584 | 0.220132 | 0.036* |
| C21 | 0.3342(2) | −0.0649(3) | 0.0731(2) | 0.0329(7) |
| H21 | 0.398233 | −0.081636 | 0.088557 | 0.039* |
| C22 | 0.2808(2) | −0.0507(3) | −0.0271(2) | 0.0331(7) |
| C23 | 0.1881(2) | −0.0279(3) | −0.0540(2) | 0.0305(7) |
| H23 | 0.153259 | −0.020610 | −0.124175 | 0.037* |
| C24 | 0.14646(19) | −0.0159(2) | 0.0244(2) | 0.0260(6) |
| H24 | 0.082400 | 0.001073 | 0.008572 | 0.031* |
| F1 | 0.51499(13) | 0.0683(2) | 0.24851(16) | 0.0565(6) |
| F2 | 0.32167(12) | −0.05875(19) | −0.10323(13) | 0.0487(5) |
| N1 | 0.14699(14) | 0.1491(2) | 0.25332(16) | 0.0217(5) |
| N2 | −0.13935(17) | 0.3893(3) | −0.19992(19) | 0.0406(7) |
| O1 | 0.26511(13) | 0.3247(2) | 0.05647(15) | 0.0343(5) |
| O2 | 0.05247(13) | −0.04342(18) | 0.18753(15) | 0.0322(5) |
| O3 | 0.20505(13) | −0.06847(18) | 0.31622(15) | 0.0334(5) |
| S1 | 0.14712(5) | −0.00734(6) | 0.22628(5) | 0.0238(2) |
Source of material
The starting materials 3-pyridinecarboxaldehyde (1.07 g, 10.0 mmol), 2-fluorobenzaldehyde (1.24 g, 10.0 mmol) and 4-piperidone hydrate hydrochloride (1.35 g, 10.0 mmol), were dissolved in acetic acid (20 mL). This mixture was passed through by dry HCL gas for 30 min resulting in a clear solution. After stirring at room temperature for about 24 h [monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC)], the precipitate was collected and washed with cold acetone. The precipitate was added into 100 mL water, and then aqueous Na2CO3 solution was added until pH value was adjusted to about 7. The mixture was filtered and subsequently washed by water to provide yellow precipitates. The precipitates were purified on silica gel by column chromatography using methanol/petroleum ether/EtOAc (10:10:1, v/v/v) as the eluent to afford a yellow intermediate. Next, the yellow intermediate (0.59 g, 2.0 mmol), and 4-fluorobenzenesulfonyl chloride (0.43 g, 2.2 mmol) were mixed in 50 mL of dichloromethane. Two drops of pyridine were added and the mixture was stirred for about 6 h at room temperature, and inspected by TLC. The precipitate was collected, washed with water and recrystallized from dichloromethane/methanol (1:1, v/v) to get light yellow crystals of title compound.
The anti-inflammatory activities of title compound were evaluated by inhibition of LPS-induced NO secretion on RAW264.7 cells. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC, 30 M) was used as a reference standard. In preliminary experiments, the title compound had no significant toxicity at 6.0 M on mouse RAW264.7 macrophages. RAW264.7 cells were pretreated with 30 M of PDTC or with 6.0 M of title compound for 2.0 h. After treatment with LPS (1.0 g/mL) for 22 h, the collected culture media were centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 10 min. The expression levels of NO secretion in the media were determined by ELISA with an ELISA kit (eBioScience, San Diego, CA). The experiment was carried out in triplicate.
Experimental details
All H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with d(C—H) = 0.99 Å (methylene), Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) and d(C—H) = 0.95 Å (aromatic), Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Comment
Curcumin, 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)1,6-hepta-dien-3,5-dion, a natural product from Curcuma longa, has been proved to show anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, antioxidant, antibacterial activities. Its clinical application was limited because of its low bioactivities, poor aqueous solubility and false positive problem [4]. In order to overcome these defects, a series of novel curcumin analogues have been reported, such as (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(arylidene)-4-piperidone derivatives (BAPs). They were previously synthesized as better antitumor and anti-inflammatory agents [5], [6]. BAPs contain two α,β-unsaturated keto groups, and show greater predilection or sequential interaction for bio-thiols in tumors rather than normal cell [7]. In a previous study, some strong electron-withdrawing substituent groups (Such as -NO2, -CN, -CF3) were assigned to both sides of BAPs. Their antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities were improved to different extent. Some crystal structure and bioactivity of 4-((E)-((E)-5-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-oxopiperidin-3-ylidene)methyl)benzonitrile (BAP-1), (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-cyanobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one (BAP-2), (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)-1-((4-(trifluoromethyl) phenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one (BAP-3) were reported [8], [9], [10].
If changing one side of BAPs to 3-pyridine substituents, while another side of BAPs is substituted by fluoro in ortho position, dissymmetric BAPs will be generated [11]. Adding a N-phenylsulfonyl moiety, the desired and improved antitumor activities and anti-inflammatory activity of BAPs could be found. In this study, we report herein crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one.
Single-crystal structure analysis reveals that there is only one BAP molecule in the asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure (cf. the figure). Bond lengths and angles are all in the expected ranges. The central 3,5-bis(arylidene)-4-piperidone expand both sides in a linear fashion, and pyridyl and 2-fluorobenzylidene on both sides of central piperidone adopt the E stereochemistry of the olefinic double bonds [12]. The dihedral angles between pyridyl and central piperidone is 12.5(4)°, while the dihedral angles between 2-fluorobenzylidene and central piperidone is 53.1(2)°. In addition, the N-phenylsulfonyl substituents are going to stretch in the direction of the carbonyl group of central piperidone. The molecule looks like an “organic clip” [13], [14]. The dihedral angles between N-phenylsulfonyl group and piperidone ring is 22.8(2)°. In title compound, the peripheric heteroatoms (Such as F, N, O, S) can act as hydrogen bonding acceptors for bioactive molecules with the aim of creating more potent antitumor activities and anti-inflammatory activity [15].
It is known to all that the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as NO, TNF-α and IL-6, can indicate the degree of inflammation [16]. In our study, the effect of title compound on NO production in RAW264.7 cells induced by LPS was examined by ELISA. PDTC was used as a reference standard. After treatment with PDTC, the express rate for NO production in RAW264.7 cells was 68.32 ± 2.69%. After treatment with title compound, the express rate of NO production was significantly increased, which could reach 49.19 ± 1.50%. The result showed that title compound displayed potential inhibitory effects on LPS-induced NO secretion than PDTC.
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 81601049
Funding statement: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81601049) and Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2019MB032).
References
1. Rigaku, O. D.: CrysAlisPRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England (2017).Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Nelson, K. M.; Dahlin, J. L.; Bisson, J.; Graham, J.; Pauli, G. F.; Walters, M. A.: The essential medicinal chemistry of curcumin. J. Med. Chem. 60 (2017) 1620–1637.10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00975Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Li, N.; Xin, W. Y.; Yao, B. R.; Cong, W.; Wang, C. H.; Hou, G. G.: N-phenylsulfonyl-3,5-bis(arylidene)-4-piperidone derivatives as activation NF-κB inhibitors in hepatic carcinoma cell lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 155 (2018) 531–544.10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.06.027Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Zhang, L. S.; Chen, Q.; Hou, G. G.; Zhao, W.; Hou, Y.: Hydroxyl-substituted double Schiff-base condensed 4-piperidone/cyclohexanones as potential anticancer agents with biological evaluation. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 34 (2019) 264–271.10.1080/14756366.2018.1501042Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
7. Li, N.; Xin, W. Y.; Yao, B. R.; Wang, C. H.; Cong, W.; Zhao, F.; Li, H. J.; Hou, Y.; Meng, Q. G.; Hou, G. G.: Novel dissymmetric 3,5-bis(arylidene)-4-piperidones as potential antitumor agents with biological evaluation in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 147 (2018) 21–33.10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.01.088Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Liu, L. D.; Liu, S. L.; Hou, G. G.: Crystal structure of 4-((E)-((E)-5-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-oxopiperidin-3-ylidene)methyl)benzonitrile, C26H18F2N2O3S. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 233 (2018) 1063–1065.10.1515/ncrs-2018-0174Suche in Google Scholar
9. Li, X. Y.; Meng, Q. G.; Hou, G. G.: Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-cyanobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl) sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one, C27H18FN3O3S. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) 771–773.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0097Suche in Google Scholar
10. Sun, Y.; Wang, S. X.; Hou, G. G.: Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)-1-((4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (2/1), C53H38Cl2F6N6O14S2. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) 1047–1049.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0253Suche in Google Scholar
11. Yao, B. R.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S. L.; Suo, H. D.; Zhang, Y. L.; Wei, H.; Wang, C. H.; Zhao, F.; Cong, W.; Xin, W. Y.; Hou, G. G.: Dissymmetric pyridyl-substituted 3,5-bis(arylidene)-4-piperidones as anti-hepatoma agents by inhibiting NF-κB pathway activation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 167 (2019) 187–199.10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.02.020Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Yao, B. R.; Li, N.; Wang, C. H.; Hou, G. G.; Meng, Q. G.; Yan, K.: Novel asymmetric 3,5-bis(arylidene)piperidin-4-one derivatives: synthesis, crystal structures and cytotoxicity. Acta Crystallogr. C74 (2018) 659–665.10.1107/S2053229618006605Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Hou, G. G.; Zhao, H. J.; Sun, J. F.; Lin, D.; Dai, X. P.; Han, J. T.; Zhao, H.: Synthesis, structure and luminescence of Co-crystals with hexagonal channels: arranging disposition and π-π interactions. CrystEngComm 15 (2013) 577–585.10.1039/C2CE25759ASuche in Google Scholar
14. Thakur, A.; Manohar, S.; Vélez Gerena, C. E.; Zayas, B.; Malhotra, S.; Rawat, D.: Novel 3,5-bis(arylidiene)-4-piperidone based monocarbonyl analogs of curcumin: anticancer activity evaluation and mode of action study. MedChemComm 5 (2014) 576–586.10.1039/C3MD00399JSuche in Google Scholar
15. Li, N.; Bai, X. Y.; Zhang, L. S.; Hou, Y.: Synthesis, crystal structures and anti-inflammatory activity of four 3,5-bis(arylidene)-N-benzenesulfonyl-4-piperidone derivatives. Acta Crystallogr. C74 (2018) 1171–1179.10.1107/S2053229618013232Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
16. Su, C. M.; Hou, G. G.; Wang, C. H.; Zhang, H. Q.; Yang, C.; Liu, M.; Hou, Y.: Potential multifunctional agents with anti-hepatoma and anti-inflammation properties by inhibiting NF-κB activation. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 34 (2019) 1287–1297.10.1080/14756366.2019.1635124Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2019 Yue Sun et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{5-fluorine-2-(((4-(1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl) imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}copper(II), C32H28CuF2N4O4
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of N′-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-fluorobenzohydrazide monohydrate, C16H17FN2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl) ethylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C15H12ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-[4-(1H)-imidazolyl phenyl]-(2-methylphenyl)methanimine, C17H15N3
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-4-(2-(phenylethynyl)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole, C23H17N3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[{μ2-1,5-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)pentane-κ2P:P′}dichloridocadmium(II)], C29H30CdCl2P2
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-N2-((3-methylquinolin-8-yl)sulfonyl)-Nω′-nitro-L-argininate - ethanol (1/1), C19H28N6O7S
- The crystal structure of trans-carbonyl-(diphenylcyclohexyl-phosphine-κP)iodidomethyl-(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)rhodium(III), C25H28INO3PRh
- Crystal structure of N-(amino(pyrazin-2-yl)methylene)-6-methylpyridin-1-ium-3-carbohydrazonate-κ3O,N,N′)-(dinitrato-κ1O)zinc(II), C12H12N8O7Zn
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-(tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)chromium(III) chloride — methanol (1/3), CrC27H33Cl3N7O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ4-piperazine-1,4-bis(2-hydroxypropanesulfonato-κ8O,O′:O′,N:N′,O′′:O′′,O′′′))silver(I)], C10H24Ag2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2–2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κO)-oktakis(3-chlorobenzyl-κC)tetratin(IV), C84H52Cl8F16O10Sn4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-{4-[(4-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone O-methyl oxime, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)zinc(II)], {C20H30N4O4P2S4Zn}n
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(3-iodopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C15H12IN3O2
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-(μ2-methanoato-k2O:O′)-(μ2–bis(di-p-tolylphosphino)cyclohexylamine-κ2P:P′)dirhenium(I), C42H45NO8P2Re2
- The cocrystal structure of 1′-hydroxy-1H,1′H-[5,5′-bitetrazol]-1-olate and 1,10-phenanthrolin-1-ium, C14H10N10O2
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-2-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)ethynyl)pyridin-1-ium bromide,C24H24BrN
- Crystal structure of (5,5′-bitetrazole-1,1′-diolate)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline)-copper(II), C26H16CuN12O2
- Crystal structure of bis(ammonium) diaqua-tetrakis(4-hydroxybenzoato)-manganese(II) tetrahydrate, [NH4]2[C28H24MnO14] ⋅ 4(H2O)
- The crystal structure of 3-chloro-1-hydrazino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene, C6H4ClN5O6
- Crystal structure of catena-[(μ2-pyrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-ethyldithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C12H24CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-pyrazine-N,N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-S,S′)cadmium(II) acetonitrile di-solvate], [C16H32CdN2O4P2S4⋅2(C2H3N)]n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{(μ2-N1,N2-bis[(pyridin-4-yl)methyl]ethanediamide-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)} — acetonitrile (1/1), C26H42N4O6P2S4Zn⋅C2H3N
- Crystal structure of tetraqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)benzoato-κO)cobalt(II), C16H22O10Co
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-dimethyl dithiophosphato-κ2-S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C16H22CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(E)-2-(((5-((trimethylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol], C12H15N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(N-o-tolyl-1,1-di-p-tolylphosphanamine–κ1P)-(methoxydi-p-tolylphosphane-κ1P)palladium(II), C36H39Cl2NOP2Pd
- The crystal structure of the triclinic polymorph of hexameric (trimethylsilyl)methyllithium, C24H66Li6Si6
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′O)cobalt(III) 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane, C34H22CoN8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of benzyl 5-oxo-5-phenyl-2-(quinolin-2-yl)pentanoate, C27H23NO3
- Crystal structure of 5,5-dimethyl-3-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl 4-(2,2-dichloroacetyl)-3,4-dihydro-2 H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazine-7-carboxylate, C19H19Cl2NO5
- Crystal structure of dipentyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C18H28O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dicadmium(II)], C30H18Cd2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of 2,7-diiodo-1,3,6,8-tetramethyl-bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine, C14H14B2F4I2N4
- A dinuclear Eu(III) complex in the crystal structure of dodecaaqua-bis(μ2-4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzoato-κ2O:O′) bis(5-(4-carboxylatophenyl)tetrazol-1-ide) tetrahydrate, C32H50Eu2N16O24
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one, C24H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one-methanol-hydrate (2/1/1), C53H50F2N6O10S2
- Crystal structure of 4-dimethylamino-pyridin-1-ium uracil-1-acetate, C13H16N4O4
- Crystal structure of dimethylammonium 5-fluorouracil-1-acetate, C8H12N3O4F
- Crystal structure of bis(N′-((5-(ethoxycarbonyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-N-ethylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2N,O)nickel(II), C22H30N8O4S2Ni
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-((bis-pyrazol-1-yl)methane-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexafluorophosphate. (C17H23ClN4RhF6P)
- The crystal structure of 5-(benzofuran-2-carbonyl)-N-cyclohexyl-5,6-dihydrophenanthridine-6-carboxamide, C29H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-yl acetate, C11H8O4
- The crystal structure of 2-nitroisophthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-9-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino [2′,1′:1,6]pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H17FN4O
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl-κC)(bis(2-hydroxyethyl) carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)(2,2′-imino-diethanolato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C16H25FN2O4S2Sn
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-bromophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18BrF3N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18ClF3N2O3S
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridomanganate(II), C10H16Cl4MnN2
- The crystal structure of 3-carboxy-5-methylpyridin-1-ium-2-carboxylate, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methoxy-N-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato κ3O,N,N′)zinc(II), C30H28N6O4Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(4,4′-dichloro-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)platinum(II) — acetone (1/1), C13H12Cl4N2PtO
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-2,10-dimethoxy-3,9-diphenyl-3,9-diazatetracyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C42H42F2N2O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,3E)-2-hydroxy-5-methylisophthalaldehyde O,O-di(2-((((E)-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)oxy)ethyl) dioxime, C35H32N4O7
- The crystal structure of 2-phenyl-4,6-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazine, C15H11N3O2
- Crystal structure of 7-(2-{4-[(4-bromophenyl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}ethoxy)-2H-chromen-2-one, C22H23BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(3-ethyl-1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-3-bromo-benzoic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-cadmium(II), C30H28N8O2Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-methoxy-2H-pyran-2-one, C12H9FO3
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-3-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)butanoic acid, C14H18O4
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-6-methoxy-2-methyl-5-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)pyridine, C13H19BBrNO3
- The crystal structure of 6-methyl-3,20-dioxo-19-norpregna-4,6-dien-17-yl acetate–2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (1/1), C30H36O8
- The crystal structure of (5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)-(pyridine-κ1N)copper(II), C20H16ClCuN3O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-cyano-N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)acetohydrazide, C11H3N5O
- Crystal structure of (2,7-dihexyl-9,9-dimethyl-9H-xanthene-4,5-diyl)bis(diphenylphosphane), C51H56OP2
- Crystal structure of 5-((bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)methyl)quinolin-8-ol, C22H20N4O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)thiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C28H20FN3O2S
- The crystal structure of [(tetra-μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′)]dierbium(III) C66H34N4O12F12Er2
- Crystal structure of bis(3-chloro-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-k3N,N′,O)nickel(II), C26H20N8O2Cl2Ni
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C27H21N5O
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)-N,N-dimethylformimidamide, C9H13N3O2S
- Crystal structure of η6-p-cymene-iodido-(N-isopropyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate(V), C19H26IN2F6Ru
- Crystal structure of 6-iodo-3-phenyl-2-propylquinazolin-4(3H)-one, C17H15IN2O
- Low temperature redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[[tri-4-fluorobenzyltin(IV)]μ2-pyridine-4-carboxylato-κ2N:O], {C27H22F3NO2Sn}n
- Crystal structure of bis(2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrachloridozincate(II), C10H13Cl4N2Zn
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-hydrazono-5-nitroindolin-2-one – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C8H6N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-cyanoacetic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-zinc(II), C18H16N10O2Zn
- Crystal structure and photochromism of 1-(2,5-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-2-[2-methyl-5-(benzaldoxime)-3-thienyl] perfluorocyclopentene, C23H17F6NOS2
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{5-fluorine-2-(((4-(1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl) imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}copper(II), C32H28CuF2N4O4
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of N′-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-fluorobenzohydrazide monohydrate, C16H17FN2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl) ethylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C15H12ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-[4-(1H)-imidazolyl phenyl]-(2-methylphenyl)methanimine, C17H15N3
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-4-(2-(phenylethynyl)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole, C23H17N3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[{μ2-1,5-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)pentane-κ2P:P′}dichloridocadmium(II)], C29H30CdCl2P2
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-N2-((3-methylquinolin-8-yl)sulfonyl)-Nω′-nitro-L-argininate - ethanol (1/1), C19H28N6O7S
- The crystal structure of trans-carbonyl-(diphenylcyclohexyl-phosphine-κP)iodidomethyl-(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)rhodium(III), C25H28INO3PRh
- Crystal structure of N-(amino(pyrazin-2-yl)methylene)-6-methylpyridin-1-ium-3-carbohydrazonate-κ3O,N,N′)-(dinitrato-κ1O)zinc(II), C12H12N8O7Zn
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-(tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)chromium(III) chloride — methanol (1/3), CrC27H33Cl3N7O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ4-piperazine-1,4-bis(2-hydroxypropanesulfonato-κ8O,O′:O′,N:N′,O′′:O′′,O′′′))silver(I)], C10H24Ag2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2–2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κO)-oktakis(3-chlorobenzyl-κC)tetratin(IV), C84H52Cl8F16O10Sn4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-{4-[(4-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone O-methyl oxime, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)zinc(II)], {C20H30N4O4P2S4Zn}n
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(3-iodopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C15H12IN3O2
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-(μ2-methanoato-k2O:O′)-(μ2–bis(di-p-tolylphosphino)cyclohexylamine-κ2P:P′)dirhenium(I), C42H45NO8P2Re2
- The cocrystal structure of 1′-hydroxy-1H,1′H-[5,5′-bitetrazol]-1-olate and 1,10-phenanthrolin-1-ium, C14H10N10O2
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-2-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)ethynyl)pyridin-1-ium bromide,C24H24BrN
- Crystal structure of (5,5′-bitetrazole-1,1′-diolate)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline)-copper(II), C26H16CuN12O2
- Crystal structure of bis(ammonium) diaqua-tetrakis(4-hydroxybenzoato)-manganese(II) tetrahydrate, [NH4]2[C28H24MnO14] ⋅ 4(H2O)
- The crystal structure of 3-chloro-1-hydrazino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene, C6H4ClN5O6
- Crystal structure of catena-[(μ2-pyrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-ethyldithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C12H24CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-pyrazine-N,N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-S,S′)cadmium(II) acetonitrile di-solvate], [C16H32CdN2O4P2S4⋅2(C2H3N)]n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{(μ2-N1,N2-bis[(pyridin-4-yl)methyl]ethanediamide-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)} — acetonitrile (1/1), C26H42N4O6P2S4Zn⋅C2H3N
- Crystal structure of tetraqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)benzoato-κO)cobalt(II), C16H22O10Co
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-dimethyl dithiophosphato-κ2-S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C16H22CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(E)-2-(((5-((trimethylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol], C12H15N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(N-o-tolyl-1,1-di-p-tolylphosphanamine–κ1P)-(methoxydi-p-tolylphosphane-κ1P)palladium(II), C36H39Cl2NOP2Pd
- The crystal structure of the triclinic polymorph of hexameric (trimethylsilyl)methyllithium, C24H66Li6Si6
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′O)cobalt(III) 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane, C34H22CoN8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of benzyl 5-oxo-5-phenyl-2-(quinolin-2-yl)pentanoate, C27H23NO3
- Crystal structure of 5,5-dimethyl-3-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl 4-(2,2-dichloroacetyl)-3,4-dihydro-2 H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazine-7-carboxylate, C19H19Cl2NO5
- Crystal structure of dipentyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C18H28O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dicadmium(II)], C30H18Cd2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of 2,7-diiodo-1,3,6,8-tetramethyl-bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine, C14H14B2F4I2N4
- A dinuclear Eu(III) complex in the crystal structure of dodecaaqua-bis(μ2-4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzoato-κ2O:O′) bis(5-(4-carboxylatophenyl)tetrazol-1-ide) tetrahydrate, C32H50Eu2N16O24
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one, C24H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one-methanol-hydrate (2/1/1), C53H50F2N6O10S2
- Crystal structure of 4-dimethylamino-pyridin-1-ium uracil-1-acetate, C13H16N4O4
- Crystal structure of dimethylammonium 5-fluorouracil-1-acetate, C8H12N3O4F
- Crystal structure of bis(N′-((5-(ethoxycarbonyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-N-ethylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2N,O)nickel(II), C22H30N8O4S2Ni
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-((bis-pyrazol-1-yl)methane-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexafluorophosphate. (C17H23ClN4RhF6P)
- The crystal structure of 5-(benzofuran-2-carbonyl)-N-cyclohexyl-5,6-dihydrophenanthridine-6-carboxamide, C29H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-yl acetate, C11H8O4
- The crystal structure of 2-nitroisophthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-9-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino [2′,1′:1,6]pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H17FN4O
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl-κC)(bis(2-hydroxyethyl) carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)(2,2′-imino-diethanolato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C16H25FN2O4S2Sn
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-bromophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18BrF3N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18ClF3N2O3S
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridomanganate(II), C10H16Cl4MnN2
- The crystal structure of 3-carboxy-5-methylpyridin-1-ium-2-carboxylate, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methoxy-N-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato κ3O,N,N′)zinc(II), C30H28N6O4Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(4,4′-dichloro-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)platinum(II) — acetone (1/1), C13H12Cl4N2PtO
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-2,10-dimethoxy-3,9-diphenyl-3,9-diazatetracyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C42H42F2N2O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,3E)-2-hydroxy-5-methylisophthalaldehyde O,O-di(2-((((E)-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)oxy)ethyl) dioxime, C35H32N4O7
- The crystal structure of 2-phenyl-4,6-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazine, C15H11N3O2
- Crystal structure of 7-(2-{4-[(4-bromophenyl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}ethoxy)-2H-chromen-2-one, C22H23BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(3-ethyl-1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-3-bromo-benzoic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-cadmium(II), C30H28N8O2Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-methoxy-2H-pyran-2-one, C12H9FO3
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-3-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)butanoic acid, C14H18O4
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-6-methoxy-2-methyl-5-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)pyridine, C13H19BBrNO3
- The crystal structure of 6-methyl-3,20-dioxo-19-norpregna-4,6-dien-17-yl acetate–2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (1/1), C30H36O8
- The crystal structure of (5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)-(pyridine-κ1N)copper(II), C20H16ClCuN3O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-cyano-N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)acetohydrazide, C11H3N5O
- Crystal structure of (2,7-dihexyl-9,9-dimethyl-9H-xanthene-4,5-diyl)bis(diphenylphosphane), C51H56OP2
- Crystal structure of 5-((bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)methyl)quinolin-8-ol, C22H20N4O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)thiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C28H20FN3O2S
- The crystal structure of [(tetra-μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′)]dierbium(III) C66H34N4O12F12Er2
- Crystal structure of bis(3-chloro-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-k3N,N′,O)nickel(II), C26H20N8O2Cl2Ni
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C27H21N5O
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)-N,N-dimethylformimidamide, C9H13N3O2S
- Crystal structure of η6-p-cymene-iodido-(N-isopropyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate(V), C19H26IN2F6Ru
- Crystal structure of 6-iodo-3-phenyl-2-propylquinazolin-4(3H)-one, C17H15IN2O
- Low temperature redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[[tri-4-fluorobenzyltin(IV)]μ2-pyridine-4-carboxylato-κ2N:O], {C27H22F3NO2Sn}n
- Crystal structure of bis(2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrachloridozincate(II), C10H13Cl4N2Zn
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-hydrazono-5-nitroindolin-2-one – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C8H6N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-cyanoacetic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-zinc(II), C18H16N10O2Zn
- Crystal structure and photochromism of 1-(2,5-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-2-[2-methyl-5-(benzaldoxime)-3-thienyl] perfluorocyclopentene, C23H17F6NOS2

